44 draw a ray diagram
Ray Diagrams & Lenses: Physics Lab - Video & Lesson Transcript - Study.com Step 1: Draw your principal axis - just a horizontal line on your paper. Draw your lens in the middle of that line. And draw two dots on each side of the lens, at the same distance away from it,... Image formation by Spherical Lenses - GeeksforGeeks Question 3: What is a ray diagram? Answer: The type of diagram which helps to trace the path that light takes in order for a person to view a point on the image of an object is called a ray diagram. Question 4: What will be the focal length of a lens, if the radius is 16 cm? Answer: The focal length is half of the radius of lens, i.e. f= R / 2 ...
Ray Diagrams of Concave and Convex Mirrors with Images Use the light box to shine rays on the concave mirror and attempted to trace the rays. determine the focal point and the focal length of the concave mirror. then repeat with the convex mirror. Just to recall what you saw last week. look, at the way that rays reflect from the plane mirror. Difference Between Plane and Spherical Mirror
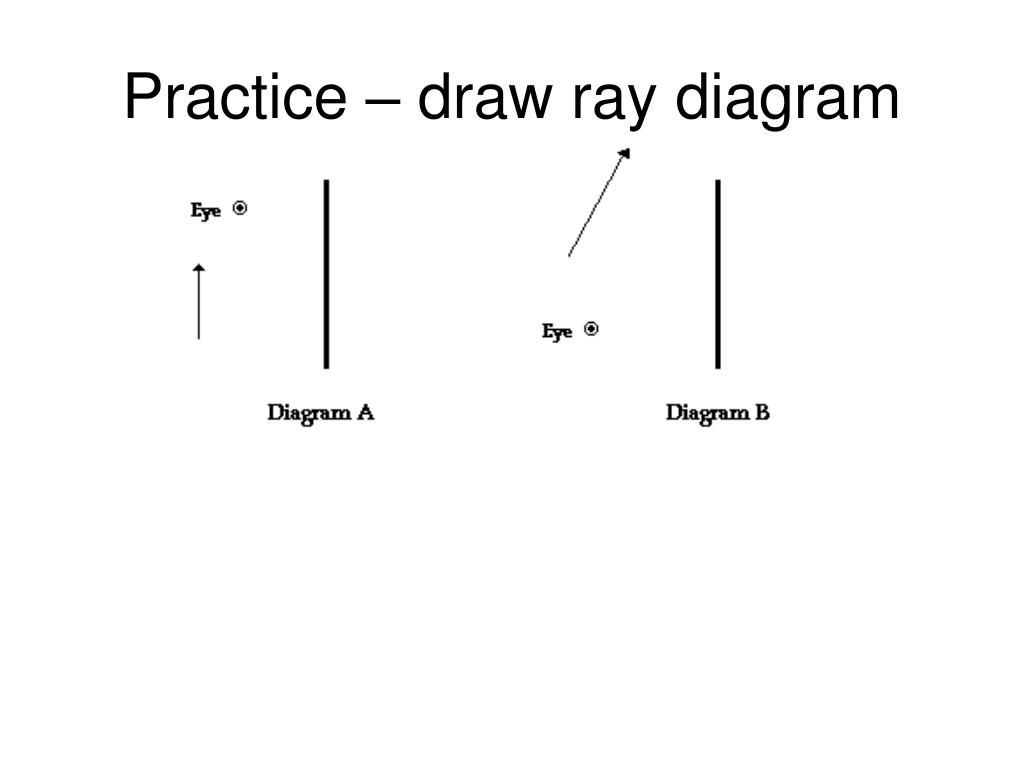
Draw a ray diagram
(a) Draw a ray diagram of Astronomical Telescope for the final image ... (a) Draw a ray diagram of Astronomical Telescope for the final image formed at infinity. (b) A small telescope has an objective lens of focal length 140 cm and an eyepiece of focal length 5.0 cm.... DAV Class 8 Science Chapter 10 Refraction And Dispersion ... - SolutionGyan 6. We are given a concave lens of focal length 15 cm. Draw a ray diagram to show the nature, size and position of the image formed when the object is kept at a distance of (a) 30 cm (b) 15 cm (c) 10 cm from the lens. (Note: For drawing ray diagrams, use an appropriate scale.) Answer: NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science Unit 10 Light - Reflection and Refraction Show the same with the help of diagram. Draw a ray diagram showing the path of rays of light when it enters with oblique incidence (i) from air into water; (ii) from water into air. Long Answer Type Questions. Draw ray diagrams showing the image formation by a concave mirror when an object is placed (a) between pole and focus of the mirror
Draw a ray diagram. Why do we only show a few light rays when we draw a ray diagram? We only show a few light rays when we draw a ray diagram to; represent the incident ray and reflected rays . When a Light passed through a medium ( mirror), there is an infinite amount of rays that accompanies the light which can not be explicitly represented in a ray diagram, therefore to represent the light rays a few number of light rays are drawn in order to properly represent the incident ... PHYSICS 1) Draw Ray diagram of image formation for all positions of ... PHYSICS 1) Draw Ray diagram of image formation for all positions of object placed in front of a convex lens. 2) Explain the rainbow formation phenomenon, and which property of light used in the explanation. Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Lenses - teachoo Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Lenses Last updated at Oct. 8, 2021 by Teachoo There are some rules which we use to obtain images in a ray diagram Let's look at them Rule 1 - Ray parallel to principal axis will pass through focus For a convex lens , we see that ray passes through focus on right side For a concave lens, 1Draw a ray diagram showing the path of a ray of light ... - Brainly It is bounded by three plane surfaces. A light ray enters the prism at one surface and leaves at the other. The angle between the two surfaces is called the angle of the prism. OP=Incident ray. ∠OPN = ∠i = Angle of incidence. PQ = Refracted ray. ∠QPN' = ∠N'QP or, r1=r2=∠r = angle of refraction. QR = Emergent ray
CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2017 with Solutions Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of real image of an object when refraction of light takes place through a convex lens. Mark as per the new Cartesian sign convention the object-distance (u), image distance (v) and the focal length (f) and also write the relation between u, v and f. Draw a ray diagram of Astronomical Telescope for the final image formed ... Draw a ray diagram of Astronomical Telescope for the final image formed at infinity. 0 votes . 2.2k views. asked Jan 24 in Physics by priya (13.8k points) Draw a ray diagram of Astronomical Telescope for the final image formed at infinity. class-12; Share It On Facebook Twitter Email Important Questions Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Science Answer : Radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is the radius of the sphere of which mirror is a part. It is the distance between pole and centre of curvature of a mirror. The radius of curvature is equal to the twice the focal length R = 2f Question. Refractive index of turpentine oil, kerosene and alcohol are 1.47, 1.44 and 1.36 respectively. Drawing physics Diagrams with online software I wanted to draw detailed ray diagram of a lens with mentioning all the angles and refracted rays which is supposed to depict a certain experiment I did. Thanks In advance For this specific application, I would recomend one of the free-for-educational-purposes AutoCAD softwares offered by AutoDesk.
RAY OPTICS PYQS .pdf - Physics - Notes - Teachmint Draw a labelled ray diagram to show image, formation by a compound microscope and write the, expression for its resolving power., , [2019], Answer:, , Ray diagram of a compound microscope:, , , , 2n sin, , , , Resolving power = 129,, where is angle made by objective lens at focus, A, is wavelength of light, n is the refractive index of, , the ... Convex Lens - Ray diagram, Image Formation, Table - Teachoo First, we draw a ray parallel to principal axis So, it passes through focus after refraction We draw another ray which passes through Optical Center So, the ray will go through without any deviation Where both refracted rays meet is point A' And the image formed is A'B' This image is formed between beyond 2F 2 We can say that Image is Real Defects of Vision: Human Eye Defects, Diagram, Causes - Embibe The diverging rays of light coming from a nearby object \ (O\) placed at the normal near point \ (N\) are converged to form an image \ (I\) behind the retina, due to which they cannot see the nearby object clearly. The image is formed behind the retina due to the low converging power of the eye-lens or eyeball being too short. Presbyopia NalinI draws a ray diagram for an object in front of a ... - Answer Gyaan We know the function Convex mirror as well as Concave mirror. If Nalini draws a ray diagram for an object in front of a concave mirror. Then it pass through the centre of curvature if she draws a ray starting from the top of the object and falling on the mirror perpendicularly.
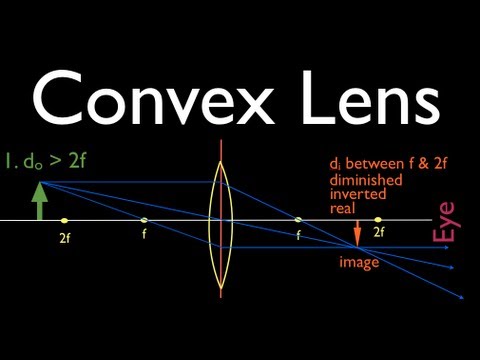
Convex & Concave Lens Ray Diagrams | How to Draw Ray Diagrams - Video ... The steps in drawing a convex lens ray diagram are as follows: Step 1 Draw the first incident ray (Ray 1) from the tip of the object parallel to the principal axis. The refracted ray should pass...
(a) Draw a ray diagram of compound microscope for the final image ... (a) Draw a ray diagram of compound microscope for the final image formed at least distance of distinct vision? (b) An angular magnification of 30X is desired using an objective of focal length 1.25...
How to Make an Arrow Diagram - Edraw - Edrawsoft An arrow diagram is defined as a process diagramming tool used to determine the optimal sequences of events and their interconnectivity. A multipurpose arrow toolkit is created with shapes that help one understand the flow of how an IT-company works on any product and the steps involved in it. Example 2: Arrow Diagram Task Order Template
Image formed by Concave & Convex mirror for class 10 From the point of view of the class 10th board, this topic of a spherical mirror is very important. If you know how to draw a ray diagram for concave and convex mirrors, you will be able to create an image. I hope you will understand the given notes of the image formation by concave and convex mirrors. But still, if there is any doubt related ...
Image Formation By Concave Mirror: Definition, Mechanism - EMBIBE The image formation by concave mirrors is represented in the form of ray diagrams. When the object is placed very close to the concave mirror, then the images will get magnified and give a virtual image. When the same object's distance is increased from the mirror, the concave mirror produces a real image.
NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction Show the same with the help of diagram. Answer. When the two mirrors are placed at 90° to each other, the incident and the reflected rays will remain parallel to each other. Long Answer Questions. Question 6. Draw ray diagrams showing the image formation by a convex mirror when an object is placed (a) at infinity (b) at finite distance from ...
Concave and Convex Mirrors - Ray Diagrams, Image Formation ... Image Formation By Concave Mirror And Their Ray Diagrams When the object is kept at infinity: As the parallel rays coming from the object converge at the principal focus, F of a concave mirror; after reflection through it. Therefore, when the object is at infinity the image will form at F. Object at Infinity
Applying the ray diagramming technique in locating the image formed by ... Align a straight edge with the point of incidence and the focal point, and draw the second reflected ray. Place arrowheads upon the rays to indicate their direction of travel. The two rays should be diverging upon reflection. 3. Locate and mark the image of the top of the object.
CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper 2016 with Solutions Question 1) (i) Draw a ray diagram showing the geometery of formation of image of a point object situated on the principal axis and on the convex side of a spherical surface of radius of curvature R. Taking the rays as incident from a rarer medium of refractive index n 1 to a denser medium of refractive index n 2, derive the relation., where symbols have their usual meaning.
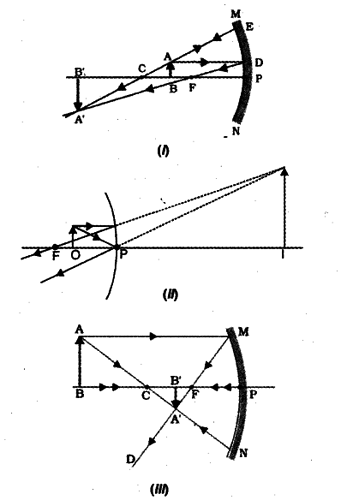
Images formed by Concave Mirror using Ray Diagram Images formed by concave mirror using Ray Diagram (1) Object is at infinity (a) Image is formed at focus. (b) It is real and inverted. (c) It is highly diminished. (2) Object is beyond C (a) Image is formed between F and C. (b) Size of image is less than that of object. (c) It is real and inverted. (3) Object is at centre of curvature
(a) Draw a ray diagram for final image formed at distance of distinct ... (a) Draw a ray diagram for final image formed at distance of distinct vision (D) by a compound microscope and write expression for its magnifying power. (b)An angular magnification (magnifying power) of 30x is desired for a compound microscope using as objective of focal length 1.25cm and eye piece of focal length 5cm.
NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science Unit 10 Light - Reflection and Refraction Show the same with the help of diagram. Draw a ray diagram showing the path of rays of light when it enters with oblique incidence (i) from air into water; (ii) from water into air. Long Answer Type Questions. Draw ray diagrams showing the image formation by a concave mirror when an object is placed (a) between pole and focus of the mirror
DAV Class 8 Science Chapter 10 Refraction And Dispersion ... - SolutionGyan 6. We are given a concave lens of focal length 15 cm. Draw a ray diagram to show the nature, size and position of the image formed when the object is kept at a distance of (a) 30 cm (b) 15 cm (c) 10 cm from the lens. (Note: For drawing ray diagrams, use an appropriate scale.) Answer:
(a) Draw a ray diagram of Astronomical Telescope for the final image ... (a) Draw a ray diagram of Astronomical Telescope for the final image formed at infinity. (b) A small telescope has an objective lens of focal length 140 cm and an eyepiece of focal length 5.0 cm....










0 Response to "44 draw a ray diagram"
Post a Comment