35 g protein coupled receptors diagram
Jan 08, 2021 · G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) represent the largest protein family encoded by the human genome. Located on the cell membrane, they transduce extracellular signals into key physiological ... G protein can refer to two distinct families of proteins. Heterotrimeric G proteins, sometimes referred to as the "large"; G proteins, are activated by G protein-coupled receptors and are made up of alpha (α), beta (β), and gamma (γ) subunits. "Small"; G proteins (20-25kDa) belong to the Ras superfamily of small GTPases.
Nov 08, 2017 · Introduction. Based on their canonical structure, G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), which are sometimes termed heptahelical or 7-transmembrane receptors, are the largest family of membrane receptors in humans and numerous other species.
G protein coupled receptors diagram
The G protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPER) is a seven-transmembrane-domain receptor that mediates non-genomic estrogen related signaling. G Protein-Coupled Estrogen Receptor: A Potential Therapeutic Target in Cancer. G protein−coupled receptors (GPCRs) regulate facets of growth, development, and environmental sensing in eukaryotes, including filamentous fungi. The largest predicted GPCR class in these organisms is the Pth11-related, with members similar to a protein required for disease in the plant... G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs), otherwise known as G-proteins, are a diverse family of receptors found in a huge range of tissues throughout the body. Structure of G-Proteins. G-protein coupled receptors are composed of a transmembrane region crossing the lipid bilayer seven times...
G protein coupled receptors diagram. Adhesion G protein-coupled receptors in nervous system development and disease. Nature reviews Neuroscience 17, 550-561 (2016). The N terminus of the adhesion G protein-coupled receptor GPR56 controls receptor signaling activity. The Journal of biological chemistry 286, 28914-28921... The large family of G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) contains a diverse group of membrane-bound signaling molecules. Learn how activated GPCRs relay messages by heterotrimeric GTP-binding proteins. G-Protein-Coupled Receptors [GPCRs] • largest family of transmembrane proteins in the human genome with more than 800 unique GPCRs. GPCR Structure • each GPCR is composed of 7 transmembrane helices connected by extracellular and intracellular loops. [Source](/r/IAmA/comments/lmuxq6/) # For proper formatting, please use [Old Reddit](https://old.reddit.com/r/tabled/comments/ooekv5/) Rows: ~80 Questions|Answers :--|:-- What are the effects of marijuana use upon the lungs? I’ve always heard that it’s “less bad than tobacco” but are we talking potentially negligible effects, or like “you’re 1% less like to get cancer, but you’re still getting cancer”.|Smoking anything is bad for your lungs. Vaping is better than smoking. Edibles are better th...
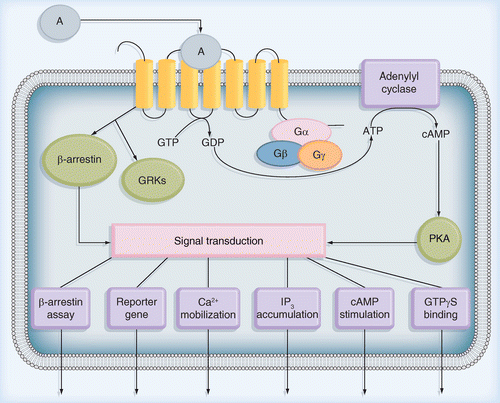
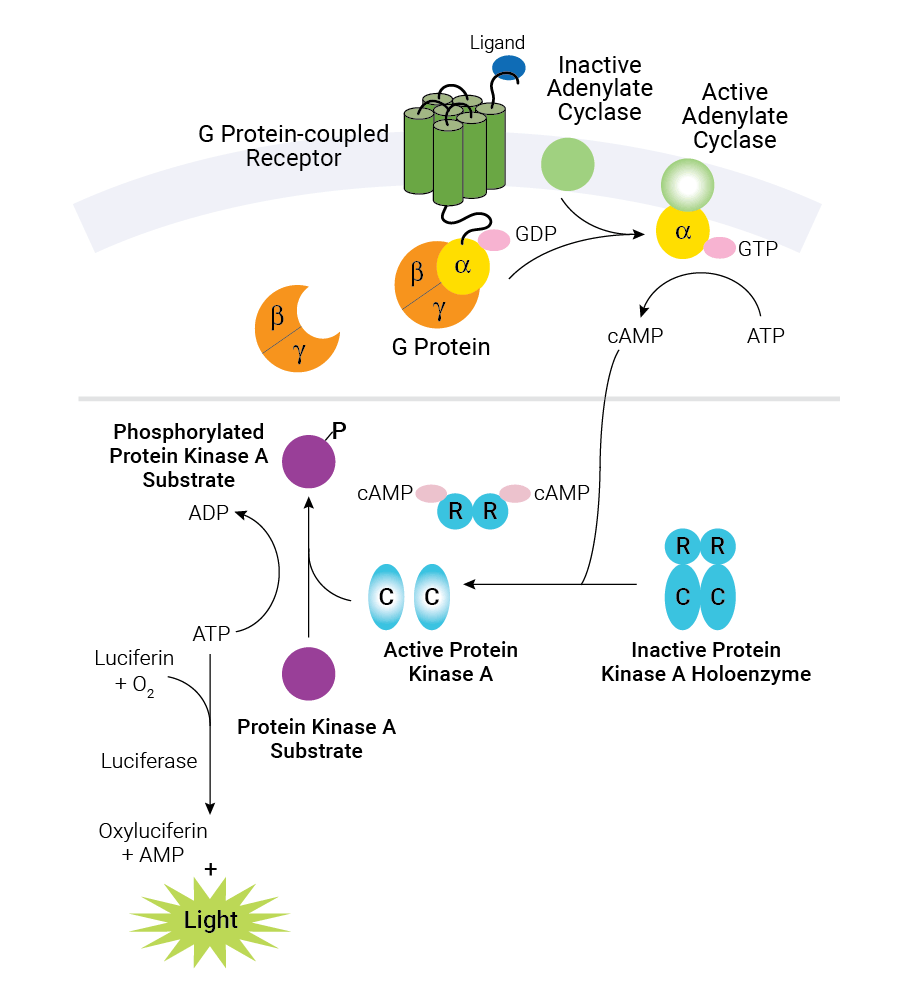
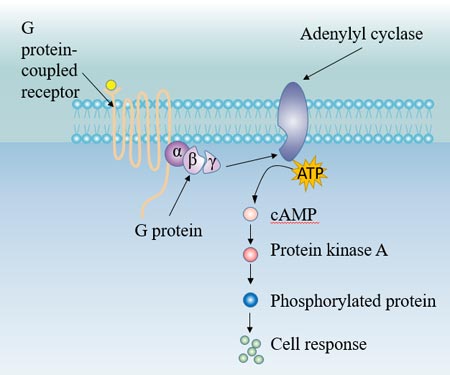
G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR), protein located in the cell membrane that binds extracellular substances and transmits signals from these substances to an intracellular molecule called a G protein (guanine nucleotide-binding protein). GPCRs are found in the cell membranes of a wide range of. G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are the largest class of membrane proteins in the human genome. The term "7TM receptor" is commonly used interchangeably with "GPCR", although there are some receptors with seven transmembrane domains that do not signal through G proteins. Diagram - G-protein coupled receptor common downstream activation pathways. In this diagram, lines ending in arrows (such as acting on adenylyl cyclase protein-coupled receptors. The visual G protein transducin was, in addition, the first heterotrimeric G protein whose struc-ture was solved (12). G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors...
G protein‐coupled receptors comprise a large class of proteins that regulate many physiological functions such as sight, taste, smell, neurotransmission, cardiac output, and pain perception. In response to ligand binding, GPCRs activate heterotrimeric guanine nucleotide binding proteins (G... G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptor, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR)... The superfamily of G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) is very diverse in structure and function and its members are among the most pursued targets for drug development. We identified more than 800 human GPCR sequences and simultaneously analyzed 342 unique functional nonolfactory human... Start studying G protein coupled receptor. Learn vocabulary, terms and more with flashcards, games and other study tools. the largest family of cell-surface receptors transmembrane receptors all very similar in structure extremely widespread and diverse in their functions.
This video ";G-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCRs)" is part of the Lecturio course "Biochemistry" ► WATCH the complete course on...
G protein-coupled receptors: These comprise a large protein family of transmembrane receptors that sense molecules outside the cell and activate inside signal transduction pathways and, ultimately, cellular responses. Any adrenergic effects on cells are generally mediated by G protein-coupled receptors.
Protein Sorting or Protein Trafficking or Protein Targeting: The proteins synthesized in the cell have to be translocated to the nucleus or other target organelles. Newly synthesized polypeptides have a signal sequence (which is a polypeptide) consisting of 13-36 amino acids. It is known as leader sequence.
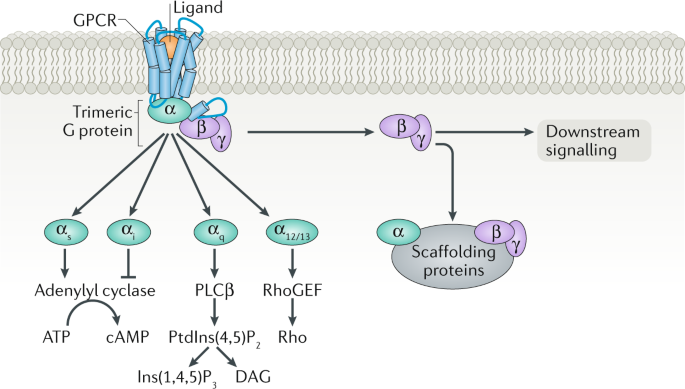
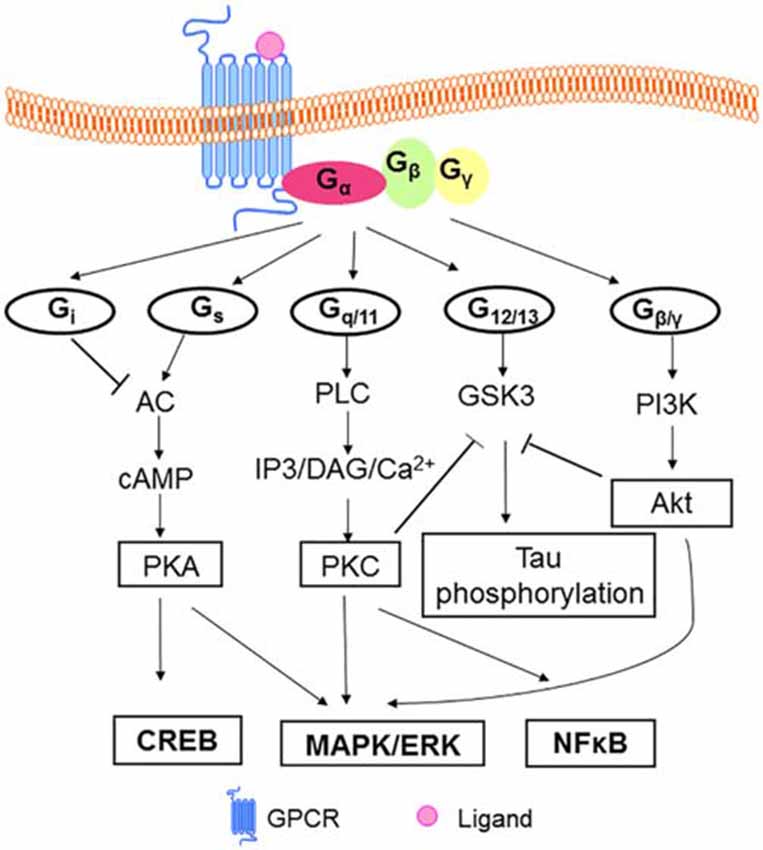
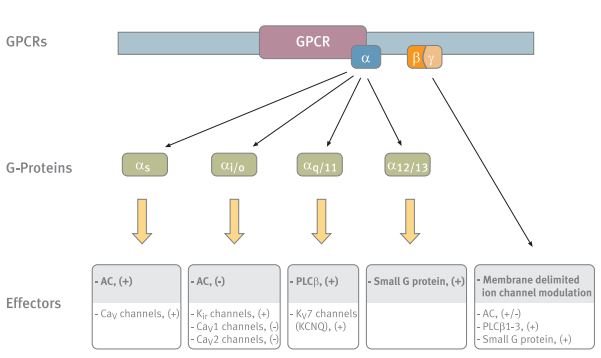
G q protein alpha subunit is a family of heterotrimeric G protein alpha subunits.This family is also commonly called the G q/11 (G q /G 11) family or G q/11/14/15 family to include closely related family members. G alpha subunits may be referred to as G q alpha, G αq, or G q α. G q proteins couple to G protein-coupled receptors to activate beta-type phospholipase C (PLC-β) …
G protein-coupled receptors. Overview. G protein binding and dissociation can be observed with GFP fusions. G protein effector mechanisms. GPCR structure. All GPCRs (with the exception of rhodopsin) are located in the cytoplasmic membrane. The snake diagram on the left shows the...
G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCR) constitute one of the biggest families of membrane proteins. In spite of the fact that they are highly relevant to pharmacy, they have remained poorly explored. One of the main bottlenecks encountered in structural-functional studies of GPCRs is the difficulty to produce...
The G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily comprises the largest and most diverse group of proteins in mammals. GPCRs are responsible for every aspect of human biology from vision, taste, sense of smell, sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous functions, metabolism, and immune...
G-protein-coupled receptors receive signals that arrive on the cell membrane surface and are received by the G protein. The most common type of surface receptor is called a G-protein-coupled receptor. A G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) works in conjunction with G protein...
14). Both PTH receptors belong to the class B G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). As a class B GPCR, PTH1R contains an N-terminal extracellular domain (ECD) with three conserved disulfide bonds and a C-terminal domain with seven transmembrane helices. In addition to PTH, PTH1R also...
https://physoc.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1113/expphysiol.2007.040048 It seems that an enzyme/protein, ACE2 (not ACE) ~~which binds to the ACE2 receptor~~ *which is found in the cell membrane,* is protective in lung tissue against ARDS. *[diagram of ACE2 activity](https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/The-angiotensin-converting-enzyme-receptor-axis%3A-a-Fraga-Silva-Silva/875a86aae2ec748a07a70d7810d4beaeae43aa37) scroll down in link* It is known that the ACE2 receptor is the binding ...
G-protein coupled receptors are ligand binding receptors that indirectly affect changes in the cell. The actual receptor is a single polypeptide that transverses the cell membrane seven times creating intracellular and extracellular loops. The extracellular loops create a ligand specific pocket which binds...
The G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) superfamily comprise similar proteins arranged into families or classes thus making it one of the If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given.
G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) represent one of the largest and most diverse groups of proteins in the genome. Heterotrimeric G proteins have a crucial role as molecular switches in signal transduction pathways mediated by G-protein-coupled receptors.
G-Protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) are a group of seven transmembrane proteins which bind signal molecules outside the cell, transduct the signal into the cell and finally cause a cellular response. The GPCRs work with the help of a G-Protein which binds to the energy rich GTP.
(A) Diagram of the G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR)/G-protein activation cycle and different types of cytoplasmic G-protein regulators. (B) Diagram of the experimental approach used to control the activating input for G-protein regulators and simultaneously monitor the G-protein activity output.
G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) [1]are the largest group of plasma membrane receptors of which rhodopsin and adrenergic receptors are the most familiar. They are integral plasma membrane proteins that transduce signals from extracellular ligands to signals in intracellular relay proteins, the...
Jan 08, 2021 · Introduction. G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) represent the largest protein family encoded by the human genome. Located on the cell membrane, they transduce extracellular signals into key physiological effects. 1 Their endogenous ligands include odors, hormones, neurotransmitters, chemokines, etc., varying from photons, amines, carbohydrates, …
Types of signaling molecules and the receptors they bind to on target cells. Intracellular receptors, ligand-gated ion channels, G protein-coupled receptors, and …
Hey everyone, I’m Bill and I’m currently in my 2nd year of a BBiomed single degree here at Monash. A few months ago, I’ve put up an expression of interest for a biomed + chem study skills post à la allevana and luneax, but man, I’ve been swamped with uni work for the past 9 weeks (thank you very much Monash for that 3/4 sem break /s). I’ll write a quick paragraph on every single subject I did, but mainly focusing on pitfalls to beware of because these are probably the most valuable for future st...
G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) signaling is crucial for many physiological processes. A signature of such pathways is high amplification, a concept originating from retinal rod phototransduction, whereby one photoactivated rhodopsin molecule (Rho*) was long reported to activate several hundred...
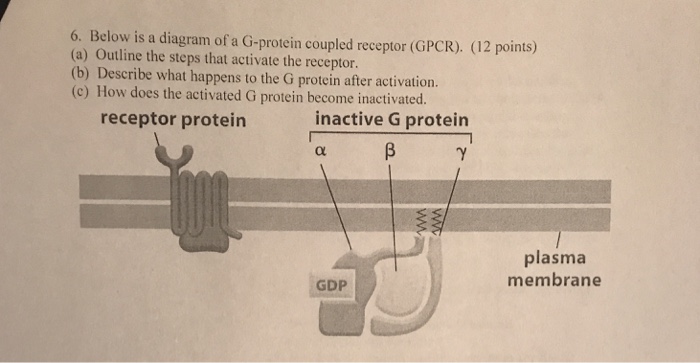
Hi i couldn't find the answer to this elsewhere so i thought i'd try here, When a GPCR exchanges the GDP of its g protein and the subunits split into alpha and a b/y dimer, does the b/y dimers have any function in the signal transduction (or any function at all)? The places ive seen only ever talk about the alpha subunit, and diagrams just show the b/y dimer remaining at the receptor. Also what actually couples the G-Protein to the intracellular domain when inactive? is it just hydrogen bonding...
G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs), otherwise known as G-proteins, are a diverse family of receptors found in a huge range of tissues throughout the body. Structure of G-Proteins. G-protein coupled receptors are composed of a transmembrane region crossing the lipid bilayer seven times...
G protein−coupled receptors (GPCRs) regulate facets of growth, development, and environmental sensing in eukaryotes, including filamentous fungi. The largest predicted GPCR class in these organisms is the Pth11-related, with members similar to a protein required for disease in the plant...
The G protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPER) is a seven-transmembrane-domain receptor that mediates non-genomic estrogen related signaling. G Protein-Coupled Estrogen Receptor: A Potential Therapeutic Target in Cancer.















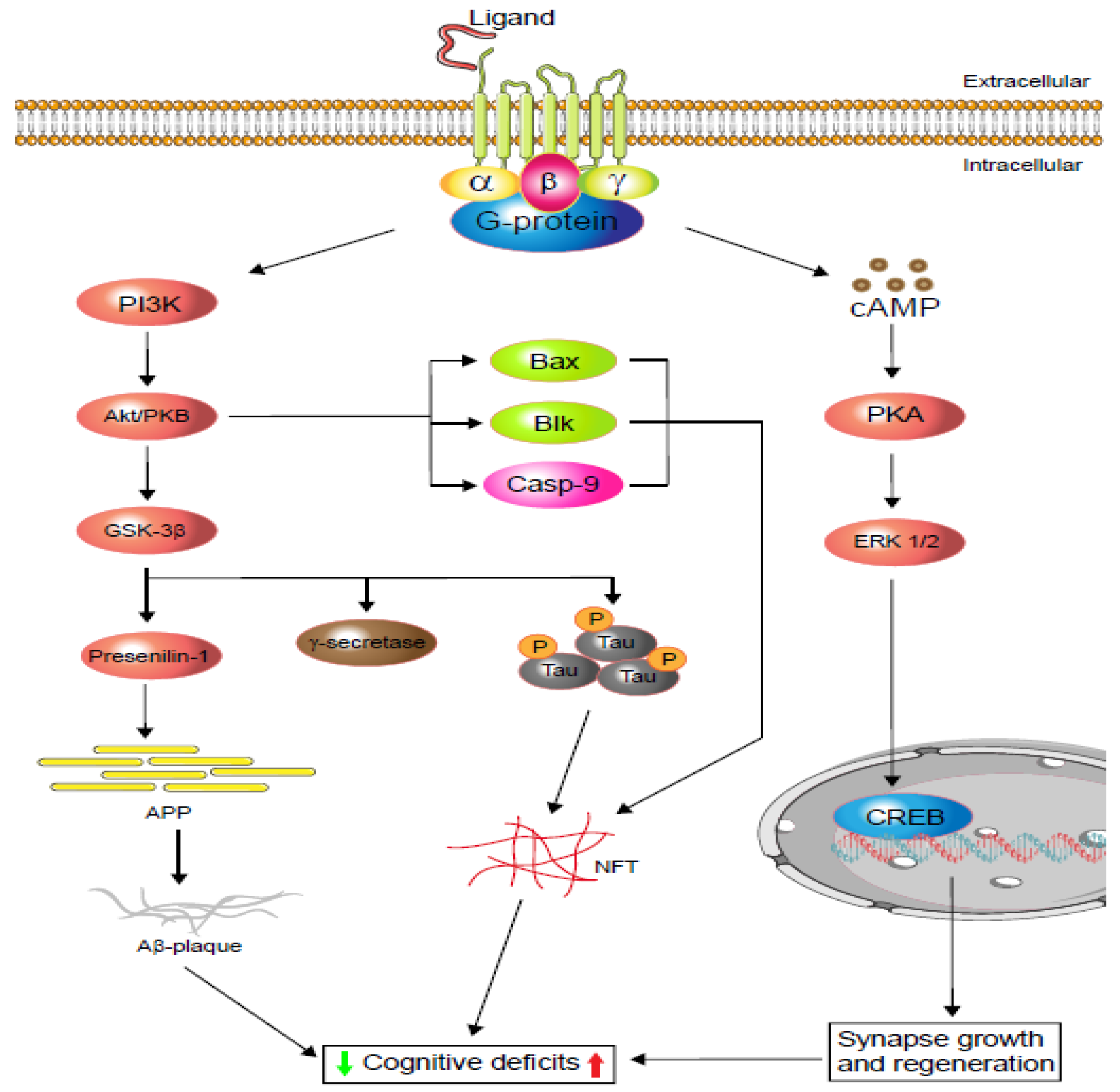
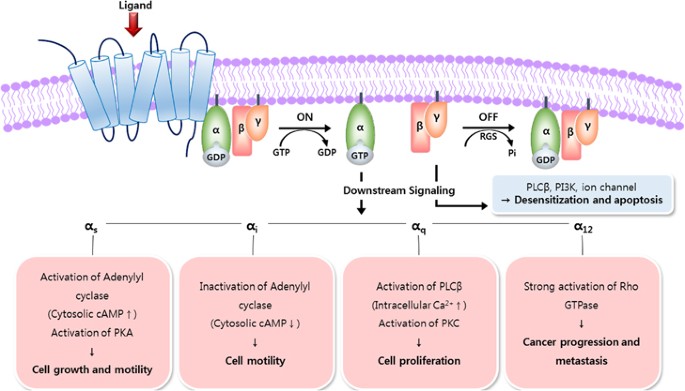



0 Response to "35 g protein coupled receptors diagram"
Post a Comment