38 refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. long-run equilibrium price will be
PDF ECO 211 Microeconomics Yellow Pages ANSWERS Unit 3 - Harper College 3. The diagrams portray short-run equilibrium, but not long-run equilibrium. 4. The diagrams portray long-run equilibrium, but not short-run equilibrium. 2. Refer to the above diagrams, which pertain to a purely competitive firm producing output q and the industry in which it operates. In the long run we should expect: 1. firms to enter the ... Monopolistic Competition in the Long-run - CliffsNotes Monopolistic Competition in the Long-run The difference between the short‐run and the long‐run in a monopolistically competitive market is that in the long‐run new firms can enter the market, which is especially likely if firms are earning positive economic profits in the short‐run.
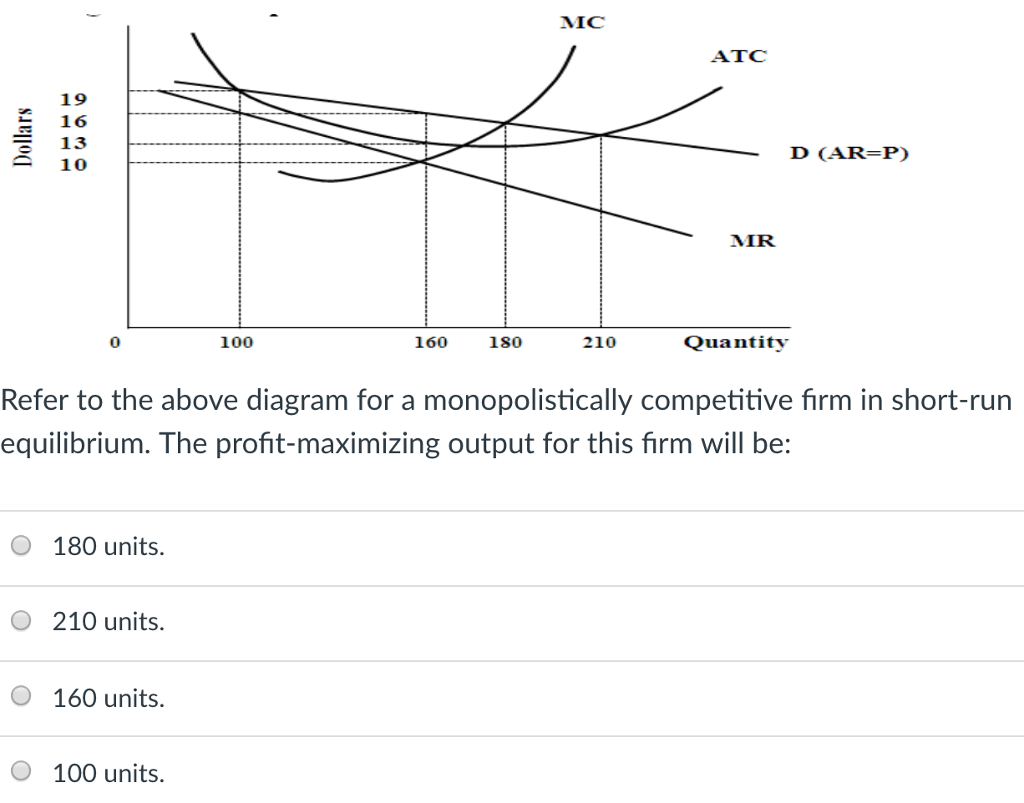
Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm ... The correct answer is: many firms producing differentiated products. Question16 Correct Mark 1.00 out of 1.00 Refer to the above diagram for a noncollusive oligopolist. We assume that the firm is initially in equilibrium at point Ewhere the equilibrium price and quantity are P and Q.
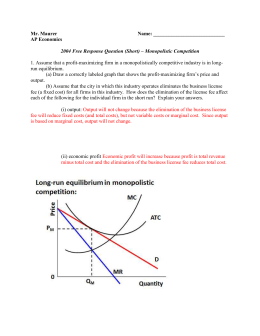
Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. long-run equilibrium price will be
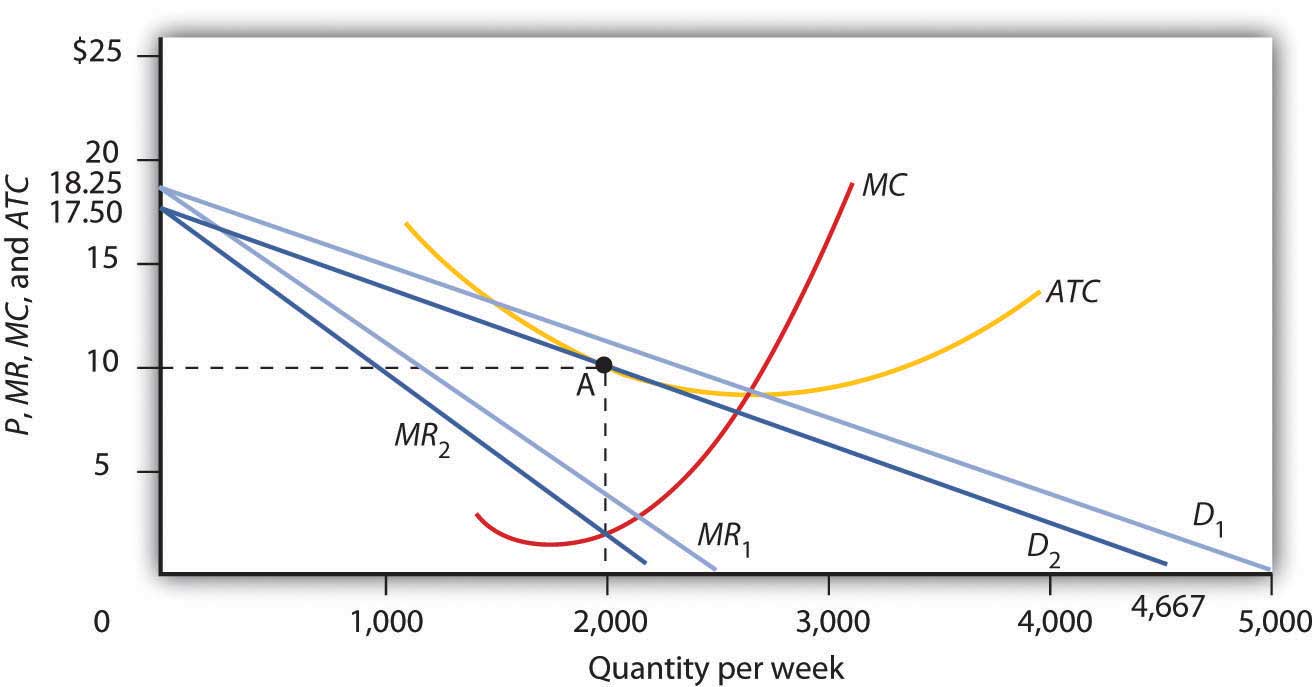
8.4 Monopolistic Competition - Principles of Microeconomics In the long run, what price will this firm charge for its output? a) $10. b) A price less than $10 and greater than $6. c) $6. d) A price less than $6 and greater than $4. The following TWO questions refer to the diagram below. 3. Which of the four diagrams illustrates a long run equilibrium for a monopolistically competitive firm? a) Figure 1 ... Draw and explain a diagram to show the long-run equilibrium in a ... The following diagram shows the equilibrium in a monopolistically competitive market in the long run: In the long run, due to the entry and exit of firms in the industry, the demand curve shifts, due to which the price becomes equal to the average total cost where each firm earns zero economic profits. Solved > 21.The price elasticity of a monopolistically competitive firm ... Question : 21.The price elasticity of a monopolistically competitive firm's demand curve : 1637280. 21. The price elasticity of a monopolistically competitive firm's demand curve varies: A. inversely with the number of competitors and the degree of product differentiation. B. directly with the number of competitors and the degree of product ...
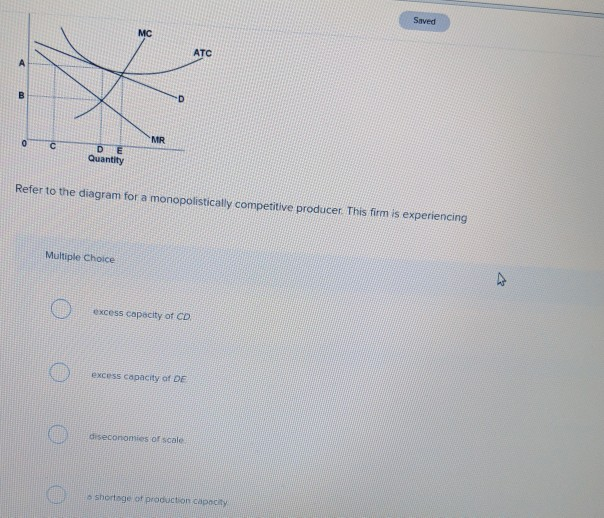
Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. long-run equilibrium price will be. Microeconomics Chapter 13 Flashcards | Quizlet When a monopolistically competitive firm is in long-run equilibrium, MR = MC and minimum ATC > P. Refer to the above graphs. A short-run equilibrium that would produce profits for a monopolistically competitive firm would be represented by graph A. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive producer. This firm is experiencing Solved > 11) Long-run equilibrium under monopolistic competition and ... 11) Long-run equilibrium under monopolistic competition and perfect competition is similar in that A) firms produce at the minimum point of their average cost curves. B) price equals marginal cost. C) firms break even. D) price equals marginal revenue. Figure 13-7 12) Refer to Figure 13-7. What is the profit maximizing output level? A) Q1 units Monopolistic Competition: Short-Run Profits and Losses, and Long-Run ... Hence, the long-run equilibrium for monopolistic competition will equate the market price to the average total cost, where marginal revenue = marginal cost, as shown in the diagram below. Remember, in economics, average total cost includes a normal profit. Long run equilibrium for a monopolistically competitive firm where ... The following TWO questions refer to the diagram below, which illustrates the demand, marginal revenue, and relevant cost curves for a monopolistically competitive firm. 1. How many units of output should this firm produce, in order to maximize profits? a) 10. b) 25. c) 30. 2. In the long run, what price will this firm charge for its output?
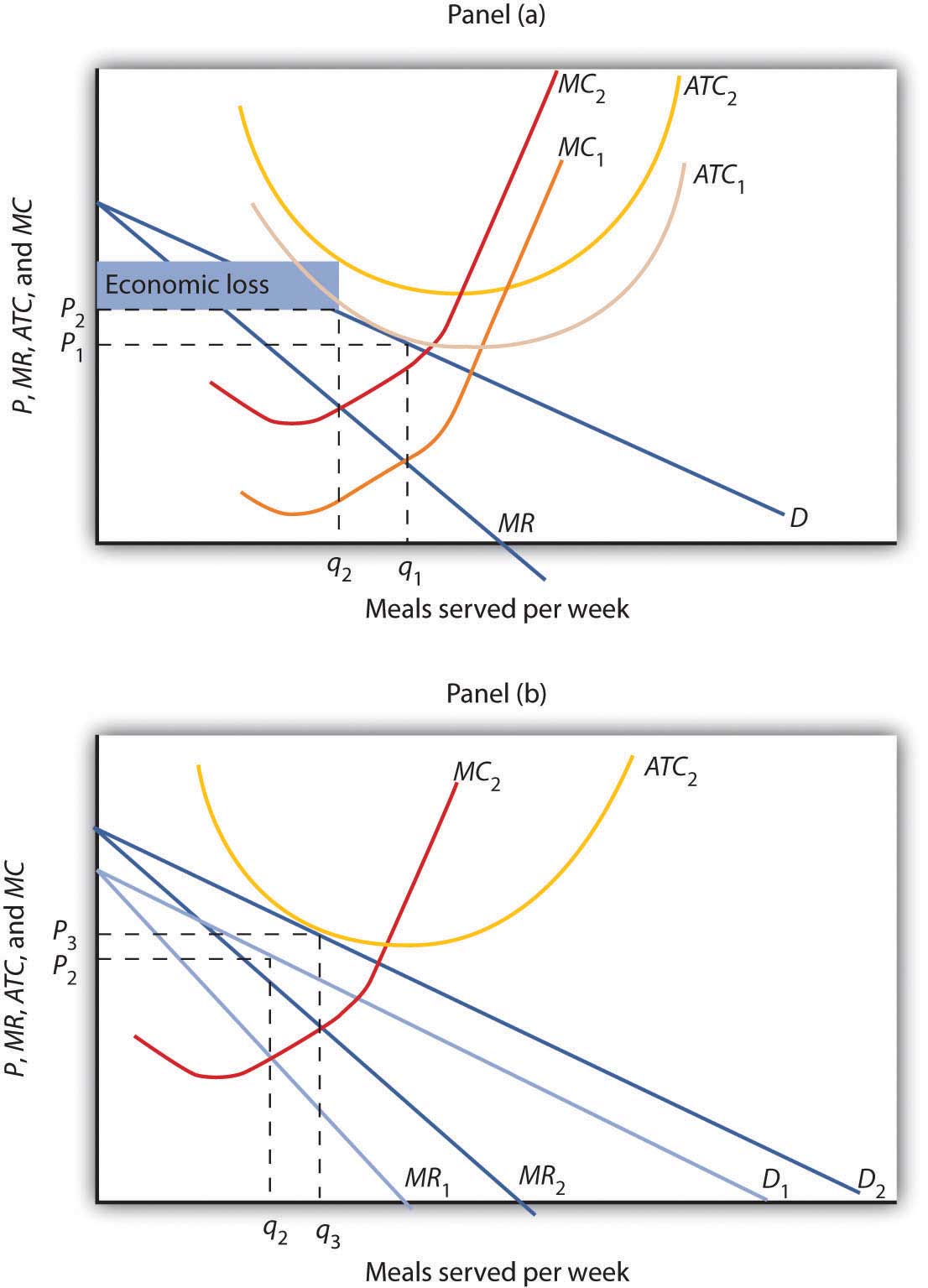
Answered: Refer to the diagrams, which pertain to… | bartleby A: Long-run equilibrium for a monopolistically competitive firm is shown in the following diagram. question_answer Q: In the long-run equilibrium of a monopolistically competitive industry, the zero-profit point is to… MACRO Exam 3 Flashcards | Quizlet In the long-run, the price charged by a monopolistically competitive firm seeking to maximize profit will: 160. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. The profitmaximizing ... Profit of $480. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This ... Solved 1.Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically | Chegg.com This problem has been solved! 1.Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. Long-run equilibrium output will be: a. b. d. 2.Refer to the diagram. In short-run equilibrium, the monopolistically competitive firm shown will set its price: a. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically - Course Hero Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. Assume the firm is part of an increasing-cost industry. In the long run firms will:enter this industry, causing demand to fall and the ATC curve to shift upward.
Equilibrium of the Monopolist: Short-Run and Long-Run Equilibrium In figure 6.2 the equilibrium of the monopolist is defined by point ɛ, at which the MC intersects the MR curve from below. Thus both conditions for equilibrium are fulfilled. Price is P M and the quantity is X M. The monopolist realizes excess profits equal to the shaded area AP M CB. Note that the price is higher than the MR. Answered: In a long-run equilibrium, would a… | bartleby Solution for In a long-run equilibrium, would a perfectly competitive firm and a monopolistically competitive firm produce at the level of output that minimizes… PDF Econ 1013 2nd MT F 2013 - Compiler Press A monopolistically competitive firm is allocatively inefficient because in the long-run equilibrium A) MC is greater than price. B) price is greater than LRAC at QL. C) LRAC is not at its minimum. D) price is greater than MC at QL. E) none of the above -- the long-run equilibrium is allocatively efficient. 19) 20) Refer to Figure 11-3. In the ... Monopolistic Competition: Features, Price Determination, Examples Long-run equilibrium. If firms in a monopolistic competition earn super-normal profits in the short-run, then new firms will have an incentive to enter the industry. As these firms enter, the profits per firm decrease as the total demand gets shared between a larger number of firms. This continues until all firms earn only normal profits.
Draw a diagram of the long-run equilibrium in a monopolistically ... Verified Textbook Solution: Principles of Microeconomics (8th Edition). Mankiw. ISBN:9781337096874Category: Economics Draw a diagram of the long-run equilibrium in a monopolistically competitive market. « Back 0 ♥ 0 Draw a diagram of the long-run equilibrium in a monopolistically competitive market. How is price related to average total Continue Reading
Monopolistic Competition Equilibrium| Long-run, Short-run In a monopolistically competitive market, the short-run equilibrium occurs when each firm's plant size is fixed and the total number of firms in the market is also fixed. However, analyzing the behavior of a monopolistically competitive firm is more difficult than analyzing the behavior of a perfectly competitive firm.
revmncmp - Harper College In long-run equilibrium a monopolistically competitive firm will: A. earn an economic profit. B. realize all economies of scale. C. equate price and marginal cost. D. have excess production capacity. This is the end of the test. When you have completed all the questions and reviewed your answers, press the button below to grade the test.
Chapter 13 Study Set - Subjecto.com Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm will realize an economic:
Question: 1.Refer to the diagram above. The monopolistically ... 1.Refer to the diagram above. The monopolistically competitive firm shown: a. will realize allocative efficiency at its profit-maximizing output. b. cannot operate at a loss. c. is in long-run equilibrium. d. is realizing an economic profit. 2.Refer to the above cost data for a purely competitive seller:
Long-Run Equilibrium (With Diagram)| Economics In monopoly, on the other hand, long- run equilibrium occurs at the point of intersection between the monopolist's marginal revenue (MR) and long-run marginal cost (LMC) curves. Since at the minimum point of the LAC curve, LAC = LMC, we have price = LMC in the long-run equilibrium of the competitive firm.
micro econ Ch. 13 - Subjecto.com Monopolistically competitive firms: may realize either profits or losses in the short run but realize normal profits in the long run. Refer to the diagrams, which pertain to monopolistically competitive firms. Short-run equilibrium entailing economic loss is shown by: diagram c only.
8.4 Monopolistic Competition - Principles of Microeconomics - BCcampus The following TWO questions refer to the diagram below, which illustrates the demand, marginal revenue, and relevant cost curves for a monopolistically competitive firm. 1. How many units of output should this firm produce, in order to maximize profits? a) 10. b) 25. c) 30. d) 60. 2. In the long run, what price will this firm charge for its output?



0 Response to "38 refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. long-run equilibrium price will be"
Post a Comment