44 refer to the diagram. in equilibrium the firm
Equilibrium of a Firm in Factor Market (With Diagram) In summation, there are two conditions required for attaining equilibrium in the factor market under perfect competition, which are as follows: i. MRP = MFC ii. MRP curve intersects marginal cost from above (as shown in Figure-5) However, from Figure-5, we cannot determine whether the organization would earn profit or incur loss. Equilibrium of a Firm under Monopolistic Competition Thus E is the equilibrium point. Corresponding to this equilibrium point, the firm produces OQ output and sells it at a price OP. Thus, the firm earns pure profit to the extent of PARB since total revenue (OPAQ) exceeds total cost of production (OBRQ). A firm, in the short run, may earn only normal profit if MC = MR < AR = AC occurs.
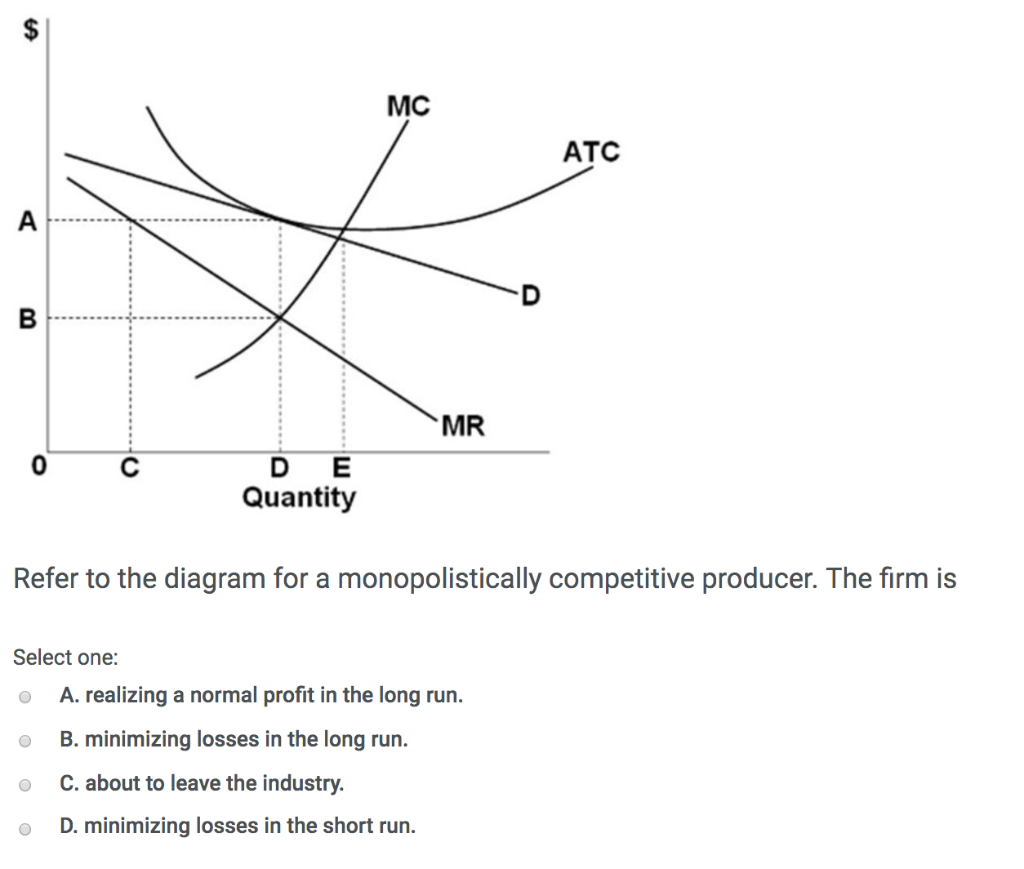
Microeconomics Chapter 13 Flashcards - Quizlet A short-run equilibrium that would produce profits for a monopolistically competitive firm would be represented by graph A. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive producer. This firm is experiencing excess capacity of DE. Assume the top six firms comprising an industry have market shares of 10, 8, 8, 5, 5, and 4 percent.

Refer to the diagram. in equilibrium the firm
Refer to the diagram for a non collusive oligopolist Refer to the diagram for a non collusive oligopolist. We assume that the firm is initially inequilibrium at pointE, where the equilibrium price and quantity areP and Q. If the firm's rivals will ignore any price increase but match any price reduction, the firm's marginal revenue curve will be (moving from left to right) A. D1ED2B. Solved 7. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically | Chegg.com Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. Assume the firm is part of an increasing-cost industry. In the long run firms will: A) leave this industry, causing both demand and the ATC curve to shift upward. B) enter this industry, causing demand to rise and the ATC curve to shift downward. Econ Chapter 13 & 14 HW review Flashcards & Practice Test - Quizlet Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. The firm's profit-maximizing price will be. $16. Refer to the diagram, in short-run equilibrium, the monopolistically competitive firm shown will set its price ... Refer to the diagram, where the numerical data show profits in millions of dollars. Beta's ...
Refer to the diagram. in equilibrium the firm. Refer to the diagram The monopolistically competitive firm shown A will ... Refer to the diagram. If all monopolistically competitive firms in the industry have profit circumstances similar to the firm shown above, A. new firms will enter the industry. B.some firms will exit the industry. C.all firms will exit the industry.D.no firms will enter the industry. revolig - Harper College Refer to the above diagram. marginal revenue curves are based on the assumption that: A. the firm has no immediate rivals. B. rivals will match both a price increase and a price decrease. C. rivals will match a price increase, but ignore a price decrease. D. revmncmp - Harper College Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm's profit-maximizing price will be: A. $10. B. $13. C. $16. D. $19. 5. R-1 F25030. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. ... Test Bank Chapter 24 Pure Monopoly Flashcards - Cram.com 34. Refer to the above diagram. This firm is selling in: A) a market in which there are an extremely large number of other firms producing the same product. B) an imperfectly competitive market. C) a market in which demand is elastic at all prices. D) a purely competitive market.
The following questions refer to the accompanying market diagram. The following questions refer to the accompanying market diagram. The following questions refer to the accompanying market diagram. PC and QC are the equilibrium price and quantity if the firm behaves competitively, and PM and QM are the equilibrium price and quantity if the firm is a simple monopoly. econ exam #2 Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to the above diagram showing the average total cost curve for a purely competitive firm. At the long-run equilibrium level of output, this firm's total revenue: 400 ch 13 Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to the diagram. In equilibrium the firm:..... over time oligopolistic industries may promote more rapid product development and greater improvement of production techniques than if they were purely competitive. Refer to the diagram. In short-run equilibrium, the monopolistically competitive firm shown will set its price: Answered: Consider a baseline long run steady… | bartleby Business Economics Q&A Library Consider a baseline long run steady state equilibrium where output is 20 trillion dollars, and the price level is 100. Note: price expectation is the same as the price level at the long run steady state equilibrium & unemployment is 5% or lower a) In the top panel, draw the baseline long run steady state equilibrium (call it A).
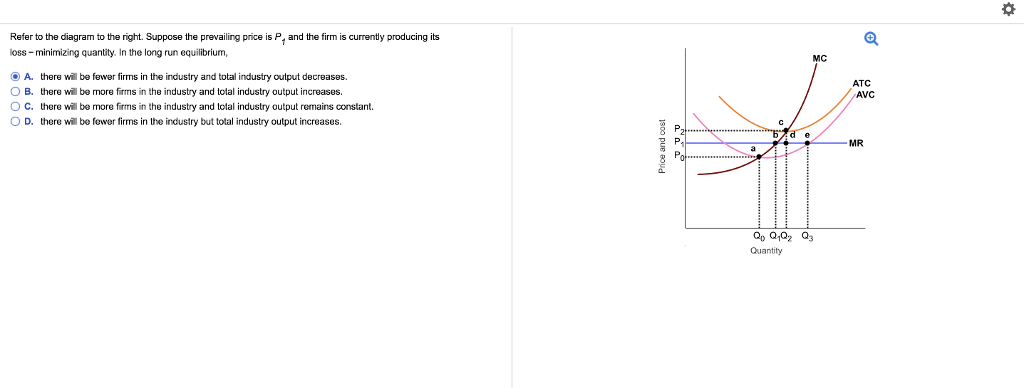
Question 8 1 1 point The diagram portrays A a competitive firm that is ... Question 8 1 / 1 point The diagram portrays: A) a competitive firm that is realizing an economic profit. B) the equilibrium position of a competitive firm in the long run. C) the loss-minimizing position of a competitive firm in the short run. D) a competitive firm that should shut down in the short run. B ) Top 3 Theories of Firm (With Diagram) - Economics Discussion Let PV f refer to the present value of the firm and π 1, π 2,. . . . . , π n refer to profits in the next n time ... The equilibrium of the profit-maximizing firm occurs simultaneously on the input and output sides — i.e., a firm which is maximising its profit by choosing an output at which marginal cost equals marginal revenue is ... Economics Micros Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to the above diagram. At P2, this firm will: A. produce 44 units and realize an economic profit. ... Refer to the above diagram. In equilibrium the firm: A. is realizing an economic profit of ad per unit. B. should close down in the short run. C. is incurring a loss. Equilibrium of Firm and Industry: Definitions, Conditions and Difficulties A firm is said to be in equilibrium when it maximizes its profit. It is the point when it has no tendency either to increase or contract its output. Now, profits are the difference between total revenue and total cost. So in order to be in equilibrium, the firm will attempt to maximize the difference between total revenue and total costs.
Chapter 12,13,14 Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to the above diagram. Assuming no union or relevant minimum wage, the firm represented will hire: a. Q2 workers and pay a W4 wage rate. b. Q2 workers and pay a W1 wage rate. c. Q3 workers and pay a W2 wage rate. d. Q4 workers and pay a W1 wage rate
Project Management: Tools & Techniques Regardless of the project management structure chosen, management must realize that a dynamic state of equilibrium between limited personnel and financial resources and the objectives of the project will be necessary if project management is to be successful in their particular organization. Before touching on the major tools and techniques of ...
Equilibrium of the Firm in the Short Run (With Diagram) The firm is in equilibrium when it maximizes its profits (11), defined as the difference between total cost and total revenue: Π = TR - TC Given that the normal rate of profit is included in the cost items of the firm, Π is the profit above the normal rate of return on capital and the remuneration for the risk- bearing function of the entrepreneur.
12.1 The Economics of Pollution – Principles of Economics Then refer to the first column of that row to determine the equilibrium price. In this case, the equilibrium price and quantity when only private costs are taken into account would be at a price of $10 and a quantity of five. Step 4. Identify the equilibrium price and quantity when the additional external costs are taken into account.
Solved 1.Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically - Chegg This problem has been solved! 1.Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. Long-run equilibrium output will be: a. b. d. 2.Refer to the diagram. In short-run equilibrium, the monopolistically competitive firm shown will set its price: a.
ECO 211 Microeconomics Yellow Pages ANSWERS Unit 3 - Harper College 2. The diagrams portray both long-run and short-run equilibrium. 3. The diagrams portray short-run equilibrium, but not long-run equilibrium. 4. The diagrams portray long-run equilibrium, but not short-run equilibrium. 2. Refer to the above diagrams, which pertain to a purely competitive firm producing output q and the industry in which it ...
Chapters 9, 10, 11, & 12 Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm's profit-maximizing price will be A. $10. B. $13. C. $19. D. $16. D. 13. Suppose the Herfindahl indexes for industries A, B, and C are 1,200, 5,000, and 7,500 respectively. These data imply that A. market power is greatest in industry B.
IB Economics practice: paper 1 (SL and HL) - Academia.edu Jun 04, 2015 · 7.4 (a) Using diagrams, explain under what [10 marks] conditions a perfectly competitive firm will 6.4 (a) Using a diagram, explain the relationships (i) continue to produce in the short run between the average product and marginal even though it is making a loss, and (ii) shut product curves, and the average variable cost down in the short run.



0 Response to "44 refer to the diagram. in equilibrium the firm"
Post a Comment