39 the equation for the demand curve in the below diagram
Econ 121 Connect (Quizzes) Flashcards | Quizlet (Advanced analysis) Answer the question on the basis of the following information. The demand for commodity X is represented by the equation P = 100 - 2Q and supply by the equation P = 10 + 4Q. Refer to the given information. The equilibrium quantity is: 15 Refer to the table. Demand Curve - Definition, Shift, Elasticity, Examples - WallStreetMojo Movements Along the Demand Curve Upward and downward movements on the graph are brought out by changes in price (and not other factors). There is an inverse relationship between price and demand. Upward Movement: If the curve moves upward, the price of goods increases—demand falls at the same rate.
DERIVATION OF THE DEMAND CURVE - WikiEducator It is the demand curve that shows relationship between price of a good and its quantity demanded. In this section we are going to derive the consumer's demand curve from the price consumption curve . Figure.1 shows derivation of the consumer's demand curve from the price consumption curve where good X is a normal good.

The equation for the demand curve in the below diagram
(Advanced analysis) The equation for the supply curve in the below ... in a market for figs (Q, measured in kilograms) monthly demand and supply is given by:... in a market for figs (Q, measured in kilograms) monthly demand and supply is given by: market equilibrium price is p*= 12 market equilibrium quantity is q* = 40,000 a) compute the price elasticity of supply of figs and the price elasticity of demand of figs at the equilibrium point. As per the below diagram, the current position of the demand curve is D ... As per the below diagram, the current position of the demand curve is D 1 , and the price of a portal power bank, which is a normal good. i.e. is $3. If there is an increase in consumer income, will the demand curve shift from D 2 or to D 3 . Question Chapter 3, Problem 17P To determine amydiduch.weebly.com › algebra-of-supply--demandAlgebra of Supply & Demand - ECON 101: THE BASICS A simple linear equation for demand might be QD = 30 – 1/3 P, where the intercept (here, 30) accounts for the current values of all of those determinants other than the product’s price (i.e. incomes, preferences, etc.). Thus, a demand equation assumes all other things are held constant except price and quantity demanded (our “ceteris ...
The equation for the demand curve in the below diagram. › the-economy › bookUnit 15 Inflation, unemployment, and monetary policy - CORE In the boom shown, the upward shift in the aggregate demand curve reduces the unemployment rate, which in turn creates a bargaining gap of 1%. In the recession shown, the downward shift in the aggregate demand curve increases the unemployment rate, which in turn creates a bargaining gap of 0.5%. What is Inverse demand function? Definition and explanation. - Penpoin MC = MR → 12 + 2Q = 24 - 4Q → 6Q = 24 - 12 → Q = 2 So, the company's profit will be at maximum if it produces/sells 2 units. Third, as the inverse supply function, the inverse demand function, is useful when drawing demand curves and determining the slope of the curve. Economists usually place price (P) on the vertical axis and quantity (Q) on the horizontal axis. Demand curve formula - Economics Help The demand curve shows the amount of goods consumers are willing to buy at each market price. A linear demand curve can be plotted using the following equation. Qd = a - b (P) Q = quantity demand a = all factors affecting price other than price (e.g. income, fashion) b = slope of the demand curve P = Price of the good. Inverse demand equation en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Inverse_demand_functionInverse demand function - Wikipedia Definition. In mathematical terms, if the demand function is Q = f(P), then the inverse demand function is P = f −1 (Q). The value P in the inverse demand function is the highest price that could be charged and still generate the quantity demanded Q. This is useful because economists typically place price (P) on the vertical axis and quantity (Q) on the horizontal axis in supply-and-demand ...
Demand Curve Questions and Answers | Homework.Study.com You are the manager of a monopolistically competitive firm, and your demand and cost functions are given by Q = 36 - 4P and C (Q) = 4 + 4Q + Q^2. Calculate your firm s maximum profits. View Answer... 5 Determinants of Demand With Examples and Formula - The Balance The 5 Determinants of Demand. The five determinants of demand are: The price of the good or service. The income of buyers. The prices of related goods or services—either complementary and purchased along with a particular item, or substitutes bought instead of a product. The tastes or preferences of consumers will drive demand. Examples of Demand Curve (With Diagram) | Microeconomics Fig. 7.13 presents the PCC and demand curves for perfect substitutes — such as blue ink. (x1) and black ink (x2) for a colour-blind person. The demand for x1is zero when p1is greater than p2, any quantity on the budget line when p1= p2and m/p1when p1is less than p2. The PCC shows these possibilities as in Fig. 7.13(a). › open-economyMundell-Fleming Model: Meaning and Main Message (With Diagram) Here the supply of money equals its demand and demand for money varies inversely with r* and the positively with Y. In this model, M remains exogenously fixed by the central bank. The new LM curve, as shown in Fig. 12.2(b), is vertical — since the equation (2) has no relation to the exchange rate.
› oligopoly › cournotsCournot's Duopoly Model (With Diagram) - Economics Discussion Thus, the reaction curve of firm A is the locus of points of highest profits that firm A can attain, given the level of output of rival B. It is called ‘reaction curve’ because it shows how firm A will determine its output as a reaction to B’s decision to produce a certain level of output, A’s reaction curve is shown in figure 9.6. › ~ghong › fina3334CHAPTER 10 MARKET POWER: MONOPOLY AND MONOPSONY intercept of the inverse demand curve on the price axis is 27. The slope of the inverse demand curve is the change in price divided by the change in quantity. For example, a decrease in price from 27 to 24 yields an increase in quantity from 0 to 2. Therefore, the slope is − 3 2 and the demand curve is P = 27 −1.5Q. The marginal revenue ... Demand Curve - Understanding How the Demand Curve Works Following the original demand schedule for high-quality organic bread, assume the price is set at P = $6. At this price, the quantity demanded would be 2000. If the price were to change from P = $6 to P = $4, it would cause a movement along the demand curve, as the new quantity demanded would be 3000. Other Resources PDF Economics 101 Answers to Homework #4 Q1: Derive a demand curve the information provided for situation 1, derive the demand curve for Y. (Assume that the demand curve for Y is a straight line.) ANSWER: a and b. The graph is as follows: ... Combine the two above equations we get: Ya/Xa = Px/Py = (1/2) Rearrange this equation we have: Xa=2Ya, plug it into BL1, we can solve: Xa=6, Ya=3. Thus
Demand Curve: Definition, Types, and How It Works - The Balance The demand curve is a visual representation of how many units of a good or service will be bought at each possible price. It plots the relationship between quantity and price that's been calculated on the demand schedule, which is a table that shows exactly how many units of a good or service will be purchased at various prices. As you can see ...
Law of Demand: Schedule, Curve, Function, Assumptions and Exception In the linear demand function, AD/AP is constant and the resultant demand curve is a straight line. For example, if a=100 and b=5, then the demand function can be represented by the following equation: Dx = 100 - 5 (Px)
6 Main Types of Demand Curves (With Diagram) - Economics Discussion That is why, from the point of view of elasticity measurement,it shall be assumed that the demand curves are negatively sloped straight lines. Suppose, such a straight line demand curve is: P = a - bq ; a > 0, b > 0 (2.9) The slope or the straight line (2.9), as shown in fig. 2.8, is dp/dq = -b < 0 and its vertical intercept is a > 0.
› economics › moneyKeynes Theory of Demand for Money (Explained With Diagram) At a still lower rate of interest (and still higher bond price), Tie more bulls will become bears and the speculative demand for higher still. Thus, Keynes derived a downward-sloping aggregate speculative demand curve for money with respect to the “a rate of interest, as shown in Figure 11.2.
Solved The data below represent a demand schedule. Product | Chegg.com In the diagram below, draw a demand curve. Instructions: Use the tool provided 'Demand' to graphically show demand. This line should only contain the two endpol Demand Schedule Demand Product price Quantity demanded b. Use the midpoint formula for Eg to determine price elasticity of demand for each of the four possible $1 price changes.
3.3 Demand, Supply, and Equilibrium - Principles of Macroeconomics A Decrease in Demand. Panel (b) of Figure 3.10 "Changes in Demand and Supply" shows that a decrease in demand shifts the demand curve to the left. The equilibrium price falls to $5 per pound. As the price falls to the new equilibrium level, the quantity supplied decreases to 20 million pounds of coffee per month.
Market Demand Curve Schedule, Equation & Examples - Study.com To calculate market demand, a general equation can be used: {eq}Q=f (P)=q1+q2+q3 {/eq} In this equation, q1, q2, and q3 are individual demand curves that are added together while factoring in price...
The Market Demand Curve in 6 Easy Pictures | CU Online Generally speaking, the market demand curve is a downward slope; that is, as price increases, demand decreases. The reverse of this is also true; as price decreases, demand increases. The job of someone providing a product is to find the "sweet spot" on the demand curve: the point at which price and demand are both optimal. The market ...



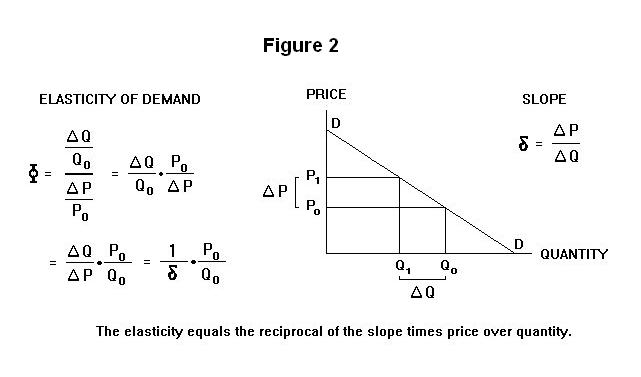
0 Response to "39 the equation for the demand curve in the below diagram"
Post a Comment