43 cs molecular orbital diagram
Electrical doping in halide perovskites | Nature Reviews Materials 23.03.2021 · Electrical doping (that is, intentional engineering of carrier density) underlies most energy-related and optoelectronic semiconductor technologies. However, for … Stanford University UNK the , . of and in " a to was is ) ( for as on by he with 's that at from his it an were are which this also be has or : had first one their its new after but who not they have
PDF Miessler-Fischer-Tarr5e SM Ch 05 CM - University of California, Irvine The populations of the bonding (8 electrons) and antibonding (4 electrons) molecular orbitals in the diagram suggest a double bond. c. The 2s, 2s *, 2p, and 2p *orbitals exhibit C vsymmetry, with the NF bond axis the infinite-fold rotation axis. The 2pand 2p * orbitals exhibit Cssymmetry.

Cs molecular orbital diagram
Quantum Numbers and Electron Configurations - Purdue University The next element has two electrons and the second electron fills the 1s orbital because there are only two possible values for the spin quantum number used to distinguish between the electrons in an orbital. He (Z = 2): 1s 2. The third electron goes into the next orbital in the energy diagram, the 2s orbital. Li (Z = 3): 1s 2 2s 1 Recent defect passivation drifts and role of additive ... These shallow level or deep level defects are further categorized into different structural or surface defects. Huang et al. established that the structural defects formed in the perovskite films are shallow level, which formed due to the antibonding between an iodine p orbital and the s orbital of Pb lone pair. On the other hand, the deep ... CS2 Lewis Structure - Learnool In the periodic table, carbon lies in group 14, and sulfur lies in group 16.. Hence, carbon has four valence electrons and sulfur has six valence electrons.. Since CS 2 has one carbon atom and two sulfur atoms, so…. Valence electrons of one carbon atom = 4 × 1 = 4 Valence electrons of two sulfur atoms = 6 × 2 = 12. And the total valence electrons = 4 + 12 = 16
Cs molecular orbital diagram. CS2 Lewis Structure, Hybridization, Polarity and Molecular Shape In CS2 molecule, two double bonds are formed consisting of eight valence electrons. Thus it takes up eight valence electrons out of 16 valence electrons. These valence electrons that form the double bond with the Carbon atom are in 2s and 2p orbital of the Carbon atom. These orbitals then combine, creating the hybrid of sp orbitals. What is the molecular orbital diagram for C2^ - Toppr Ask What is the molecular orbital diagram for C 2−? What is the molecular orbital diagram for. C. 2. CS2 Lewis Structure, Hybridization, Molecular Shape, and Polarity Total valence electrons is CS2 = 12+4 = 16. 2. According to Step 2, carbon is the least electronegative having the highest bonding sites. C is the central atom here. 3. The skeleton diagram of CS2 is drawn below. 4. We can check and find out that both the sulfur atoms have fulfilled their octet rule here. PDF Chem 344 - Homework 9 due Friday, Apr. 11, 2014, 2 PM orbitals are used. So CS is like C≡O except you use 3s,3p orbitals for . the example thus ignores 1s on C and 1s,2s,2p on S Similar point, Cl uses 3s,3p and Br ... P16.17) Sketch a molecular orbital energy diagram for CO and place the electrons in the levels appropriate for the ground state. The AO ionization energies are O2s: 32.3 eV; ...
Draw the molecular orbital diagram of CS. Determine bond order ... Draw the molecular orbital diagram of CS. Determine bond order, magnetism, spin multiplicity, and HOMO/LUMO. Colton B. Liberty University Answer Draw the molecular orbital diagram of the valence shell of a F 2 + ion, and use it to determine the bond order in the ion. Chemistry: An Atoms-Focused Approach Chapter 5 What is X-ray Fluorescence (XRF)? - Horiba Primary X-rays knock out an electron from one of the orbitals surrounding the nucleus within an atom of the material. A hole is produced in the orbital, resulting in a high energy, unstable configuration for the atom. To restore equilibrium, an electron from a higher energy, outer orbital falls into the hole. Solved How many unpaired electrons are there when 1 Carbon | Chegg.com The molecular orbitals; Question: How many unpaired electrons are there when 1 Carbon and 1 Sulfur atom combine to form (CS)? and DRAW the molecular orbital diagram for it, showing all the details of each orbital. How many unpaired electrons are there in CN- and DRAW the molecular orbital diagram for it, showing all the details of each orbital. How To Find an Valence Cesium Electron Configuration (Cs) Every element has its own Cesium Electron Configuration whereas here the electronic configuration for the element Cs is written as [Xe] 6 s1. The melting point of cesium is 83.3 o F and if we convert it to Celsius form, then it will be written as 28.5o C among the five elemental metals, cesium is one of the elements which are at room temperature.
Molecular orbitals in Carbon Monoxide - ChemTube3D Molecular orbitals in Carbon Monoxide CONTROLS Click on the CO molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals. See how carbon monoxide acts as a ligand on transition metals. Explore bonding orbitals in other small molecules ChemEd DL Application: Models 360 - University of Minnesota The molecular structure has been optimized at the B3LYP/6-31g* level of theory. Charges used for electrostatic maps are computed using the NBO method. The molecular vibrations are Quantum Numbers and Electron Configurations - Purdue University Most of the space occupied by the fifth orbital lies along the Z axis and this orbital is called the 3d z 2 orbital. The number of orbitals in a shell is the square of the principal quantum number: 1 2 = 1, 2 2 = 4, 3 2 = 9. There is one orbital in an s subshell (l = 0), three orbitals in a p subshell (l = 1), and five orbitals in a d subshell ... Answered: One of the molecular orbitals of carbon… | bartleby Transcribed Image Text: One of the molecular orbitals of carbon disulfide, CS, (S=C=S) is shown below. Identify the type of orbital. Identify the type of orbital. A) o B) o* C) п D) T* E) nonbonding
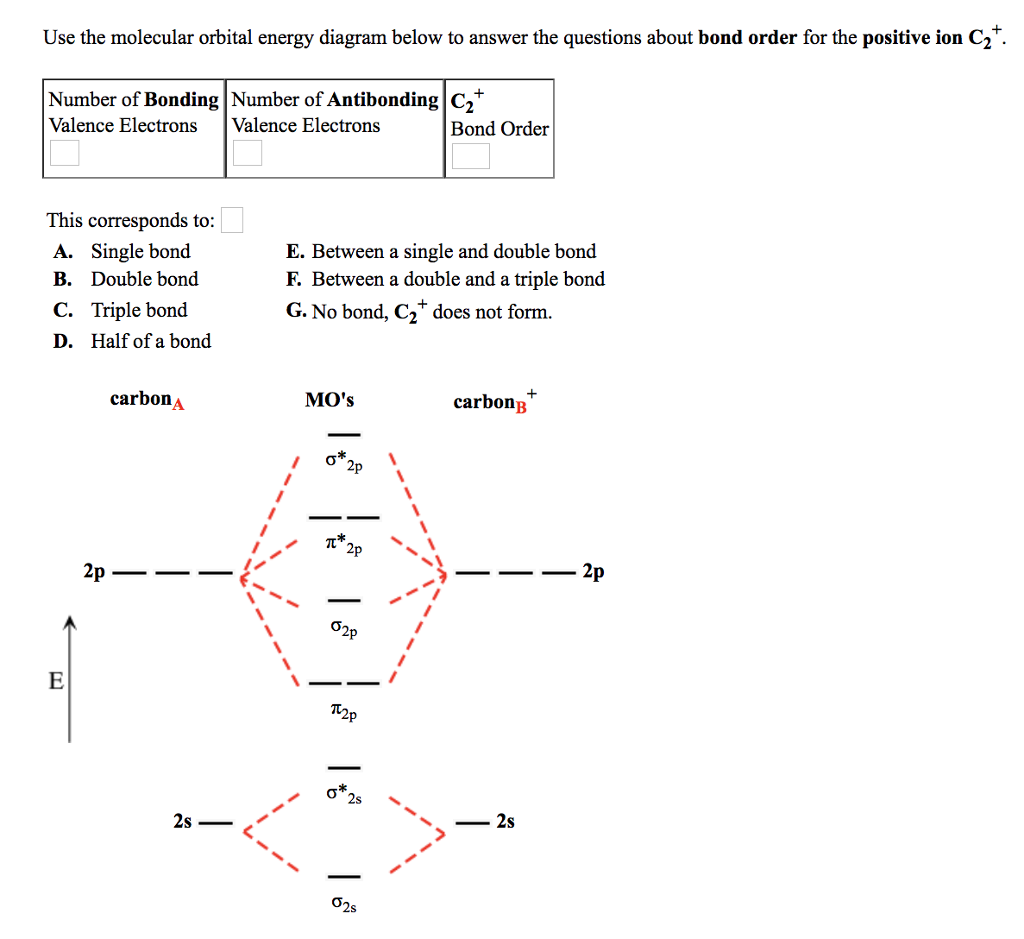
MET 2023 Exam - Dates, Registration, Eligibility, Admit 23.08.2022 · Covalent bonding: Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory and shapes of simple molecules, molecular orbital theory (MOT)-linear combination of atomic orbitals (qualitative approach), energy level diagram, rules for filling molecular orbitals : Covalent bonding: Bonding and anti-bonding molecular orbitals, bond order, electronic configuration of …
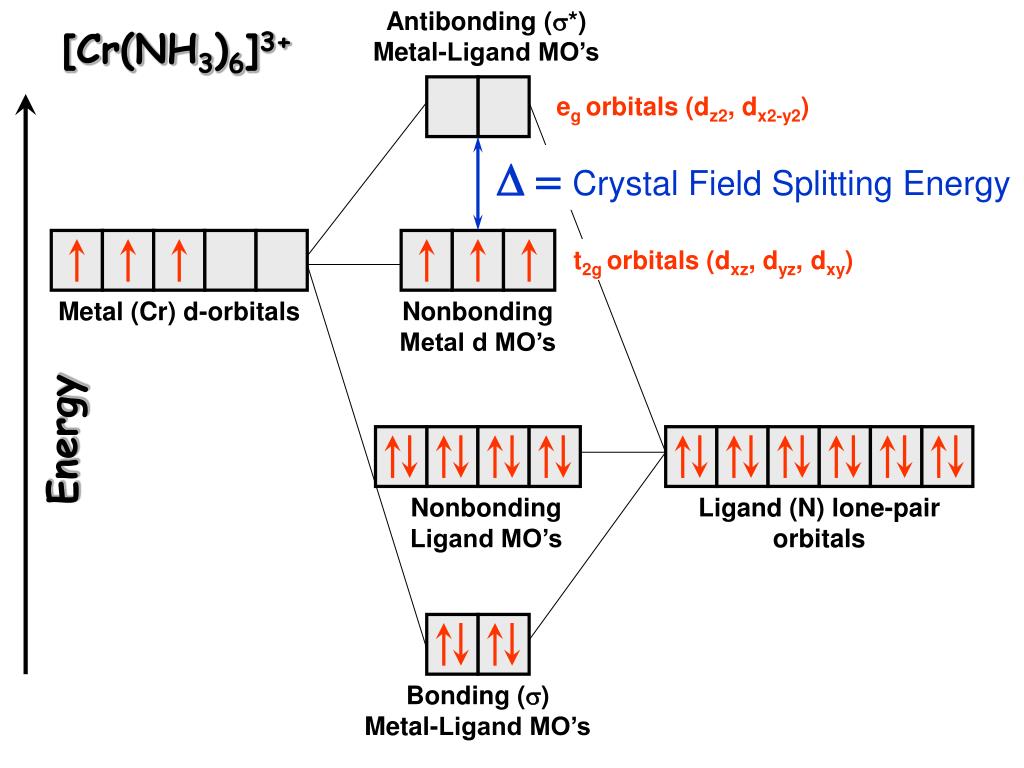
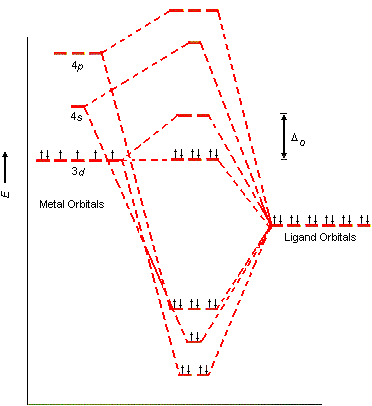
d-Metal Complexes - uml.edu The effect on the molecular orbital diagram is as follows. The gap between the t 2g and e g set will change, because the t 2g set is involved in bonding, so there is not a bonding t 2g set, and an antibonding t 2g set of orbitals. The gap, represented as D o becomes the gap between the t 2g set of antibonding orbitals and the e g set of orbitals.
Molecular Symmetry - The Chemistry Guru Molecular Symmetry. Any object is called as symmetrical if it has mirror symmetry, or 'left-right' symmetry i.e. it would look the same in a mirror. For example : a cube , a matchbox, a circle. Further it can be said ; a sphere is more symmetrical compare to a cube. Cube looks the same after rotation through any angle about the diameter ...
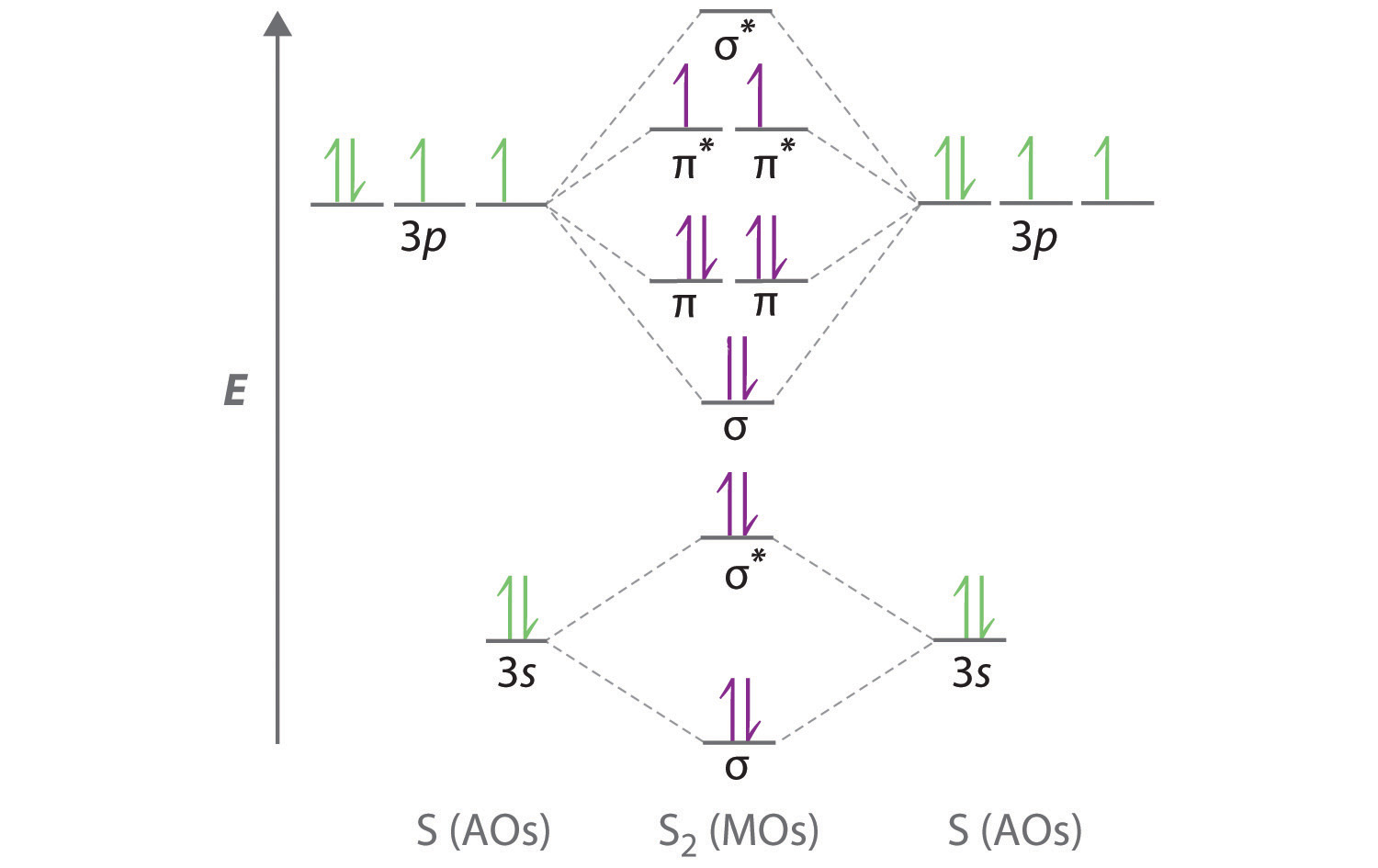
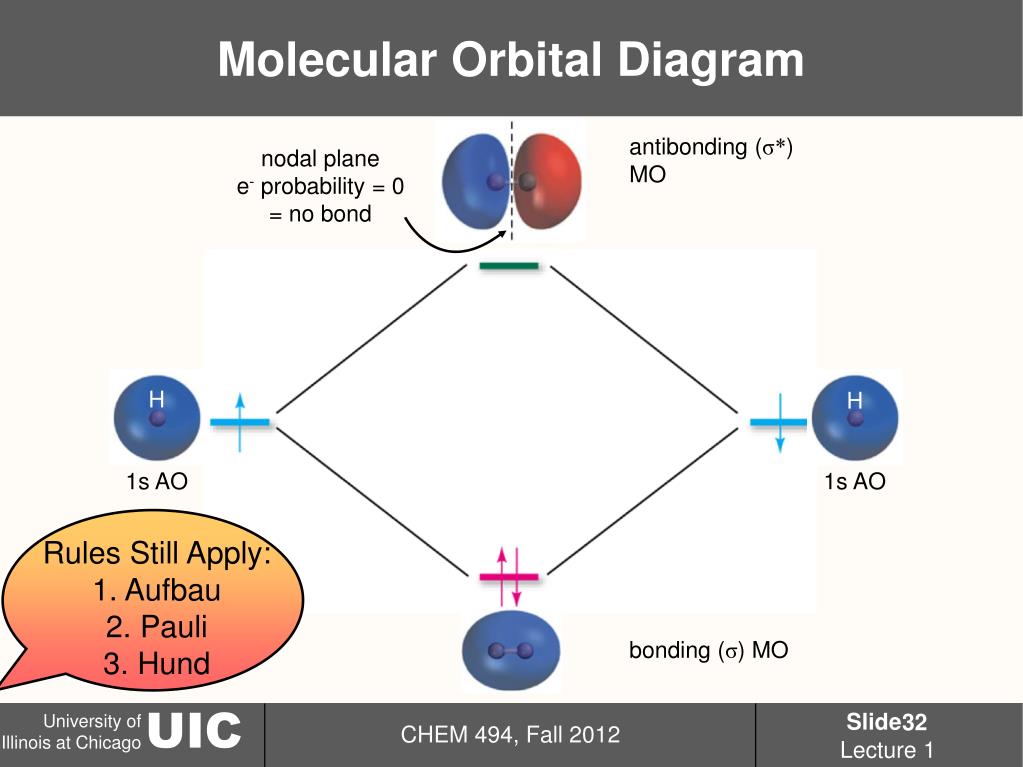
Molecular Orbital Theory - Purdue University The two electrons associated with a pair of hydrogen atoms are placed in the lowest energy, or bonding, molecular orbital, as shown in the figure below. This diagram suggests that the energy of an H 2 molecule is lower than that of a pair of isolated atoms. As a result, the H 2 molecule is more stable than a pair of isolated atoms.
Atomic Orbital Diagram of a Neutral Atom of Cesium - YouTube Is this the correct atomic orbital diagram for a neutral atom of cesium (Cs)? Please indicate "true" or "false" accordingly on your Google quiz form.
Ferric oxide nanoclusters with low-spin FeIII anchored Fe 2 O 3, as an earth-abundant photocatalyst for water purification, has attracted great attention.However, the high-spin Fe III in traditional Fe 2 O 3 restricts its catalytic performance. In this work, based on the nanocrystal size alteration strategy, cubic Fe 2 O 3 nanoclusters (3–4 nm) with low-spin Fe III were successfully anchored on six-fold cavities of the supramolecular …
PDF MO Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules - University of California, Irvine 2p orbital offluorine. The 13.6 eV σ* 1s nb H σ nb H-F of 2sis hydrogeninteracts nonbonding. 18.6eV 2p SoH-Fhasoneσbond andthreeloneelectron pairsonfluorine 40.2eV 2s Photoelectron energies In oleculeswithmorethan onetype of atom,MOsareform ed from AOs that have different 2pa energies. π* σ Consider σ* CO: LUMO HOMOis isoncarbon oncarbon too! 2pb
Inorganic Chemistry 4th edition, Catherine Housecroft Inorganic Chemistry 4th edition, Catherine Housecroft
Solved A partial Mo (molecular orbitals) diagram for CS is - Chegg A partial Mo (molecular orbitals) diagram for CS is shown on the picture. a) Considering only electronegativity values, place the 3p atomic orbital for sulfur in the correct location. [Select] Answer Bank b ь b) In this diagram, which orbital is the LUMO? [Select] b) In this diagram, which orbital is the LUMO?
Molecular Nitrogen and Related Diatomic Molecules The molecular orbital diagram of carbon monoxide, CO, is show below. On the left you can see all of the orbitals. On the right, the total valence electrons (4 from C, 6 from O) have been added to the orbitals. BackCompassTablesIndexIntroductionNext Professor Patricia Shapley, University of Illinois, 2012
Diagram - Wikipedia A diagram is a symbolic representation of information using visualization techniques. Diagrams have been used since prehistoric times on walls of caves , but became more prevalent during the Enlightenment . [1]
d-Metal Complexes - uml.edu The effect on the molecular orbital diagram is as follows. The gap between the t 2g and e g set will change, because the t 2g set is involved in bonding, so there is not a bonding t 2g set, and an antibonding t 2g set of orbitals. The gap, represented as D o becomes the gap between the t 2g set of antibonding orbitals and the e g set of orbitals.
CN- lewis structure, molecular orbital diagram, and, bond order In the third step, fill the molecular orbitals using the energy and bonding properties of the overlapping atomic orbitals. 4. Draw the MO diagram of CN and fill it with electrons. After that, with the help of the CN Molecular orbital diagram, you can easily predict its properties like bond order, bond length, para-magnetic, or diamagnetic, etc.
What is the molecular geometry of the CS2 molecule? | Socratic The central carbon atom will form double bonds with the two sulfur atoms. These bonds will account for 8 of the 16 valence electrons of the molecule. The remaining 8 valence electrons will be placed as lone pairs, two on each sulfur atom. Now, molecular geometry is determined by the hybridization of the central atom.
Stanford University UNK the , . of and in " a to was is ) ( for as on by he with 's that at from his it an were are which this also be has or : had first one their its new after but who not they have






0 Response to "43 cs molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment