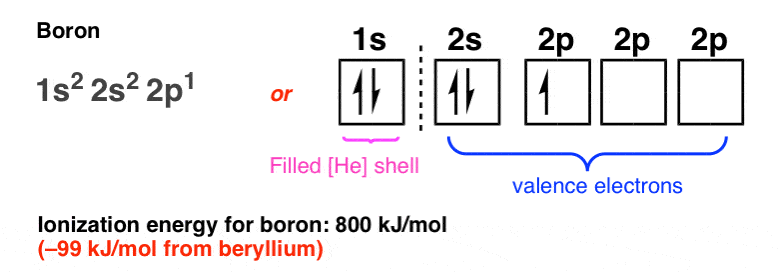
36 orbital diagram for boron
The molecular orbital diagrams of , and are drawn in the attached image. There is no unpaired electron present in the MO diagram of and all the electrons are paired up so it is diamagnetic in nature. There is one unpaired electron present in the MO diagram of and therefore it is paramagnetic in nature.
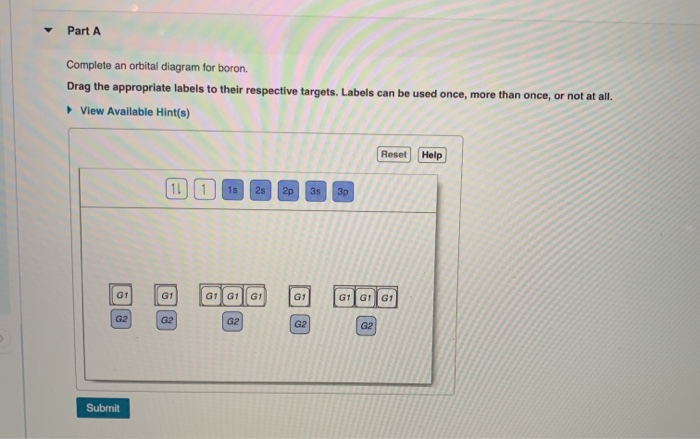
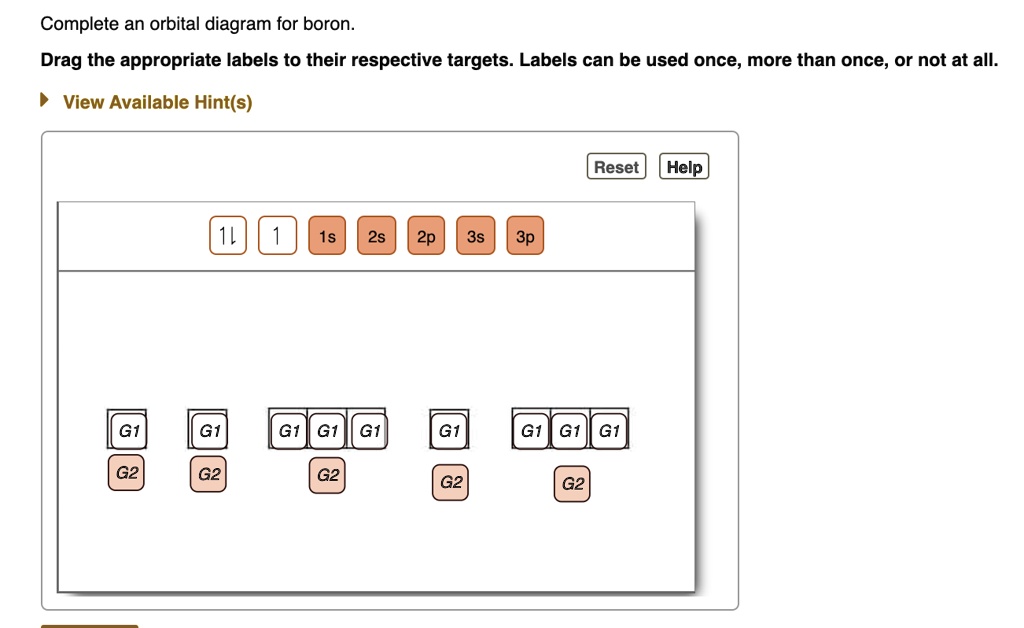
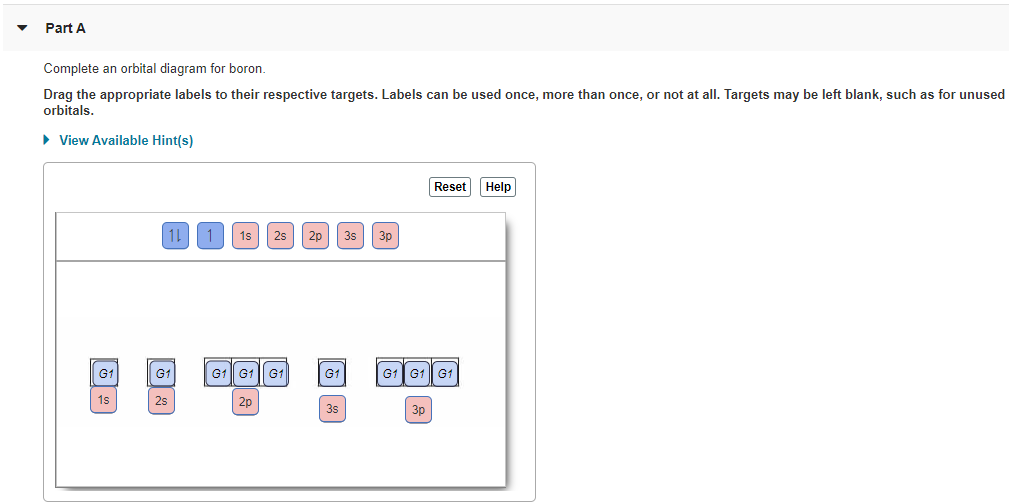
Question: Orbital Diagrams Draw an orbital diagram for boron. Use this tool to draw the orbital diagram. Is, 2s,2p, 3s, 3p,3d, 4s,4p,4d, 4f 5s, 5p, 5d, 5f, 6s, 6p, 6d, 7s, 7p, 7d. This problem has been solved! See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading. Show transcribed image text
In this video, we will explore the rules to follow when drawing orbital diagrams. We also determine the orbital diagram of boron.

Orbital diagram for boron
Each boron atom has one 2s and three 2p valence orbital s. The 2s orbital s will overlap to for m 2sσ and 2sσ ... 11.11.2016 · So the bond order of B2 is equal to 1, which you can get by drawing the molecular orbital diagram and per for ming the equation Bond Order = .5 * (# of bonding electrons - # of antibonding electrons).
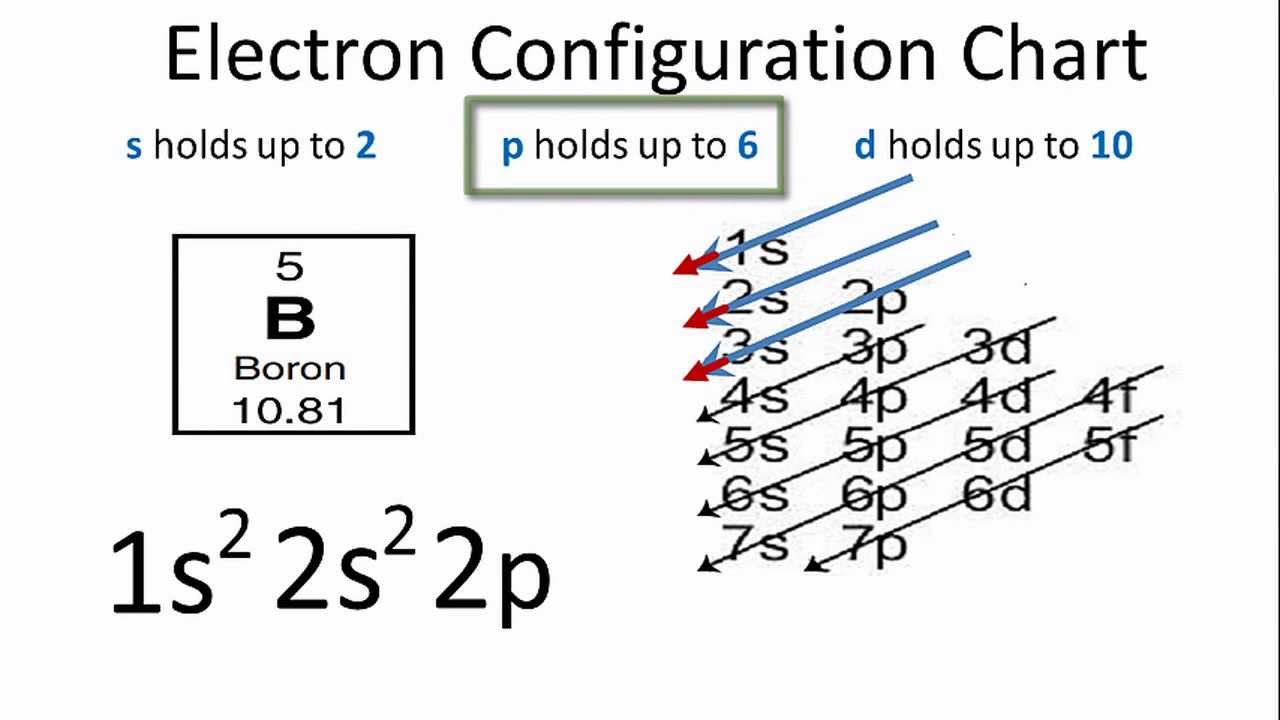
Electron configurations are a shorthand form of an orbital diagram, describing which orbitals are occupied for a given element. For example, 1s22s22p1 is the electron configuration of boron. Use this tool to generate the electron configuration of arsenic (As).
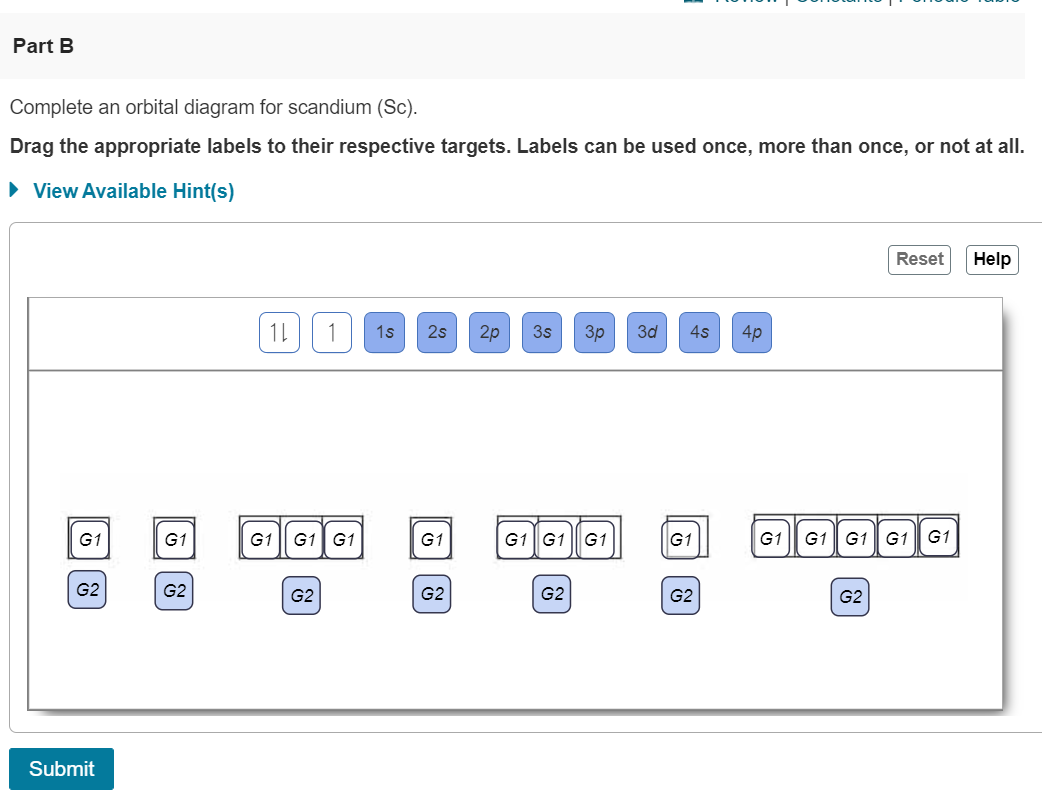
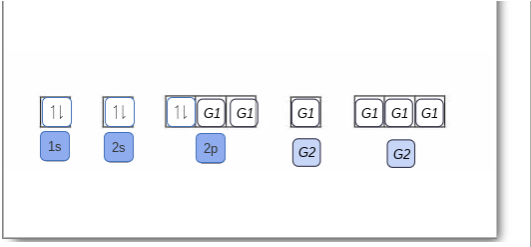
Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. Complete an orbital diagram for boron. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Labels can be used once, more than once, or not at all. Complete an orbital diagram for scandium (Sc). Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Labels can be used once more than once, or not ...
Orbital diagram for boron.
To write the orbital diagram for the Boron atom (B) first we need to write the electron configuration for just B. To do that we need to find the number of e...
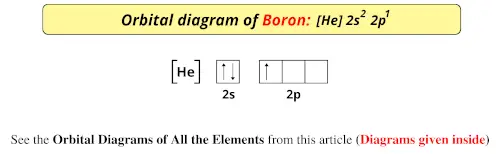
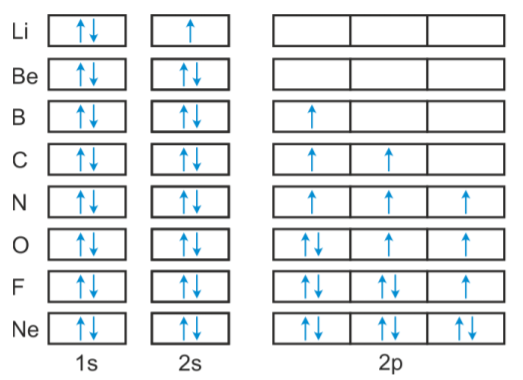
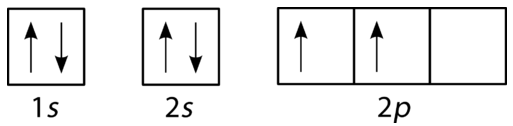
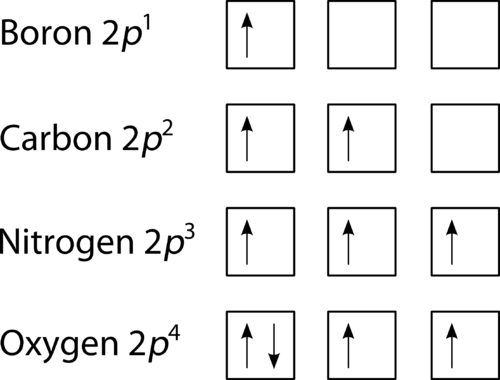
The orbital diagram for boron as shown has the one electron in the 2p orbital. The electron can be placed in any of the three 2p orbitals. The electron configuration for boron is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 1. The energy level diagram for boron is show below. For the next element, carbon, the sixth electron must be placed in the correct orbital.
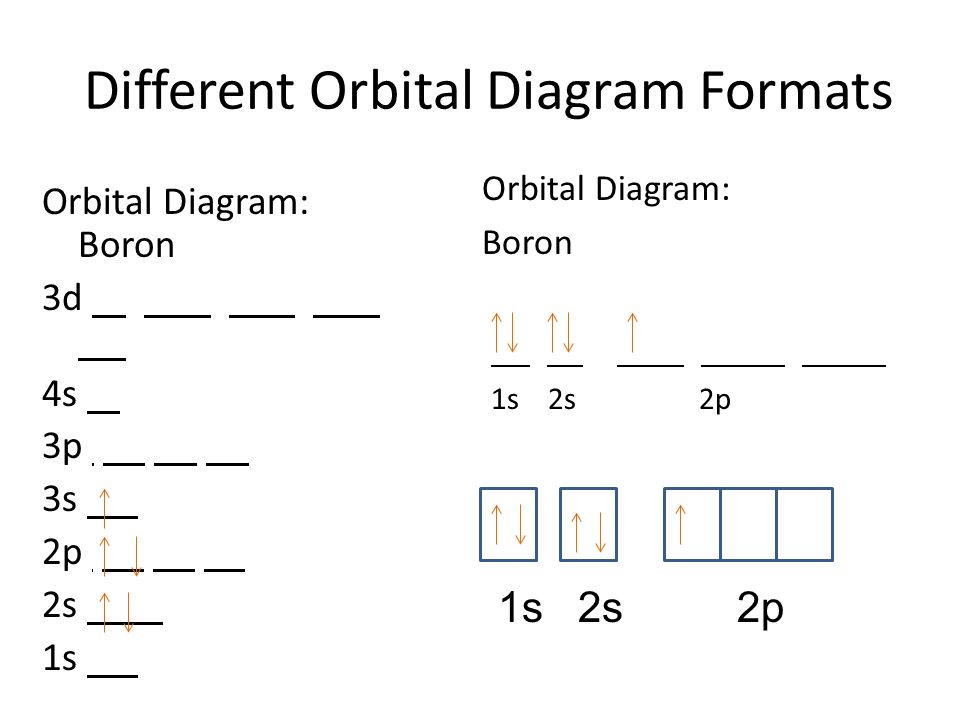
Boron is the fifth element with a total of 5 electrons. The electron configuration of boron is 1s²2s²2p¹ which means that there are two electrons in the 1s orbital two electrons in the 2s orbital and one electron in the 2p orbitals. This gives us an orbital filling diagram of. The remaining electron will go in the 2p orbital.
Orbital diagram of Boron (B) 6: Orbital diagram of Carbon (C) 7: Orbital diagram of Nitrogen (N) 8: Orbital diagram of Oxygen (O) 9: Orbital diagram of Fluorine (F) 10: Orbital diagram of Neon (Ne) 11: Orbital diagram of Sodium (Na) 12: Orbital diagram of Magnesium (Mg) 13: Orbital diagram of Aluminum (Al) 14:
Mar 18, 2019 · Use this tool to draw the orbital diagram. Show transcribed image text Orbital Diagrams Draw an orbital diagram for boron. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.Electron Configuration for Boron (B)Electron Configuration for Boron (B)
The orbital filling diagram of boron. I skipped past beryllium because I was getting bored. The electron configuration of boron is 1s²2s²2p¹, which means that there are two electrons in the 1s orbital, two electrons in the 2s orbital, and one electron in the 2p orbitals. This gives us an orbital filling diagram of.
The Electron Configuration Video Lessons. Concept: Concept: Example: Problem: Complete an orbital diagram for boron. Complete an orbital diagram for scandium (Sc).
The orbital filling diagram of boron. I skipped past beryllium because I was getting bored. The electron configuration of boron is 1s²2s²2p¹, which means that there are two electrons in the 1s orbital, two electrons in the 2s orbital, and one electron in the 2p orbitals. This gives us an orbital filling diagram of:
Complete an orbital diagram for boron. Boron is the fifth element with a total of 5 electrons. Use this tool to draw the orbital diagram. Therefore the b electron configuration will be 1s22s22p1. Lower energy subshells fill before higher energy subshells. Use the buttons at the top of the tool to add orbitals.
What is the Orbital Notation for boron? Boron has the electronic configuration:- 1s2, 2s2, 2p1 Why molecular orbital diagram of O2 and N2 are different? They have different numbers of valence...
Bf3 Molecular orbital Diagram - Bf3 Molecular orbital Diagram , D3h Boron Trifluoride is Loaded
Boron is the fifth element with a total of 5 electrons. In writing the electron configuration for Boron the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for B goes in the 2s orbital. The remaining electron will go in the 2p orbital.
Orbital Diagram For Boron - Quantum Dots Derived From Two Dimensional Materials And Their how to find the electron dot diagram for boron quora a chemistry book perhaps boron has 5 electrons 3 are in the valence shell so boron can use those electrons to bond with three other atoms b here
May 11, 2018 · A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. Boron is the fifth element with a total of 5 electrons.
Draw an orbital diagram for scandium (Sc). Use this tool to draw the orbital diagram. How many orbitals are there in the third shell (n = 3)? Express your answer numerically as an integer. Show the orbital-filling diagram for N (nitrogen). Stack the subshells in order of. Question: Draw an orbital diagram for boron.
Electron configuration of boron (B) atom through orbital diagram Atomic energy levels are subdivided into sub-energy levels. These sub-energy levels are called orbital. The sub energy levels are expressed by ‘l’. The value of ‘l’ is from 0 to (n – 1). The sub-energy levels are known as s, p, d, f.
(a) Starting with the orbital diagram of a boron atom, describe the steps needed to construct hybrid orbitals appropriate to describe the bonding in BF3. (b) What is the name given to the hybrid orbitals constructed in (a)? (c) On one origin, sketch the large lobes of the hy- brid orbitals constructed in part (a). (d) Are there any
We can illustrate the comparison of orbitals and electron distribution in an isolated boron atom and in the bonded atom in BH 3 as shown in the orbital energy level diagram in Figure 7.5.8. We redistribute the three valence electrons of the boron atom in the three sp 2 hybrid orbitals, and each boron electron pairs with a hydrogen electron when B–H bonds form.
We have to draw the molecular orbital diagram for ${{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}$ molecule. The ${{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}$ molecule is formed by the combination of two boron atoms. The two boron atoms are linked by a covalent bond. The atomic number of boron is 5. The electronic configuration of boron is as follows: $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^1}$
The orbital diagram for boron as shown has the one electron in the 2p orbital. An orbital diagram is used to show how the orbitals of a subshell areoccupied by electrons. 12 Votes An atom of boron atomic number 5 contains five electrons. 1st s2 2nd s2p6 3rd s2p6d10. Since 1s can only. We will also calculate their bond order and determine if t.
An atom of boron (atomic number 5) contains five electrons. The n = 1 shell is filled with two electrons and three electrons will occupy the n = 2 shell. Because any s subshell can contain only two electrons, the fifth electron must occupy the next energy level, which will be a 2p orbital. Click to see full answer
There are no remaining hybrid orbitals. There is one p orbital on boron but there is no adjacent atom with another p orbital. Add it to the molecular orbital diagram as a non-bonding molecular orbital. There are a total of 6 electrons to add to the molecular orbital diagram, 3 from boron and 1 from each hydrogen atom. sp Hybrid Orbitals in BeH2
orbital on each fluorine is perpendicular to the BF 3 plane and capable of forming out-of-plane pi interactions (ð z).! The 2p x orbital points toward the B atom and forms sigma interactions (ó)! The 2p y orbital is parallel to the BF 3 plane and has the potential to form in-plane pi interactions (ð 2). The symmetries of the central boron AOs are as follows: s = A 1 ' (p x
This is the general MO diagram you need to fill with the valence electrons of BN Boron has 3 valence electrons, and nitrogen has 5 valence electrons, this makes 8 electrons. You have to start filling the orbitals from those with lowest energy to those with higher energy. So, 2 electrons on σ2s , two electrons on σ∗2s, two electrons on σ2p .
Part A. Complete an orbital diagram for boron. Draw orbital diagrams, and use them to derive electron configurations To understand how to draw orbital diagrams, and how they are used to write electron configurations. The electron configuration of an element is the arrangment of its electrons in their atomic orbitals.
• MO diagrams can be built from group orbitals and central atom orbitals by considering orbital symmetries and energies. • The symmetry of group orbitals is determined by reducing a reducible representation of the orbitals in question. This approach is used only when the group orbitals are not obvious by inspection.
Bromine Orbital Diagram. Answer to Write the electron configuration and give the orbital diagram of a bromine (Br) atom (Z = 35). the σ bonds. I've drawn the overlaps below in the MO diagrams. Each bromine would donate one 4pz electron to form a σ -bonding orbital. Answer to Draw an orbital diagram for each element: (a) magnesium; (b ...


















0 Response to "36 orbital diagram for boron"
Post a Comment