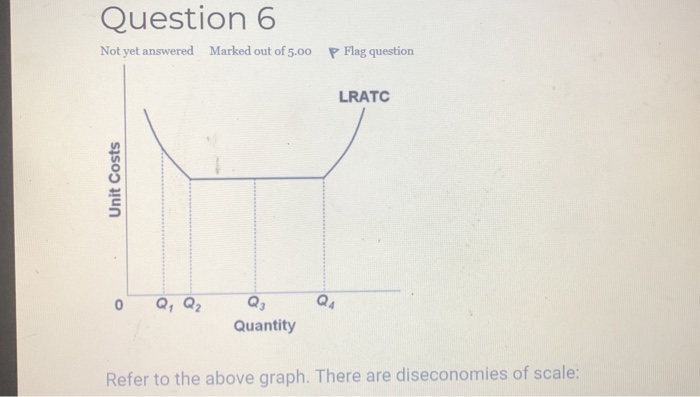
38 refer to the diagram. diseconomies of scale
Economies of Scale - Corporate Finance Institute Economies of scale refer to the cost advantage experienced by a firm when it increases its level of output. The advantage arises due to the inverse relationship between per-unit fixed cost and the quantity produced. The greater the quantity of output produced, the lower the per-unit fixed cost. Economies of scale also result in a fall in ... Solved Refer to the below diagram. Diseconomies of scale ... - Chegg Refer to the below diagram. Diseconomies of scale: Long-run ATC Output O begin at output Q 1. O are in evidence at all output levels. O begin at output Q3. O occur over the Q1-Q 3 range of output. If a monopolist is producing at that output at which price equals average-variable cost in the short run, then the firm is breaking even. O True O False
Diseconomies of scale Flashcards | Quizlet internal diseconomies of scale are diseconomies of scale that occur within a firm for a number of reasons - communication issues because lots of people working together in a business it can be difficult to ensure people are communicating correctly - organisation and control - lack of motivation external diseconomies of scale

Refer to the diagram. diseconomies of scale
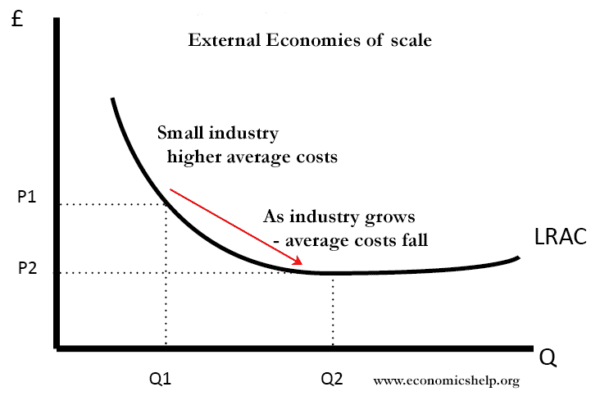
Economies of Scale: Definition, Types, Internal, and External Please refer below diagram. This diagram displays an illustration of economies of scale. This diagram shows that if a company increases output from Q1 to Q2, the average cost decreases from C1 to C2. ... As an example, diseconomies of scale could occur with conflict on the management decisions, conflict on inter-department communication, less ... CHAPTER 2 MACRO QUESTIONS 2 Flashcards - Quizlet Refer to the above diagram. For output level Q, per unit costs of C are: O A. unobtainable and imply the inefficient use of resources. O B. unobtainable, given resource prices and the current state of technology. O C. obtainable, but imply the inefficient use of resources. O D. obtainable and imply that resources are being combined efficiently. C atc wiring diagram ups Economies diseconomies reaping. 30 refer to the diagram. diseconomies of scale_. [download 25+] wiring diagram ups system Specification 1788-1. 9 Pictures about Specification 1788-1 : Uninterruptible Power Supply Wiring Diagram, Specification 1788-1 and also Specification 1788-1.
Refer to the diagram. diseconomies of scale. 80 refer to the above data economies of scale are - Course Hero Diseconomies of scale arise primarily because:of the difficulties involved in managing and coordinating a large business enterprise. In the above diagram it is assumed that:all costs are variable. Refer to the above diagram. Economies of scale:occur over the 0Q 1 range of output. Refer to the above diagram. Diseconomies of scale:begin at output ... Economies of Scale vs. Diseconomies of Scale - Quickonomics In that context, we can distinguish between (1) economies of scale, (2) diseconomies of scale, and (3) constant returns to scale. 1. Economies of Scale. Economies of scale occur when the long-run average cost falls as the quantity of output increases. That means larger quantities can be produced at a lower average unit cost than smaller quantities. Diseconomies of scale | bartleby Refer to the above diagram. Diseconomies of scale? arrow_forward What is wrong with this graph? a. It gives no information about the units for the variables. b. it uses different scale on the two axes c. it has no data d. it doesn't label variable on the two axes arrow_forward I already did the graph but I need help with question 17 to 22 Solved > 51. Refer to Figure 13-9. This:1520628 ... | ScholarOn c. output levels less than M. d. All of the above are correct as long as the firm is operating in the long run. 52. Refer to Figure 13-9. At output levels greater than N, the firm experiences. a. economies of scale. b. constant returns to scale. c. diseconomies of scale.
Diseconomies of Scale - Definition, Examples, Causes Diseconomies of Scale Graph The curve is divided into three states - Causes of Diseconomies of Scale #1 - Employee Costs #2 - Communication Failure #3 - Administration Costs #4 - Compliance Costs Solution for Diseconomies of Scale Diseconomies of Scale Video Recommended Articles Diseconomies of Scale Example Diseconomies vs Economies of Scale | Graphs & Examples - Study.com Economies of Scale is the concept referring to a business event where the price of an item or product decreases as the production of the same item or product increases. Diseconomies of scale ... Economies of Scale Diagram | Quizlet Diseconomies of Scale the firm becomes too big causing AC to rise as output rises Minimum efficient scale the lowest level of output where AC is at the minimum LRAC curve of a firm shows the minimum or lowest average total cost at which a firm can produce any given level of output in the long run (when all inputs are variable). Subjects Economies and Diseconomies of Scale - VEDANTU External Diseconomies of Scale: External Diseconomies of Scale are the external factors that result in the increase in the production per unit of a product within an organisation. The external factors that act as a restrain to expansion may include the cost of production per unit, scarcity of raw materials, and low availability of skilled labours.
Handout: Long Run Economies and Diseconomies of Scale The minimum efficient scale (MES) is the output for a business in the long run where the internal economies of scale have been fully exploited. It corresponds to the lowest point on the long run average total cost curve, point A in the diagram, and is also known as the output of long run productive efficiency. Hence, the MES achieves production ... Refer to the above diagram diseconomies of scale a - Course Hero A.In the range of diseconomies of scale. Diseconomies of scale is the phase in which a company experiences cost disadvantages owing to rise in the output level and organizational operations, it is caused by lack of motivation and also proper coordination between the employees because there are many employees and the management gets difficult. Economies of Scale (With Diagram) - Economics Discussion Subsequently we will examine the possibility of negative economies (diseconomies) as the plant grows beyond a certain size. There are various possible classifications of economies of scale. We will adopt the classification which is shown schematically in figure 4.35. Economies and Diseconomies of Scale - Toppr-guides Economies of scale refer to these reduced costs per unit arising due to an increase in the total output. Diseconomies of scale, on the other hand, occur when the output increases to such a great extent that the cost per unit starts increasing. In this article, we will look at the internal and external, diseconomies and economies of scale.
Diseconomies of Scale - Guide and Examples of Rising Marginal Costs Causes of Diseconomies of Scale Diseconomies of scale may result from several factors, including communication breakdown, lack of motivation, lack of coordination, and loss of focus by the management and employees. 1. Communication Breakdown Communication is important in any organization, especially in managing economies of scale.
Economies and Diseconomies of Scale - Economics Discussion Economies of scale are defined as the cost advantages that an organization can achieve by expanding its production in the long run. In other words, these are the advantages of large scale production of the organization. The cost advantages are achieved in the form of lower average costs per unit. It is a long term concept.
Refer to the above diagram this firms average fixed - Course Hero The above diagram shows the short-run average total cost curves for five different plant sizes of a firm. The position of these five curves in relation to one another reflects: A) economies and diseconomies of scale. B) the effect of fixed costs on ATC as output increases. C) the law of constant costs. D) the law of diminishing returns.
Solved Unit Costs Long-Run ATC 0 Q₁ Q₂ Q₂ Output Refer to | Chegg.com Expert Answer. Diseconomies of scale occur when a business expands so …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Unit Costs Long-Run ATC 0 Q₁ Q₂ Q₂ Output Refer to the diagram. Diseconomies of scale Select one: a. begin at output Q₁- b. occur over the Q₁Q3 range of output. Oc. begin at output Q3. O d. are in evidence at all ...
Economies and diseconomies of scale explain a the a source of economies of scale . 159. The minimum efficient scale of a firm: A. is realized somewhere in the range of diseconomies of scale.B. occurs where marginal product becomes zero.C. is in the middle of the range of constant returns to scale.D. is the smallest level of output at which long-run average total cost is minimized. D.
Diseconomies of Scale - Economics Help Diseconomies of scale occur when long-run average costs start to rise with increased output. Economies of scale occur up to Q1. After output Q1, long-run average costs start to rise. Reasons for dis-economies of scale Poor communication in a large firm. It can be hard to communicate ideas and new working practices.
Diseconomies of Scale Definition - Investopedia The diagram below illustrates a diseconomy of scale. At point Q*, this firm is producing at the point of lowest average unit cost. If the firm produces more or less output, then the average cost...
Microeconomics Flashcards - Quizlet A. as extra units of a variable resource are added to a fixed resource, marginal product will decline beyond some point. B. because of economies and diseconomies of scale a competitive firm's long-run average total cost curve will be U-shaped. C. the demand for goods produced by purely competitive industries is downsloping.
Economies & Diseconomies of scale Flashcards | Quizlet What are diseconomies of scale? Diseconomies of scale occur when a firm increases output and this leads to an increase in average cost of production. Examples of diseconomies of scale Bureaucracy As a firm grows larger, decision making processes becomes more complicated and lengthy - this wastes time and potentially increases average costs.
atc wiring diagram ups Economies diseconomies reaping. 30 refer to the diagram. diseconomies of scale_. [download 25+] wiring diagram ups system Specification 1788-1. 9 Pictures about Specification 1788-1 : Uninterruptible Power Supply Wiring Diagram, Specification 1788-1 and also Specification 1788-1.
CHAPTER 2 MACRO QUESTIONS 2 Flashcards - Quizlet Refer to the above diagram. For output level Q, per unit costs of C are: O A. unobtainable and imply the inefficient use of resources. O B. unobtainable, given resource prices and the current state of technology. O C. obtainable, but imply the inefficient use of resources. O D. obtainable and imply that resources are being combined efficiently. C
Economies of Scale: Definition, Types, Internal, and External Please refer below diagram. This diagram displays an illustration of economies of scale. This diagram shows that if a company increases output from Q1 to Q2, the average cost decreases from C1 to C2. ... As an example, diseconomies of scale could occur with conflict on the management decisions, conflict on inter-department communication, less ...











0 Response to "38 refer to the diagram. diseconomies of scale"
Post a Comment