37 refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. curve c represents
21. Refer to the above diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve represents: C A. total revenue and marginal revenue. B. marginal revenue only.C. total revenue and average revenue. D. average revenue and marginal revenue. 22. Marginal revenue is the: A. change in product price associated with the sale of one more unit of ... (c) The share of total farm receipts earned by the largest farms has been increasing during the past two decades. (d) None of the above (that is, all statements are true). 12. Which of the following statement(s) is (are) false? (a) The U.S. economy represents a purely capitalistic system. (b) The current U.S. Secretary of Agriculture is Tom ...
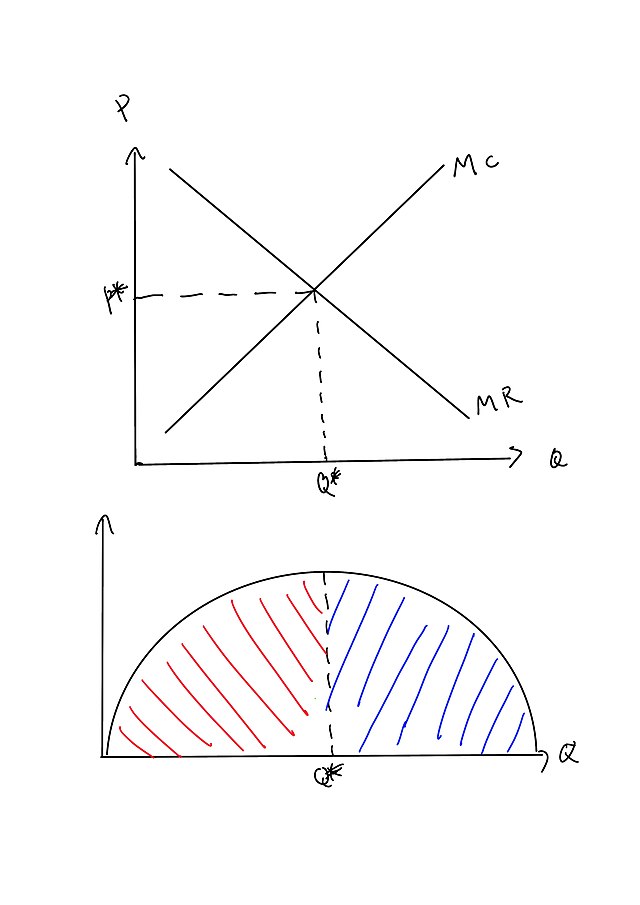
Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve C represents: ... Assume a purely competitive firm is maximizing profit at some output at which long-run average total cost is at a minimum. Then: there is no tendency for the firm's industry to expand or contract. In long-run equilibrium, purely competitive markets: maximize the sum of consumer surplus and producer ...
Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. curve c represents
Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve C represents: average revenue and marginal revenue. If a firm in a purely competitive industry is confronted with an equilibrium price of $5, its marginal revenue: will also be $5. Curve (3) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's: total revenue curve. Refer to the data. This firm is selling its output in a(n ... A) Each type of firm faces a downward sloping demand curve. B) Each type of firm produces a homogeneous product. C) In the long run, firms in both industries make zero economic profit. D) Each type of firm competes on product quality and price. Answer: C . 32) Excess capacity is the . A) difference between a perfectly competitive firm's and a ... Get the detailed answer: Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. What does curve c represent? a) total revenue and marginal reve
Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. curve c represents. Refer to the above diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve A represents: total revenue only ... competitive firm. Curve C represents:. Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve A represents Multiple Choice A. total revenue only. B. marginal revenue only. C. total revenue and marginal revenue. D. total revenue and average revenue. A) Both purely competitive and monopolistic firms are "price takers." B) Both purely competitive and monopolistic firms are "price makers."; C) A purely competitive firm is a "price taker," while a monopolist is a "price maker." D) A purely competitive firm is a "price maker," while a monopolist is a "price taker." Refer to Figure 8.4 for a perfectly competitive market and firm. Which of the following is most likely to occur, ceteris paribus? A) The firm will exit in the long run. B) The firm will shutdown in the short run. C) The firm will increase output. D) The firm will raise its price.
Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve C represents: average revenue and marginal revenue. Marginal revenue is the: change in total revenue associated with the sale of one more unit of output. Firms seek to maximize: total profit. In the short run, a purely competitive firm that seeks to maximize profit will produce: where total revenue exceeds total cost by ... Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. The shutdown point is at a price of . P2. P1. P3. P4. A purely competitive firm is precluded from making economic profits in the long run because. there are no barriers to enter the industry. Refer to the diagrams. At price b and quantity a, diagram (A) represents. the pure monopoly model. Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve C represents: A. total revenue and marginal revenue. B. marginal revenue only. C. total revenue and average revenue. Correct D. average revenue and marginal revenue. D) The demand curves are perfectly elastic for both a purely competitive firm and a purely competitive industry. Answer: A. Use the following to answer questions 30-31: Type: G Topic: 2 E: 416 MI: 172 30. Refer to the above diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve A represents: A) total revenue and marginal revenue.
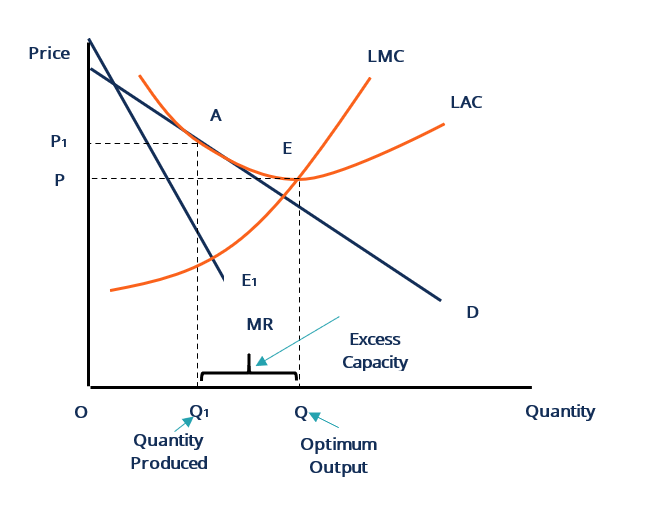
The diagram represents the short run rather than the long run because A)the MR curve cuts the ATC curve from below. B)the firm is earning an economic profit. C)the MR curve and the D curve do not coincide. D)the firm is incurring an economic loss. 30) 31)The figure above shows a monopolistically competitive firm in the short run. During the ... Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve C represents: D. Average revenue and marginal revenue. Average revenue equals marginal revenue. 8) Firms seek to maximize: C. Total Profit. The segment of the firm's marginal-cost curve that lies above the ... Refer to the above diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve A ... Rating: 5 · 1 review Assume the price of a product sold by a purely competitive firm is $5. Given the data in the accompanying table, at what output is total profit highest in the short run? ... Which point above is definitely not on a competitive firm's short-run supply curve? A. A. B. B. C. C. D. D. 24. ... Which area in the graph represents the amount the firm ...
The firm will produce at a loss at all prices: A) above P_1. B) Question: Use the following to answer questions 16-19: Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. The lowest price at which the firm should produce (as opposed to shutting down) is: A) P_1. B) P_2. C) P_3. D) P_4.
Refer to the diagram which pertains to a purely competitive firm curve c represents. A firm is producing an output such that the benefit from one more unit is more than the cost of producing that additional unit. Purely competitive firms monopolistically competitive firms and pure monopolies all earn zero economic profits in the long run. Producing less output than allocative efficiency ...
Refer to the diagram. If this somehow was a costless product (that is, the total cost of any level of output was zero), the firm would maximize profits by: ANSWER: producing Q2 units and charging a price of P2. 192. The demand curve faced by a pure monopolist: ANSWER: is less elastic than that faced by a single purely competitive firm. 193.
Marginal Cost and the Firm's Supply Curve. For a perfectly competitive firm, the marginal cost curve is identical to the firm's supply curve starting from the minimum point on the average variable cost curve. To understand why this perhaps surprising insight holds true, first think about what the supply curve means.
Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve A represents: A. total revenue and marginal revenue. B. Marginal revenue only. C. Total revenue and average revenue. D. Total revenue only. 10. Marginal revenue is the: A. Change in product price associated with the sale of one more unit of output. B.
20. Refer to the above diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve A represents: A. total revenue and marginal revenue. B. marginal revenue only. C. total revenue and average revenue. D. total revenue only.
Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve C represents ... average revenue and marginal revenue. Refer to the data in the accompanying table. Assuming total fixed costs equal to zero, the firm's ... economic profit is $16. Refer to the accompanying diagram. This firm will earn only a normal profit if product price is ... P3. Refer to the diagram. At output level ...
For a purely competitive firm. Refer to the above diagram which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Over which price range is the demand. Total revenue and marginal revenue. Curve 2 horizontal line in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms. 2 answer the question based on the following data.
21. Refer to the above diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve C represents: A. total revenue and marginal revenue. B. marginal revenue only. C. total revenue and average revenue. D. average revenue and marginal revenue.
Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve C represents. answer choices . total revenue and marginal revenue. marginal revenue only. total revenue and average revenue. average revenue and marginal revenue. Tags: Question 20 .
Refer to the above diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve C represents: D. average revenue and marginal revenue. 63. A purely competitive seller's average revenue curve coincides with: C. both its demand and marginal revenue curves. 64. Refer to the above short-run data.
Refer to the above diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve C represents:. average revenue and marginal revenue. 22. Marginal revenue is the:. change in total revenue associated with the sale of one more unit of output. 23. Firms seek to maximize: C. total profit. 24. A competitive firm in the short run can determine the profit-maximizing (or loss-minimizing) output by ...
Refer to the above diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve represents: C A. total revenue and marginal revenue. B. marginal revenue only. C. total revenue and average revenue. D. average revenue and marginal revenue. 30.
• Question 1 1 out of 1 points Refer to the above diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve represents: C Answer. Selected Answer: average revenue and marginal revenue. Correct Answer: average revenue and marginal revenue.
Refer to the above diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve A represents: A. total revenue and marginal revenue. B. marginal revenue only. C. total revenue and average revenue. D. total revenue only. Answer: D Topic: Demand as seen by a purely competitive seller. Learning Objective: 11-02: List the conditions required for ...
D) only to a purely competitive firm. Answer: C. Type: A Topic: 4 E: 430 MI: 186 185. If the long-run supply curve of a purely competitive industry slopes upward, this implies that the prices of relevant resources: A) will fall as the industry expands. C) rise as the industry contracts. B) are constant as the industry expands. D) rise as the ...
Get the detailed answer: Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. What does curve c represent? a) total revenue and marginal reve
A) Each type of firm faces a downward sloping demand curve. B) Each type of firm produces a homogeneous product. C) In the long run, firms in both industries make zero economic profit. D) Each type of firm competes on product quality and price. Answer: C . 32) Excess capacity is the . A) difference between a perfectly competitive firm's and a ...
Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve C represents: average revenue and marginal revenue. If a firm in a purely competitive industry is confronted with an equilibrium price of $5, its marginal revenue: will also be $5. Curve (3) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's: total revenue curve. Refer to the data. This firm is selling its output in a(n ...





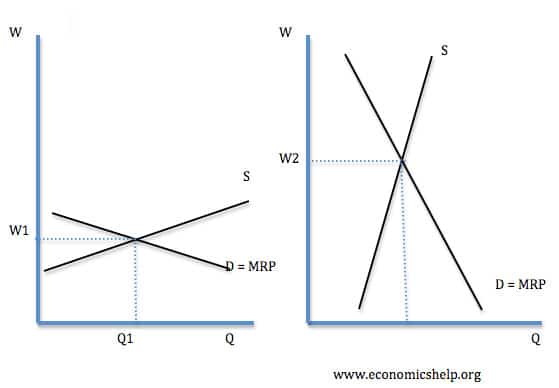
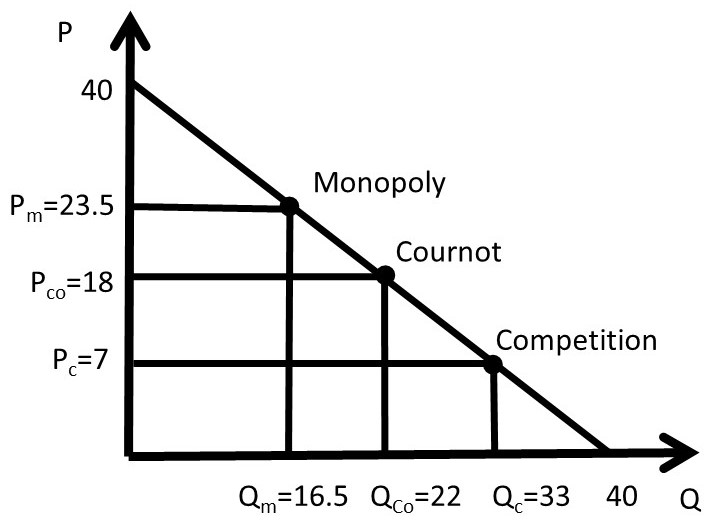
/producer_surplus_final-680b3c00a8bb49edad28af9e5a5994ef.png)
/MinimumEfficientScaleMES2-c9372fffba0a4a1ab4ab0175600afdb6.png)



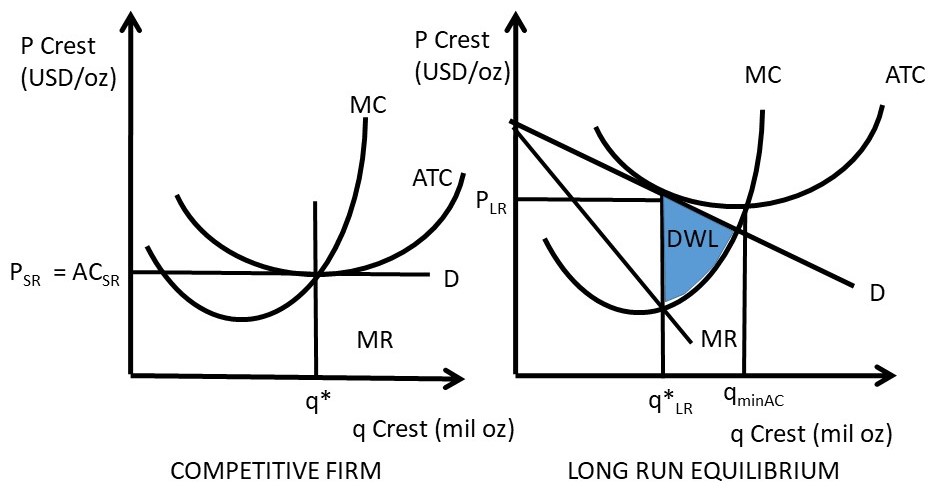

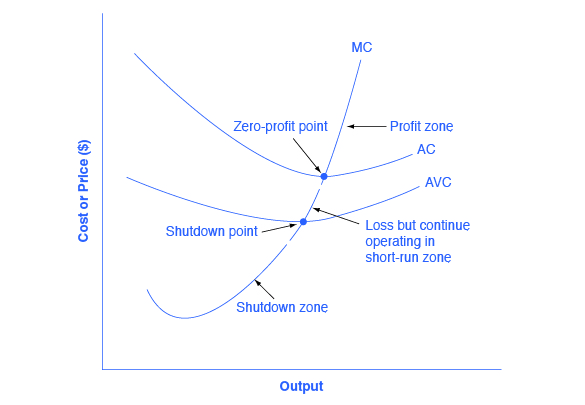


0 Response to "37 refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. curve c represents"
Post a Comment