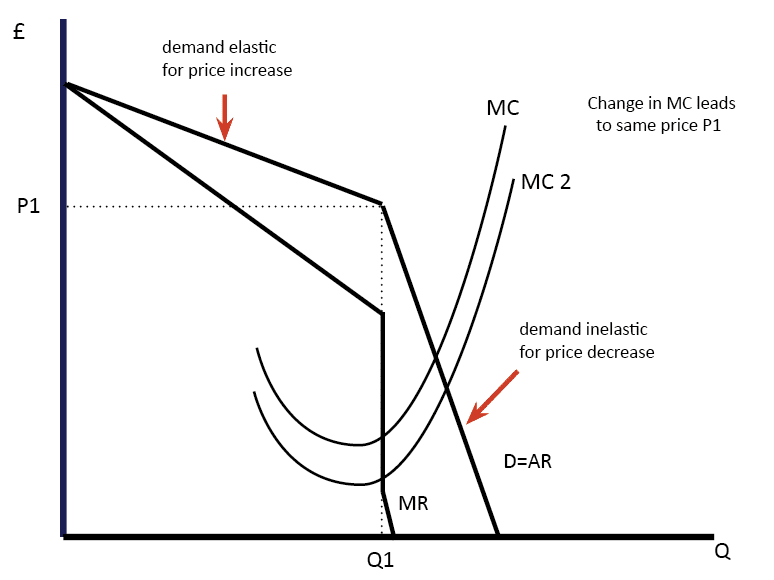
38 the diagram shows two product demand curves. on the basis of this diagram, we can say that
Demand Curve - Definition, Shift, Elasticity, Examples The demand curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between price and demand. The graphs show the commodity's price on the Y-axis and quantity on the X-axis. It follows the economics law of demand. According to the law of demand, when product price decreases, its demand increases and vice-versa. Unit 6 The firm: Owners, managers, and employees - CORE When we say that ‘Apple outsourced its component production’ or ‘the firm sets a price of $10.75’, we mean that the decision-making process in the firm resulted in these actions. 3 Figure 6.1 shows a simplified picture of the firm’s actors and decision-making structure.
Shifts in Demand and Supply (With Diagram) - Economics Discussion So we first consider (1) rightward shift of the demand curve (i.e., a rise in the demand for a commodity) causes an increase in the equilibrium price and quantity (as is shown by the arrows in Fig. 9.3). 2. A Fall in Demand: Next we may consider the effect of a fall in demand. Demand may fall due to changes in the conditions of demand.
/EquilibriumQuantity-3d51042295814ceda425f70c182d9e76.png)
The diagram shows two product demand curves. on the basis of this diagram, we can say that
PDF Topic 2: Basic theoretical tools used in international trade But we will often use basic partial-equilibrium tools (supply and demand for one good or factor) to illustrate ideas. So let's work on these tools. Trade equilibrium for one good with 2 countries A familiar idea: basic supply and demand (diagram). No-trade equilibrium quantity and price. You may have studied the idea of a price ceiling at ... 3.2 Shifts in Demand and Supply for Goods and Services - Principles of ... Six factors that can shift demand curves are summarized in Figure 5. The direction of the arrows indicates whether the demand curve shifts represent an increase in demand or a decrease in demand. Notice that a change in the price of the good or service itself is not listed among the factors that can shift a demand curve. Demand Curve - Investopedia Demand Curve: The demand curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity demanded for a given period of time. In a typical ...
The diagram shows two product demand curves. on the basis of this diagram, we can say that. Solved (17) The above diagram shows two product demand | Chegg.com (17) The above diagram shows two product demand curves. OnP the basis of this diagram we can say that: (a) over range P1P2 price elasticity of demand is greater for D1 than for D2. (b) over range P1P2 price elasticity of demand is greater for D2 than for D1. (©) over range P1P2 price elasticity is the same for the two demand curves. (d) not enough What Are Supply and Demand Curves? - From MindTools.com The result is a major change in total demand and a major shift in the demand curve. And, with a shift in demand, the equilibrium point also changes. You can see this in Figure 4, where Demand Curve 2 differs from Demand Curve 1, shown in Figure 1. At each price point, the total demand is less, so the demand curve shifts to the left. Micro Midterm Flashcards - Quizlet Assuming that the firm is motivated by self-interest and that the 20 units that can be produced with each technique can be sold for $2 per unit, the firm will: A) realize an economic profit of $10. B) realize an economic profit of $4. C) shut down rather than incur a loss by producing. D) not earn any economic profit. a Answered: The diagram below shows demand and… | bartleby The diagram below shows demand and supply curve for Kimchi. The government imposes per-unit of tax on the Kimchi and this is shown by the shift of the supply c S1. Answer the following questions based on the diagram. Price (RM) SO 10 8 4 Quantity 50 100 a. Define market equilibrium.
Demand and Supply of Labour (Explained With Diagram) However, this backward sloping Curve may sometimes be true of certain workers, the supply curve of labour to industry as a whole will normally slope upwards from left to right (as shows in Fig. 31.2) Interaction of Demand and Supply: We have now analysed the demand side as well as the supply side of labour. The diagram shows two product demand curves on the The diagram shows two product demand curves. On the basis of this diagram, we can say that A. over range P1P2, price elasticity of demand is greater for D1than for B.over rangeP1P2, price elasticity of demand is greater forD2 than for C.over rangeP1P2, price elasticity is the same for the two demand curves. Supply and Demand | Equilibrium Example and Graph The supply and demand graph can be used to visually see how a change in demand and/or supply changes quantity bought and sold in a market and the market price. The following graph shows supply and demand curves for rides market: You can see visually that the market clearing number of rides is close to 23,000 at a price of $2.7 per km. The Demand Curve Explained - ThoughtCo To calculate the slope of a demand curve, take two points on the curve. For example, use the two points labeled in this illustration. Between those points, the slope is (4-8)/ (4-2), or -2. Note again that the slope is negative because the curve slopes down and to the right.
Indifference Curve: Definition, Indifference Map, MRS, Examples etc. The diagram shows an Indifference curve (IC). Any combination lying on this curve gives the same level of consumer satisfaction. Another name for it is Iso-Utility Curve. Indifference Map An Indifference Map is a set of Indifference Curves. It depicts the complete picture of a consumer's preferences. Chpt 4 - Subjecto.com Assume product A is an input in the production of product B. In turn product B is a complement to product C. We can expect a decrease in the price of A to. increase the supply of B and increase the demand for C. With a downsloping demand curve and an upsloping supply curve for a product, placing an excise tax on this product will: EC 232 Ch. 6 Flashcards | Quizlet The elasticity of demand for a product is likely to be greater: -the greater the amount of time over which buyers adjust to a price change. -the smaller the number of substitute products available. -if the product is a necessity, rather than a luxury good. -the smaller the proportion of one's income spent on the product. 3.5 Demand, Supply, and Efficiency - Principles of Economics The familiar demand and supply diagram holds within it the concept of economic efficiency. One typical way that economists define efficiency is when it is impossible to improve the situation of one party without imposing a cost on another. Conversely, if a situation is inefficient, it becomes possible to benefit at least one party without imposing costs on others.
Appendix B: Indifference Curves – Principles of Economics Jul 06, 2022 · Thus, Lilly’s preferences will include an infinite number of indifference curves lying nestled together on the diagram—even though only three of the indifference curves, representing three levels of utility, appear on Figure 1. In other words, an infinite number of indifference curves are not drawn on this diagram—but you should remember ...
Econ Questions Flashcards | Quizlet This is scarcity - the economic situation in which our resources fail to satisfy all our wants. Therefore, scarcity means making rational decisions as to where we should allocate resources in order to produce efficiently and satisfy as many consumer wants as possible. Rational decisions always involve a choice of one product or service over ...
0 Response to "38 the diagram shows two product demand curves. on the basis of this diagram, we can say that"
Post a Comment