39 the diagram below represents a spontaneous reaction (δg
Solved The diagram below represents a spontaneous reaction | Chegg.com Question: The diagram below represents a spontaneous reaction (deltaG < 0). Drag the labels to the correct bins. This problem has been solved! See the answer Show transcribed image text Expert Answer 100% (22 ratings) Left side must include REACTANTS right side (on the bottom) must be products, since they must be accordingly to the r … Part A The image represents a spontaneous gaseous reaction at a ... Part A The image represents a spontaneous, gaseous reaction at a constant temperature T K. Predict whether Δ H, Δ S, and Δ G for this reaction are positive, negative, or zero. ΔG ˂ 0 for spontaneous reactions Moles of gases decreases, meaning entropy (ΔS) decreases If the sign of Δ G is negative and the sign of Δ S is negative then ΔH must be negative Part B For the gaseous reaction ...
Ellingham diagram Explanation - Thermodynamics of Metallurgy - BYJUS H.G.T Ellingham proposed the Ellingham diagram to predict the spontaneity of reduction of various metal oxides. Ellingham diagram was basically a curve which related the Gibbs energy value with the temperature. Gibbs energy is given as: ΔG = ΔH - TΔS Where ΔH is the change in enthalpy and ΔS is the change in entropy.
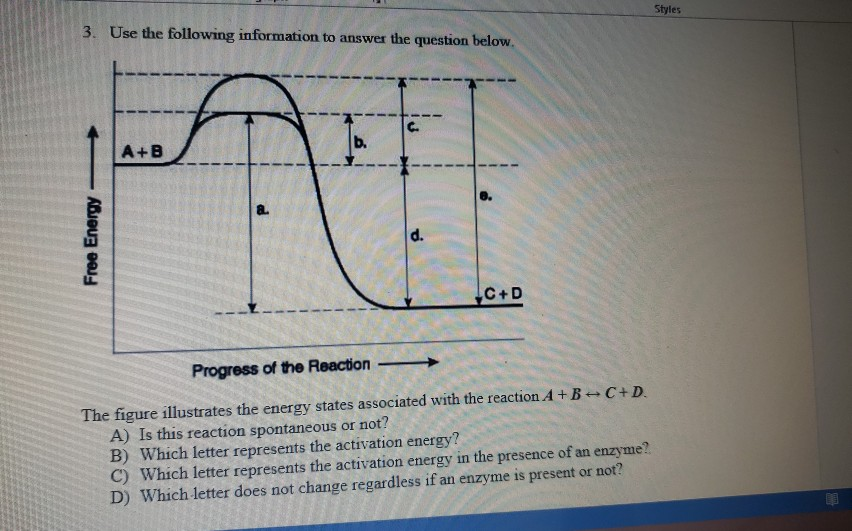
The diagram below represents a spontaneous reaction (δg
Test: Ellingham's Diagram & Its Applications: Thermodynamic Principles ... Eilingham diagram represents a graph of ΔG° vs T. ... Hence this reaction is not spontaneous. *Multiple options can be correct. Test: Ellingham's Diagram & Its Applications: Thermodynamic Principles of Metallurgy - Question 14. Save. Consider the Ellingham diagram given below. Which metal(s) in the diagram can be extracted at 1100 K using ... Thermodynamics Flashcards | Quizlet adding a catalyst Classify each of the following processes as spontaneous or nonspontaneous. I. H2O (l) → H2O (g) T = 25°C, vessel open to atmosphere with 50% relative humidity II. H2O (s) → H2O (l) T = 25°C, P = 1 atm I and II are both spontaneous. The reaction A (g) → B (g) is spontaneous under standard conditions. Which of the following Answered: A В | bartleby Containers A, B, and C are attached by closed stopcocks of negligible volume. If each particle shown in the picture represents 10 6 particles, (a) How many blue particles and black particles are in B after the stopcocks are opened and the system reaches equilibrium?
The diagram below represents a spontaneous reaction (δg. Potential Energy Diagrams - Kentchemistry.com In this diagram, the activation energy is signified by the hump in the reaction pathway and is labeled. At the peak of the activation energy hump, the reactants are in the transition state, halfway between being reactants and forming products. This state is also known as an activated complex. Effect of a Catalyst Solved The diagram below represents a spontaneous reaction - Chegg Question: The diagram below represents a spontaneous reaction (deltaG degree < 0). Drag the labels to the correct bins. uncatalyzed rx'n Delta G degree standard free E of activation products reactants catalyzed rx?n This problem has been solved! See the answer Show transcribed image text Expert Answer 100% (63 ratings) Chem 180 Exam 3 Flashcards | Quizlet spontaneous spontaneous nonspontaneous Qualitative Predictions about Entropy Entropy is the randomness of a system. At the molecular level, entropy can be described in terms of the possible number of different arrangements of particle positions and energies, called microstates. The more microstates the system has, the greater its entropy. Which ionic equation represents a spontaneous reaction that can occur ... A redox reaction occurs when electrons are transferred from a substance that is oxidized to one that is being reduced. The reductant is the substance that loses electrons and is oxidized in the process; the oxidant is the species that gains electrons and is reduced in the process.
Electrochemistry Basics - Chemistry LibreTexts Aug 07, 2021 · For a spontaneous reaction, E cell is positive and ΔG (Gibbs free energy, used to determine if a reaction occurs spontaneously) is negative. Thus, when ΔG is negative the reaction is spontaneous. Merging electrochemistry with thermodynamics gives this formula: \[\Delta G = -n F E_{cell} \] Insight into the mechanism of deep NO photo-oxidation by ... Subsequently, DFT calculations were developed on the basis of reaction pathway to deeply reveal the enhancement of the adsorption/activation of NO reactant on BTO and BTO-7 by analyzing the Gibbs free energy in Fig. 8. Intuitively, the Gibbs free energies of oxidation path (NO → NO 2 → NO 3-) on BTO are higher than that of BTO-7. The ... Spontaneous reactions and ΔG° - Jack Westin The Gibbs free energy of a reaction dictates where a reaction is spontaneous (-ΔG) or nonspontaneous (+ΔG). This is due to the components of the free energy equation (ΔG = ΔH -TΔS) that add up to be negative or positive. While an exothermic reaction (-ΔH) may suggest spontaneous reaction, a high temperature (T) or large entropy (ΔS) may ... Coordinating single-atom catalysts on two-dimensional ... Zhang et al. fabricated a new joint electronic system by integrating highly dispersed Fe single atoms into g-C 3 N 4 for the photocatalytic hydrogen evolution reaction (Fig. 4a) . In this SAC system, the band structure of g-C 3 N 4 was significantly optimized by compositing the Fe single atoms inside the structure, causing the desirable ...
Gibbs free energy - Wikipedia The reaction will only be allowed if the total entropy change of the universe is zero or positive. This is reflected in a negative ΔG, and the reaction is called an exergonic process. If two chemical reactions are coupled, then an otherwise endergonic reaction (one with positive ΔG) can be made to happen. Metabolism - PMC - PubMed Central (PMC) Aug 24, 2020 · If on the other hand, ΔG is positive, and you are looking up at the hill, then the reaction is unfavourable or not spontaneous, i.e. the reaction is ENDERGONIC, or in the case of heat, endothermic. As reactions can be reversible, if the forward reaction has a positive ΔG, then the reverse reaction will be negative, therefore the reaction ... A reaction is spontaneous if ΔG is ___? negative, positive, or zero ... The change in free energy (ΔG) is the difference between the heat released during a process and the heat released for the same process occurring in a reversible manner. The sign of ΔG gives an indication for the spontaneity of the reaction: If ΔG is negative, the reaction is spontaneous. If ΔG = zero, the reaction is at equilibrium. AAMC MCAT Practice Exam 1 Cp Solutions - MCAT Content That means we’re looking for an answer with a positive ΔS°. The test-maker also mentions the reaction is spontaneous so we’re looking for an answer with negative ΔG°. negative ΔG° and positive ΔS°. Right away we have a strong answer choice. We said the reaction is spontaneous so we’re looking for an answer with negative ΔG°.
PDF CHEM1101 2014-J-12 June 2014 The diagram below represents the ... CHEM1101 2013-J-11 June 2013 • The diagram below represents the Gibbs free energy change associated with the formation of four different oxides. Using the free energy data above, write down the equation and indicate with an arrow the direction of the expected spontaneous reaction under the following conditions.
Answered: A В | bartleby Containers A, B, and C are attached by closed stopcocks of negligible volume. If each particle shown in the picture represents 10 6 particles, (a) How many blue particles and black particles are in B after the stopcocks are opened and the system reaches equilibrium?
Thermodynamics Flashcards | Quizlet adding a catalyst Classify each of the following processes as spontaneous or nonspontaneous. I. H2O (l) → H2O (g) T = 25°C, vessel open to atmosphere with 50% relative humidity II. H2O (s) → H2O (l) T = 25°C, P = 1 atm I and II are both spontaneous. The reaction A (g) → B (g) is spontaneous under standard conditions. Which of the following
Test: Ellingham's Diagram & Its Applications: Thermodynamic Principles ... Eilingham diagram represents a graph of ΔG° vs T. ... Hence this reaction is not spontaneous. *Multiple options can be correct. Test: Ellingham's Diagram & Its Applications: Thermodynamic Principles of Metallurgy - Question 14. Save. Consider the Ellingham diagram given below. Which metal(s) in the diagram can be extracted at 1100 K using ...

0 Response to "39 the diagram below represents a spontaneous reaction (δg"
Post a Comment