39 which structure in the diagram is responsible for bringing in amino acids
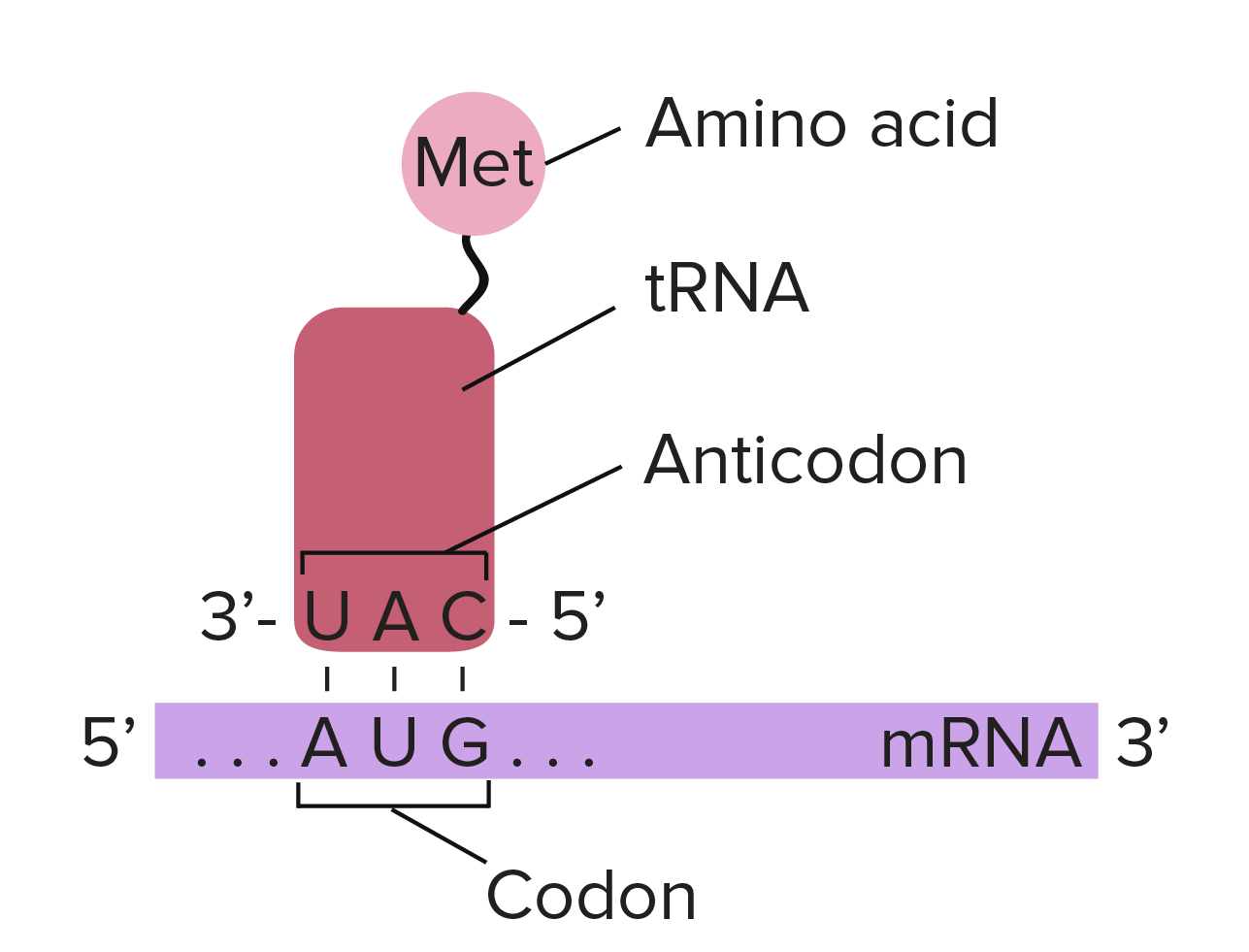
Anticodon - Definition, Function and Examples | Biology Dictionary tRNAs are responsible for bringing the correct amino acids to be added to the protein, according to the mRNA's instructions. Their anticodons, which pair-bond with codons on mRNA, allow them to perform this function. Function of Anticodons Look at the diagram Which structure is responsible for bringing in the ... Find an answer to your question Look at the diagram Which structure is responsible for bringing in the amino acids? •1 •2 •3 •4
Biology 5.09 Quiz Flashcards | Quizlet Gravity Created by ashleynicolette Terms in this set (4) Which structure is responsible for bringing in the amino acids? 2 Which two structures are first to combine in translation? 1 and 4 Which structure holds the original code from the DNA gene? 4 Which structure will become the product of translation? 3

Which structure in the diagram is responsible for bringing in amino acids
Which structure is responsible for bringing in the amino acids? (Points ... Which structure is responsible for bringing in the amino acids? (Points : 1) - 1604096 Chapter 2: Protein Structure - Chemistry - Western Oregon University The upper diagram displays the cis and trans conformations of two adjacent amino acids noted as X and Y which indicate any of the 20 amino acids, except for proline. In the trans conformation the R-group from amino acid X is rotated away and on the other side of the molecule when compared with the R-group from amino acid Y. 4 Levels of Protein Structure (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion The primary structure of a protein is the order of these amino acids in the backbone of each of the polypeptide chains comprising the molecule. The primary structure of a polypeptide chain is delineated beginning with the amino acid occupying the polypeptide's N-terminus.
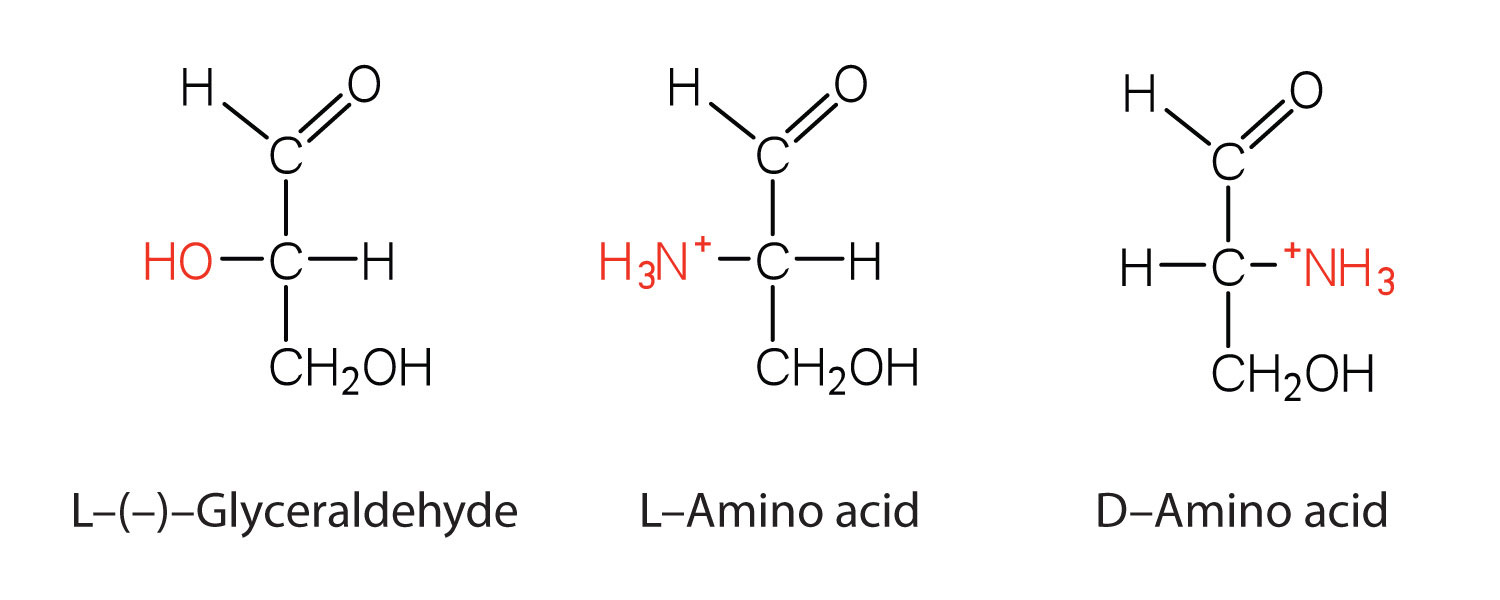
Which structure in the diagram is responsible for bringing in amino acids. Monosaccharides: Definition, Structure & Examples - Study.com Functional group - a group categorized by atoms or bonds that are responsible for the chemical reactivity within the molecules Ketose - a monosaccharide which contains a ketone group in an inner atom RNA Types: 3 Main Types of RNA (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion The following points highlight the top three types of RNA. The types of RNA are: 1. Transfer RNA (tRNA) 2. Messenger RNA (mRNA) and 3. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA). RNA Type # 1. Transfer RNA (tRNA): It delivers amino acids to ribosome and decodes the information of mRNA. Each nucleotide triplet codon on mRNA represents an amino acid. tRNA Structure, Function, and Synthesis - Study.com The tRNA structure is that of a string of RNA that is folded into a series of loops. One end has an amino acid attached, shown in blue as the Acceptor stem in the diagram. The opposite end has a... Essential Amino Acids: Chart, Abbreviations and Structure Amino acids are in an equilibrium between two acids with the proton (H+) moving between the amino group and the carboxyl group as shown below. In such an equilibrium, the weaker acid always predominates. As ammonia is a weaker acid than carboxylic acid, the equilibrium will lie to the left (on the "zwitterion" side).
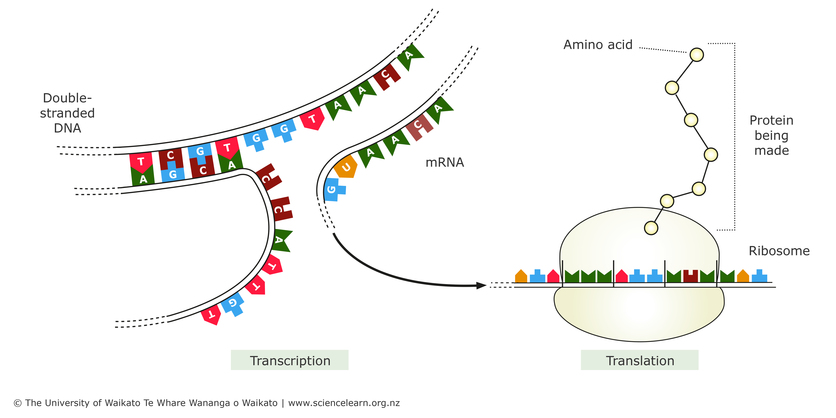
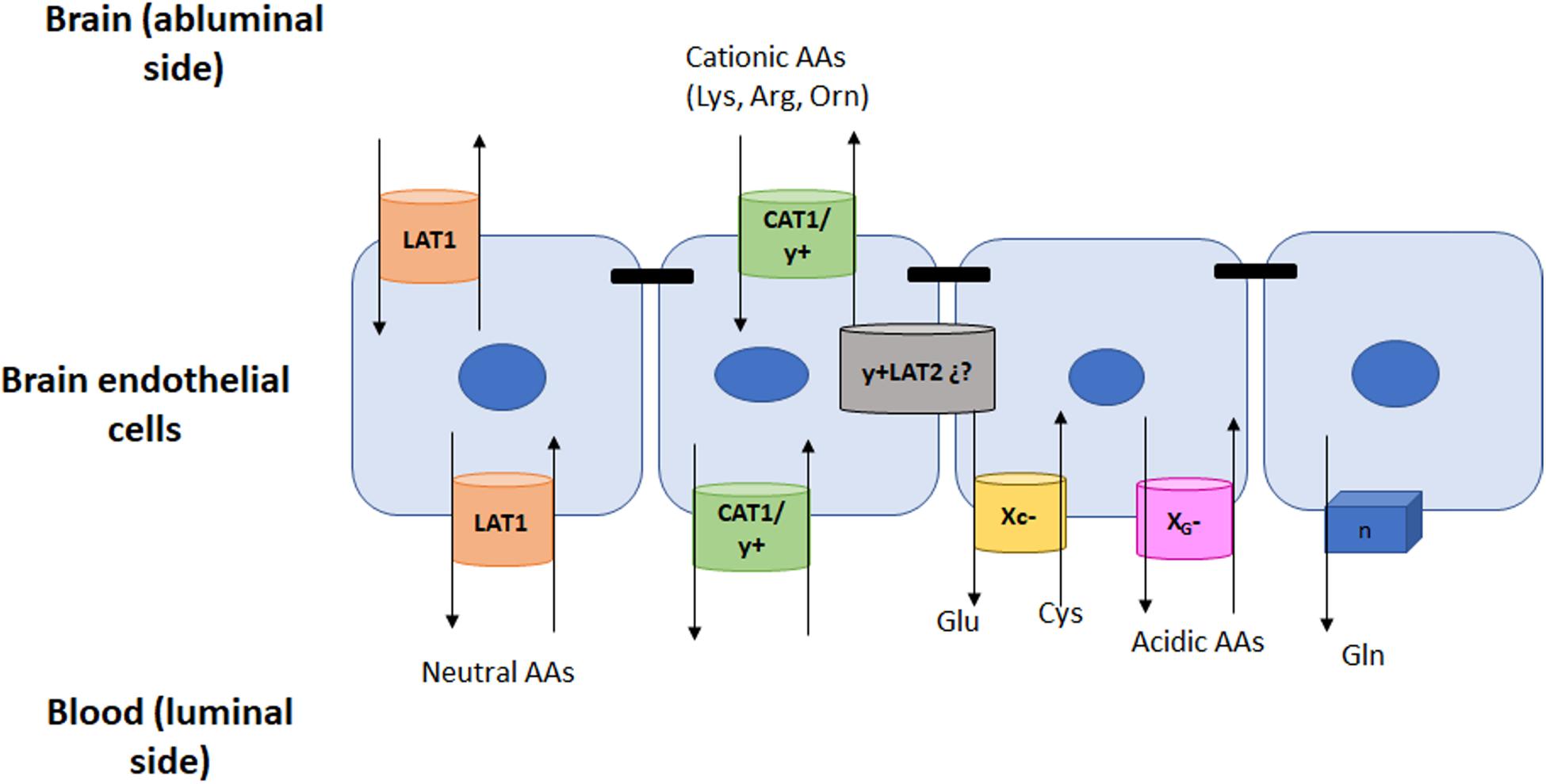
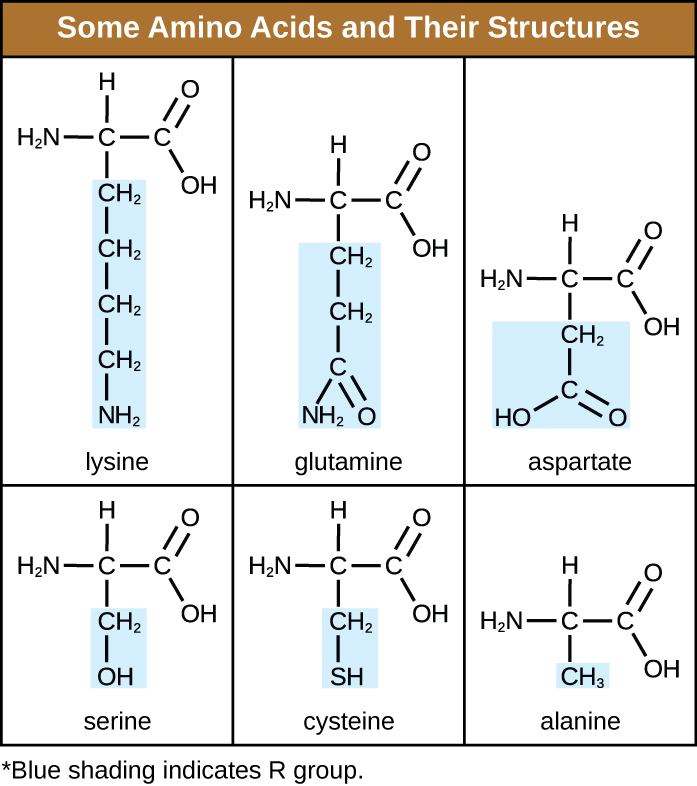
Amino Acids Structure and Properties - Study.com The central carbon is like the backbone of the amino acid. It connects all the other parts together. The central carbon is attached to a hydrogen atom, an amino group, a carboxyl group and a ... Transfer RNA (tRNA) - Definition, Types and Function - Biology Dictionary tRNA Definition. Transfer RNAs or tRNAs are molecules that act as temporary carriers of amino acids, bringing the appropriate amino acids to the ribosome based on the messenger RNA ( mRNA) nucleotide sequence. In this way, they act as the intermediaries between nucleotide and amino acid sequences. tRNAs are ribonucleic acids and therefore ... From RNA to Protein - Molecular Biology of the Cell - NCBI Bookshelf An mRNA Sequence Is Decoded in Sets of Three Nucleotides. Once an mRNA has been produced, by transcription and processing the information present in its nucleotide sequence is used to synthesize a protein.Transcription is simple to understand as a means of information transfer: since DNA and RNA are chemically and structurally similar, the DNA can act as a direct template for the synthesis of ... Enzymes - Structure, Classification, and Function - BYJUS Enzymes are a linear chain of amino acids, which give rise to a three-dimensional structure. The sequence of amino acids specifies the structure, which in turn identifies the catalytic activity of the enzyme. Upon heating, the enzyme's structure denatures, resulting in a loss of enzyme activity, which typically is associated with temperature.
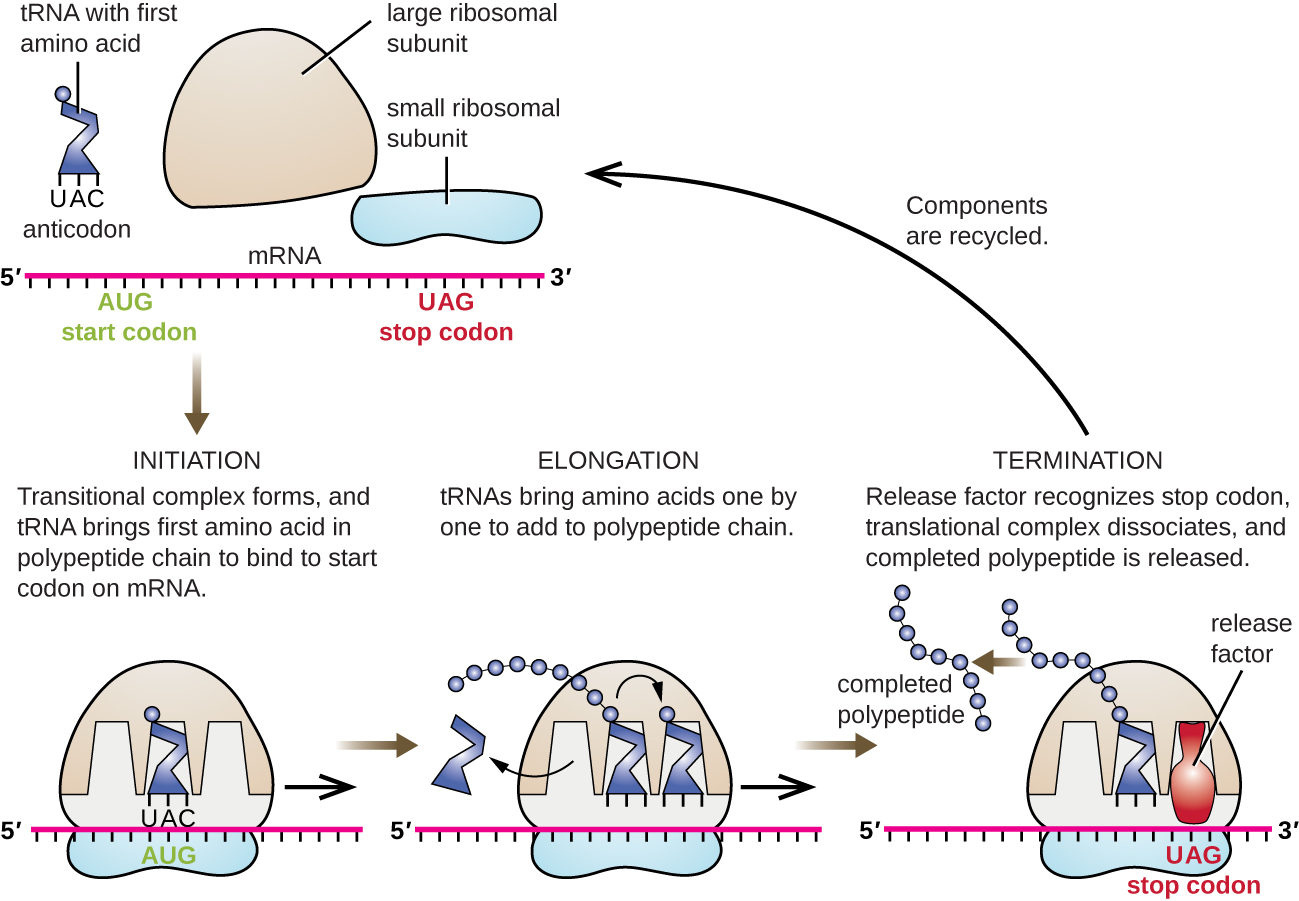
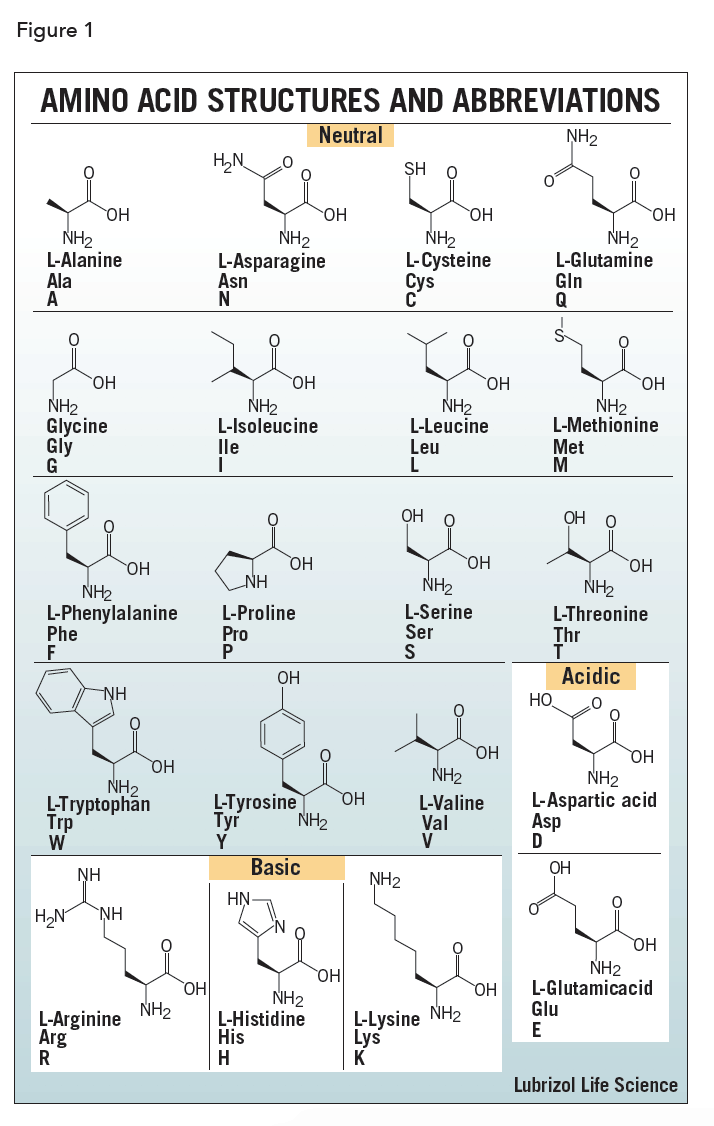
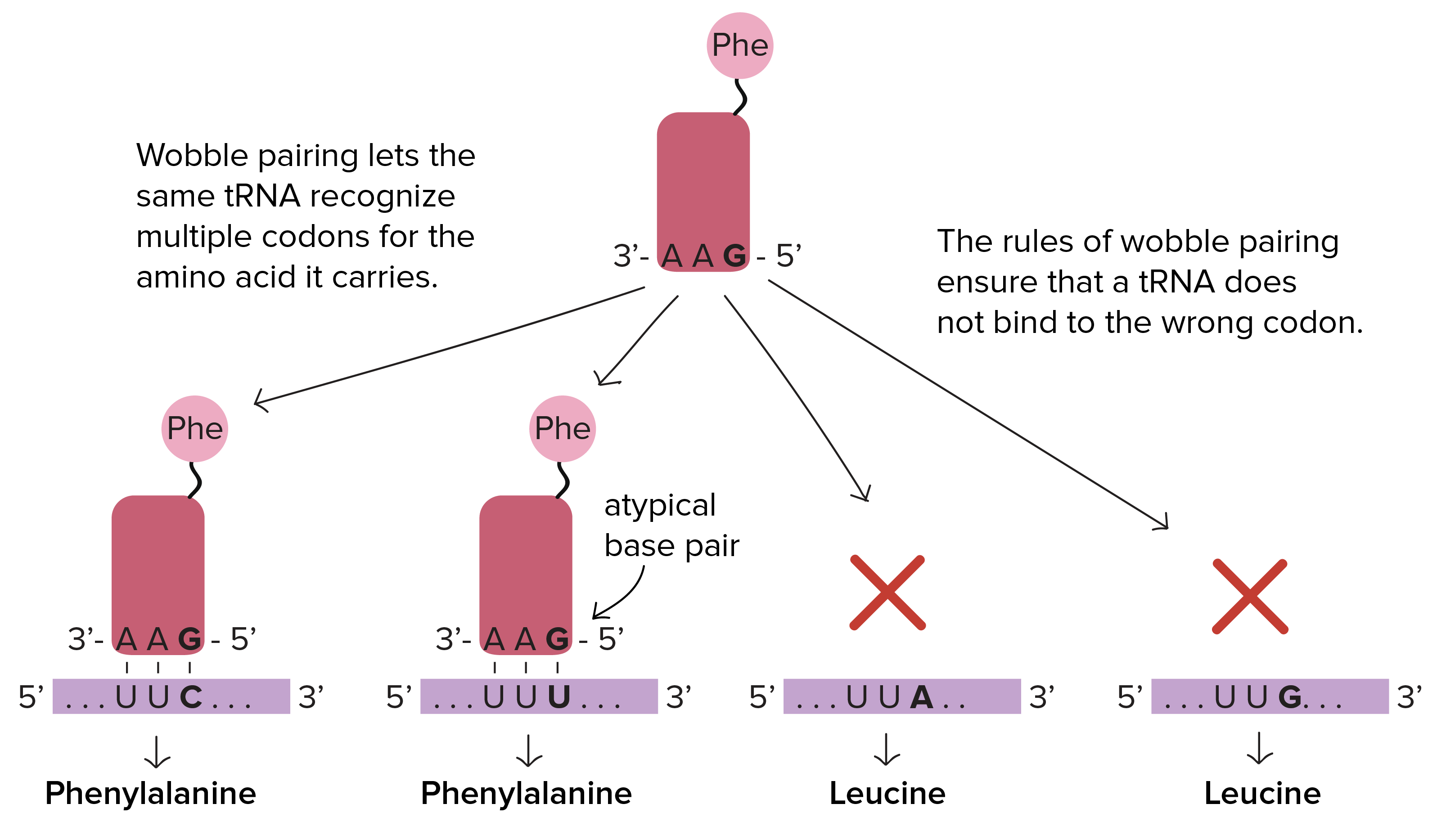
DNA Translation - Initiation - Elongation - TeachMePhysiology Each codon codes for a particular amino acid. Every tRNA molecule possesses an anticodon that is complementary to the mRNA codon, and at the opposite end lies the attached amino acid. tRNA molecules are therefore responsible for bringing amino acids to the ribosome in the correct order, ready for polypeptide assembly. PDF Proteins & Amino Acids - Harvard University The specific order of amino acids in a protein is known as its primary structure. It is this sequence that determines the three-dimensional architecture of a protein. A famous experiment that proves that all the information necessary for proper folding of a protein is contained in its primary structure is presented in the next chapter. K12 Biology Semester 2 Unit 1 Flashcards | Quizlet RNA is made from DNA Which Structure in the diagram is responsible for bringing in amino acids tRNA Which two structures contain codons and anticodons mRNA and tRNA Recommended textbook solutions Biology 1st Edition Kenneth R. Miller, Levine 2,591 solutions Biology 1st Edition Kenneth R. Miller, Levine 2,470 solutions Texas Science Fusion: Grade 7 Biochemistry, Essential Amino Acids - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf Essential amino acids, also known as indispensable amino acids, are amino acids that humans and other vertebrates cannot synthesize from metabolic intermediates. These amino acids must be supplied from an exogenous diet because the human body lacks the metabolic pathways required to synthesize these amino acids.[1][2] In nutrition, amino acids are classified as either essential or non-essential.
What is a Dipeptide? | Formation, Structure & Examples Amino acids consist of the amino (NH2) and carboxyl (COOH) functional groups. Peptide bonds form between the carboxyl group of amino acid 1, and amino group of amino acid 2. Water is removed as a ...
5.09 Quiz: RNA Makes Protein Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to the diagram to answer the question. Which structure is responsible for bringing in the amino acids? ... Which structure will become the product of translation? Missing Metadata. 3. Sets found in the same folder. Biology 5.08 Quiz. 3 terms. ashleynicolette.
Placenta: Structure and Functions (Explained with Diagram) Structure: Placenta is a structure that establishes firm connection between the foetus and the mother. From the outer surface of the chorion a number of finger like projections known as chorionic villi grow into the tissue of the uterus. These villi penetrate the tissue of the uterine wall of the mother and form placenta.
Which structure is responsible for bringing in the amino acids? [Solved ... 1. What structure is responsible for bringing in amino acids? 2. Which molecule brings the amino acid that matches the current codon to the ribosome? 3. What is responsible for bringing the amino acid to ribosome? 4. Which structure is responsible for delivering the amino acids to the mRNA during translation? 5. Which type of RNA is responsible ...
Lysozyme - Structure, Examples, Function, Mechanism and ... - VEDANTU Structure of Lysozyme. A single peptide chain of around 129 amino acids makes up the condensed structure of lysozyme from hen egg white (hen egg white lysozyme or egg lysozyme). The residues of amino acid are numbered from the terminal α-group (N) to the terminal carboxyl-group (C). The circles show every fifth and every tenth residue is numbered.
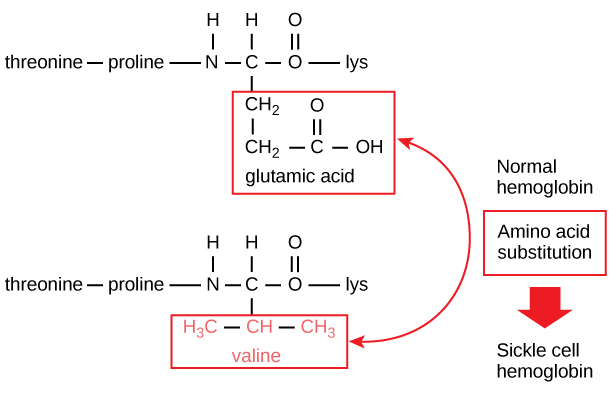
Tertiary Structure of Protein | Biology Dictionary The primary structure of a protein, which is the simple chain of amino acids held together by peptide bonds, is what determines the higher-order, or secondary and tertiary, structures by dictating the folding of the chain. Every amino acid has a unique side chain, or R-group, which is what gives amino acids their distinct properties.
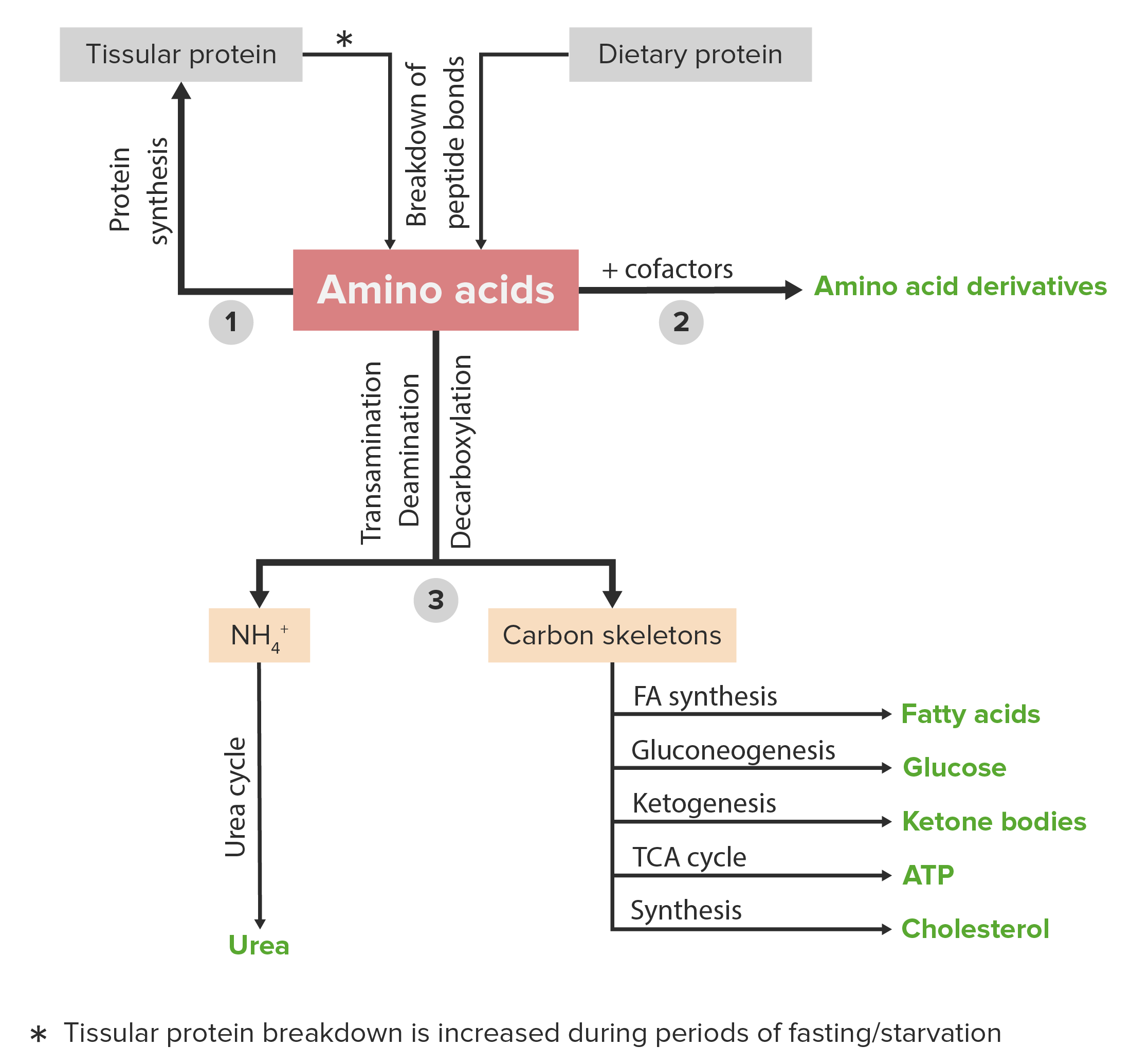
Protein Synthesis: Definition, Steps, and Diagram - Research Tweet The process of creating polypeptide chains is called protein synthesis. The process completes with an implication of amino acid synthesis, transcription, translation, and post-translational events in a biological system. The formation of amino acids from carbon sources like glucose is termed amino acid synthesis. It is a set of biochemical ...
5.09 Quiz: RNA makes protein Flashcards | Quizlet Look at the diagram. Which structure is responsible for bringing in the amino acids? 2 Which two structures are first to combine in translation? 1 and 4 Which structure holds the original code from DNA gene? 4 Which structure will become the product of translation. ...
What is an amino acid residue? - Study.com Amino acids are linked by the carboxyl group on one amino acid-binding to the amino group on another amino acid in a bond known as a peptide bond. We represent a protein as a linear string of amino...
Four Types of Protein Structure - ThoughtCo Proteins are biological polymers composed of amino acids. Amino acids, linked together by peptide bonds, form a polypeptide chain. One or more polypeptide chains twisted into a 3-D shape form a protein. Proteins have complex shapes that include various folds, loops, and curves. Folding in proteins happens spontaneously.
Role And Structure Of Ribosomes - Translation - MCAT Content - Jack Westin Incoming aminoacyl-tRNAs (a tRNA with an amino acid covalently attached) enter the ribosome at the A site. The peptidyl-tRNA (a tRNA carrying the growing polypeptide chain) is held in the P site. The E site, located right next to the P site, holds empty tRNAs just before they exit the ribosome.
4 Levels of Protein Structure (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion The primary structure of a protein is the order of these amino acids in the backbone of each of the polypeptide chains comprising the molecule. The primary structure of a polypeptide chain is delineated beginning with the amino acid occupying the polypeptide's N-terminus.
Chapter 2: Protein Structure - Chemistry - Western Oregon University The upper diagram displays the cis and trans conformations of two adjacent amino acids noted as X and Y which indicate any of the 20 amino acids, except for proline. In the trans conformation the R-group from amino acid X is rotated away and on the other side of the molecule when compared with the R-group from amino acid Y.
Which structure is responsible for bringing in the amino acids? (Points ... Which structure is responsible for bringing in the amino acids? (Points : 1) - 1604096



























0 Response to "39 which structure in the diagram is responsible for bringing in amino acids"
Post a Comment