45 fungal life cycle diagram
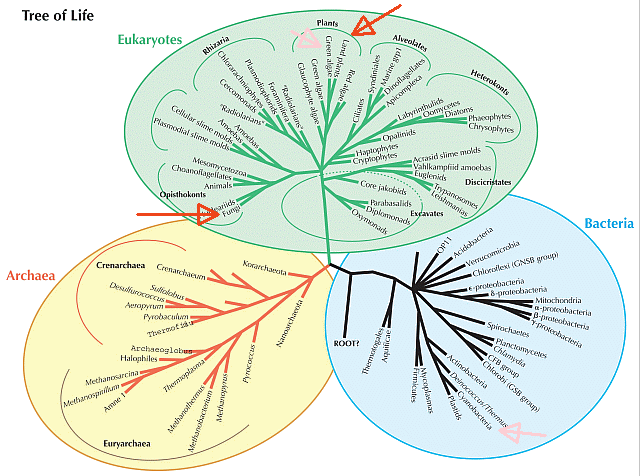
fungus - Life cycle of fungi | Britannica Life cycle of fungi In the life cycle of a sexually reproducing fungus, a haploid phase alternates with a diploid phase. The haploid phase ends with nuclear fusion, and the diploid phase begins with the formation of the zygote (the diploid cell resulting from fusion of two haploid sex cells). Fungi Diagram Illustrations, Royalty-Free Vector Graphics ... - iStock Mushroom anatomy life cycle stages diagram Mushroom anatomy life cycle stages diagram, vector illustration labeled circular scheme. From spore release to inoculation, germination, mycelial expansion and hyphal knot to the primordia formation. fungi diagram stock illustrations ... Labeled fungi reproduction. Life cycle of ascomycota vector ...
Life Cycle of Aspergillus (With Diagram) | Fungi In this article we will discuss about the life cycle of aspergillus with the help of suitable diagrams. Mycelium of Aspergillus: It is well developed and made up of a loosely interwoven mass of hyaline, bright or pale coloured, extensively branched, septate hyphae. Some of the hyphae ramify superficially upon the substratum.
Fungal life cycle diagram
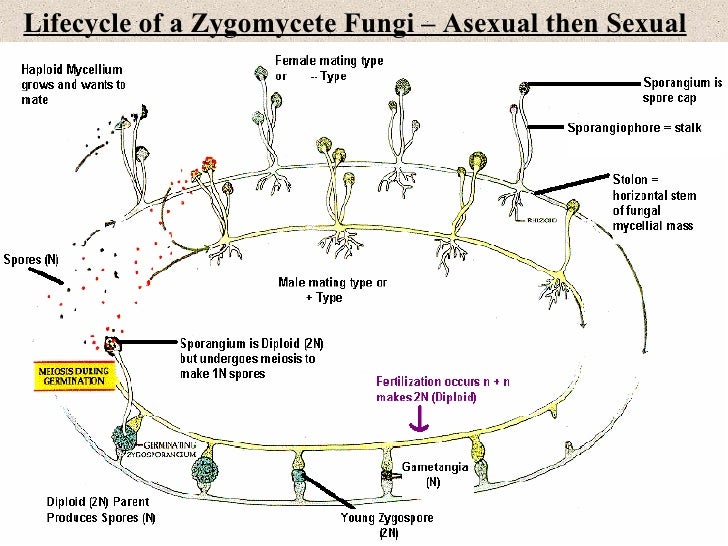
General Fungi Life Cycle | Creately General Fungi Life Cycle by MacKenzie Campbell Edit this Template Use Creately's easy online diagram editor to edit this diagram, collaborate with others and export results to multiple image formats. The basic life cycle of Fungi cycle diagram visual organizer graphic organizer edu education Fungi life cycle Flowchart Templates Org Chart Templates Understanding the Fungal Reproductive Cycle | GNFO The life cycle of a fungus is divided into two parts, called anamorphic and teleomorphic stages. During the anamorphic stage, the fungus is able to reproduce asexually. The teleomorphic stage is known as the fruiting stage. It is defined by the organism's ability to reproduce sexually. When referring to a fungus including both of these stages ... Life Cycle of Albugo (With Diagram) | Oomycetes In this article we will discuss about the life cycle of albugo with the help of suitable diagrams. Mycelium of Albugo: It is well developed and consists of branched, aseptate, coenocytic hyphae. The hyphae live and ramify in the intercellular spaces of the susceptible host tissue. The hyphal wall contains cellulose and not chitin.
Fungal life cycle diagram. The Life Cycle of Mold: How This Fungi Grows - QIPA Most forms of indoor mold follow the same four-stage life-cycle: Hypae growth, Spore formation, Spore liberation (dispersal), and Spore germination. Without the ideal conditions for growth (source of moisture, nutrients, and oxygen) mold cannot grow. Mold is ubiquitous in that it has the ability to grow in both indoor and outdoor environments. Fungal Structure - The Biology Notes Structure of fungal hypha. Hypha is characterized as a tube-like structure with a rigid wall that contains a moving slug of protoplasm. The length of the hypha varies in different fungal species; however, the diameter ranges from 2 to 30 micrometers and depends on the species and growth stage of the organism. The growth occurs at the tip of the ... Biology of Fungi - Arkansas State University Generalized Life Cycle of Fungi III. Human-fungus Interactions BRIEF INTRODUCTION TO THE KINGDOM FUNGI The Kingdom Fungi is an ensemble of diverse species. suggests that all fungal species are not derived from a single common ancestor, consequently the Fungi are polyphyletic (multiple genealogies or lineages). I. COMMON CHARACTERISTICS OF FUNGI Life Cycle of Ascomycetes (With Diagram) | Fungi The stage during which a fungus reproduces asexually is known as asexual stage or asexual cycle or conidial stage or imperfect stage. Under favourable climatic conditions the asexual stage may be repeated resulting in the production of conidia in profuse quantities.
The Life Cycle of Fungi - Mold Help The Life Cycle of Fungi. in Mold Overview. The life cycle of fungi can follow many different patterns. For most of the molds indoors, fungi are considered to go through a four-stage life cycle: spore, germ, hypha, mature mycelium. Brundrett (1990) showed the same cycle pattern using an alternative diagram of the developmental stages of a mould. Life Cycle of Phyllactinia (With Diagram) | Fungi In this article we will discuss about the life cycle of phyllactinia with the help of suitable diagrams. Mycelium of Phyllactinia: The mycelium is partly internal and partly found on the surface of the host. The mycelium spreads on both the surfaces of the host. The hyphae are branched, septate and uninucleate. 5 Stages in Life cycle of Puccinia - Plant Science 4 U Basidial stage on Wheat. • In the following spring, teleutospores germinate by forming promycelium. Promycelium comes out of the germ pore of each cell. The diploid nucleus enters promycelium and undergoes meiosis forming four haploid nuclei. • These nucleus are separated by the formation of a cross wall. fungi life cycle pdf - Robbin Arce All fungi begin their life cycle in. The mycelium continues to grow until the right environmental conditions trigger it to grow into a tightly packed above-ground mass. Fertile layer with asci 4. In the life cycle of a sexually reproducing fungus a haploid phase alternates with a diploid phase.
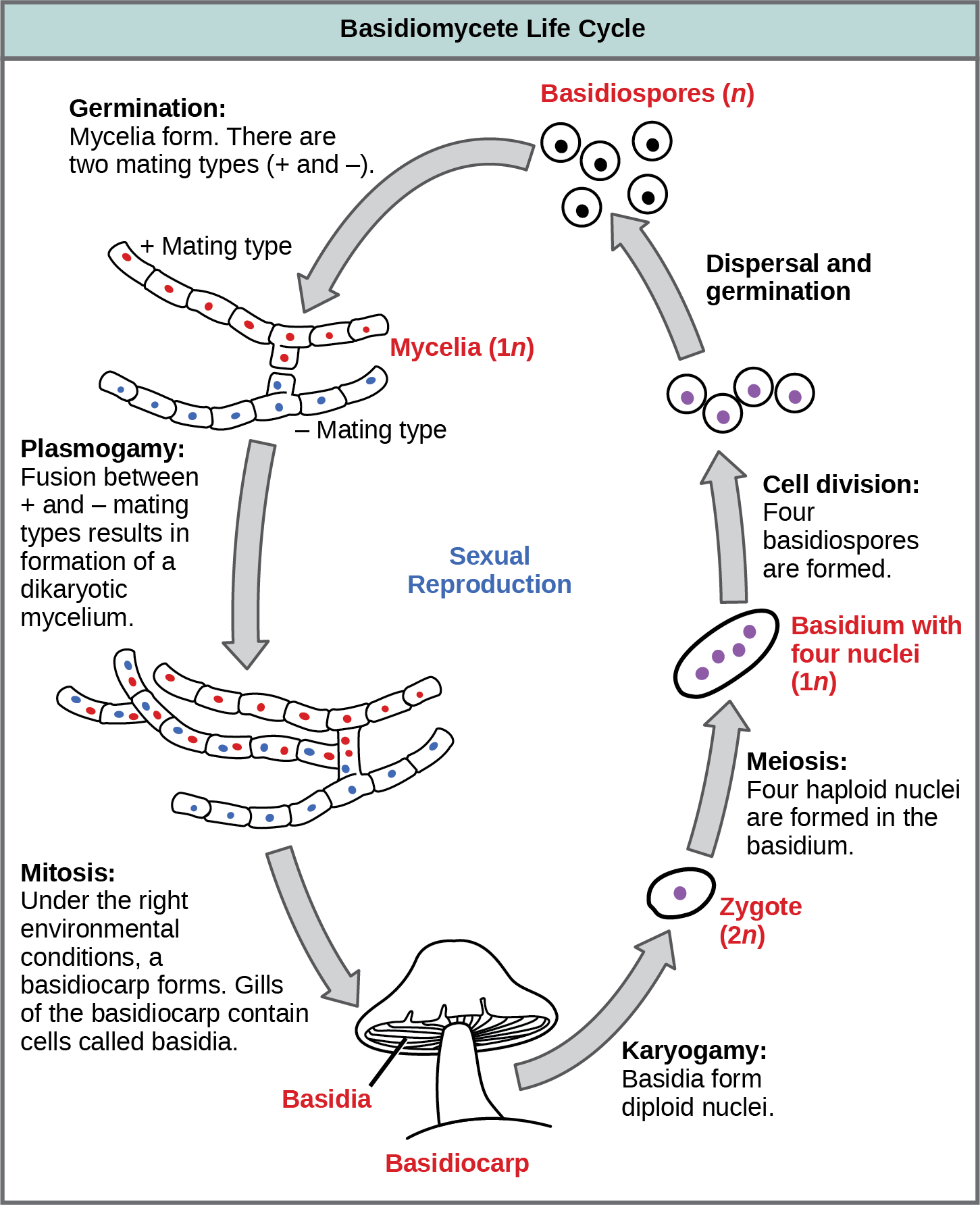
Fungi - Microbiology Fungal life cycles are unique and complex. Fungi reproduce sexually either through cross- or self-fertilization. Haploid fungi form hyphae that have gametes at the tips. Two different mating types (represented as "+ type" and "- type") are involved. BYJUS BYJUS Mycelium - Structure, Reproduction, Differences with Hyphae The life cycle of most fungi starts with the production of spores that germinate to form hyphal threads. Given that most of these fungi are sessile, apical extension/growth of the hyphae ultimately results in the formation and growth of the mycelia (mycelial network). ... This is showed in the diagram below: This image shows how the mycelium ... Intro to the Fungi Life Cycle - PlantSnap The first phase of the fungal life cycle is the spore phase. All fungi begin as spores that are 'haploid,' meaning they only have one copy of all their genetic information. This is similar to human sex cells, like sperm and eggs. These spores can travel vast distances from where they were produced by hitching a ride on another organism or ...
Lifecycle - fungus-like protists Life Cycle of Fungus-like protists. A fungus-like protist lives a part of its life as a haploid cell and the other part as a diploid cell. The haploid cell will usually join with another haploid cell to make a diploid cell. This cell will continue to grow and will have many nuclei. Once the cell gets mature enough it will form sporangium.
CRDEssay: fungi: life cycle of - Concordia University For most of the molds indoors, fungi are considered to go through a four-stage life cycle: spore, germ, hypha, mature mycelium. Brundrett (1990) showed the same cycle pattern using an alternative diagram of the developmental stages of a mould. The majority of mold fungi do not have sexual stages and following this simple life cycle pattern.
Fungi Life Cycle - Life Cycle and Important FAQs - VEDANTU Sexual 1. Spore (Haploid) The spore phase is the initial stage of the fungal life cycle. All fungi start as haploid spores, which means they only have one copy of their genetic information. This is similar to sperm and eggs, which are similar to human sex cells.
fungi life cycle diagram - Full Grown Journal Pictures Library Feb 24, 2022 · The diagram below shows the generalized life cycle of fungi. The life cycle of fungi can follow many different patterns. Spore germ hypha mature mycelium. The life cycle of an ascomycete is characterized by the production of asci during the sexual phase. First lets focus on fungi life cycles that involve sexual reproduction.
PDF Structure, Characteristics and Reproduction of Fungi Ii Multicellular Fungal Life Cycles 7. Plant pathogens with sexual and asexual reproduction on multiple hosts. Example: Puccinia graminis(barberry-wheat rust; basidiomycete). Sexually produced basidiospores infect barberries. Spermogonia are reproductive structures that are produced on the upper surface of the barberry leaves.
Fungal life cycles - spores and more — Science Learning Hub Spores of mushrooms form on special hyphae on the surface of thin gills that form in a circle hanging on the underside of the cap. The cap has a curved shape (poroharore) so that the rain droplets run off and the spores keep dry. Mushrooms must shed their spores fast as both mushrooms and spores often live for only a few days.
Life Cycle of Penicillium (With Diagram) | Fungi It is accomplished by the most common method of fragmentation. The hyphae break up into short segments. Each segment or fragment grows by repeated division into a full-fledged mycelium. In some species, the mycelium forms compact resting bodies, the sclerotia. Sclerotia enable the species to survive periods of stress or to hibernate.
Life Cycle of Albugo (With Diagram) | Oomycetes In this article we will discuss about the life cycle of albugo with the help of suitable diagrams. Mycelium of Albugo: It is well developed and consists of branched, aseptate, coenocytic hyphae. The hyphae live and ramify in the intercellular spaces of the susceptible host tissue. The hyphal wall contains cellulose and not chitin.
Understanding the Fungal Reproductive Cycle | GNFO The life cycle of a fungus is divided into two parts, called anamorphic and teleomorphic stages. During the anamorphic stage, the fungus is able to reproduce asexually. The teleomorphic stage is known as the fruiting stage. It is defined by the organism's ability to reproduce sexually. When referring to a fungus including both of these stages ...
General Fungi Life Cycle | Creately General Fungi Life Cycle by MacKenzie Campbell Edit this Template Use Creately's easy online diagram editor to edit this diagram, collaborate with others and export results to multiple image formats. The basic life cycle of Fungi cycle diagram visual organizer graphic organizer edu education Fungi life cycle Flowchart Templates Org Chart Templates



0 Response to "45 fungal life cycle diagram"
Post a Comment