38 carbon monoxide phase diagram
Phase Diagram of Argon—Carbon Monoxide - AIP Publishing ABSTRACT. The phase diagram Ar-CO has been determined by cooling curves and x‐ray diffraction. Like the Ar-N 2 system, a solid solution of hcp structure extends over essentially the entire range of concentration at temperatures just under the solidus, but unlike the Ar-N 2 system, the hcp phase decomposes (eutectoidally) into a fcc Ar‐rich phase ... Solved Answer ALL parts a) - c). Copper oxide is a catalyst | Chegg.com Question: Answer ALL parts a) - c). Copper oxide is a catalyst for low temperature carbon monoxide oxidation. a) Explain how you could determine experimentally whether the oxygen involved in the reaction mechanism is in the gas phase, adsorbed on the catalyst or from the catalyst lattice. b) Explain, with the aid of a diagram, the origin of ...
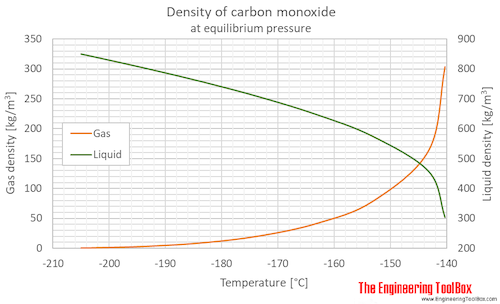
Carbon monoxide | Gas Encyclopedia Air Liquide Latent heat of fusion (at melting point) 30.024 kJ/kg. Melting point. - 205.07 °C. Boiling point. - 191.5 °C. Latent heat of vaporization (at boiling point) 214.68 kJ/kg. Liquid density (at boiling point)
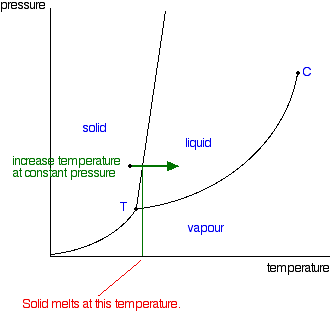
Carbon monoxide phase diagram
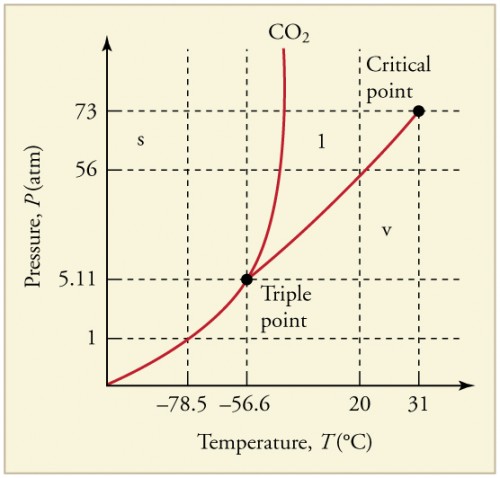
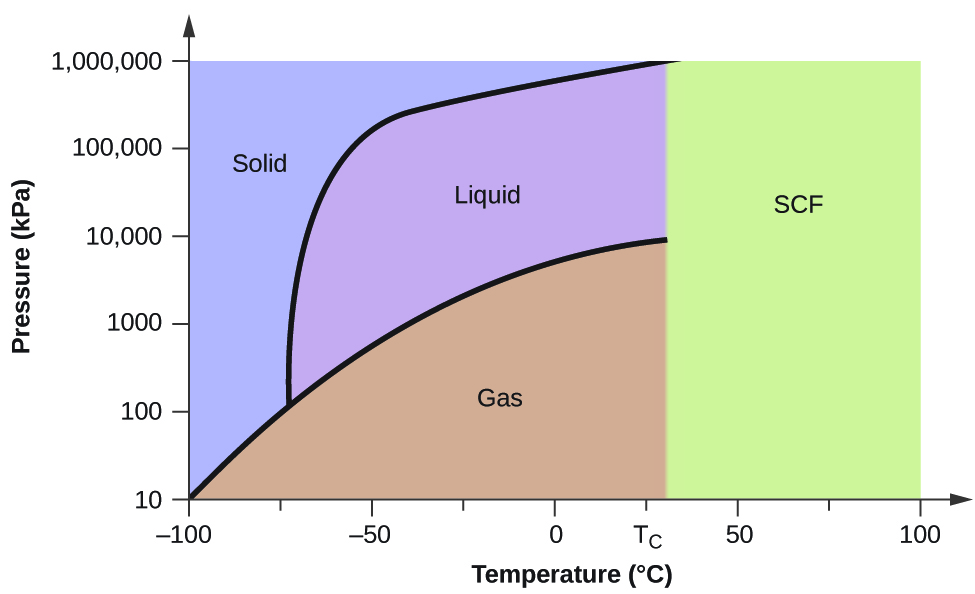
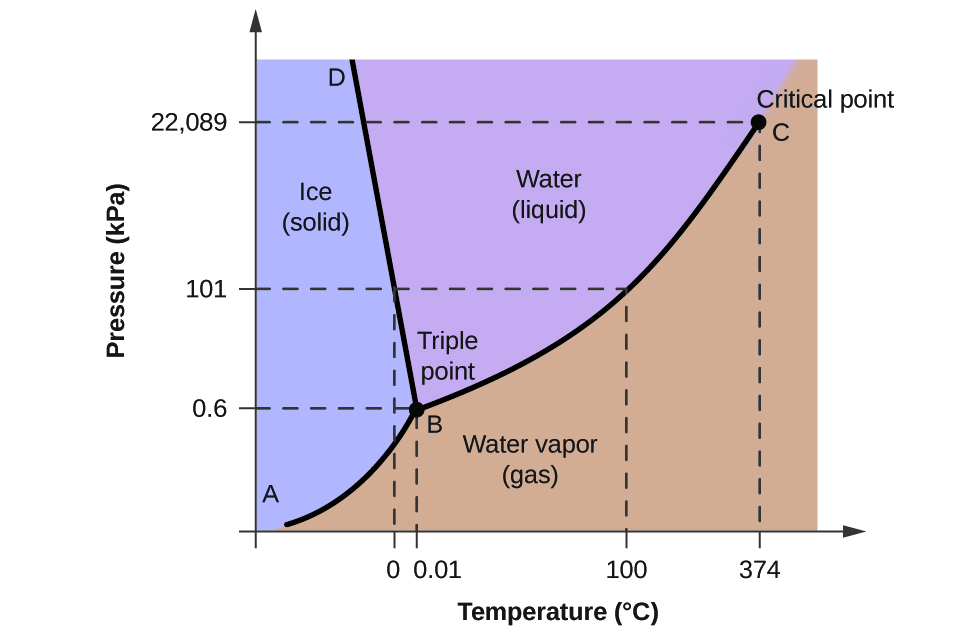
Can carbon monoxide exist in a solid or liquid form? No, carbon monoxide does not sublimate like carbon dioxide. Here is the phase diagram from CO2 and water (Sorry, can't see to find a CO one) The vertical axis is pressure, the horizontal is pressure. You'll see if you start at the bottom left and follow the red and blue lines, both water and CO2 have a single interface line between solid and gas and then fork eventually to have a liquid state in between. Phase Diagrams - Chemistry - University of Hawaiʻi Consider the phase diagram for carbon dioxide shown in as another example. The solid-liquid curve exhibits a positive slope, indicating that the melting point for CO 2 increases with pressure as it does for most substances (water being a notable exception as described previously). Notice that the triple point is well above 1 atm, indicating that carbon dioxide cannot exist as a liquid under ambient pressure conditions. Carbon phase - Big Chemical Encyclopedia The molecular orbitals of gas phase carbon monoxide, (a) Energy diagram indicating how the molecular orbitals arise from the combination of atomic orbitals of carbon (C) and oxygen (O). Conventional arrows are used to indicate the spin orientations of electrons in the occupied orbitals.
Carbon monoxide phase diagram. Electrosorbed carbon monoxide monolayers on Pt(111). We also confirm that the ( {radical}19 x {radical}19)-13CO structure is stable at lower CO partial pressure. This C phase transforms discontinuously to an IC phase (a first-order phase transition). A tentative phase diagram and a brief review of structure details of the (2 x 2)-3CO and ( {radical}19 x {radical}19)-13CO phases will be presented. phase diagrams of pure substances - chemguide The phase diagram shows that the water would first freeze to form ice as it crossed into the solid area. When the pressure fell low enough, the ice would then sublime to give water vapour. In other words, the change is from liquid to solid to vapour. I find that satisfyingly bizarre! The phase diagram for carbon dioxide Phase Diagram of Argon—Carbon Monoxide - AIP Publishing Like the Ar-N 2 system, a solid solution of hcp structure extends over essentially the entire range of concentration at temperatures just under the solidus, but unlike the Ar-N 2 system, the hcp phase decomposes (eutectoidally) into a fcc Ar‐rich phase and a primitive cubic CO‐rich phase at 53°K; the eutectoid point is at 66% CO. Carbon monoxide - Wikipedia Carbon monoxide ( chemical formula CO) is a colorless, highly poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simplest molecule of the oxocarbon family.
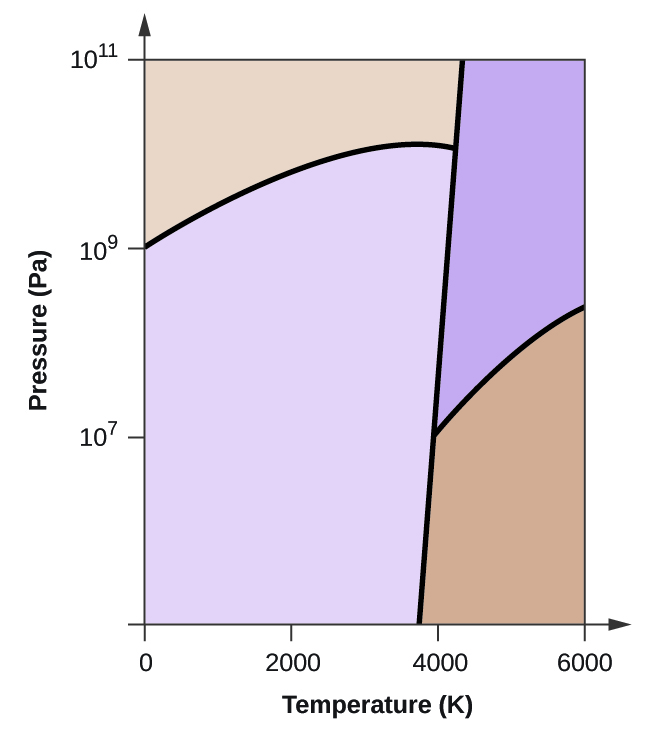
PDF 4. CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL INFORMATION - Agency for Toxic Substances and ... Carbon monoxide is a highly poisonous, odorless, colorless, and tasteless gas. It is very flammable in air over a wide range of concentrations (George 2001) and burns in air with a bright blue flame (O'Neil et al. 2006). It becomes a liquid at 81.62 K (-191.53 °C) and is insoluble in water above 70 °C (George 2001). Iron-Carbon Phase Diagram Explained [with Graphs] - Fractory The weight percentage scale on the X-axis of the iron carbon phase diagram goes from 0% up to 6.67% Carbon. Up to a maximum carbon content of 0.008% weight of Carbon, the metal is simply called iron or pure iron. It exists in the α-ferrite form at room temperature. From 0.008% up to 2.14% carbon content, the iron carbon alloy is called steel. Carbon dioxide - Wikipedia Carbon dioxide (chemical formula CO 2) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms, found in the gas state at room temperature.. In the air, carbon dioxide is transparent to visible light but absorbs infrared radiation, acting as a greenhouse gas.It is a trace gas in Earth's atmosphere at 417 ppm (about 0.04%) by ... PDF Phase diagram: hydrogen - University of Illinois Chicago Phase diagram: xenon 103 supercritical 10 solid liquid crltlcalpomt 10-1 saturation curve sublim ation curve 20 40 60 100 t em rat u re (K) eltill curve supercritical liquid critical point solid sa turation curve gas triple point 10-2 sublim ation curve 10-6 100 200 300 400 tern p e rat u re (K)
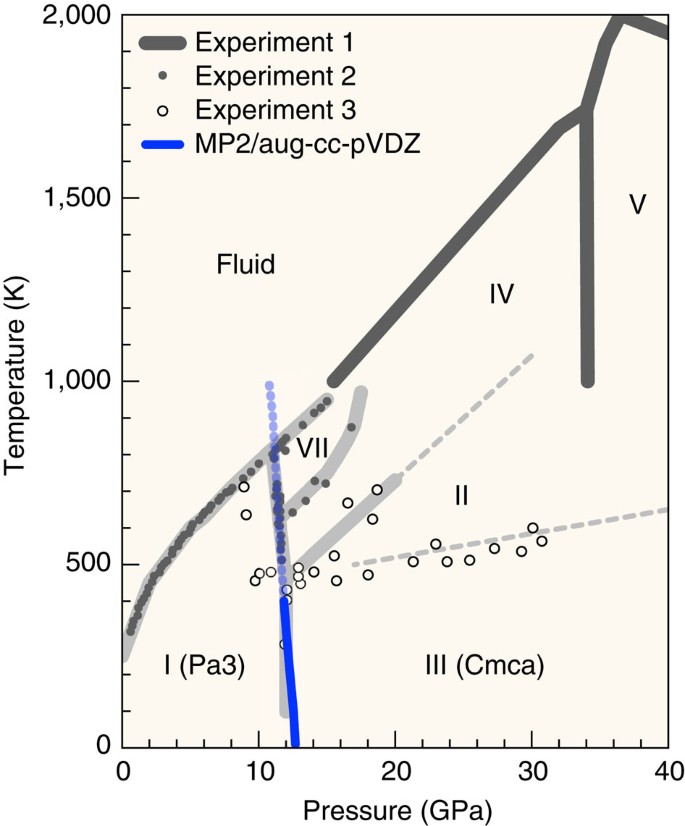
Answered: Sketch the phase diagram for Carbon… | bartleby ASK AN EXPERT Engineering Chemical Engineering Q&A Library Sketch the phase diagram for Carbon Monoxide and include the triple point values, solid phase, liquid phase, gas phase and normal boiling point temperature and pressure Carbon Monoxide - Thermophysical Properties - Engineering ToolBox Phase diagram included. Carbon Monoxide - Specific Heat vs. Temperature - Carbon Monoxide Gas - CO - specific heat of at temperatures ranging 175 - 6000 K. Carbon Monoxide and Health Effects - Exposure to Carbon Monoxide - CO and health effects. Ethane - Thermophysical Properties - Chemical, Physical and Thermal Properties of Ethane - C2H6. Consider the phase diagram of carbon dioxide below 9. Consider the phase diagram of carbon dioxide below: Which term best describes the process that occurs in going from point D to point C? a) vaporization b) condensation c) sublimation d) deposition e) fusion. Point D is in gas phase and point C is in solid phase. The transition of substance from solid to gas directly is termed as sublimation. Ab initio investigation of solid carbon monoxide phase diagram at low ... The presented approach could determine locations of phases α and ε of carbon monoxide crystal in the phase diagram, and has special prospects in promoting the exploration of investigating new crystals from experiments under high-pressure and low-temperature conditions with potentially important applications. Graphical Abstract
Phase Diagram and Transformations of Iron Pentacarbonyl to nm Layered ... The phase diagram indicates a limited stability of Fe(CO)5 within a pressure-temperature dome formed below the liquid- phase II- polymer triple point at 4.2 GPa and 580 K. ... D. & Mills, R. L ...
Phase Diagram of Argon—Carbon Monoxide - NASA/ADS The phase diagram Ar-CO has been determined by cooling curves and x-ray diffraction. Like the Ar-N2 system, a solid solution of hcp structure extends over essentially the entire range of concentration at temperatures just under the solidus, but unlike the Ar-N2 system, the hcp phase decomposes (eutectoidally) into a fcc Ar-rich phase and a primitive cubic CO-rich phase at ...
Carbon Dioxide - Thermophysical Properties - Engineering ToolBox Phase diagram included. Carbon dioxide, CO2, is a colourless and odorless gas. It is relatively nontoxic and noncombustible, but it is heavier than air and may asphyxiate by the displacement of air. When CO 2 is solved in water, the mild carbonic acid, is formed. Cooled CO 2 in solid form is called dry ice. Carbon dioxide phase diagram
Carbon Monoxide Carbon Monoxide (CO) is a colorless and odorless gas slightly heavier than air. It is highly toxic and at low to medium concentration in air, it forms a flammable and explosive mixture. It is classified as one of the major air pollutants. There are a number of processes for its production from carbon dioxide, oxygen, coke and steam.
Carbon monoxide - NIST Carbon monoxide. Formula: CO. Molecular weight: 28.0101. IUPAC Standard InChI: InChI=1S/CO/c1-2. Copy Sheet of paper on top of another sheet. IUPAC Standard InChIKey: UGFAIRIUMAVXCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N. Copy Sheet of paper on top of another sheet. CAS Registry Number: 630-08-. Chemical structure:
Carbon monoxide | CO - PubChem Carbon monoxide | CO | CID 281 - structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, biological activities, safety/hazards/toxicity information, supplier lists, and more.
PDF EXAMPLE #2: Carbon Monoxide, CO - uoguelph.ca Carboxyhemoglobin (COHb) is a stable complex of carbon monoxide and hemoglobin that forms in the red bloods cells when CO is inhaled (or produced through normal metabolism). Large quantities of CO inhibit the delivery of O 2 to the body because: 1) CO binds approximately 230 times more strongly to the Fe(II) than O 2
Phase Diagram of Carbon Dioxide | Request PDF - ResearchGate The effect of Eley-Rideal (ER), diffusion of nitrogen and carbon monoxide on the phase diagram is investigated. The steady reactive state is observed while using Langmuir-Hinsehelwood (LH ...
Ab initio investigation of solid carbon monoxide phase diagram at low ... After full structural optimization and accurate Gibbs free energy calculation of α-CO and ε-CO with MP2 theory and aug-cc-pVDZ basis set, the experimental phase diagram and the calculated phase boundaries at 0-200 K and 0-10 GPa is shown in Fig. 7. The present MP2 calculation predicts that the α-ε transition temperature of carbon monoxide decreases slightly as pressure increases, including 92 K at 2 GPa, 54 K at 3 GPa, and 36 K at 4 GPa.
Carbon monoxide phase diagram? - ResearchGate Comparatively little is known about the phase diagram of carbon monoxide, especially at the higher pressures. Some of the Graph available attached here, CO Phase D iagram.png 25.85 KB CO Phase dia...
Molecular Orbitals for Carbon Monoxide - Newcastle University The Molecule. CO is a very stable 10-valence-electron molecule, isoelectronic with [CN] - and with N 2, which has a slightly lower bond dissociation energy than CO. The formal bond order of CO is 3, from about one σ- bond and two π- bonds. Its most important property is burning in air to give CO 2 , in the combustion of fossil fuels.
Carbon phase - Big Chemical Encyclopedia The molecular orbitals of gas phase carbon monoxide, (a) Energy diagram indicating how the molecular orbitals arise from the combination of atomic orbitals of carbon (C) and oxygen (O). Conventional arrows are used to indicate the spin orientations of electrons in the occupied orbitals.
Phase Diagrams - Chemistry - University of Hawaiʻi Consider the phase diagram for carbon dioxide shown in as another example. The solid-liquid curve exhibits a positive slope, indicating that the melting point for CO 2 increases with pressure as it does for most substances (water being a notable exception as described previously). Notice that the triple point is well above 1 atm, indicating that carbon dioxide cannot exist as a liquid under ambient pressure conditions.
Can carbon monoxide exist in a solid or liquid form? No, carbon monoxide does not sublimate like carbon dioxide. Here is the phase diagram from CO2 and water (Sorry, can't see to find a CO one) The vertical axis is pressure, the horizontal is pressure. You'll see if you start at the bottom left and follow the red and blue lines, both water and CO2 have a single interface line between solid and gas and then fork eventually to have a liquid state in between.


















0 Response to "38 carbon monoxide phase diagram"
Post a Comment