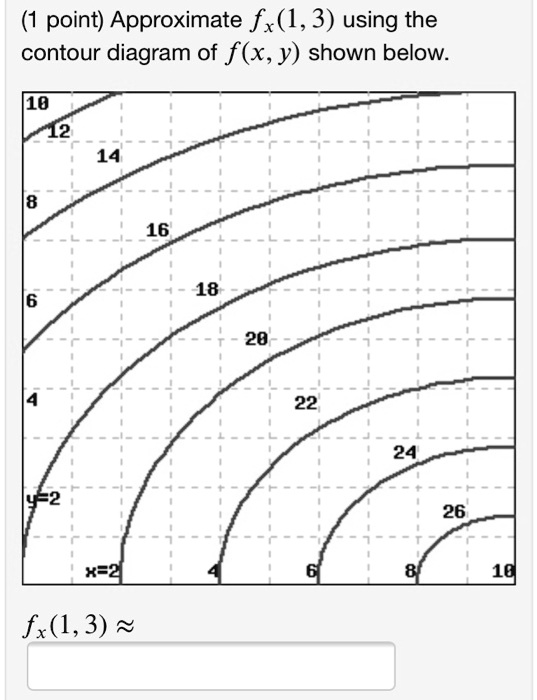
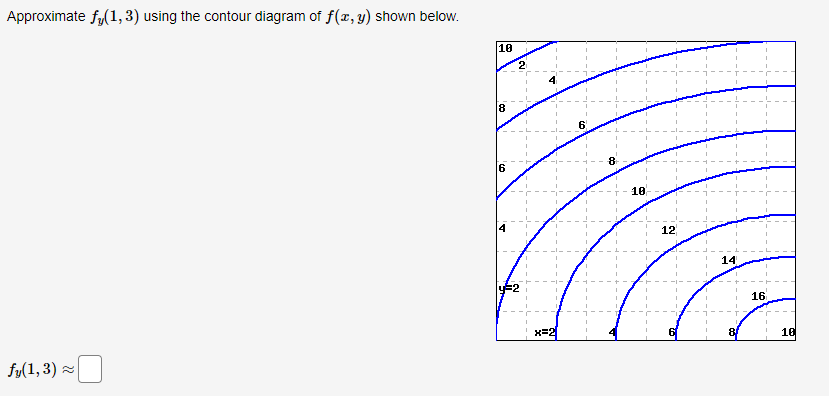
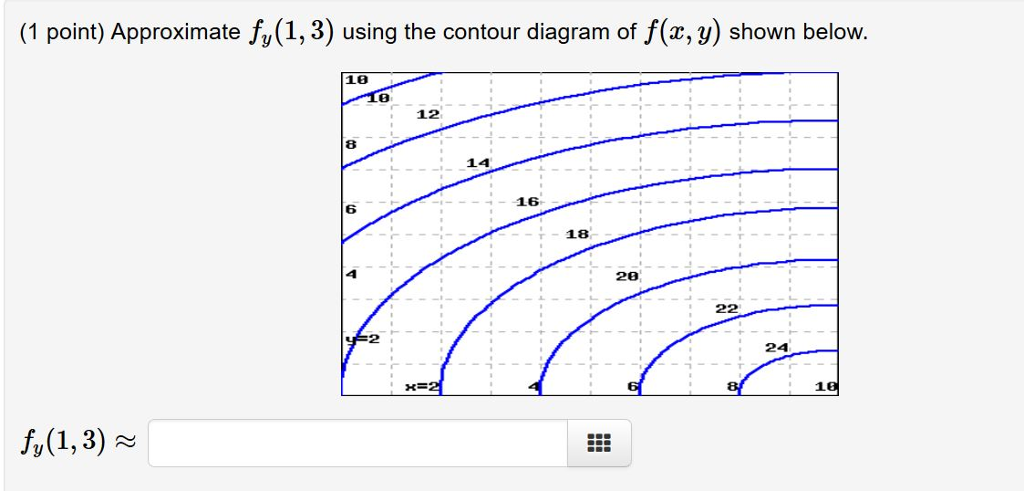
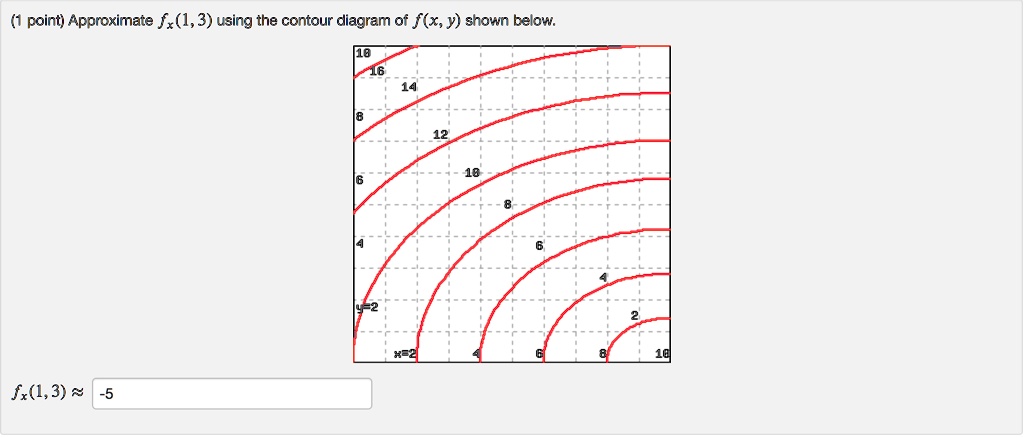
40 approximate fy(1,3) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below.
ASSIGNMENT 6 SOLUTION JAMES MCIVOR 1. Stewart 14.3.10 [3 pts] A contour map for a function fis given. Use it to estimate f x(2;1) and f y(2;1). Solution: We can estimate f
Question: Approximate fy(1, 3) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below. This problem has been solved! See the answer ...
Question: Approximate fy(1,3) using the contour diagram of f(x, y) shown below. f_y(1, 3) almostequalto ______. This problem has been solved! See the answer ...
Approximate fy(1,3) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below.
Section 14.5 (3/23/08) Directional derivatives and gradient vectors Overview: The partial derivatives fx(x0,y0) and fy(x0,y0) are the rates of change of z = f(x,y) at (x0,y0) in the positive x- and y-directions.Rates of change in other directions are given by directional
The partial derivative f z, for instance, is simply the derivative of f ( x, y, z) with respect to z, keeping the variables x AND y fixed now. Information about the partial derivatives of a function z = f ( x, y) can be detected also from the contour map of f. Indeed, as one knows from using contour maps to learn whether a path on a mountain is ...
Figure 10.3: At left, the graph of f(x;y) = 3 x 2y; at right, its contour plot. (h)Explain how your results are reflected in Figure10.4. Compare this limit to the limit in
Approximate fy(1,3) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below..
In Exercises 1-6, use the contour diagram of f in Figure 14.31 to decide if the specified directional derivative is positive, negative, or approximately zero. 1.
2 LINEAR APPROXIMATIONS In Example 1, we found that an equation of the tangent plane to the graph of the function f(x, y) = 2 x2 + y2 at the point (1, 1, 3) is: z = 4 x + 2 y – 3
Graphs of Surfaces and Contour Diagrams - 1 Picturing f(x;y): Contour Diagrams (Level Curves) We saw earlier how to sketch surfaces in three dimensions. However, this is not always easy to do, or to interpret. A contour diagram is a second option for picturing a function of two variables.
2. Level curves of G (x, y) are shown in the figure below. Find its approximate x- and y-derivatives at (3, 3). Ans: {10/1.3, 10/1.4} 3. Let the figure below be the contour diagram of f (x,y ). Find an approximate x derivative at (2, 2) by using the centered difference quotient. Ans:1/2 4.
Let f(x,y) denote a function of two variables and suppose that every circle centered at the origin is a level curve, then the graph z = f(x,y) is a sphere ... whose gradient is always nonzero. Suppose that fy = 2 fx. Then the level curves of f(x,y) are straight lines of slope -2. False. Find an equation of the tangent plane to the parametric ...
This problem has been solved! ... Approximate fy(1,3) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below. 1 point) Approximate f,(1,3) ...
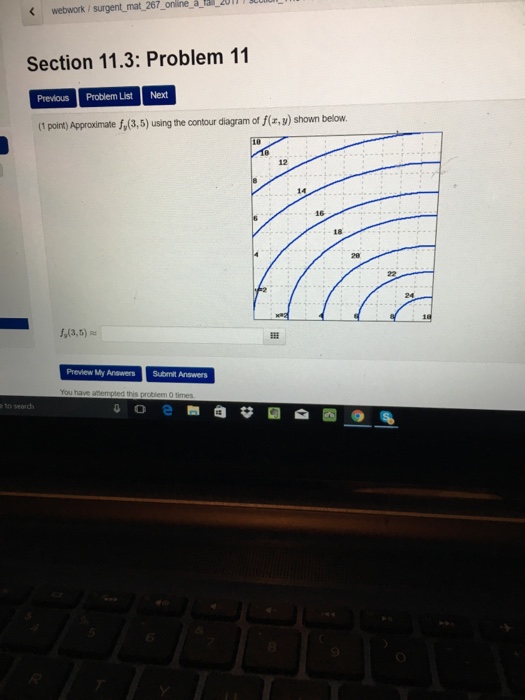
16 1 point Approximate f x 3 5 using the contour diagram of f x y shown below f from MATE 3063 at UPR Mayagüez
Question: Approximate fy(1, 3) using the contour diagram of f(x, y) shown below. 10 2 8 10 12 14 16 x=2 8 10 fy(1,3) · This problem has been solved! · Expert ...
If f(x,y)=3x^2−2y^2, find the value of the directional derivative at the point (−4,4) in the direction given by the angle θ=2π/5 -22.63 (1 point) For each of the following functions, find the maximum and minimum values of the function on the circular disk: x^2+y^2≤1.
27 Tangent Planes to Level Surfaces Suppose S is a surface with equation F(x, y, z) = k, that is, it is a level surface of a function F of three variables, and let P(x 0, y 0, z 0) be a point on S. Let C be any curve that lies on the surface S and passes through the point P.Recall that the curve C is described by a continuous vector function r(t) = 〈x(t), y(t), z(t)〉.
Question: Approximate fy(1,3) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below. The lower left corner is (0,0). fy(1,3)? ...
This video explains how to use the slope of a secant line to determine the value of a partial derivative using a contour map.Site: http://mathispower4u.com
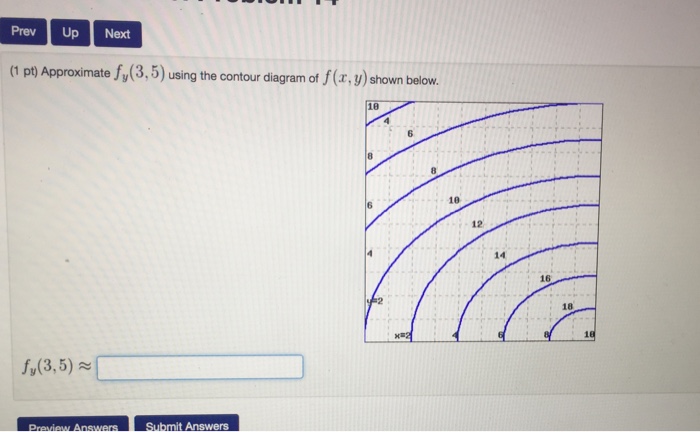
Question: Approximate fy(3,5) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below. This problem has been solved! See the answer ...
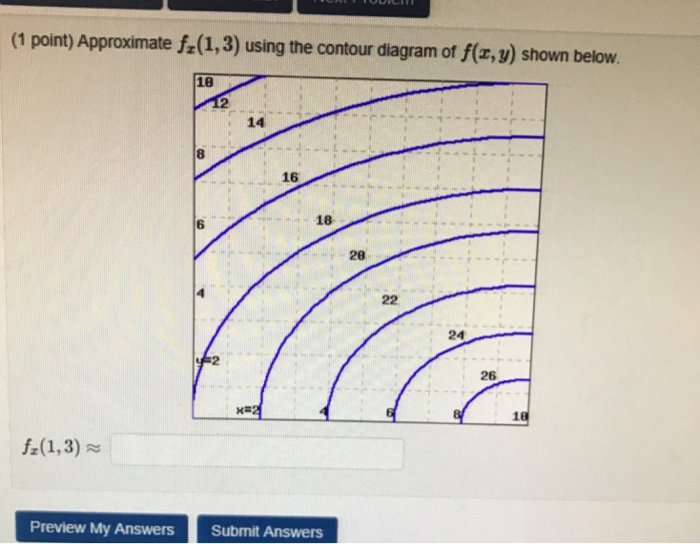
February 21, 2021 - Answer to approximate fx(1,3) using ... the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below. This video explains how to use the slope of a secant line to determine the value of a partial derivative using a contour map.site: mathispower4u. (1 pt) approximate f y (1, 3) using the contour diagram ...
(fy), so if we fix x and allow y to vary, fyy is the rate of change of fy as y increases. The level curves are closer together (in the y -direction) at points above P than at those below P , demonstrating that f increases more quickly with respect to y above P .
Answer to Approximate fx(3,5) using the contour diagram of f(x, y) shown below....
Approximate fy(1,3) using the contour diagram of f(x, y) shown below. fy(1,3) ≈ 18 18 16 14 12 6 18 6 x=2 10. Show transcribed image text ...
of the contour f(x;y) = k, as shown in Figure 16.1.3. Figure 16.1.3: Doug: maybe z= x2 y2 is better? SHERMAN: I'm OK with xy, it's just a matter of perspective. EXAMPLE 1 Sketch the traces of the surface z= xywith the planes 1. z= 1, Calculus October 22, 2010. 1080 CHAPTER 16 PARTIAL DERIVATIVES 2. x= 1, 3. y= x,
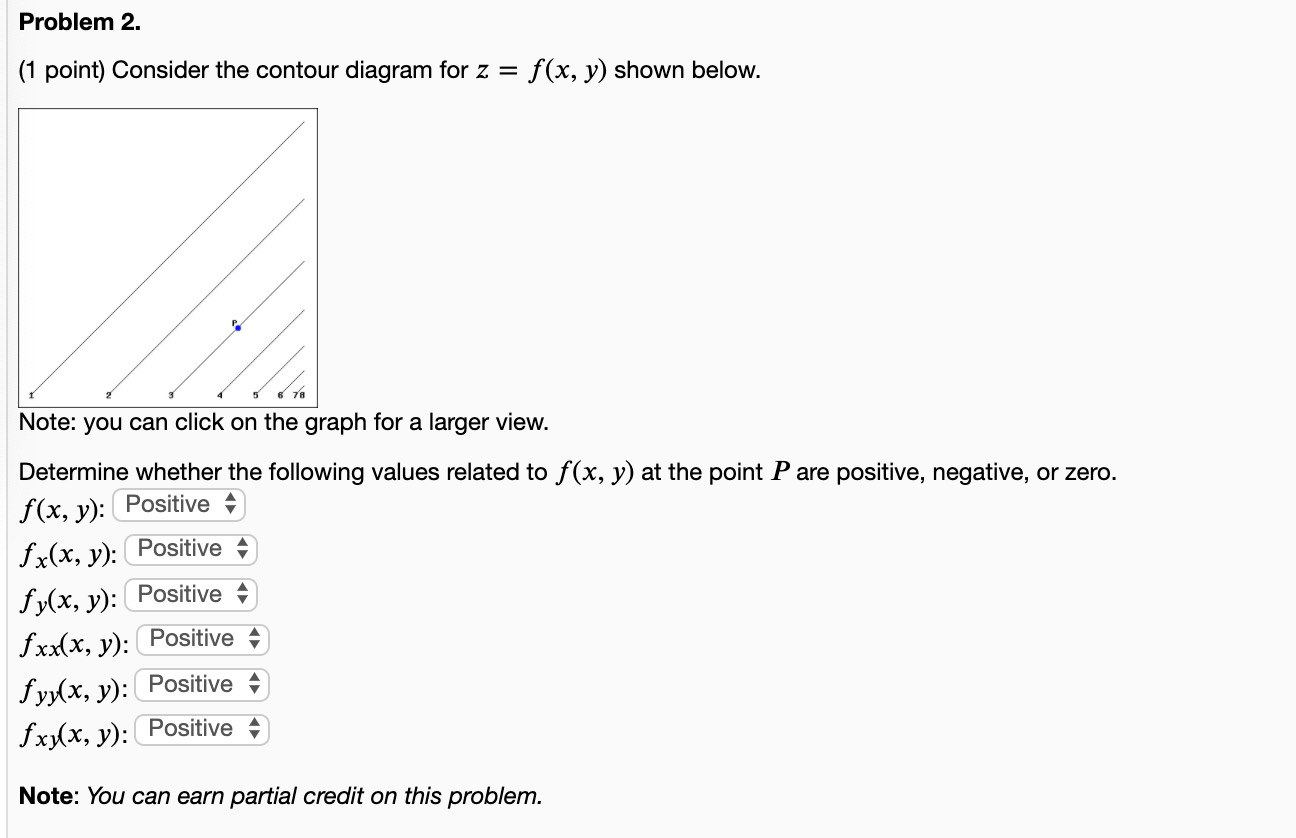
Math 205 HWK 11 Solns continued §14.7 p687 Problem 19, §14.7, p687. Use the given level curves of the function z = f(x,y) to decide the sign (positive, negative, or zero) of each of the following partial derivatives at the point P indicated
352 Chapter 14 Partial Differentiation k; in general this is called a level set; for three variables, a level set is typically a surface, called a level surface. EXAMPLE 14.1.5 Suppose the temperature at (x,y,z) is T(x,y,z) = e−(x2+y2+z2). This function has a maximum value of 1 at the origin, and tends to 0 in all directions.
See the answer See the answer done loading. Approximate f x (1,3) using the contour diagram of f (x,y) shown below. Solve for f x (1,3) = ????? Expert Answer. Who are the experts? Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 100% (21 ratings)
Answer to Approximate fy(3,5) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below. ...
Show transcribed image text Approximate fy(1, 3) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below. Posted 11 months ago Show transcribed image text Use the contour diagram for f(x, y) shown below to estimate the directional derivative of f in the direction v at the point R (a) At the point p = (2, 2) in the direction v = i, the directional ...
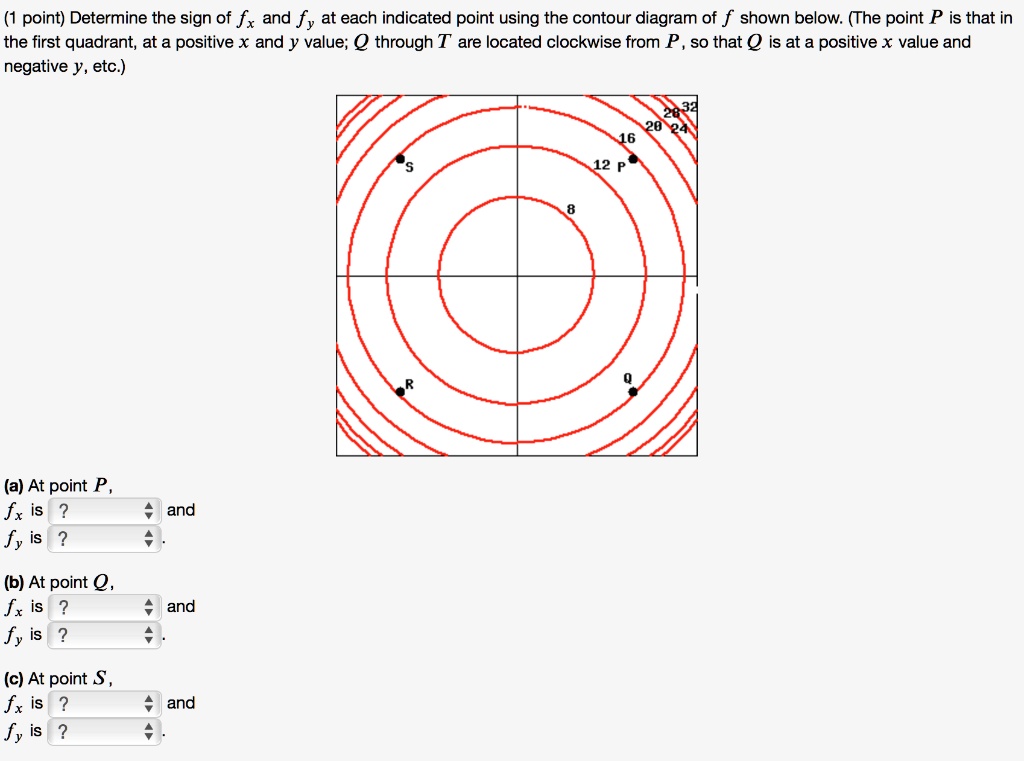
3 3. Determine the sign of f x and f y at the point using the contour diagram of f in the gure below. (a) P (b) Q (c) R (d) S 4. Approximate f x(3;5) using the contour diagram of f(x;y) shown in the gure below.
20. Use the contour diagram for f (x, y) f(x,y) shown below to estimate the directional derivative of f f in the direction v ⃗ v→ at the point P. 1. The function f has continuous second derivatives, and a critical point at (− 3,− 2) Suppose 2. The function f f has continuous second derivatives, and a critical point at (6,− 9) (6,−9 ...
Transcribed image text: (1 point) Approximate fy(1,3) using the contour diagram of f(x, y) shown below. 10 8 8 I - - - re - ------ 12-- -- --- - ---T-14 ...
• Revisit the function f (x,y) = x ln y2 − x. Sketch the domain, as done in Figure 3 of the text. Then go on to sketch the set of points (x, y) where f (x, y) = 0, f (x,y) > 0, f (x,y) < 0. • Pass around some interesting solid figures, and have the students attempt to sketch the appropriate contour lines for the solids. WORKSHOP/DISCUSSION
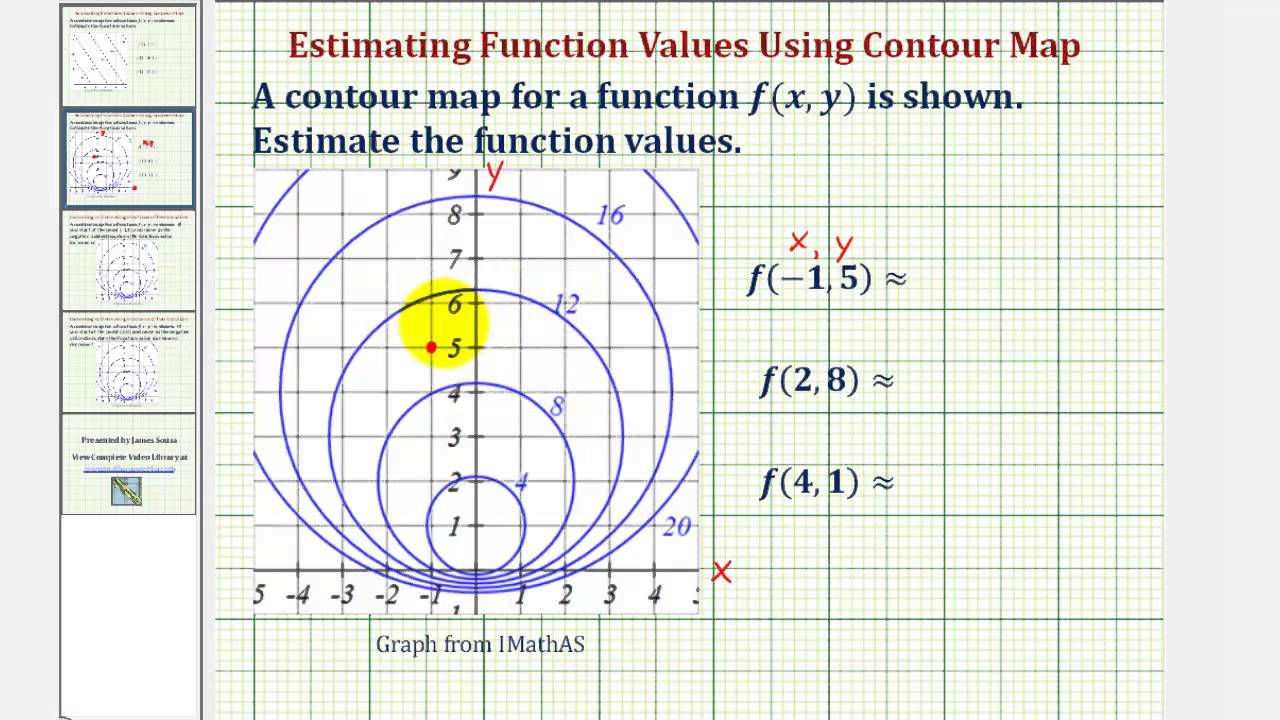
f(x+u1h,y)− f(x,y) h = fy. Example 1.3. If the following is a contour diagram for f(x,y) with the z = 0 contour at the origin, going up by 1 for each concentric circle, ... Drawing a vector out from the point (1,1) in the direction of ~u =~i+~j, we can use a difference quotient to approximate the rate of change. Specifically, the vector ~u ...
Ask about how fx changes in the y-direction and about fy. 6. Figure 9.7 is a contour diagram for f(x,y) with the x and y axes in the usual directions. At the point P, if x increases, what is true of fx(P)? If y increases, what is true of fy(P)? (a) Have the same sign and both increase. (b) Have the same sign and both decrease.
Solution for Approximate fx(1,3) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below.
Question: Approximate fy(1, 3) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below. 10 12 8 10 8 x=2 10 fy(1,3) · This problem has been solved! · Expert Answer. Who ...
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. from contour map., f (3,5) = 10 now …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Approximate f_y (3, 5) using the contour diagram of g (x, y) shown below. F (x, y) approximate.
A contour diagram for a function f(x;y) is shown in the gure below. (a) On the graph, sketch a reasonably accurate estimate of the gradient r~f at each of the points A, B, and C.
4 Gradients and directional derivatives in the plane Remark 4.1. The partial derivatives f x and f y tell us the rate of change of f parallel to the coordinate axes. In this section, we consider partial derivatives
Using the contour diagram for fx y in figure 836 decide whether each of these partial derivatives is
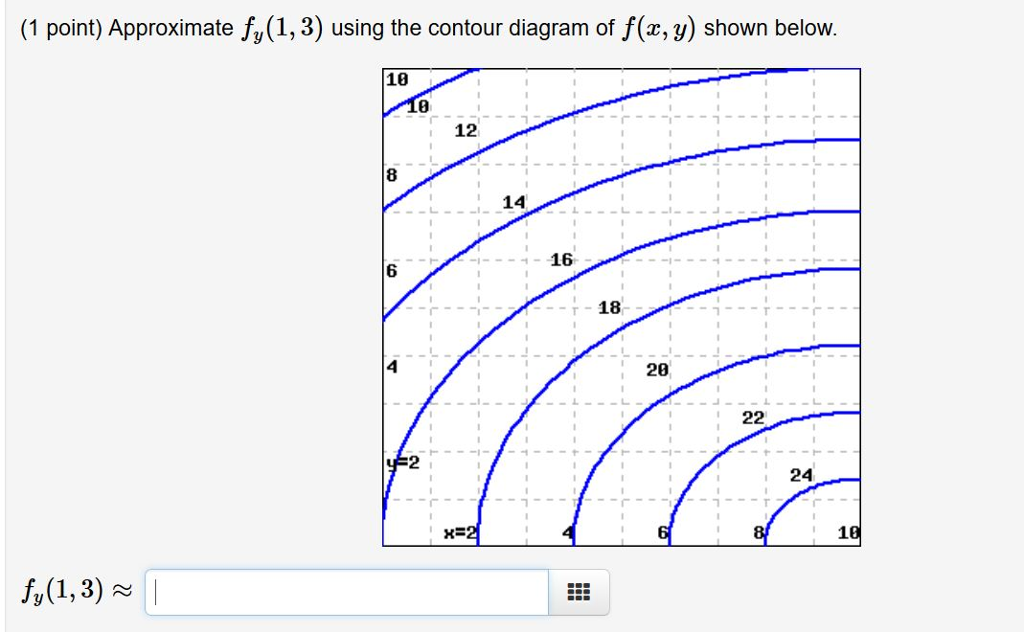









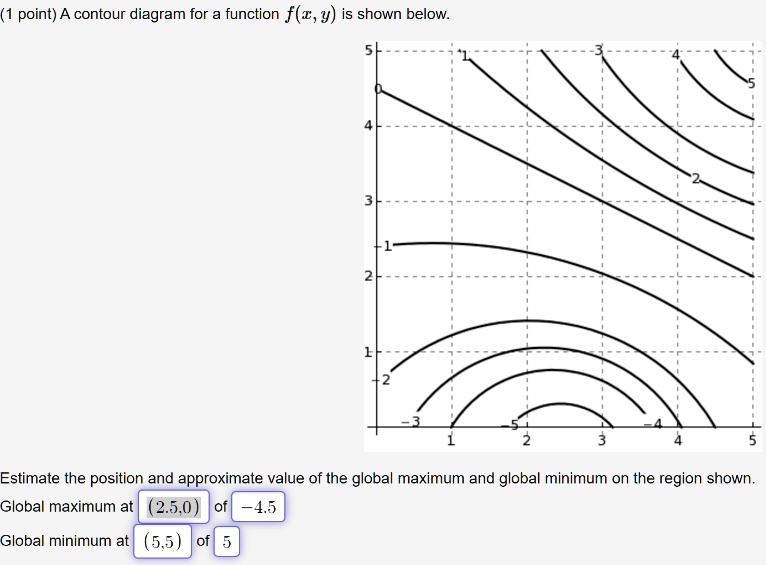
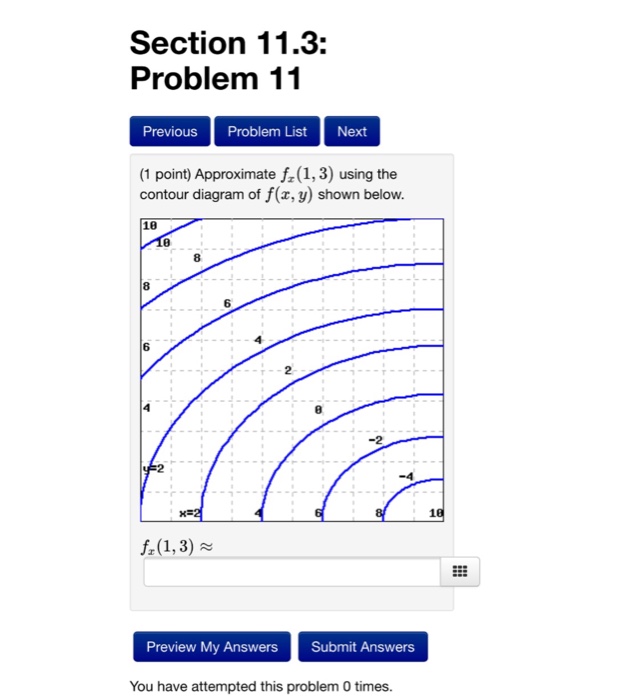

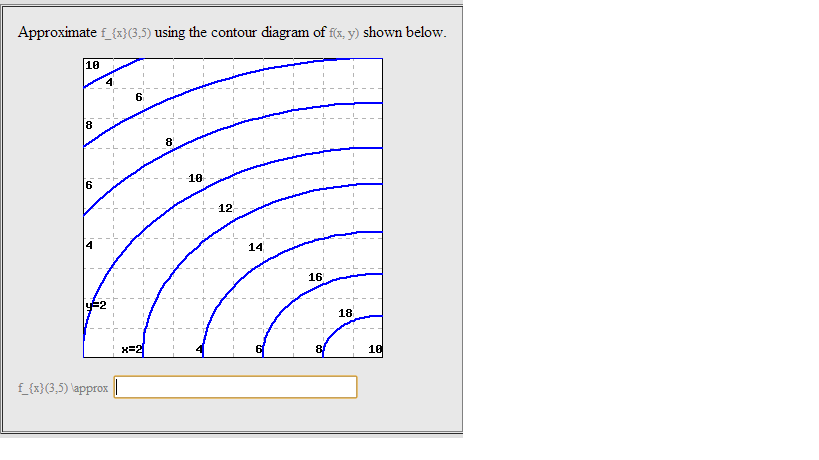






0 Response to "40 approximate fy(1,3) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below."
Post a Comment