38 sn2 reaction coordinate diagram
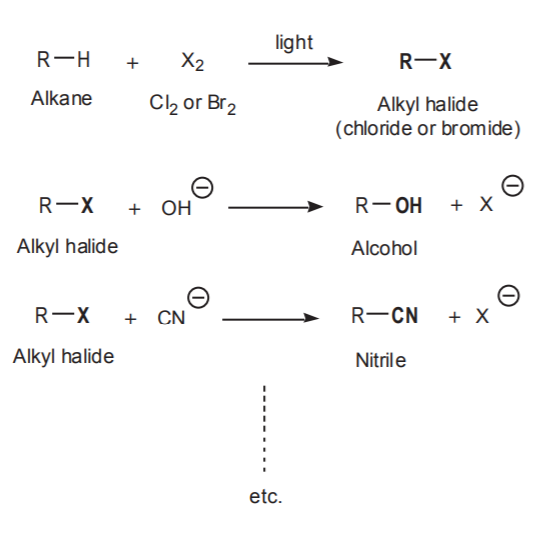
Nucleophilic Substitution and Beta Elimination - SN1 SN2 E1 E2 Reactions The SN2 reaction is a Bimolecular Nucleophilic Substitution reaction. You can recognize that an SN2 reaction took place, as follows: A nucleophile sits on the molecule where a leaving group used to be. You have a strong nucleophile / attacker in solution. Key points of an SN2 Reaction All explained in the videos below. SN1 & SN2 (3.3.4) | CIE A Level Chemistry Revision Notes 2022 | Save My ... The S N 2 mechanism is a one-step reaction The nucleophile donates a pair of electrons to the δ+ carbon atom to form a new bond At the same time, the C-X bond is breaking and the halogen (X) takes both electrons in the bond ( heterolytic fission) The halogen leaves the halogenoalkane as an X - ion
PDF player.uacdn.net Reaction Coordinate labelled OH Reaction Coordinate Reaction Coordinate O product Of this reaction is : ... Decreasing the concentration Of an electrophile in a typical SN2 reaction by a factor of 3 will cause the reaction ratio to : (a) increase by a factor of 3 ... Energy profile diagram for an exothermic reaction, A B C —s D, is given ...

Sn2 reaction coordinate diagram
Chapter 7: Alkyl Halides Flashcards - Quizlet A reaction coordinate diagram for the SN2 reaction shown would have _____ transition state(s) and _____ reactive intermediates. D Select the statement that correctly explains why backside attack by the nucleophile is preferred in SN2 reactions. Table of contents for Organic chemistry TABLE OF CONTENTS PART I: AN INTRODUCTION TO THE STUDY OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 1. ELECTRONIC STRUCTURE AND BONDING * ACIDS AND BASES 1.1 The Structure of an Atom 1.2 How the Electrons in an Atom Are Distributed 1.3 Ionic and Covalent Bonds 1.4 How the Structure of a Compound Is Represented 1.5 Atomic Orbitals 1.6 An Introduction to Molecular Orbital Theory 1.7 How Single Bonds Are Formed ... SN1 vs SN2 [with printable chart] Is it an SN1, SN2, E1 E2 reaction? The factors that will decide SN1 vs SN2 and whether it is SN1, SN2, E1, E2: 1) Do you have a strong nucleophile? If you do, it will favor an S N 2 reaction in the S N 1 vs S N 2 fight. If it is a mediocre nucleophile, it will favor an S N 1 reaction. This is because of the two mechanisms.
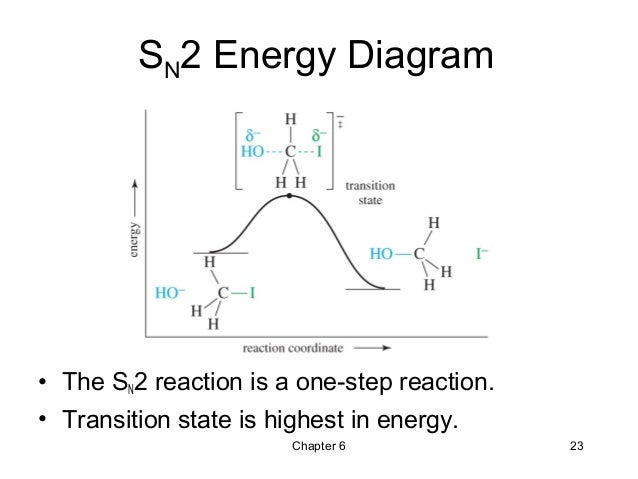
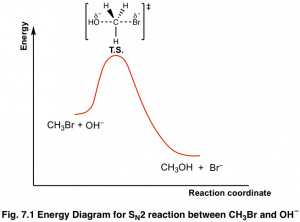
Sn2 reaction coordinate diagram. SN2 versus E2 Competition of F- and PH2- Revisited - PMC (a) Activation strain analysis and (b) energy decomposition analysis of the S N 2 and E2 reactions between 1 and PH 2-, where the energy values are projected on the C α ···Cl bond stretch, computed at ZORA-OLYP/QZ4P. (c) Schematic molecular orbital diagram of the most important HOMO X- -LUMO 1 orbital interaction, where X - = F - or PH 2- Energy profile (chemistry) - Wikipedia SN1 vs SN2 The S N 1 and S N 2 mechanisms are used as an example to demonstrate how solvent effects can be indicated in reaction coordinate diagrams. SN1: Figure 10 shows the rate determining step for an S N 1 mechanism, formation of the carbocation intermediate, and the corresponding reaction coordinate diagram. The SN1 Reaction Mechanism and SN1 Practice Problems The fast reaction of the carbocation with the nucleophile is the driving force of the S N 1 reaction since it pulls the equilibrium to the right according to the Le Châtelier's principle.. S N 1 - A Two-Step Mechanism. Let's break down all the steps in the following S N 1 reaction by looking at the energy diagram:. Step [1] Breaking the C - LG bond. In this rate-determining step, a ... SN2 Mechanism - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Reaction Coordinate Diagram of an S N 2 Reaction The reaction of hydroxide ion with chloromethane occurs in a single step. The activation energy, Ea, reflects the stability of the transition state, which depends upon the structure of the substrate, the nucleophile, and the leaving group. Sign in to download full-size image Figure 9.4.
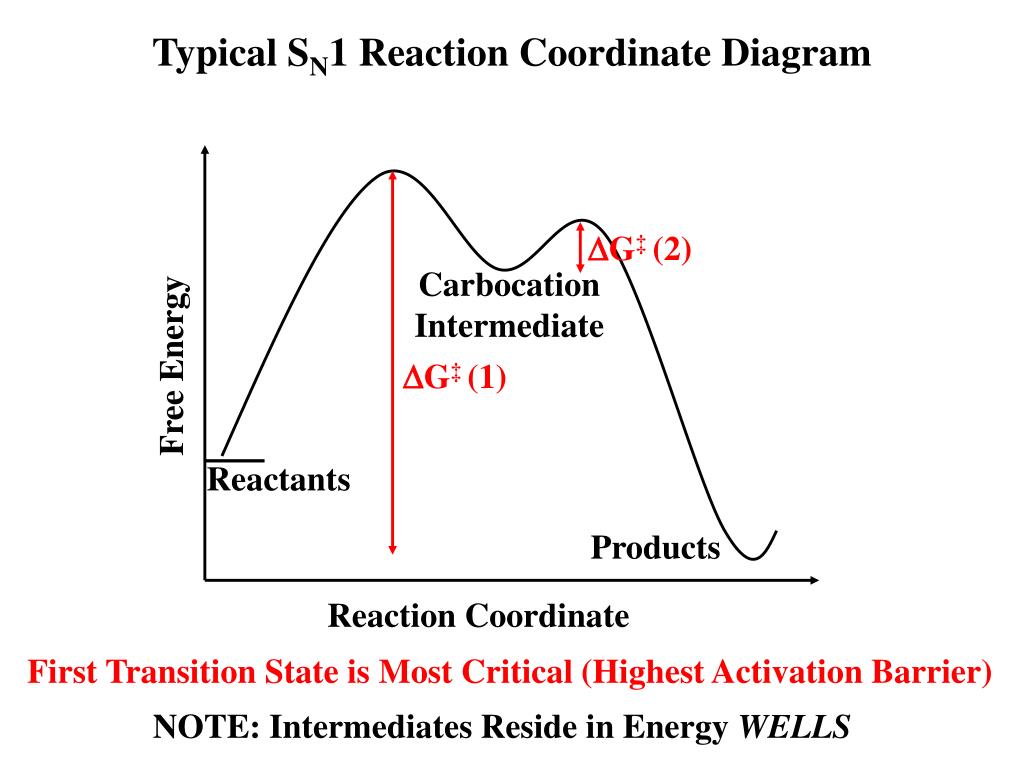
Reaction Coordinate Diagrams The diagram below is called a reaction coordinate diagram. It shows how the energy of the system changes during a chemical reaction. In this example, B is at a lower total energy than A. This is an exothermic reaction (heat is given off) and should be favorable from an energy standpoint. The energy difference between A and B is E in the diagram. SN1 Mechanism - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Figure 9.5 shows a reaction coordinate diagram for the S N 1 mechanism. The rate of the reaction depends on the energy barrier to the formation of the carbocation intermediate. The energy barrier in the second step, the reaction of the nucleophile with the carbocation, is much smaller, so step 2 is very fast. SOCl2 Mechanism For Alcohols To Alkyl Halides: SN2 versus SNi Feb 10, 2014 · A Study of the Reaction of Alcohols with Thionyl Chloride William E. Bissinger and Frederick E. Kung Journal of the American Chemical Society 1947, 69 (9), 2158-2163 DOI: 10.1021/ja01201a030 A nice study on the reaction of alcohols with SOCl2, useful if one is looking for a place to start optimization of this reaction (with regards to ... SN2 with alkyl halides - ChemistryScore The S N 2 reaction is stereospecific and always takes place with inversion of configuration. The nucleophile attacks the alkyl halide from the opposite side of the leaving group ( backside attack) and the overall reaction is the one-step transformation. All the bond formations and breakages occur simultaneously.
PDF 201 Nucleophilic Substitution This pathway is a concerted process (single step) as shown by the following reaction coordinate diagrams, where there is simultaneous attack of the nucleophile and displacement of the leaving group. ... In an SN2 reaction, the transition state has 5 groups around the central C atom. As a consequence of the steric requirements at this center, less PDF SN1 and SN2 Reactions - Illinois Institute of Technology The S N 2 Reaction Notes: In the SN2 reaction, the nucleophile attacks from the most δ+ region: behind the leaving group. This is called a back-side attack. This back-side attack causes an inversion (study the previous slide): after the leaving group leaves, the other substituents shift to make room for the newly-bonded nucleophile, changing the stereochemistry of the molecule. SN2 versus SN2′ Competition | The Journal of Organic Chemistry Several characteristic trends for the S N 2 (attack at the σ*) and S N 2′ (attack at the π*) pathways can be derived from the computed activation strain diagrams (ASDs). For all studied reactions, the aliphatic S N 2 reaction pathway goes with a lower strain energy than the allylic S N 2′ analog (see also Figure S1 ). Which would undergo SN2 reaction faster in the following ... - Toppr Ask Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions - SN2. 18 mins. Characteristics of SN2 Reactions. 7 mins. Optical Activity. 10 mins. Conditions for Optical Activity. ... Important Diagrams > Common misconceptions > Memorization tricks > Cheatsheets > Practice more questions . ... Circles Coordinate Geometry What is Democracy? Why Democracy?
SN2 reaction - Wikipedia The SN2 reaction is a type of reaction mechanism that is common in organic chemistry. In this mechanism, one bond is broken and one bond is formed synchronously, i.e., in one step. S N 2 is a kind of nucleophilic substitution reaction mechanism, the name referring to the Hughes-Ingold symbol of the mechanism.
Nucleophilic Substitution (SN1, SN2) - Organic Chemistry S N 2) Nucleophilic substitution is the reaction of an electron pair donor (the nucleophile, Nu) with an electron pair acceptor (the electrophile). An sp 3 -hybridized electrophile must have a leaving group (X) in order for the reaction to take place. Mechanism of Nucleophilic Substitution
Difference Between SN1 and SN2 - Nucleophilic Substitution Reaction SN2 reaction is a bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction. The detachment of the original negatively charged functional group and the attachment of the new negatively charged functional group or anion happen simultaneously forming an intermediate. There is step 2. The replacement gets completed at the end. 5.
The Solvay Process: Process, Products & Environmental Issues Jan 11, 2022 · The total chemical reaction in the ammonia-soda process is represented as follows: 2 N a C l + C a C O 3 N a 2 C O 3 + C a C l 2 . This reaction between sodium chloride and calcium carbonate does ...
SN2 - Chemistry LibreTexts In the S N 2 reaction, the addition of the nucleophile and the departure of the leaving group occur in a concerted (taking place in a single step) manner, hence the name S N 2: substitution, nucleophilic, bimolecular. In the S N 2 reaction, the nucleophile approaches the carbon atom to which the leaving group is attached.
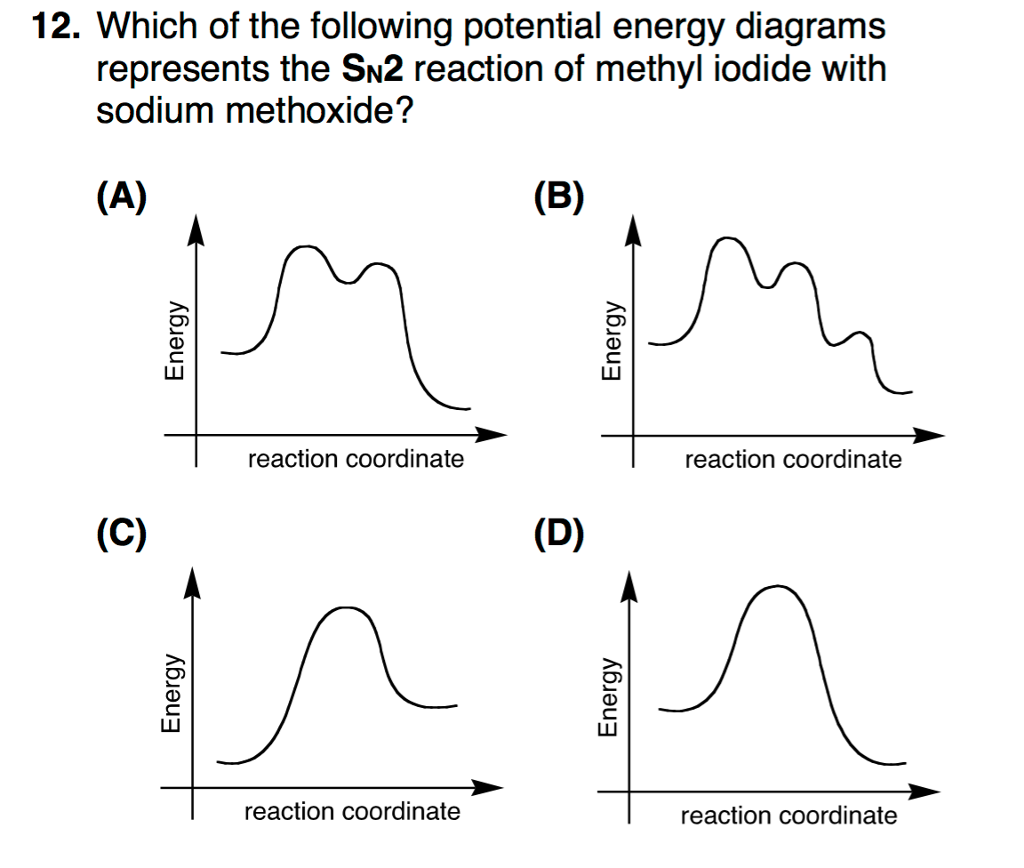
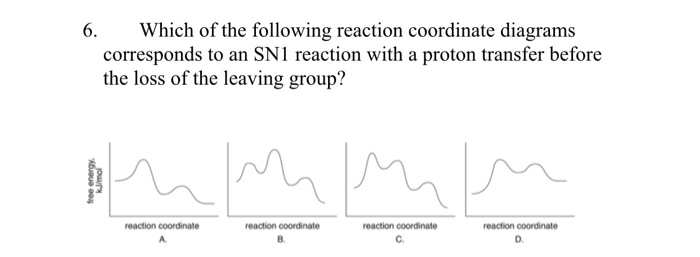
What is the Difference Between a Transition State and an ... Type 2 is to count the number of intermediates, transitions states, or the mechanistic steps in the reaction based on the diagram. The reaction diagram above has 2 intermediates and 3 transition states, so it is a 3-step reaction. Finally, the last question you can expect is a question about the shape or a nature of the transition state itself.
7.10: The SN2 Mechanism - Chemistry LibreTexts The S N 2 mechanism. There are two mechanistic models for how an alkyl halide can undergo nucleophilic substitution. In the first picture, the reaction takes place in a single step, and bond-forming and bond-breaking occur simultaneously. (In all figures in this section, 'X' indicates a halogen substituent). This is called an ' SN2' mechanism.
SN1 Reaction Mechanism - Detailed Explanation with Examples - BYJUS Step 1 The carbon-bromine bond is a polar covalent bond. The cleavage of this bond allows the removal of the leaving group (bromide ion). When the bromide ion leaves the tertiary butyl bromide, a carbocation intermediate is formed. As mentioned earlier, this is the rate-determining step of the S N 1 mechanism.
RAJASTHAN PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION, AJMER Reaction Mechanism: Inductive, Mesomeric and Hyper-conjugation, Addition and substitution, Electrophilic addition and substitution reaction, Nucleophilic addition and substitution reactions (SN1 and SN2), Elimination reactions. Directive influence of functional group.
Reagent Friday: Lithium Di-isopropyl Amide (LDA) Aug 05, 2011 · Alkylation of enolates with alkyl halides is an SN2 reaction, and SN2 reactions will only occur at sp3-hybridized carbons. In the reaction you describe, only the 1-carbon is sp3-hybridized, and thus the enolate will perform substitution at C-1. The C-Br bond at C2 will be unaffected. Sorry for taking so long to get back to you.
BYJUS BYJUS
How does temperature affect SN1 and SN2 reactions? | Socratic Organic Chemistry Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions (SN1 and SN2) and Elimination Reactions (E1 and E2) SN1 and SN2 Reactions 1 Answer Truong-Son N. Aug 11, 2015 The higher the temperature, the faster a non-biological reaction tends to occur. For SN 1 and SN 2 reactions, the higher the temperature, the more elimination products you get.
Difference Between SN1 and SN2 Reactions - Pediaa.Com The rate of the SN2 reaction can be expressed by rate = K [R-LG] [Nu - ]. In inorganic chemistry, this reaction also called "associative substitution" or "interchange mechanism." The following figure illustrates the mechanism of S N 2 reaction. Here, nucleophile attacks the opposite direction of the leaving group.
Difference Between SN1 and SN2 Reactions In SN2 reactions, one bond is broken, and one bond is formed simultaneously. In other words, this involves the displacement of the leaving group by a nucleophile. This reaction happens very well in methyl and primary alkyl halides whereas very slow in tertiary alkyl halides since the backside attack is blocked by bulky groups.
The SN2 Reaction Mechanism - Master Organic Chemistry The SN2 Mechanism Proceeds Through A Concerted Backside Attack Of The Nucleophile Upon The Alkyl Halide. The best explanation we have for what happens in this reaction is that it proceeds through what organic chemists refer to as a backside attack. The nucleophile approaches the alkyl halide 180° from the C-Br bond, and as the C- (nucleophile ...
SN1 vs SN2 [with printable chart] Is it an SN1, SN2, E1 E2 reaction? The factors that will decide SN1 vs SN2 and whether it is SN1, SN2, E1, E2: 1) Do you have a strong nucleophile? If you do, it will favor an S N 2 reaction in the S N 1 vs S N 2 fight. If it is a mediocre nucleophile, it will favor an S N 1 reaction. This is because of the two mechanisms.




0 Response to "38 sn2 reaction coordinate diagram"
Post a Comment