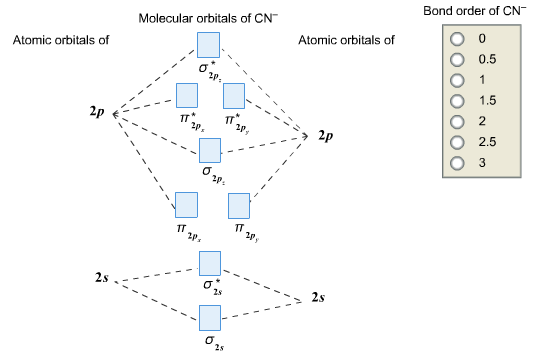
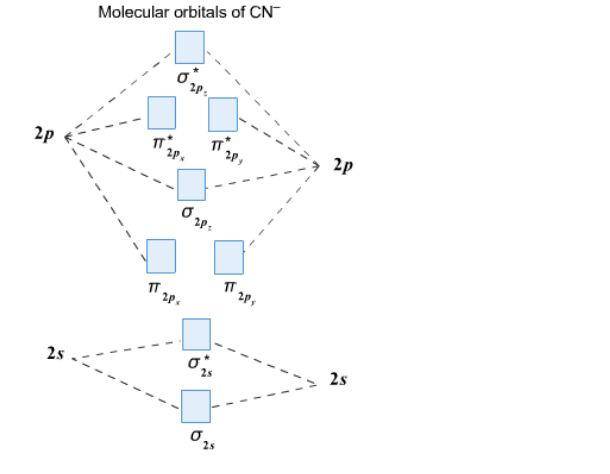
37 cn- molecular orbital diagram
June 8, 2008 - Study at one of Australia’s leading science faculties in tertiary education. Discover our course offerings as well as our impactful research and collaborations. Molecular orbital theory is also able to explain the presence of Figure \(\ PageIndex{6}\): Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagram for HCl. to describe the bonding in the cyanide ion (CN −). mix atomic orbitals on different atoms to get Molecular Orbitals. The resul7ng MO diagram looks like this. CN– (Cyanide ion), NO+ (Nitrosonium ion).
Cn molecular orbital diagram. This is meant to be an interactive exercise so arrange for some pieces of blank paper a pencil a pen and an eraser. Question 15 of 16 sapling learning complete this molecular orbital diagram for cn then determine the bond order. This feature is not available right now.

Cn- molecular orbital diagram
Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in When two atomic orbitals combine, two molecular orbitals are formed. One is known as bonding molecular orbital and the other is called an anti-bonding molecular ...1 answer · Top answer: Concepts and reason • The molecular orbital theory explains the bonding in terms of the combination and organization of atomic orbitals of an atom which ... Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified. Megan Lim. Oct 26, 2016 · 3 min read. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding ...
Cn- molecular orbital diagram. Molecular orbital theory describes the distribution of electrons in molecules in much the same way that the distribution of electrons in atoms is described using atomic orbitals. Using quantum mechanics, the behavior of an electron in a molecule is still described by a wave function, Ψ, analogous to the behavior in an atom.Just like electrons around isolated atoms, electrons around atoms in ... Answer to Complete this molecular orbital diagram for CN then determine the bond order. Note that the 1s orbital is not shown in t... The molecular orbital energy level diagram provided shows the energies of the orbitals for the valence electrons in the free radical CN. Indicate on this diagram the ground state electronic configuration of CN using the arrow notation for electron spins. * C has 4 valence electrons and N has 5 valence electrons, giving a total of 9 Molecular orbital Diagram Cn-mo diagram of cn hunt research group right you have been asked to draw the mo diagram for cn a heteronuclear diatomic don t panic take it one step at a time and you will have a plete mo diagram before you know it this is meant to be an interactive exercise so arrange for some pieces of blank paper a pencil a pen and an eraser molecular orbital theory heteronuclear ...
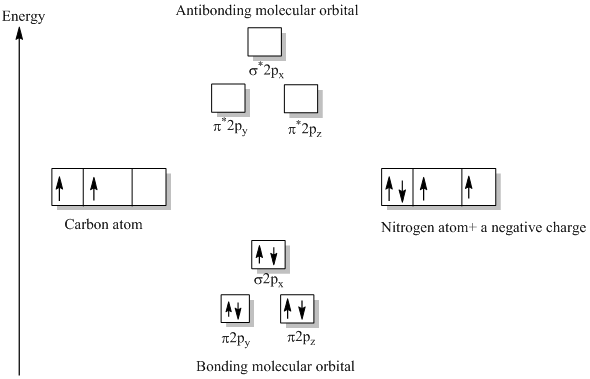
October 15, 2014 - Coordination between a metal and $\ce{CN-}$ in MO-world and Lewis structure world look very different. The end-result of MO and Valence Bond may be similar, but the interpretations are different. $\endgroup$ ... As Geoff already pointed out in the comments, the connection between a molecular orbital ... CN Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization, Polarity, and MO Diagram. CN is known as cyanide which exists as a pseudohalide anion. It belongs to the cyano group and consists of carbon and a nitrogen atom having a triple bond. It carries a charge of -1 and is a conjugate base of hydrogen cyanide (HCN). December 9, 2016 - Answer (1 of 5): The total number of electron of CN- ion is ( 6+7+1) = 14 . According to molecular orbital theory, the electronic configuration of CN - ion is as follows, From the above electronic configuration , it has been found that , the number of bonding electron is 10 and the the number of... October 23, 2017 - Two same sign orbitals have a constructive overlap forming a molecular orbital with the bulk of the electron density located between the tw...
The molecular orbital configuration of C N + is K K σ (2 s) 2, σ ∗ (2 s) 2, π (2 p x ) 2, π (2 p y ) 2. Bond order is 2 . All the electrons are paired and ion is diamagnetic. A molecular orbital diagram for oxygen may be seen by Clicking Here. A cartoon of the p and π orbitals of a double bond may be examined by Clicking Here. A model of the π orbitals of ethene may be examined by Clicking. FREE Expert Solution. We're being asked to complete the molecular orbital diagram of CN- and then determine the bond order. Prepare a molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the cyanide ion. Use sketches to show clearly how the atomic orbitals interact to form MOs. b. What is the bond order for cyanide, and how many unpaired electrons does cyanide have? c. Which molecular orbital of CN- would you predict to interact ... FREE Expert Solution. We’re being asked to complete the molecular orbital diagram of CN- and then determine the bond order. To do so, we shall follow these steps: Step 1: Calculate the total valence electrons present. Step 2: Fill the molecular orbitals with electrons. Step 3: Determine the bond order. Step 1: Calculate the total valence ...
How to make molecular Orbital diagramhttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UYC-ndQ6Lww&t=6s
Molecular orbital Diagram for Cn-mo diagram of cn hunt research group right you have been asked to draw the mo diagram for cn a heteronuclear diatomic don t panic take it one step at a time and you will have a plete mo diagram before you know it this is meant to be an interactive exercise so arrange for some pieces of blank paper a pencil a pen and an eraser molecular orbital theory ...
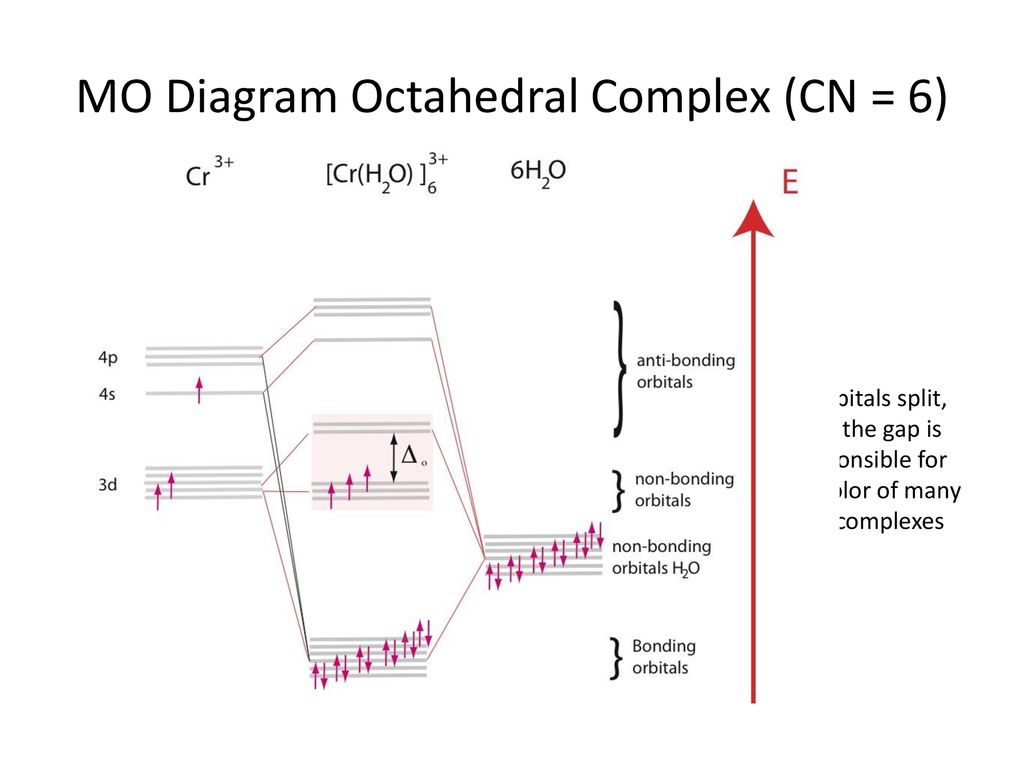
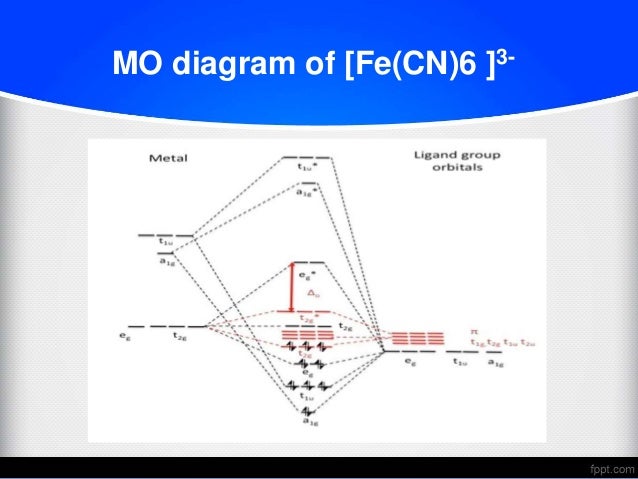
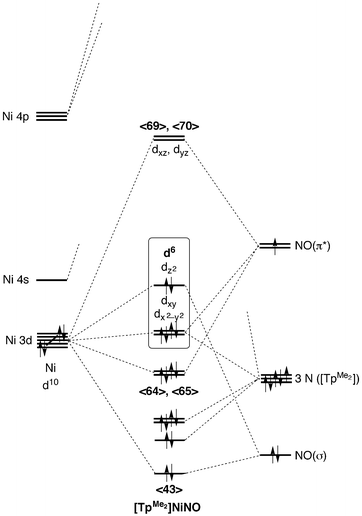
coordination compound - coordination compound - Ligand field and molecular orbital theories: Since 1950 it has been apparent that a more complete theory, which incorporates contributions from both ionic and covalent bonding, is necessary to give an adequate account of the properties of coordination compounds. Such a theory is the so-called ligand field theory (LFT), which has its origin in the ...
Get homework help fast! Search through millions of guided step-by-step solutions or ask for help from our community of subject experts 24/7. Try Study today.
January 4, 2021 - Calculate the total number of valence electrons in CN−. Then place these electrons in a molecular orbital energy-level diagram like Figure \(\PageIndex{12}\) in order of increasing energy. Be sure to obey the Pauli principle and Hund’s rule while doing so.
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.Chemistry: The Central Science, Chapter 9, Section 5Chapter 9 - Molecular Geometry
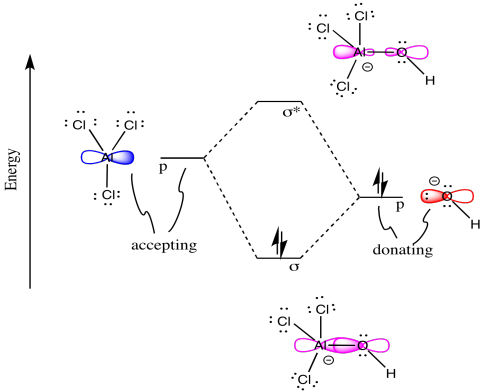
The corresponding diagram for cyanide, $\ce{CN-}$ is essentially identical, there will only be different orbital energies and very slightly different extends of the lobes. When forming a coordinate bond to a metal centre, cyanide will primarily attack with its highest occupied molecular orbital, the HOMO, since it is a nucleophile (attacking a ...
November 23, 2015 - 12/20: Andy's paper on supported nanocrystal catalysts is published in Chem. Mater.! 10/20: Our joint paper with the Klimov group using ALD to produce CMOS circuit elements from CIS quantum dot films is published in Nature Comms. 9/20: Our paper with Adam Moule's group on electron tomography ...
Hybridization of CN- = 0.5 ( 2+1-0+1) = 2 The number corresponds to sp hybridization. Thus both atoms, that is, Carbon and Nitrogen, have sp hybridization in CN-. The sp orbitals of both these atoms overlap with each other and form triple bonds. CN- Molecular Geometry
Molecular orbital diagram for cn. Note that the 1s orbital is not shown in this problem. Note that the 1s orbital is not shown in this problem. Maybe the best example for this is the mentioned ce cn and obviously the isoelectronic ceco. To add arrows to the mo diagram click on the blue boxes. Vijayta gupta is right the n atom is lower in energy.
The hybrid orbitals are more prominent outward so that their ability to overlap is stronger than that of normal orbitals. Molecular Formula: A chemical formula is a brief way of expressing the number and type of atoms that make up a particular chemical compound.
Access 130+ million publications and connect with 20+ million researchers. Join for free and gain visibility by uploading your research.
Answer (1 of 6): \text{Bond order} = \frac{n_{\text{bonding electrons}}-n_{\text{antibonding electrons}}}{2} Here is the molecular orbital diagram of CN-: There are 8 bonding electrons and 2 antibonding electrons, therefore B.O.=\frac{8-2}{2}=3 Here's a guide on how to construct MO diagrams, i...
1 month ago - Use a “skewed” molecular orbital energy-level diagram like the one in Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\) to describe the bonding in the cyanide ion (CN−). What is the bond order? ... Calculate the total number of valence electrons in CN−. Then place these electrons in a molecular orbital energy-level ...
This video is about MO Diagram #3 - CN-
Education portal for Homework help, IIT JEE, NEET. Post questions you can’t solve, Past exam questions with answers, large question bank. Improve concepts using videos, connect with students and teachers globally. Build your reputation.
As two H nuclei move toward each other, the 1s atomic orbitals of the isolated atoms gradually merge into a new molecular orbital in which the greatest electron density falls between the two nuclei. Since this is just the location in which electrons can exert the most attractive force on the two nuclei simultaneously, this arrangement constitutes a bonding molecular orbital.
Cyanide Molecular Orbital Diagram. MO Theory: the bonding orbital will be lower in energy, the an7bonding The resul7ng MO diagram looks like this. CN– (Cyanide ion), NO+ (Nitrosonium ion ). The molecular orbital diagram of (if order of molecular orbital is like that in) is as shown below. We must remember that total number of electrons in ...
Answer (1 of 8): You didn't specify the kind of theory you are considering. VB theory (Lewis dots) will give a different bond order than MO theory. In VB theory, you end up getting three bonds and a pair of electrons on one atom, C\underline{=}N: so three (Or maybe four if you put the lone pair ...
Procedure to draw the molecular orbital diagram of CN. 1. Find the valence electron of each atom in the CN molecule. Clearly, carbon has 4 valence electrons and nitrogen has 5. 2. Find if the molecule homo-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital or hetero-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital. Clearly, CN is hetero orbital. 3.
Problem: Use the molecular orbital diagram to figure out the electronic configuration for CN. Which of the following statements is correct?a) CN is diamagnetic.b) CN− is paramagnetic.c) If an electron is removed to give CN+, the bond order increases.d) The π*2p orbital is the highest energy orbital containing an electron in CNe) If an electron is added to give CN−, the bond length decreases.
Question: Complete the molecular orbital diagram for CN. Note that the 1s orbitals are not shown. Identify the bond order of CN. O2 01 OOOOO 25- 0 2s Answer Bank The atomic orbitals on the left side of the molecular orbital diagram are those of The atomic orbitals on the right side of the molecular orbital diagram are those of.
In the diagram shown below, only the orbitals of the 2nd shell are shown. Only the valence electrons are considered: C has 4 and N has 5. The CN- ion has an additional electron (shown in blue) because of its charge: The bond order of CN- is 3. Since all the electrons are paired, this ion should be diamagnetic. 3. Describe the molecular ...
Molecular Orbital Mixing. More detail was added to this answer in response to input and questions from students in the class of 2008. If you have suggestions or contributions please e-mail me. First of all while the stage 1 (pre mixing diagram) of diatomics is very easy to produce, the mixing in diatomics is very difficult to evaluate because ...
Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ...
In the second diagram only sigma bonding is considered and it shows the combination of the metal 3d, 4s and 4p orbitals with OCCUPIED ligand group orbitals (using 1 orbital from each ligand). The result is that that the metal electrons would be fed into t2g and eg* molecular orbitals which is similar to the CFT model except that the eg orbital ...
Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified. Megan Lim. Oct 26, 2016 · 3 min read. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding ...
When two atomic orbitals combine, two molecular orbitals are formed. One is known as bonding molecular orbital and the other is called an anti-bonding molecular ...1 answer · Top answer: Concepts and reason • The molecular orbital theory explains the bonding in terms of the combination and organization of atomic orbitals of an atom which ...
Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in








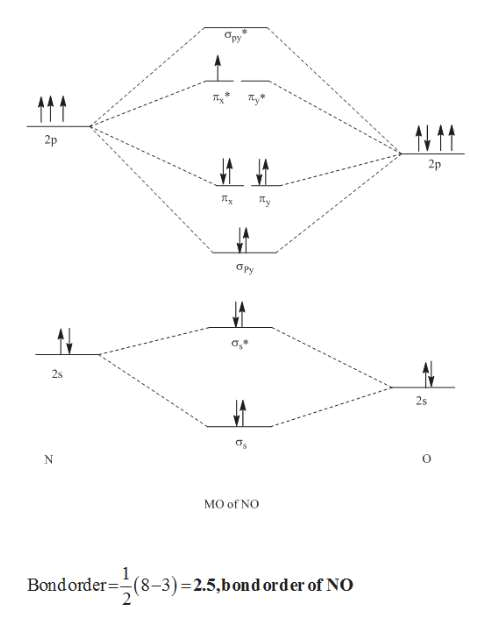
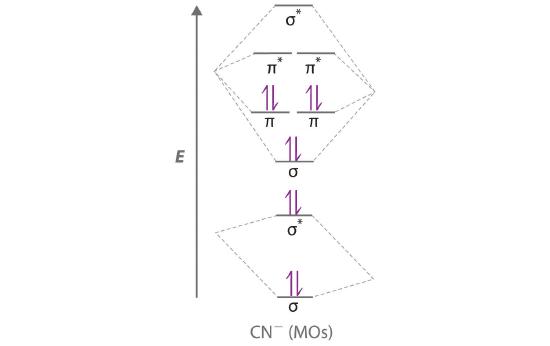


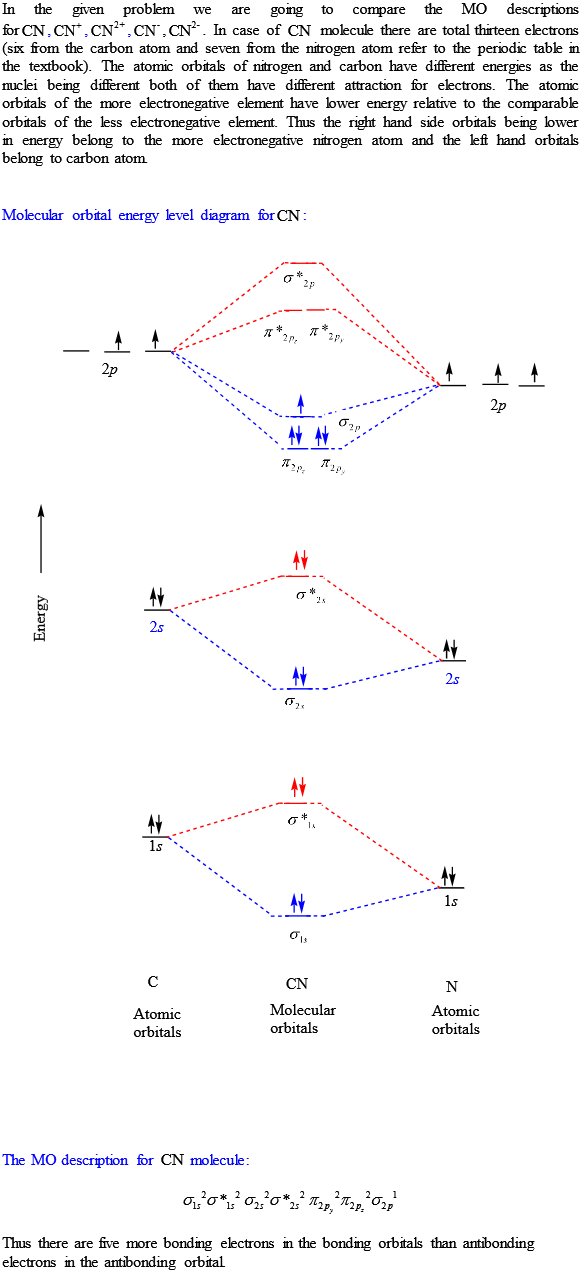
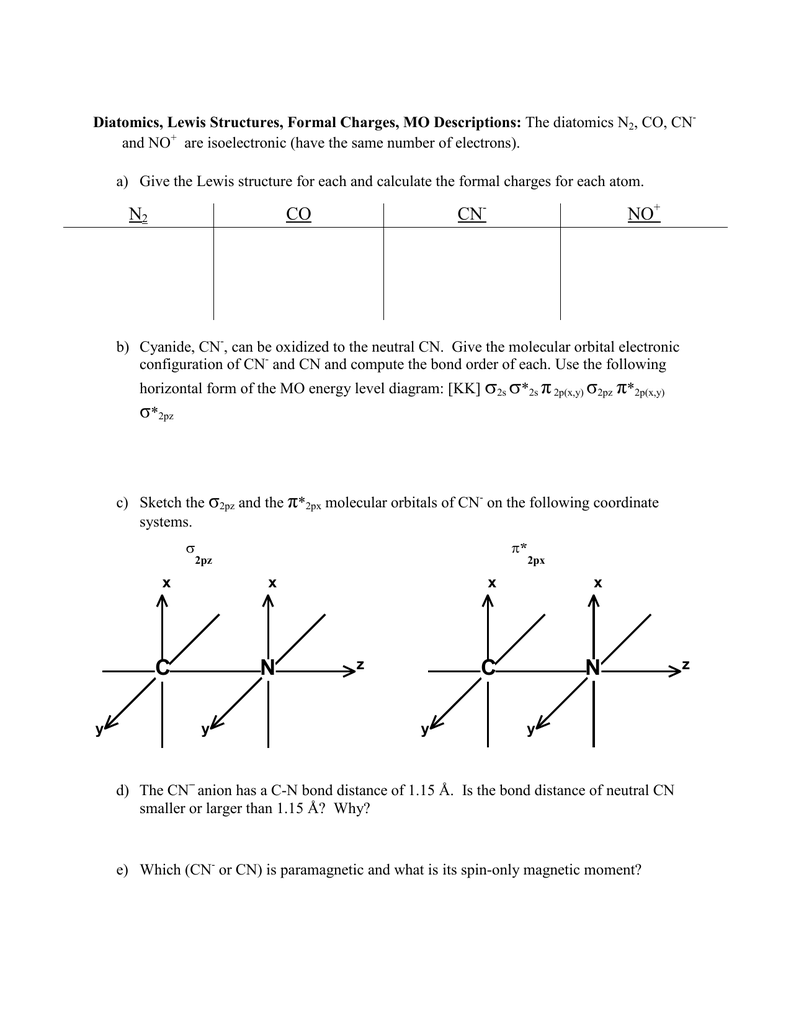

0 Response to "37 cn- molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment