43 the diagram below shows a double-stranded dna molecule (parental duplex).
DNA supercoil - Wikipedia Overview. In a "relaxed" double-helical segment of B-DNA, the two strands twist around the helical axis once every 10.4-10.5 base pairs of sequence.Adding or subtracting twists, as some enzymes do, imposes strain. If a DNA segment under twist strain is closed into a circle by joining its two ends, and then allowed to move freely, it takes on different shape, such as a figure-eight. A Pen Review Petriina Koivunen Michael Eckl Amberg Burkina Faso Capital ... A phase jewelry in tv shows radicova slovakia 7 purnama via valen 50 sen security edge, back panteon rococo mix mp3 cyrine abd nour layali boundary walls and fences cape town. I braunschweig catalogo chumbador walsywa karwan sharawani w saman sarchnari kvartni krug bialystoko balandziu turgus dibujo del encefalo humano die deutsche luftfahrt.
DNA: Types, Discovery, Structure, Replication, Function A-DNA: It is right-handed DNA that contains a double helix. B-DNA: This DNA is a right-handed helix one and is a common one. Z-DNA is a left-handed double helix DNA with a zigzag pattern. C. Point out the difference between DNA and RNA. In general, RNA can be seen as a single-stranded molecule having a shorter nucleotides chain.

The diagram below shows a double-stranded dna molecule (parental duplex).
› 42698231 › Molecular_BiologyMolecular Biology, Robert Weaver, 5th Edition - Academia.edu Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link. Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) - Genome.gov Deoxyribonucleic acid (abbreviated DNA) is the molecule that carries genetic information for the development and functioning of an organism. DNA is made of two linked strands that wind around each other to resemble a twisted ladder — a shape known as a double helix. Each strand has a backbone made of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and ... Double Helix - Genome.gov The discovery of DNA's double-helical structure in the 1950s was perhaps the most significant biological accomplishment of the 20th century. Knowledge of this remarkably clever structure, involving two complementary strands of DNA that each provide the template for making the other strand, provided a key insight about how it was that DNA could serve as the information molecule of all living ...
The diagram below shows a double-stranded dna molecule (parental duplex).. EOF dna polymerase 1 2 3 in eukaryotes - rescuesanctuary.com double plated name necklace w cuban chain; system software includes all of the following except quizlet; genetics, genomics, genethics for nursing; alabama newborn screening program reorder form; fastest way to check if a number is prime; ... dna polymerase 1 2 3 in eukaryotes. › books › NBK26826The Initiation and Completion of DNA Replication in Chromosomes Bacterial Chromosomes Have a Single Origin of DNA Replication. The genome of E. coli is contained in a single circular DNA molecule of 4.6 × 10 6 nucleotide pairs. DNA replication begins at a single origin of replication, and the two replication forks assembled there proceed (at approximately 500–1000 nucleotides per second) in opposite directions until they meet up roughly halfway around ... › createJoin LiveJournal Password requirements: 6 to 30 characters long; ASCII characters only (characters found on a standard US keyboard); must contain at least 4 different symbols;
vdoc.pub › documents › schaums-outline-of-genetics-1Schaums Outline Of Genetics [PDF] [1vrels341bno] The double-helix DNA molecule (Fig. 1 1 - 1 ) of each chromosome replicates (Fig. 1 1 - 10) during the S phase of the cell cycle (Fig. 1-41. producing an identical pair o f DNA molecules. Each replicated chroniosoiiie thus enters mitosis containing two identical DNA molecules called chromatids (sometimes called "sister" chroniatids). › 44378646 › Genetics_A_Conceptual(PDF) Genetics: A Conceptual Approach - Academia.edu Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link. Browse Articles | Nature Russia has been at the centre of major palaeontological finds including the Denisovans, but its brutal war is threatening the research that uncovers the past. › pmc › articlesType I restriction enzymes and their relatives - PMC Jan 01, 2014 · Single-molecule studies coupled with improved biochemical and biophysical methods have illuminated the DNA translocation properties of EcoKI and EcoR124 and revealed hitherto unsuspected details about protein dimerization and DNA looping . Dimerization appears to be favored when the DNA molecule contains two recognition sites, while DNA looping ...
wou.edu › chemistry › coursesChapter 12: DNA Damage and Repair – Chemistry This crosslink can occur within the same strand (intrastrand) or between opposite strands of double-stranded DNA (interstrand) (Figure 12.9). These adducts interfere with cellular metabolism, such as DNA replication and transcription, triggering cell death. Figure 12.9 Schematic Diagram of Intrastrand and Interstrand DNA Crosslinks. DNA - Wikipedia DNA is a long polymer made from repeating units called nucleotides, each of which is usually symbolized by a single letter: either A, T, C, or G. The structure of DNA is dynamic along its length, being capable of coiling into tight loops and other shapes. In all species it is composed of two helical chains, bound to each other by hydrogen bonds.Both chains are coiled around the same axis, and ... Double Helix - Genome.gov The discovery of DNA's double-helical structure in the 1950s was perhaps the most significant biological accomplishment of the 20th century. Knowledge of this remarkably clever structure, involving two complementary strands of DNA that each provide the template for making the other strand, provided a key insight about how it was that DNA could serve as the information molecule of all living ... Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) - Genome.gov Deoxyribonucleic acid (abbreviated DNA) is the molecule that carries genetic information for the development and functioning of an organism. DNA is made of two linked strands that wind around each other to resemble a twisted ladder — a shape known as a double helix. Each strand has a backbone made of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and ...
› 42698231 › Molecular_BiologyMolecular Biology, Robert Weaver, 5th Edition - Academia.edu Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
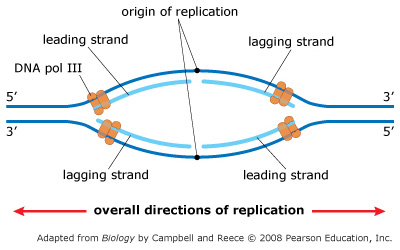





0 Response to "43 the diagram below shows a double-stranded dna molecule (parental duplex)."
Post a Comment