43 resting membrane potential diagram
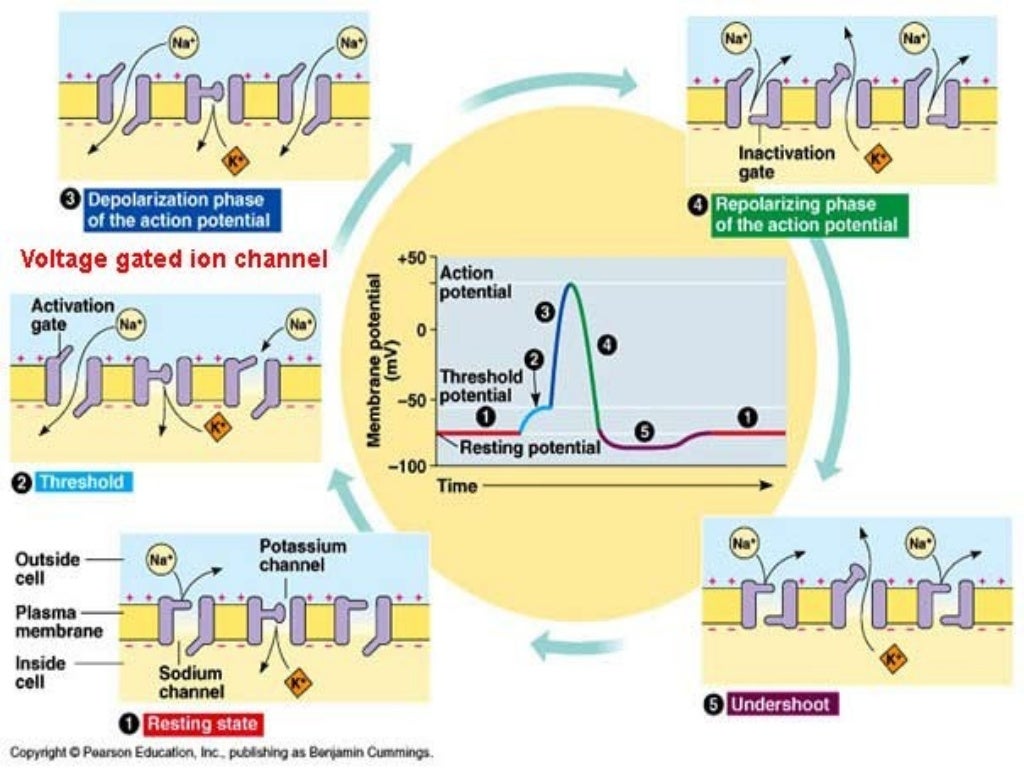
Membrane potential (resting membrane potential) (article) | Khan Academy The resting potential is determined by concentration gradients of ions across the membrane and by membrane permeability to each type of ion. In a resting neuron, there are concentration gradients across the membrane for and . Ions move down their gradients via channels, leading to a separation of charge that creates the resting potential. Resting Membrane Potential | Biology for Majors II - Lumen Learning Figure 2. The (a) resting membrane potential is a result of different concentrations of Na + and K + ions inside and outside the cell. A nerve impulse causes Na + to enter the cell, resulting in (b) depolarization. At the peak action potential, K + channels open and the cell becomes (c) hyperpolarized.
Physiology, Resting Potential - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf The resting membrane potential is the result of the movement of several different ion species through various ion channels and transporters (uniporters, cotransporters, and pumps) in the plasma membrane. These movements result in different electrostatic charges across the cell membrane. Neurons and muscle cells are excitable such that these cell types can transition from a resting state to an ...

Resting membrane potential diagram
PDF Part I: Maintaining the Resting Potential - 3D Molecular Designs This charge difference-or voltage-is called the membrane potential and is measured with a voltmeter. A membrane exhibiting membrane potential is said to be polarized. When the neuron is not sending a signal, the (resting) voltage ranges from -60 to -80 mV (millivolts). The membrane potential at rest is called the neuron's resting ... Action Potential and Resting Potential | Electrical4U The cell membrane is negative inside and positive outside. The difference in ion concentration results in the Resting Membrane Potential of the cell. The value of resting potential is between - 60mV to - 100mV. The value remains constant until an external factor disturbs the cell membrane. At the resting state, the cell is polarised. Neurones and Resting Potential - humanphysiology.academy Neurones collect and integrate information in the dendrites and cell body (perikaryon) and generate action potentials at the axon hillock. The action potentials pass rapidly along the length of the axon and release neurotransmitters at the axon terminals. Dendrites occur in large numbers, and are branches of the cell body.
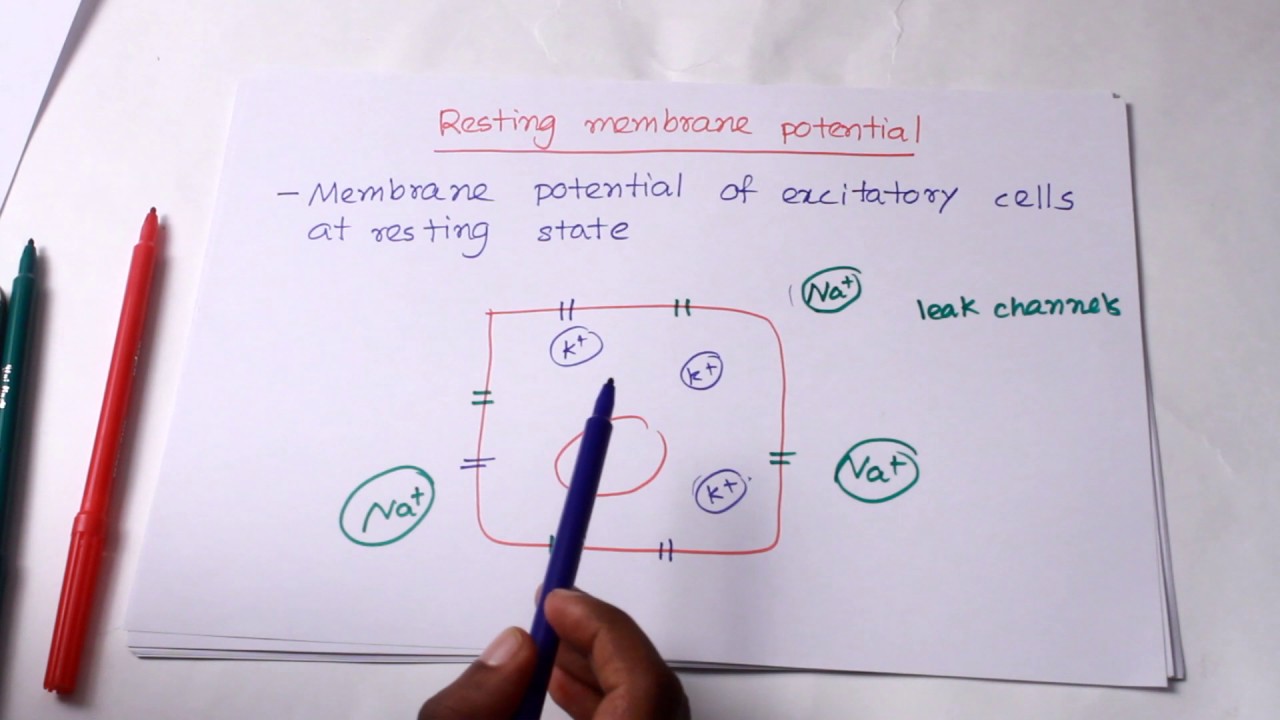
Resting membrane potential diagram. Action potentials and synapses - Queensland Brain Institute ... There are many channels sitting in the cell membrane (the boundary between a cell’s inside and outside) that allow positive or negative ions to flow into and out of the cell. Normally, the inside of the cell is more negative than the outside; neuroscientists say that the inside is around -70 mV with respect to the outside, or that the cell’s resting membrane potential is -70 mV. Membrane potential - Wikipedia Membrane potential (also transmembrane potential or membrane voltage) is the difference in electric potential between the interior and the exterior of a biological cell.That is, there is a difference in the energy required for electric charges to move from the internal to exterior cellular environments and vice versa, as long as there is no acquisition of kinetic energy or the production of ... MEMBRANE POTENTIALS - Brigham Young University-Idaho Diagram of a cell establishing a resting membrane potential. Shown are representations of a K+ channel that allows for the movement of K+ out of the cell, a closed Na+ channel that prevents movement of Na+ into the cell and a Na+/K+ ATPase pump that moves three Na+ ions out of the cell. This pump is found in almost every cell in the body. What Is the Resting Potential of a Neuron? - Study.com The resting potential of an excitable cell like a neuron or muscle cell is the electrical potential difference between the inside and outside of the cell. The inside is more negative and the...
Resting Membrane Potential - Nernst - Generation - TeachMePhysiology In electrically inactive neurones, this is known as the resting membrane potential. Its typical value lies between -50 and -75 mV. In this article, we will explore how the resting membrane potential is generated, how to calculate its approximate value and how changes in resting membrane potential may lead to significant pathology. Overview Resting potential - Wikipedia The relatively static membrane potential of quiescent cells is called the resting membrane potential (or resting voltage), as opposed to the specific dynamic electrochemical phenomena called action potential and graded membrane potential. Apart from the latter two, which occur in excitable cells (neurons, muscles, and some secretory cells in glands), membrane voltage in … 7.2: Resting, Graded and Action Potential - Medicine LibreTexts The (a) resting membrane potential is a result of different concentrations of Na+ and K+ ions inside and outside the cell. A nerve impulse causes Na+ to enter the cell, resulting in (b) depolarization. At the peak action potential, K+ channels open and the cell becomes (c) hyperpolarized. Action potential 2.2 Hodgkin-Huxley Model | Neuronal Dynamics online book In Fig. 2.6 A an action potential has been initiated by a short current pulse of 1 ms duration applied at t = 1 t=1 ms. The spike has an amplitude of nearly 100mV and a width at half maximum of about 2.5ms. After the spike, the membrane potential falls below the resting potential and returns only slowly back to its resting value of -65mV.
Generation of the Resting Membrane Potential - Grade Valley One can also measure the potential optically using dyes that alter their colours according to the potential of the membrane. Draw a simple diagram to illustrate your explanation. (Caldwell and Keynes 12-13). What is the typical value of the resting potential of a neuron (give units)? The resting potential of a neuron has a typical value of ... Wikizero - Resting potential The relatively static membrane potential of quiescent cells is called the resting membrane potential (or resting voltage), as opposed to the specific dynamic electrochemical phenomena called action potential and graded membrane potential.. Apart from the latter two, which occur in excitable cells (neurons, muscles, and some secretory cells in glands), membrane voltage in the majority of non ... Resting membrane Potential Diagram | Quizlet resting membrane potential the electrical charge of a neuron when it is not active - cells maintain voltage at membrane as consequence of ion imbalances - cells are polarized - -10 -100 mV (inside is more negative than the outside) - depends on K+ Step 1 K+ diffuse down their steep concentration gradient (out of the cell) via leakage channel. Axon Terminal - The Definitive Guide | Biology Dictionary 22.05.2020 · The resting membrane potential is defined by a lower concentration of sodium ions (Na⁺) and chloride ions (Cl⁻) inside the neuron, ... Diagram showing an increase in serotonin levels following MDMA addition. Example 2: Drugs that increase neurotransmitter presence – Drugs such as MDMA (otherwise known as ecstasy) can increase serotonin levels in a short …
Pearson Mastering A&P: Ch 11 Action Potential (AP) What is the resting membrane potential of the neuron used in the experiment?-50 mV-60 mV-70 mV-80 mV-80 mV . A neuron is placed into a recording chamber. Below are three different recordings of the neuron's initial segment under three different conditions: without stimulus, stimulus 1, and stimulus 2. The graphs produced by these three experiments are below. …
Action potential - Definition, Steps, Phases | Kenhub An action potential is defined as a sudden, fast, transitory, and propagating change of the resting membrane potential. Only neurons and muscle cells are capable of generating an action potential; that property is called the excitability. This article will discuss the definition, steps and phases of the action potential. Contents Definition Steps
Solved Short answer questions: Use diagrams where | Chegg.com Transcribed image text: Short answer questions: Use diagrams where appropriate. 1. Explain how the resting membrane potential is established and maintained. You can use a diagram(s). 2. Draw a diagram showing the time course of an action potential Label the diagram to show the different phases of the action potential, the resting membrane potential, and the equilibrium potentials for Na' and K:.
A.3.2.The Resting Potential - BasicPhysiology They show this by having an electrical potential difference between the inside of a cell and outside. 2. This difference in potential is called the ' resting potential '. This potential difference is not very big, ranging from -20mV to -90 mV but, as we shall see later, very important! (mV = millivolt; one thousand of 1 Volt). 3.
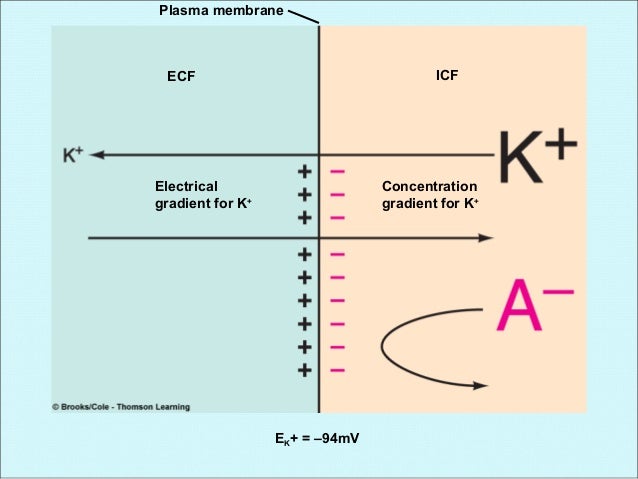
Measuring the Resting Membrane Potential | GetBodySmart In a resting axon, the distribution of cations and anions polarizes the plasma membrane. The intracellular fluid (ICF) becomes relatively negative to the extracellular fluid (ECF). A voltmeter is used to measure the charge difference (voltage or elec-trical potential) between the ECF and ICF. The greater the difference, the greater the voltage. 1 2
Resting Membrane Potential Diagram | Quizlet The cell's Na+-K+ ATPase pumps have stopped functioning You are going to record RMP from a cell using an electrode. You place your electrode and record a resting membrane potential every millisecond. You record an initial value of -70mV; however, over time you notice that your recordings become more and more positive until the RMP reaches 0mV.
Action Potential - The Resting Membrane Potential - Generation … 21.08.2021 · An action potential (AP) is the mode through which a neuron transports electrical signals. It is defined as a brief change in the voltage across the membrane due to the flow of certain ions into and out of the neuron. In this article we will discuss how an action potential is generated and how conduction of an action potential occurs.
PDF The Membrane Potential - Pearson For many neurons the resting membrane potential is close to -70 millivolts. • Color code this diagram and record the resting membrane potential for a typical neuron: ** Now is a good time to go to quiz questions 2,6 and 7: • Click the Quiz button on the left side of the screen.
Passive Membrane Properties, the Resting Potential, and Electrical ... Figure 1 shows a simple schematic view of a nerve cell membrane, greatly magnified. It is important to focus on two features of the membrane: Most of the membrane consists of a lipid bilayer.
Membrane potential: Definition, equilibrium, ions | Kenhub Jul 06, 2022 · A resting membrane potential is the difference between the electric potential in the intracellular and extracellular matrices of the cell when it isn’t excited. Every cell of the body has its own membrane potential, but only excitable cells - nerves and muscles - are capable to change it and generate an action potential .
Cell membrane - definition, structure, function, and biology Enclosed by this cell membrane are the cell’s constituents, including cell organelles and jelly-like fluids called cytosols with water-soluble molecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and substances involved in cellular activities. The cell membrane, therefore, has two key functions: 1. To be a barrier keeping the constituents of the cells in and unwanted …
Solved Review Resting Membrane Potential Examine the diagram | Chegg.com Review Resting Membrane Potential Examine the diagram and then fill in the blanks below. ECF H ICF pump C B C D Assume the large rectangle above represents a neuron at rest.
Mechanisms responsible for the cell resting membrane potential The resting membrane potential is the voltage (charge) difference between the intracellular and extracellular fluid, when the cell is at rest (i.e not depolarised by an action potential). It is generated by the opposing effects of chemical concentration gradients drivingionic diffusion across a selectively permeable membrane, and electostatic forces which oppose these gradients.
Resting Membrane Potential, Action Potential and Ionic Basis The resting membrane potential (RMP) present in this stage is -90mV. Depolarization: In this stage the membrane suddenly becomes very permeable to sodium (Na+) ions. The initially present polarized state is neutralized by inflow of Na + ions.
PDF Part I: Modeling the Resting Potential - Milwaukee School of Engineering The membrane potential at rest is referred to as the neuron's resting potential. For the purpose of this lab activity, we will consider a neuron with a resting potential of -70 mV. A membrane that exhibits a membrane potential is said to be polarized. MSOE Center for BioMolecular Modeling Synapse Kit: Section 1-2 | 2
Membrane Potential Overview, Equation, & Functions Learn what membrane potential is and how it differs from resting membrane potential. Calculate membrane potential using the membrane potential equation and examples. Updated: 02/17/2022
Neurones and Resting Potential - humanphysiology.academy Neurones collect and integrate information in the dendrites and cell body (perikaryon) and generate action potentials at the axon hillock. The action potentials pass rapidly along the length of the axon and release neurotransmitters at the axon terminals. Dendrites occur in large numbers, and are branches of the cell body.











0 Response to "43 resting membrane potential diagram"
Post a Comment