41 diagram of eukaryote cell
Structure of Eukaryotic Cells (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion There are two important structural components of the surface boundary of the cell: (i) The outer layer, the glycocalyx, and (ii) Inner component, the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane. The glycocalyx is the general name applied to any structure which lies outside the plasma membrane. Structure of eukaryotic cells • A* Biology Structure of eukaryotic cells: The ultra cellular structure of a eukaryotic cell (animals and plants)must be known with the functions of organelles: Cell surface membrane is selectively permeable to control the exchange and is mainly made up of lipids and proteins.
Eukaryotic Cell Parts, Functions & Diagram - P2 - Science Prof Online Eukaryotic Cell Structures, Functions & Diagrams - P2. Parts of the Eukaryotic Endomembrane System. Nucleus: The nucleus is typically the largest and most visible organelle in a eukaryotic cell. Bound by a double-layer nuclear membrane, the nucleus contains the cell's genome—the main genetic instructions in the form of DNA ...
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-are-prokaryotes-and-eukaryotes-129478-v41-5b69b4c546e0fb0025628d06.png)
Diagram of eukaryote cell
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › EukaryoteEukaryote - Wikipedia Eukaryotic cells are typically much larger than those of prokaryotes, having a volume of around 10,000 times greater than the prokaryotic cell. They have a variety of internal membrane-bound structures, called organelles, and a cytoskeleton composed of microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments, which play an important role in defining the cell's organization and shape. Eukaryotic Cells | Structure, Differences, Facts & Summary A eukaryotic cell consists of several membrane-bound structures in its cytoplasm. The cytoplasm of the cell is surrounded by the plasma membrane. The genetic material of the cell is present in the nucleus that is also membrane-bound. The DNA of the cell is arranged in the form of thread-like structures called chromosomes. Cell Nucleus: Definition, Structure, Function | StudySmarter The DNA in eukaryotic cells (plant, animal, fungi, and protist cells) is organized in multiple linear chromosomes.DNA is an extremely large and thin molecule that could easily get tangled and break. Thus, it is associated with proteins that help maintain its structure. The complex of DNA and proteins is called chromatin and makes up the chromosomes.In a cell that is not dividing or reproducing ...
Diagram of eukaryote cell. Eukaryotic Plant Cell (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion Cell wall consists of three parts: (i) Middle-lamella (ii) Primary wall and (iii) Secondary wall. (Cell wall formation begins at the telophase stage of the cell division. Fine granular structures called as phragmoplasts appear at the equatorial plane which condense to form cell-plate or middle-lamella. Eukaryotic Cell: Definition, structure and organelles | Kenhub The eukaryotic cells types are generally found in animals, plants, algae, and fungi. For the purpose of this article, the primary focus will be the structure and histology of the animal cell. The major differences between animal and plant cells will be explored as well. As previously stated, the fundamental components of a cell are its organelles. Eukaryotic Cell Diagram | Quizlet ER bound Ribosomes synthesize: Proteins destined for insertion into a membrane or secretion outside the cell. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Network of membrane-enclosed spaces in the cytoplasm. Smooth ER. No ribosomes. Synthesizes lipids, and detoxifies drugs and poisons. Rough ER. Has ribosomes. › watchIntroduction to Cells: The Grand Cell Tour - YouTube Compares and contrasts prokaryote cells and eukaryote cells before exploring organelle structures and functions! Video includes the modern cell theory and p...
Learn the parts of a cell with diagrams and cell quizzes Two major regions can be found in a cell. The first is the cell nucleus, which houses DNA in the form of chromosomes. The second is the cytoplasm, a thick solution mainly comprised of water, salts, and proteins. The parts of a eukaryotic cell responsible for maintaining cell homeostasis, known as organelles, are located within the cytoplasm. › cells › 3dcellInteractive Cell Models - CELLS alive Here are some KEY TERMS to help you think, explore and search for similarities and significant differences that have become the characteristics of eukaryote (animal, plant) and prokaryotic (bacteria) cells. Examples might be searching: eukaryote prokaryote reproduction or animal plant cell energy. Eukaryotic Cell Diagram Diagram | Quizlet Eukaryotic Cell Diagram STUDY Learn Flashcards Write Spell Test PLAY Match Gravity + − Created by deidreadams Terms in this set (11) Nucleus An organelle that controls the function of the cell and stores the DNA. Lysosomes Holds food, water and waste within a cell. Cytoplasm The fluid that fills a cell and keeps all internal structures in place. PDF Typical Eukaryotic Cell Diagram - stats.ijm.org Eukaryotes have evolved from the association of at least three complementary prokaryotic cells, and their subsequent development has been enriched and accelerated typical-eukaryotic-cell-diagram 4/18 Downloaded from stats.ijm.org on April 6, 2022 by guest by symbioses with other prokaryotes.
Eukaryotic Cell: Definition, Structure & Function (with Analogy ... Eukaryotic cells include animal cells - including human cells - plant cells, fungal cells and algae. Eukaryotic cells are characterized by a membrane-bound nucleus. That's distinct from prokaryotic cells, which have a nucleoid - a region that's dense with cellular DNA - but don't actually have a separate membrane-bound compartment like the nucleus. PDF Eukaryotic Cell Structure - Bellarmine University Eukaryotic Cell Envelopes • Consists of the plasma membrane and all coverings external to it • Plasma membrane is a lipid bilayer -major membrane lipids include phosphoglycerides, sphingolipids, and cholesterol, all of which contribute to strength of membrane -microdomains participate in variety of cellular processes 9 10 Eukaryotic Cell Diagram - SmartDraw Create Biology Diagram examples like this template called Eukaryotic Cell Diagram that you can easily edit and customize in minutes. 10/20 EXAMPLES EDIT THIS EXAMPLE Text in this Example: Ribosomes manufacture proteins The centriole helps organize microtubules during cell divison The nucleus is the site of most cellular genetic material, DNA Eukaryotic Chromosomes - Visible Body Eukaryotic cells have multiple chromosomes that are linear in shape. 2. Each chromosome contains a molecule of DNA that is wound tightly around clusters of histone proteins. Individual DNA molecules are extremely long, consisting of millions of base pairs (matched nucleotides) each. How do cells store such large and potentially unwieldy molecules?
Eukaryotic Cells- Definition, Characteristics, Structure, & Examples Eukaryotic cell diagram mentioned below depicts different cell organelles present in eukaryotic cells. The nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, cytoplasm, mitochondria, ribosomes, lysosomes are clearly mentioned in the diagram. Explore more about Cell organelles Eukaryotic Cell Diagram illustrated above shows the presence of a true nucleus.
quizlet.com › 101145172 › chapter-17-hw-flash-cardsChapter 17 HW Flashcards | Quizlet The diversity of cells in a multicellular eukaryote suggests that certain genes are active in some cells but not in others. Eukaryotes have many chromosomes and those chromosomes are enclosed in a nuclear envelope.
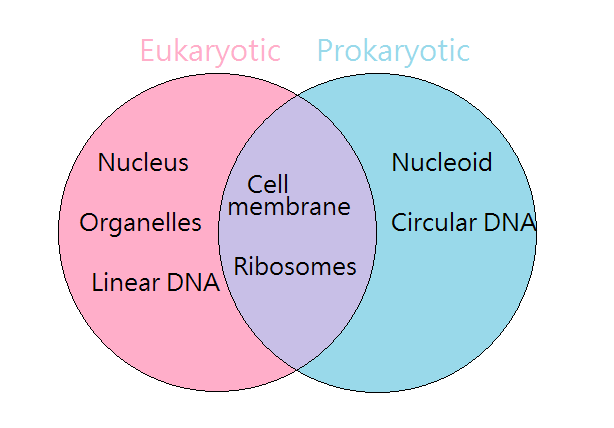
5 Differences Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells 1. Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus or nuclear membrane; eukaryotic cells have them. 2. Similar to the first difference, prokaryotes are also unicellular, while eukaryotes are multicellular organisms. 3. Prokaryotes have cell walls constructed from peptidoglycan and eukaryotes do not. 4.
› study-guides › biologyThe Structure of Prokaryote and Eukaryote Cells - CliffsNotes The cells of all prokaryotes and eukaryotes possess two basic features: a plasma membrane, also called a cell membrane, and cytoplasm. However, the cells of prokaryotes are simpler than those of eukaryotes. For example, prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus, while eukaryotic cells have a nucleus. Prokaryotic cells lack internal cellular bodies ...
Eukaryotic Cell - The Definitive Guide | Biology Dictionary The figure below shows the structure of a eukaryotic cell. This is an animal cell. The nucleus and other organelles are shown. The cytosol is the blue substance surrounding all of the organelles. Together, the cytosol with all organelles besides the nucleus is known as the cytoplasm. The Structures of an Animal Cell Eukaryotic Cell Cycle
Eukaryotic Cell Structure - Biology Wise They are among the largest cell organelles present in the eukaryotic cells. They are characterized by their own Mitochondrial DNA, RNA, and ribosomes; and hence, can self-replicate. It is the key site for production of energy in the form of ATP molecules, and thus aids photosynthesis and respiration. Plastids
Structure of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells - Unacademy Cytokinesis occurs when the cytoplasm divides to produce two genetically identical daughter cells. Parts of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells and Venn Diagram. Every cell shares a few common features, whether it is a prokaryote or eukaryote. These components include: Cytoplasm: Comprises the jelly-like fluid in which cellular structures are ...
Eukaryotic Cells | Biology I | | Course Hero The Cell Wall. In Figure 1b, the diagram of a plant cell, you see a structure external to the plasma membrane called the cell wall. The cell wall is a rigid covering that protects the cell, provides structural support, and gives shape to the cell. Fungal and protist cells also have cell walls.
Eukaryotic Cell: Structure, Characteristics & Diagram - Embibe Eukaryotic Cell Diagram The Eukaryotic cell diagram is given below: Eukaryotic Cell Examples Animal cell- Animal cells are generally smaller than plant cells and can be found in various shapes and sizes. It lacks a cell wall.
Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Cells: Similarities & Differences Only eukaryotes have membrane-bound organelles and a nucleus. Prokaryotes divide via using binary fission, while eukaryotic cells divide via mitosis. Eukaryotes reproduce sexually through meiosis, which allows for genetic variance. Prokaryotic cells reproduce asexually, copying themselves.
Cell Structure: Eukaryotic Cells | Saylor Academy Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have: A membrane-bound nucleus; Numerous membrane-bound organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and others; and; Several, rod-shaped chromosomes. Because a eukaryotic cell's nucleus is surrounded by a membrane, it is often said to have a "true nucleus".
› cells › cell_model_jsInteractive Cell Model - CELLS alive ^ Cell Overview Eukaryote Bacteria Model > ... Cell Membrane. Mitochondrion. Vacuole. ... Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum. Ribosomes. Cytoskeleton. RETURN to CELL DIAGRAM ...
Eukaryotic Cell Parts, Functions & Diagram - Science Prof Online Eukaryotic Cell Envelope & External Structures Cell Wall: The cells of plants, algae and fungi have thick, protective cell walls, which provide support, help maintain the shape of the cell, and prevent the cell from taking in too much fresh water and bursting.
Eukaryotic Cells | Biology I - Lumen Learning The endomembrane system ( endo = within) is a group of membranes and organelles (Figure 4) in eukaryotic cells that work together to modify, package, and transport lipids and proteins. It includes the nuclear envelope, lysosomes, and vesicles, the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus, which we will cover shortly.
Eukaryotic Cell: Definition, Features, Structure, Examples Eukaryotic cells are relatively large in size (0.5-12 μm). The cell wall of plant cells is made of cellulose and pectin. However, animal cells do not have a cell wall, but in many cases contain glycocalyx Present membrane-bound cell organelles. Like - Mitochondria, Golgi bodies, endoplasmic reticulum, plastids, lysosomes, etc.
› what-are-prokaryotes-andWhat Are the Differences Between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes? Jan 29, 2020 · A typical eukaryotic cell is surrounded by a plasma membrane and contains many different structures and organelles with a variety of functions. Examples include the chromosomes (a structure of nucleic acids and protein which carry genetic information in the form of genes), and the mitochondria (often described as the "powerhouse of the cell").
Cell Nucleus: Definition, Structure, Function | StudySmarter The DNA in eukaryotic cells (plant, animal, fungi, and protist cells) is organized in multiple linear chromosomes.DNA is an extremely large and thin molecule that could easily get tangled and break. Thus, it is associated with proteins that help maintain its structure. The complex of DNA and proteins is called chromatin and makes up the chromosomes.In a cell that is not dividing or reproducing ...






0 Response to "41 diagram of eukaryote cell"
Post a Comment