39 refer to the diagram. by producing at output level q,
PDF AP Unit 6 Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At output Q production will be unprofitable. True False 61. Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. The profit-maximizing price for this firm is J. True False 62. Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. PDF Practice Business and Cost - Mount Saint Mary College 22. Refer to the above diagram. For output level Q, per unit costs of Bare: A. unattainable and imply the inefficient use of resources. B. unattainable, given resource prices and the current state of technology. C. attainable, but imply the inefficient use of resources. D. attainable and imply least-cost production of this level of output.
plot_model, evaluate_model (pycaret) not producing any output ... Aug 07, 2022 · Using the evaluate_model() function which displays a user interface for all of the available plots for a given model. internally uses the plot_model() function.. It displays only one graph at a time when we pass graph name as an argument.
Refer to the diagram. by producing at output level q,
OneClass: Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q, the total ... Refer to the diagram. By producing at output level Q. A. productive efficiency is achieved but allocative efficiency ls not. B. neither productive nor allocative efficiency is achieved. C. allocative efficiency is achieved, but productive efficiency is not. D. both productive and allocative efficiency is achieved. Chapters 6, 7, 8 - Microeconomics Quiz questions - StuDocu Refer to the Figure above. The diagram above contains _____ cost curves. A) short run B) intermediate run C) long run D) both short run and long run. Answer: A. Refer to the Figure above. At output level Q A) average fixed cost is increasing. B) average variable cost equals average fixed cost. C) marginal cost is negative. ECON 202 Blanchard Exam 2 - Subjecto.com Refer to the diagram. By producing at output level Q: a. neither productive nor allocative efficiency is achieved. b. both productive and allocative efficiency are achieved. c. allocative efficiency is achieved, but productive efficiency is not. d. productive efficiency is achieved, but allocative efficiency is not.
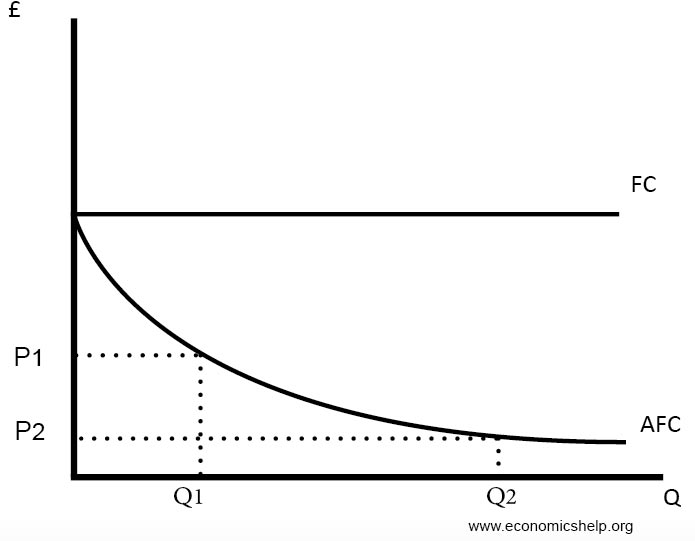
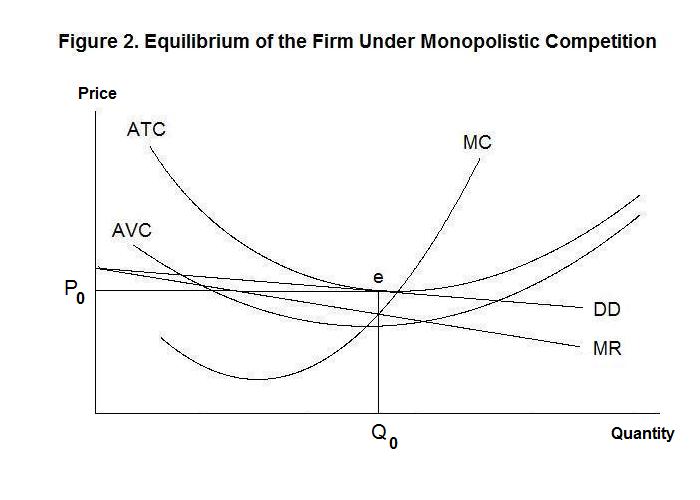
Refer to the diagram. by producing at output level q,. (Get Answer) - 31) Refer to Figure 8-7. When the output level is 100 ... When the output level is 100 units average fixed cost is A) $10. B) $8. C). 31) Refer to Figure 8-7. When the output level is 100 units average fixed cost is A) $10. B) $8. C) $5. D) This cannot be determined from the diagram. 32) Refer to Figure 8-7. When output level is 100, what is the total cost of production? A) $20 B) $1,000 C) $1,200 Solved MC ATC a. MR a, Q Quantity Refer to the diagram. By - Chegg MR a, Q Quantity Refer to the diagram. By producing at output level Q Multiple Choice allocative efficiency is achleved, but productive efficiency is not. productive efficiency is achleved, but allocative efficiency is not. both productive and allocative efficiency are achleved. nelther productive nor allocative efficiency is achieved. Answered: MC ATC AVC F AFC A Quantity Refer to… | bartleby A: Graphical analysis of cost of production is very important as it enables us to gain important…. Q: MC 90 ATC AVC 70 40 30 50 100 8. The figure above shows a firm's marginal cost, average total cost,…. Marginal cost = 70 Average total cost = 70 Average variable cost = 40. Q: A firm's total short-run cost function is C (y)=5y3−12y2+110y+9 . Pricing Policies: Objectives and Techniques (With Diagram) The concept is illustrated in the diagram below. In Figure 19.4, D and MR are the existing firm’s demand (average revenue) and marginal revenue curves, respectively. Its short-run average and marginal cost curves are shown by SRAC E and SKMC E. Here OQ* is the profit-maximizing level of output and OP* is the corresponding price.
CH 16/17 Flashcards | Quizlet A monopolistically competitive firm is currently producing 20 units of output. At this level of output the firm is charging a price equal to $20, has marginal revenue equal to $12, has marginal cost equal to $12, and has average total cost equal to $18. From this information we can infer that A. the firm is currently maximizing its profit. Use the... - Martinsville Indiana Computer Repair - Facebook 197. Refer to the above diagram. If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will: A) suffer an economic loss. B) earn a normal profit. C) earn an economic profit. D) achieve productive efficiency, but not allocative efficiency. Answer: B. Type: G Topic: 5 E: 433 MI: 189 198. Refer to the above diagram. By producing output level Q: PDF Humble Independent School District / Homepage Real domestic output Refer to the above diagram. If the equilibrium price level is PI, then: A) the equilibrium output level is Q3. B) producers will supply output level QI. C) the equilibrium output level is Q2. D) aggregate demand is AD2. Refer to the above diagram. At the equilibrium price and quantity: A) aggregate demand exceeds aggregate ... Refer to the diagram. By producing at output level Q - OneClass 11 Dec 2019 Refer to the diagram. By producing at output level Q A. productive efficiency is achieved but allocative efficiency ls not. B. neither productive nor allocative efficiency is achieved. C. allocative efficiency is achieved, but productive efficiency is not. D. both productive and allocative efficiency is achieved. Show full question + 20
Answered: 12 7 10 6. D 4 eBook o 2 4 6 8 10… | bartleby D 4 eBook o 2 4 6 8 10 Computers Refer to the diagram. If society is currently producing 9 units of bicycles and 4 units of computers and it now decides to increase computer output to 5, the cost Multiple Choice will be 2 units of bicycles. will be 1 unit of bicycies. will be zero because unemployed resources are available. Bicycles 2. Question Question 8 of 50 10 points refer to the diagram by - Course Hero Refer to the diagram. By producing at output level Q: A. neither productive nor allocative efficiency is achieved. B.both productive and allocative efficiency are achieved. C. allocative efficiency is achieved, but productive efficiency is not. D. productive efficiency is achieved, but allocative efficiency is not. Refer to the above diagram at output level q total - Course Hero Refer to the above diagram At output level Q total variable cost is A 0 BEQ B Refer to the above diagram at output level q total School Johnson County Community College Course Title ECON 230 Type Notes Uploaded By kaigefighter08 Pages 41 Ratings 95% (44) This preview shows page 14 - 17 out of 41 pages. View full document See Page 1 65. Microeconomics: Trivia Questions On Production And Cost! Quiz The total cost of producing a given level of output is A. Maximized when a corner solution exists. B. Minimized when the ratio of marginal product to input price is equal for all inputs. C. Minimized when the marginal products of all inputs are equal. D. Minimized when marginal product multiplied by input price is equal for all inputs. 10.
Refer to the diagram for athletic shoes. If the current output of shoes ... Refer to the diagram for athletic shoes. If the current output of shoes is Q 3, then society should produce fewer shoes to achieve the optimal allocation of resources. society should produce more shoes to achieve the optimal allocation of resources. resources are being allocated efficiently to the production of shoes.
Levels in Data Flow Diagrams (DFD) - GeeksforGeeks Here, we will see mainly 3 levels in the data flow diagram, which are: 0-level DFD, 1-level DFD, and 2-level DFD. 0-level DFD: It is also known as a context diagram. It's designed to be an abstraction view, showing the system as a single process with its relationship to external entities. It represents the entire system as a single bubble ...
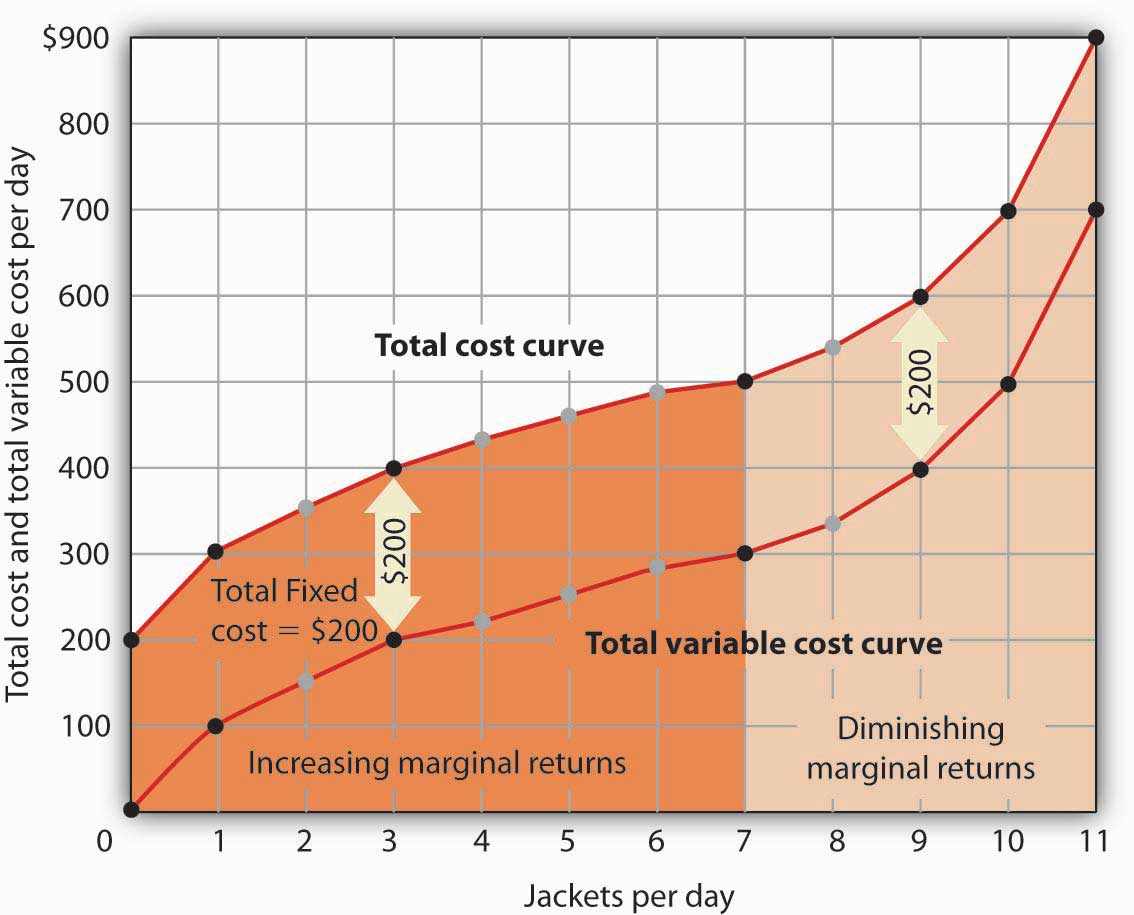
The Production Process (With Diagram) - Economics Discussion The production function is a short-run production function because it illustrates what happens to output as more and more units of the variable input, labour, are added to the fixed stock of capital. Thus Fig. 13.2 is a graphic representation of equation (2) which is the short-run production function for radios.
Chapter 8 Tutorial Answers - auknotes - Google Refer to the above diagram. A shift in the production possibilities curve from AB to CD is most likely due to: A. The use of the economy's resources in an efficient way B. An increase in the...
econ exam #2 Flashcards | Quizlet change in Q Refer to the above diagram, where variable inputs of labor are being added to a constant amount of property resources. The total output of this firm will cease to expand if a labor force in excess of Q3 is employed. Refer to the above diagram, where variable inputs of labor are being added to a constant amount of property resources.
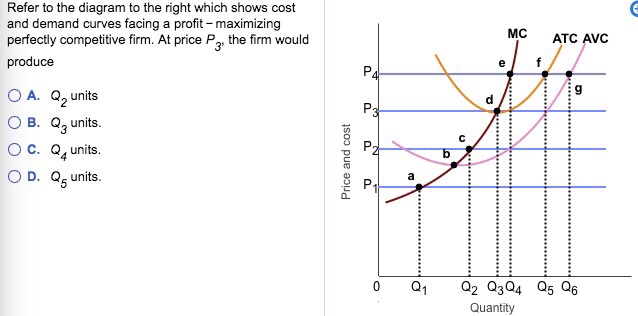
PDF Econ 1013 2nd MT F 2013 - Compiler Press 26) Refer to Figure 9-1. The diagram shows cost curves for a perfectly competitive firm. If the market price is P1, the profit-maximizing firm in the short run should A) produce output A. B) produce output B. C) produce output C. D) produce output D or shut down as it doesnʹt really matter which.
Producer's Equilibrium or Optimisation (With Diagram) 2. To maximise its output for a given cost. Thus the least cost combination of factors refers to a firm producing the largest volume of output from a given cost and producing a given level of output with the minimum cost when the factors are combined in an optimum manner. We study these cases separately. Cost-Minimisation for a Given Output:
Chapter 11 Study Questions ( Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to the diagrams, which pertain to a purely competitive firm producing output q and the industry in which it operates. In the long run we should expect: a. firms to enter the industry, market supply to rise, and product price to fall. b. firms to leave the industry, market supply to rise, and product price to fall.




0 Response to "39 refer to the diagram. by producing at output level q,"
Post a Comment