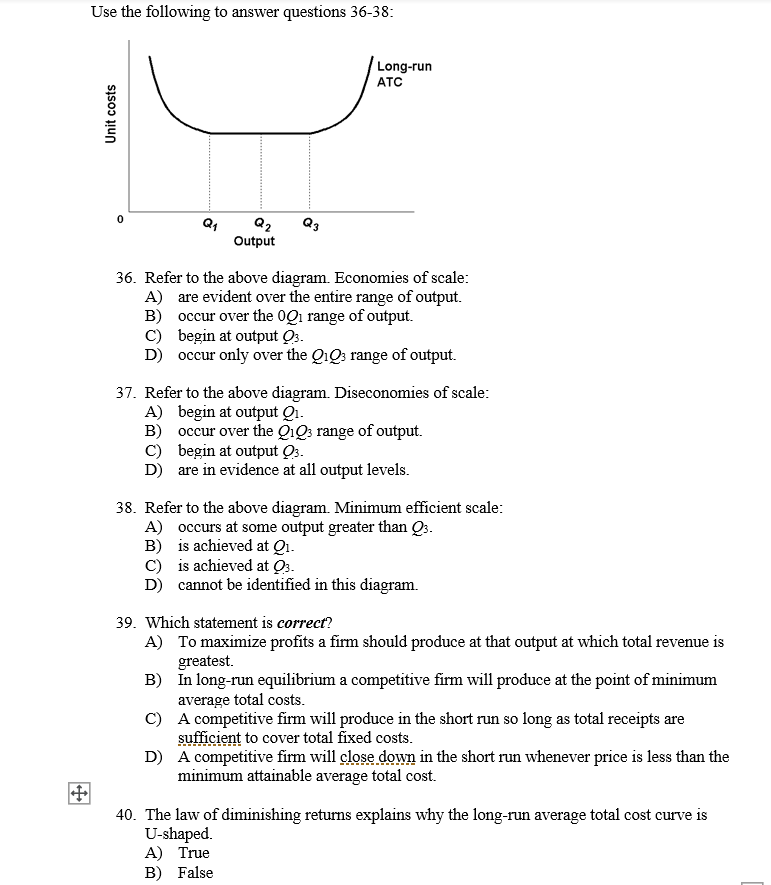
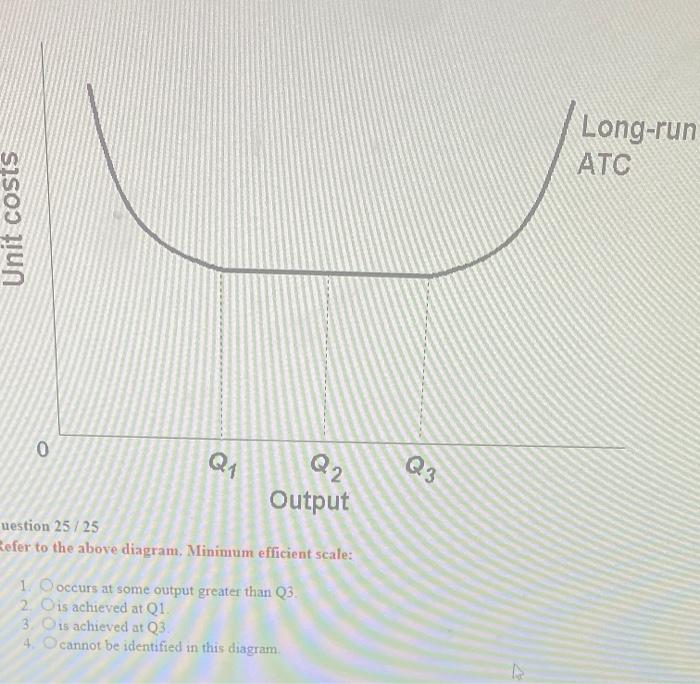
36 refer to the diagram. minimum efficient scale:
Refer to the above table. There are increasing marginal returns through the: A. ... In the diagram above LRTC = long-run total costs. The firm is experiencing: A. economies of scale. B. diseconomies of scale. C. constant returns to scale. D. minimum efficient scale. 16. R-16 REF 22-139:
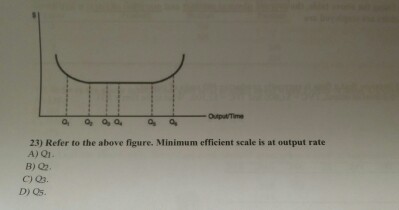
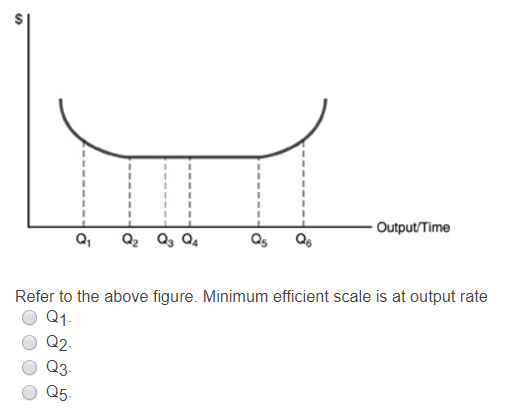
Refer to the diagram minimum efficient scale. Refer to the above diagram for output level q per. C begin at output q3. Minimum efficient scaleis achieved at q 1. Suppose a firm is in a range of production where it is experiencing economies of scale. Occurs at some output greater than q3. B occur over the 0q1 range of output.
How does the fan like diagram differ from a cladogram. A cladogram is a diagram which shows the relationship between different organisms based on their different similarities. Classify 1 7 as either lytic cycle lysogenic cycle or both. 17 organizing lifes diversity continued use the fanlike phylogenetic diagram to answer the questions.

Refer to the diagram. minimum efficient scale:
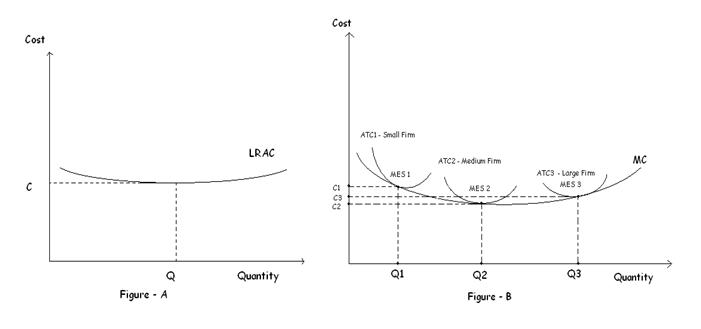
In the above diagram, with a U-shaped LRAC curve, the minimum efficient scale is Q 0. The size of a firm is often measured by its long-run output level which depends to a large extent on the minimum efficient scale. If the minimum efficient scale is low, the firm will tend to be small. Conversely, if the minimum efficient scale is high, the ...
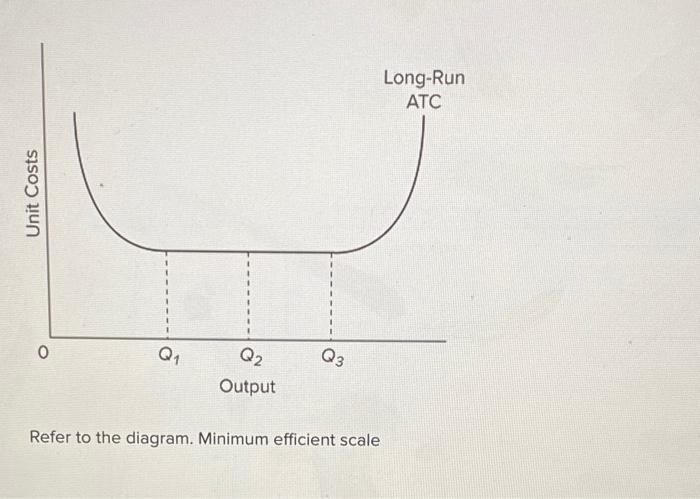
23. Refer to the above diagram. Minimum efficient scale: A. occurs at some output greater than Q3. B. is achieved at Q1. C. is achieved at Q3. D. cannot be identified in this diagram. 24. Refer to the above diagram. Constant returns to scale: A. occur over the 0Q1 range of output. B. occur over the Q1Q3 range of output. C. begin at output Q3.
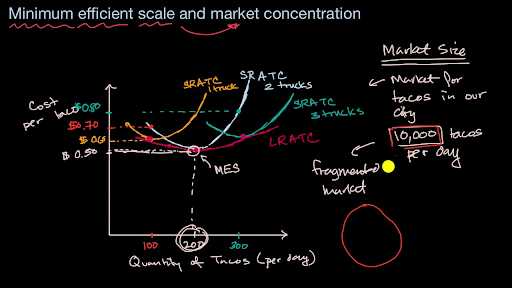
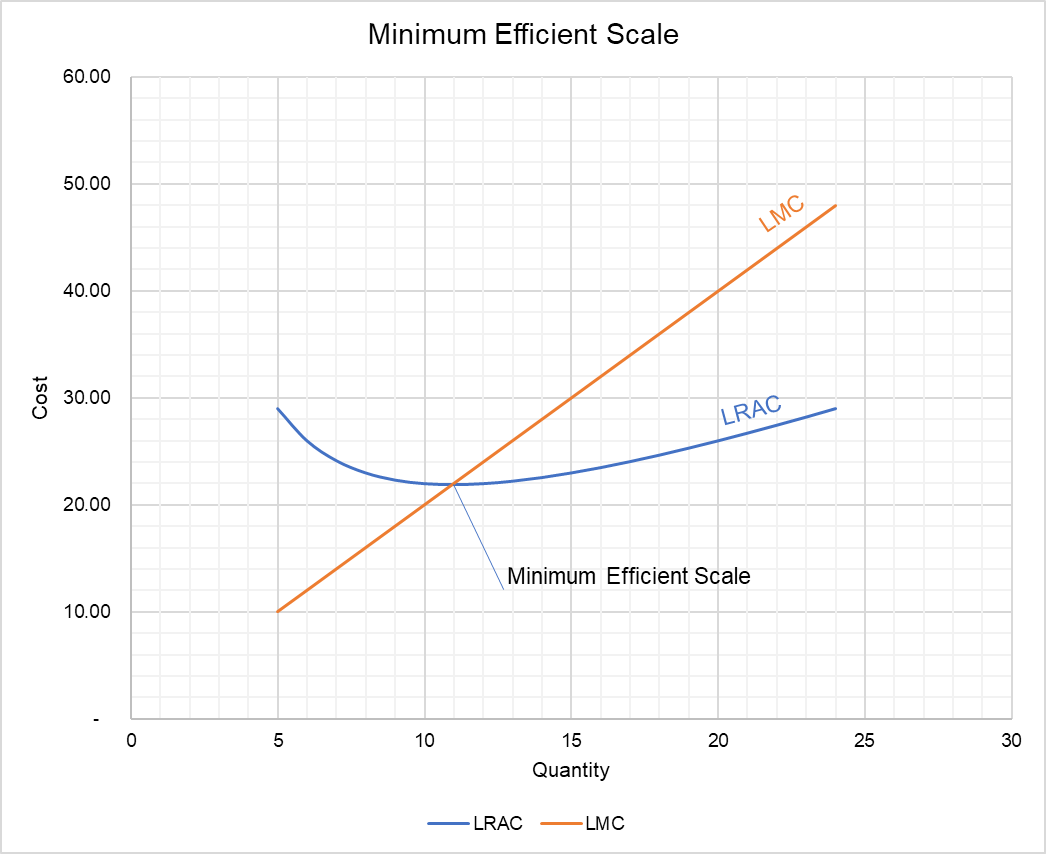
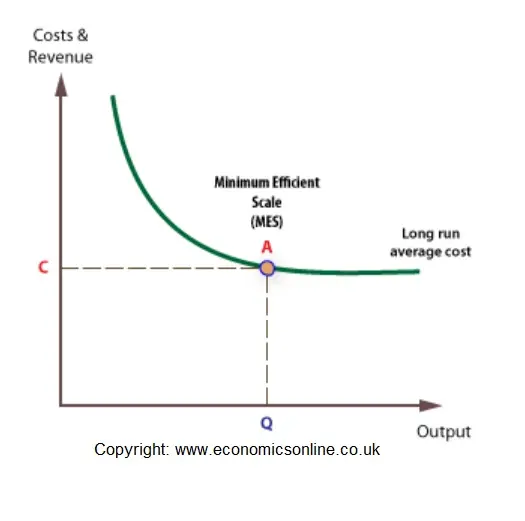
The minimum efficient scale (MES) is the balance point at which a company can produce goods at a competitive price. Achieving MES minimizes long-run average total cost (LRATC).
Refer to the diagram. minimum efficient scale:.
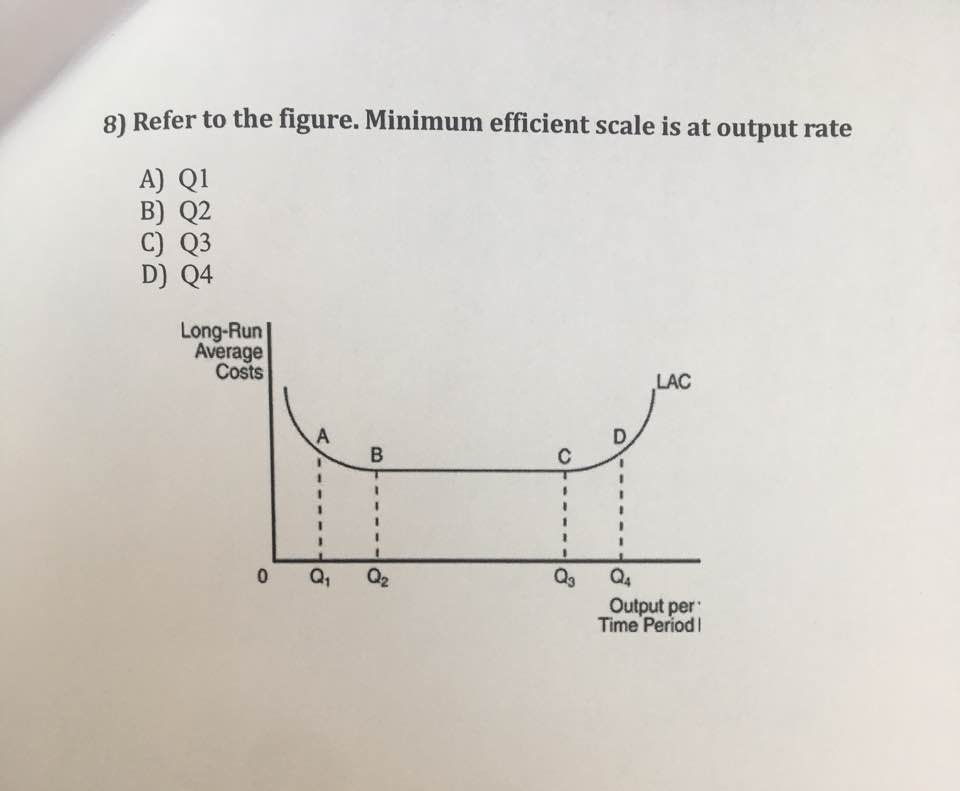
Refer to the diagram. Minimum efficient scale. Multiple Choice. occurs at some output greater than Q3. is achieved at Q1. is achieved at Q3. cannot be identified in this diagram. At what point does marginal product equal average product? Multiple Choice. where average product is equal to its minimum value; where average product is equal to its ...
Marginal product of a factor of production, for example labor, is the increase in total production that results from one unit increase in the factor of production i.e. labor if other factors, for example capital, are held constant.
Refer to the above short-run production and cost data. The curves of Figures A and B suggest that: O A. marginal product and marginal cost reach their maximum points at the same output. O B. marginal cost reaches a minimum where marginal product is at its maximum. O C. marginal cost and marginal product reach their minimum points at the same ...
The diagram 4.3 shows the LAC. Besides internal economies that a firm enjoys in the short run, it has the benefit of the scale economies in the long run. Every fixed factor with its given life span constitutes a scale of production which in the short run cannot be altered. In the long run each of these factors can be altered and replaced.
Refer to the diagram to the right. Identify the curves in the diagram. additional cost of producing an additional unit or output. Marginal cost is the. $340. Vipsana's Gyros House sells gyros. The cost of ingredients (pita, meat, spices, etc.) to make a gyro is $2.00. Vipsana pays her employees $60 per day.
Refer to the diagram. Minimum efficient scale Multiple Choice • occurs at some output greater than Q3. • is achieved at Q1. • is achieved at Q3. • cannot be identified in this diagram.
See more: Refer To The Diagram. Minimum Efficient Scale:, Chapter 2 Macro Questions 2 Flashcards Minimum Efficient Scale:, Chapter 2 Macro Questions 2 Flashcards It is also important to learn about new human relations tools and resources, which will play a key role in rewarding employees who excel.
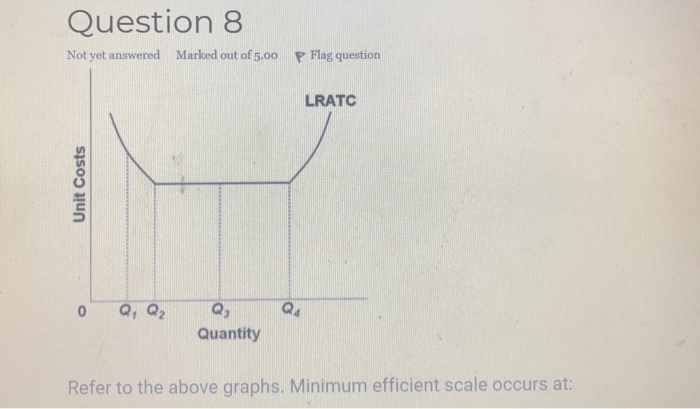
Refer to the data. At what level of output is minimum efficient scale realized? 50. If a firm doubles its output in the long run and its unit costs of production decline, we can conclude that: economies of scale (increasing returns to scale) are being realized. Refer to the diagram. Minimum efficient scale: is achieved at Q 1. If a firm ...
Refer to the Diagram. Minimum Efficient Scale: assignment 5 ch 9 flashcards refer to the data economies of scale in plant atc a are realized over the to levels of output diseconomies of scale exist over the to levels of output chandler chapter 11 micro flashcards start studying chandler chapter 11 micro learn vocabulary refer to the diagram to the right identify the minimum efficient scale of ...
Minimum efficient scale affects the number of firms that can operate in a market and the structure of markets. Refer to the above diagram. The long run average total cost curve falls. 4 units of output. Suppose a firm is in a range of production where it is experiencing economies of scale.
See more: Refer To The Diagram. Minimum Efficient Scale:, Chapter 2 Macro Questions 2 Flashcards. As valuable as these measurements are as soon as considering a stock, bond, or mutual money investment, volatility hazard is simply one the the factors you should be because can influence the high quality of one investment.
Economies of scale refer to these reduced costs per unit arising due to an increase in the total output. Diseconomies of scale occur when the output increases to such a great extent that the cost per unit starts increasing. In this article, we will look at the internal and external, diseconomies and economies of scale.
Economics. Economics questions and answers. Long-Run ATC Unit Costs 0 Q2 Q3 Output Refer to the diagram. Minimum efficient scale occurs at some output greater than Q3. is achieved at Q1 О O is achieved at Q3 cannot be identified in this diagram. Question: Long-Run ATC Unit Costs 0 Q2 Q3 Output Refer to the diagram.
A long run average cost curve is known as a planning curve. This is because a firm plans to produce an output in the long run by choosing a plant on the long run average cost curve corresponding to the output. It helps the firm decide the size of the plant for producing the desired output at the least possible cost.
In the diagram below of the lac operon what is the sugar composition of the media. The operon encodes a single polycistronic mrna with three open reading frames. The l arabinose operon also called the ara or arabad operon is an operon required for the breakdown of the five carbon sugar l arabinose in escherichia coli.
Refer to the diagram, where variable inputs of labor are being added to a constant amount of property resources. Average variable cost will be at a minimum when the firm is hiring - Q 2 workers. At an output of 1,000 units per year, a firm's variable costs are $5,000 and its average fixed costs are $3. Its total costs per year are - $8,000. Refer to the diagram.
185. Refer to the above diagram. Diseconomies of scale: A) begin at output Q1. C) begin at output Q3. B) occur over the Q1Q3 range of output. D) are in evidence at all output levels. Answer: C. Type: G Topic: 6 E: 407 MI: 163 186. Refer to the above diagram. Minimum efficient scale: A) occurs at some output greater than Q3. C) is achieved at Q3 ...
Minimum efficient scale corresponds to the lowest point on the long run average cost curve and is also known as an output range over which a business achieves productive efficiency.. MES is not a single output level - more likely, the MES is a range of outputs where the firm achieves constant returns to scale and has reached the lowest feasible cost per unit.
The minimum efficient scale (MES) is the point on the LRAC (long-run average cost) curve where a business can operate efficiently and productively at the lowest possible unit cost. The minimum efficient scale can also be a range of output for which the company receives constant returns to scale at the lowest unit cost possible. Finding the ...
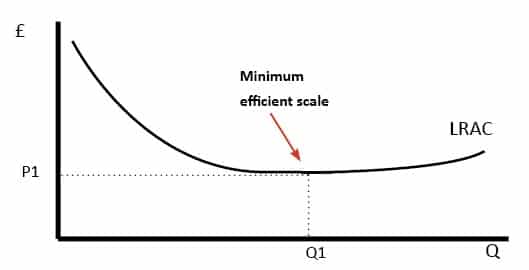
The minimum efficient scale is the plant size (or scale of operation) that a firm must reach to obtain the lowest average cost or exhaust all economies of scales. Diseconomies of Scale. The region where long run average costs remain unchanged as plant size increases is known as constant returns to scale.
The minimum efficient scale of a firm:is the smallest level of output at which long-run average total cost is minimized. If an industry's long-run average total cost curve has an extended range of constant returns to scale, this implies that:both relatively small and relatively large firms can be viable in the industry.
9. Refer to the above diagram. Minimum efficient scale: 1. occurs at some output greater than Q3. 2. is achieved at Q1. 3. is achieved at Q3. 4. cannot be identified in this diagram. 10. Suppose a firm is in a range of production where it is experiencing economies of scale.
This photo about: Refer to the Diagram. Minimum Efficient Scale:, entitled as Frontiers Refer To The Diagram. Minimum Efficient Scale: - also describes Frontiers and labeled as: please refer to kb link,refer to,refer to paytm,refer to the given diagram the economy is dissaving,refer to value not formula excel, with resolution 1596px x 1652px



/diseconomies_of_scale_final-db85c494049d42aca10deb37e214a013.png)








/diseconomies_of_scale_final-db85c494049d42aca10deb37e214a013.png)




0 Response to "36 refer to the diagram. minimum efficient scale:"
Post a Comment