38 diagram of a telescope
Reflecting Telescopes: Explanation, Diagram, Applications See the following diagram of a concave parabolic mirror. Figure 1. Concave parabolic mirror. Source: Gustavo Girardelli, Wikimedia Commons (CC BY-SA 4.0). Concave mirrors are very simple devices that can gather electromagnetic data. In the image, the electromagnetic radiation coming from astronomical objects is represented by the horizontal lines. 6 Important Parts of Telescope, their Names, Functions & Diagram Telescope Parts Diagram Telescope Parts Names Lenses Mirror Structural support or tripod Eyepiece Telescopic Tube Finderscope Parts of Telescope & Functions Lenses The lens is one of the necessary parts of a telescope. In most refracting telescopes, there are two lenses in which one is the objective lens, and the other is the eyepiece lens.
What is Galileo's Telescope? - Universe Today Description: Galileo's telescope was the prototype of the modern day refractor telescope. As you can see from this diagram below, which is taken from Galileo's own work - Sidereus Nuncius ...
Diagram of a telescope
Parts of a Telescope Diagram | Quizlet Holds up the telescope. Eyepiece. Provides further magnification and it bends the light to the shape of a human eye. Viewfinder. Find the general location of the object. Focus knob. Adjusts the eyepiece focal length, which brings the image of an object into focus (crisp, sharp image). List of telescope parts and construction - Wikipedia Honeycomb mirror. Liquid mirror. Parabolic reflector. Subsequent (sometimes optional) components realign, segment, or in some way modify the light of an incoming image: Field lens: A correcting lens placed just before the image plane of a telescope. Telecompressor or focal reducer: Optical element to decrease the telescope's focal length and ... How to understand OPD diagrams | CFF Telescopes How to interpret OPD diagrams. On the horizontal ("X") axis of the OPD diagram, there is the diameter of the lens, i.e. left side of the X axis can be considered as left side of the lens. On the vertical ("Y") axis of the diagram we can see the actual Optical Path Difference. This is usually measured in "lambda", i.e. the wavelength ...
Diagram of a telescope. Radio Telescopes: Explanation, Diagram, Facts & Parts Parts and functioning. The main parts of a single-dish radio telescope are the following: The dish or reflector: like most modern telescopes, radio telescopes are reflecting telescopes where the dish is in charge of collecting the incoming information and reflecting it towards another part. Due to the characteristic wavelength of radio waves ... What is a spot diagram, and what does it indicate about ... - Cloudy Nights A spot diagram is a geometric (as in not including diffraction) ray trace of an optical system. Say you plotted a grid of 1000 incoming parallel rays (of the same wavelength) where they enter the objective and followed each one through the system, plotting it's final location at the focal plane. Newtonian Telescope Diagram - schematron.org Diagram of a Newtonian reflector showing the light path inside. Focusers are one of the most commonly replaced or upgraded items to be found on a telescope. In some instances this is done to provide finer granularity of focus adjustment. In other cases the focuser is replaced to allow for motorized or hands free focus adjustment.5/5 (1). Schematic optical diagram of the telescope. - ResearchGate Download scientific diagram | Schematic optical diagram of the telescope. from publication: Aplanatic four-mirror system for optical telescopes with a spherical primary mirror | An exact ...
Radio Telescope Function & Diagram | What is a Radio Telescope? - Video ... The radio telescope definition is a specialized antenna and receiver used to detect radio signals from astronomical sources in the sky. An example of a radio telescope is shown in the diagram.... Newtonian Telescope Diagram Diagram showing the light path in a Newtonian reflector telescope. Newton used a metal primary mirror to capture light and. In the Newtonian, a primary mirror reflects the light to a focus that would lie in the centre of the tube so, to avoid obstructing A Newtonian Telescope diagram.**. The focal plane distance depicted in the diagram is from ... How Telescopes Form Images - Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com Diagram of Reflecting Telescope In a reflector, the objective (a mirror as opposed to a lens) is located at the back of the telescope. Light hits the mirror and focuses at an imaginary point ... How a Telescope Works - Imaging The telescope makes objects appear closer by increasing the angle of the ray bundles entering your eye. This is called angular magnification. A simple refractor telescope, shown in figures 6 and 7, consists of a long focal length lens followed by a short focal length lens.
Telescope Diagram | Access 7,000+ Templates | PowerSlides® Telescope Diagram Templates contains four slides in a cool color scheme. The first slide of the template is presented as a stylized telescope infographic. You can use this slide when displaying metrics for different product categories or company departments. The slide will be useful for HR specialists and company leaders. How does a reflecting telescope work? - Scope Tour Reflecting Telescope Diagram This diagram shows you the two curved mirrors, the eyepiece lens, and how they work. The two mirrors work for the reflection of the light. But when it comes to the eyepiece, the magnification occurs depending on the focal length between the eyepiece and the focal point. How Do Telescopes Work? | NASA Space Place - NASA Science for Kids This image of the Crab Nebula was created with information from the Hubble Space Telescope, the Spitzer Space Telescope, the Chandra X-ray Observatory, European Space Agency's XMM-Newton and the Very Large Array. Credit: NASA, ESA, NRAO/AUI/NSF and G. Dubner (University of Buenos Aires) Related Resources for Educators Galileo and the telescope - Explaining Science The ray diagram below shows that when rays of light from a distant object pass through a diverging lens they spread out, so that they appear to come from an image which is closer to the lens and reduced in size compared to the object. This is called a virtual image, because the rays of light don't actually form an image.
PDF Chapter 8 The Telescope - William & Mary Attache the object lens to a holder with rubber bands at the edge of the lens. Attach the mirror to another holder. Place the mirror at the far end of the optics rail from the light source. Place the lens 35 - 45 cm from the light source. See figure 8.3 3. Vary d until a sharp reflected image is produced at the source position. Refer to Figure 8.4 4.
Mission and Telescope Hubble's journey and the technology that makes it possible. Launched in 1990, Hubble has been visited by astronauts four times in order to make repairs and add new instruments. Each instrument that flies on Hubble has special features that let astronomers study the heavens in different ways. Hubble's unique capabilities can also be partnered ...
How to Use a Star Chart with a Telescope Suppose, for instance, you've learned Gemini as it's drawn on the monthly Sky & Telescope charts, where the stars are connected to form two stick figures holding hands. The same stars of Gemini appear on Chart 5 of Sky Atlas 2000.0 — but at a much larger scale and almost lost in a wealth of detail, as shown above. To keep the familiar naked-eye patterns in perspective, some people draw in ...
Category:Telescope diagrams - Wikimedia Commons Media in category "Telescope diagrams". The following 51 files are in this category, out of 51 total. An Account of a Catadioptrick Telescope, Made by John Hadley, Esq; F. R. S. With the Description of a Machine Contriv'd by Him for the Applying It to Use (1753) (14778323885).jpg 4,564 × 7,665; 10.91 MB.
Ray Diagrams for Telescopes - Physics Forums Diagrams of telescopes exaggerate the angles so that you can actually see the plotted rays. The magnification in a simple telescope is given by the ratio of the focal lengths of the objective and eyepiece lenses. A magnification of only 60X will take an pobject that's 1minute of arc and give you an image that's still only 1 degree wide.
Diagram of the James Webb Space Telescope's Main Components Download Options: Full Res, 5334 X 3027, PNG (5.09 MB) 2000 X 1135, JPG (601.68 KB) About This Image The James Webb Space Telescope has a cool side, which faces away from the Sun, and a hot side, which faces the Sun.
Telescopes and spectrographs - OpenLearn - Open University Figure 3 shows a diagram of a refracting telescope of this type. Figure 3 A Keplerian (refracting) telescope. Parallel rays of light from a distant object are brought to a focus by the (converging) objective lens and then diverge as they approach the eyepiece lens.
How They Work - How Telescopes Work | HowStuffWorks Amateur telescopes fit somewhere in between, and even though they are not nearly as powerful as the Hubble, they can do some incredible things. For example, a small 6-inch (15-centimeter) scope lets you read the writing on a dime from 150 feet (46 meters) away! Most of the telescopes you see today come in one of two flavors:
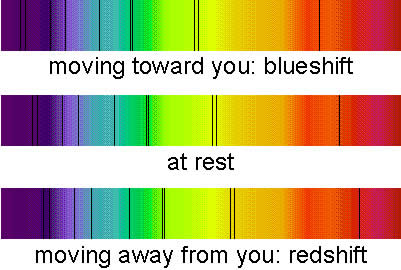
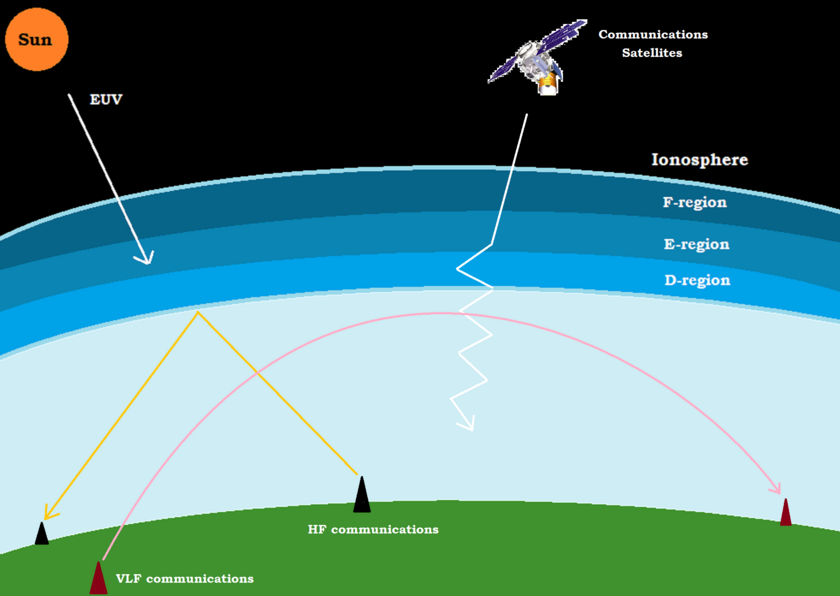
0 Response to "38 diagram of a telescope"
Post a Comment