38 spherical mirror ray diagram
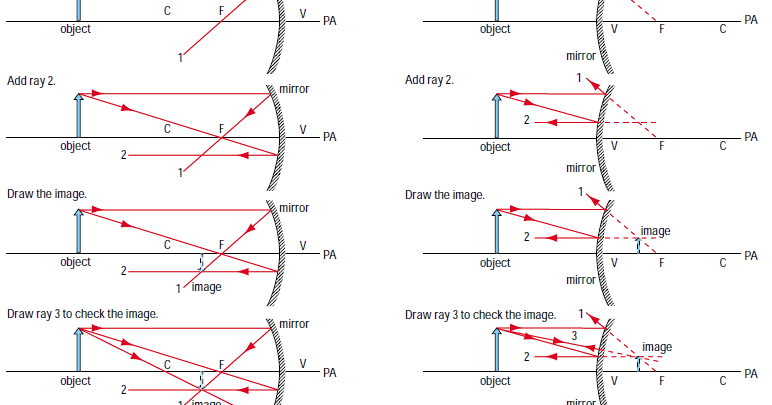
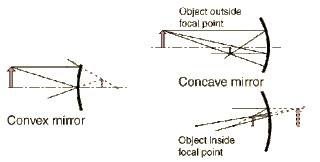
curved mirrors ray diagrams - Andedge Ray diagram for Convex mirror Centre of Curvature - The above diagram a spherical mirror is part of the imaginary sphere. The centre of the hollow sphere of which the spherical mirror forms a part. Pole (P) - The geometrical centre of the spherical mirror. PDF Spherical lenses: converging, diverging Plane mirrors Spherical mirrors ... Spherical mirror. Rays parallel to the axis get reflected through a common point the focal point or focus F. Focal length f is distance from V to F. C F V f. F ... Ray Diagrams for Convex Mirrors Ray 1: parallel to the axis then from F. Ray 2: Vertex. Ray 3: from C. • image is virtual, upright, and smaller than object
PDF 23-3 Spherical Mirrors: Ray Diagrams - Physics We will follow a process similar to that for plane mirrors to draw a ray diagram for a convex (diverging) mirror. Step 1 – First, locate the mirror’s focal point. Then, draw a light ray that leaves the tip of the object (its top) and goes parallel to the principal axis. Show how this parallel ray reflects from the mirror.
Spherical mirror ray diagram
Spherical mirrors; and Refraction - Boston University Step 1 - Draw a ray diagram. The more careful you are in constructing this, the better idea you'll have of where the image is. Step 2 - Apply the mirror equation to determine the image distance. (Or to find the object distance, or the focal length, depending on what is given.) Step 3 - Make sure steps 1 and 2 are consistent with each other. Image formation by Spherical Mirrors: Meaning, Sign Convention - Embibe Ray Diagrams of Image Formation by Spherical Mirrors. Image formation by spherical mirrors can be represented by ray diagrams. The ray diagrams of a concave mirror for different object positions and their corresponding image positions are as mentioned below: (a) Object Position: At Infinity. Image Position: At the Principal Focus Physics Tutorial: Ray Diagrams - Concave Mirrors Yet the same method works for drawing a ray diagram for any object location. 1. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw two incident rays traveling towards the mirror. Using a straight edge, accurately draw one ray so that it passes exactly through the focal point on the way to the mirror.
Spherical mirror ray diagram. Ray Diagrams for Mirrors - Georgia State University Using a ray parallel to the principal axis and one incident upon the center of the mirror, the position of the image can be constructed by back-projecting the rays which reflect from the mirror. The virtual image that is formed will appear smaller and closer to the mirror than the object. Change to concave mirror. Ray diagrams for mirrors. Spherical Mirrors - University Physics Volume 3 (a) Rays reflected by a convex spherical mirror: Incident rays of light parallel to the optical axis are reflected from a convex spherical mirror and seem to originate from a well-defined focal point at focal distance f on the opposite side of the mirror. The focal point is virtual because no real rays pass through it. BYJUS BYJUS Spherical mirror ray diagram question - Physics Stack Exchange We can rewrite the spherical equation as. r 2 − 2 r y + y 2 + x 2 = r 2 y = x 2 2 r + y 2 2 r. And when y is very small, the first term dominates. However, at larger distances off axis, the second term becomes significant and the spherical surface is no longer a good approximation of the parabolic one. As for the last part of your question ...
Spherical mirrors questions (practice) - Khan Academy Questions pertaining to spherical mirrors. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. ... Convex & concave mirror ray diagrams "Objects in the mirror are ..." actually images in the mirror. Practice: Ray diagrams. Practice: Ray diagrams and curved mirrors. Mirror formula derivation . Physics Tutorial: Spherical Aberration Spherical mirrors have an aberration - an intrinsic defect that prohibits the mirror from focusing all the incident light from the same location on an object to a precise point. The defect is most noticeable for light rays striking the outer edges of the mirror. Rays that strike the outer edges of the mirror fail to focus in the same precise location as light rays that strike the inner ... Light and Optics - Spherical Mirrors - Physics 299 The focal length (f) and radius of curvature (R) are defined in the diagram at the right. It can be shown that R = 2f. "A" in the diagram is known as the "vertex" (often labeled V). Image formation in spherical mirrors is defined by certain "characteristic" rays whose behaviour is governed by the law of reflection. Spherical mirrors, radius of curvature & focal length - Khan Academy Convex & concave mirror ray diagrams "Objects in the mirror are ..." actually images in the mirror ... in a previous video we saw that if you take a mirror which is a part of a sphere then we call such mirrors as spherical mirrors and if this mirror is small enough meaning if it's a small enough part of the sphere then if you incident parallel ...
Spherical Mirrors - The Physics Hypertextbook Curved mirrors come in two basic types: those that converge parallel incident rays of light and those that diverge parallel incident rays of light. One of the easiest shapes to analyze is the spherical mirror. Typically such a mirror is not a complete sphere, but a spherical cap — a piece sliced from a larger imaginary sphere with a single cut. PDF Spherical mirrors - University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign Ray diagrams –principal rays Mirror & magnification equations Phys. 102, Lecture 18, Slide 2 Curved mirrors Spherical mirror –section of a sphere “C ”“Concave” –iidinside surface of sphere R “Principal axis” CR “Convex” – outside surface of sphere C Line through Cand center of mirror “Principal axis” “Center of curvature” R C Concave Mirrors And Convex Mirrors - Image Formation, Ray Diagram The Ray diagram uses lines with arrows to represent the incident and reflected ray. It also helps us trace the direction in which the light travels. Plane Mirror vs Spherical Mirrors Mirrors are made into different shapes for different purposes. The two of the most prominent types of mirrors are: Plane Mirrors Spherical Mirrors PDF Concave spherical mirrors and ray diagrams R R, from the mirror. The ... The ray diagram (note that the parallel ray is refracted directly away from the focal point): The location of the image (remember that the focal length is negative) The magnification is M = -(-20 / 60) = 1/3. The image is upright, virtual and 1/3 the size of the object.
Images Formed by Spherical Mirrors - Tutorials Point Drawing the ray diagrams is an ideal way to illustrate the formation of images by spherical mirrors. The intersection of at least two reflected rays give the correct position of image of the point object. The following table illustrates the image formed by a concave mirror for different positions of the given object − Uses of Concave Mirror
Spherical Mirrors - Illinois Institute of Technology Spherical Mirrors. Bryan, Bill Joliet Catholic H.S. 1-815-727-5311. Objectives After this exercise the students should be able to: 1. Construct ray diagrams of images in spherical mirrors; 2. Find images of objects in spherical mirrors; 3. Distinguish between convex and concave mirrors; 4. Distinguish between converging light and diverging light.
09 - Ray Diagrams with Spherical Mirrors - YouTube Ray diagrams are a useful way to determine the location, orientation, size, and type of image a curved mirror will form. Learn the technique with this video....
Ray Diagrams for Spherical Mirrors - Wolfram Demonstrations Project This Demonstration lets you visualize the ray diagrams for concave and convex spherical mirrors. By manipulating the object and mirror locations, you can create real or virtual images. The ray parallel to the principal axis and the ray that hits the center of the mirror are drawn. Contributed by: Ernest Lee (March 2011)
Image Formation by Spherical Mirrors: Videos, Ray Diagrams, Exmaples Let's find out the mechanism involved in the image formation by spherical mirrors… Suggested Videos Ray Diagrams Ray diagrams are used to depict the image formation by tracing the path of light rays i.e. incident rays and reflected rays. They are drawn in order for anyone to view a point on the image of an object.
Ray Diagrams - Mirrors - YouTube 121 - Ray Diagram - MirrorsIn this video Paul Andersen explains how ray diagrams can be used to determine the size and location of a reflected image. Ray di...
Spherical Mirrors - Types, Applications and Derivation of Mirror Formula A spherical mirror is a mirror that has the shape of a piece carved out of a sphere. A spherical mirror is categorised into two forms, namely: concave and convex. On this page, we'll learn about the following: Type of spherical Mirrors . Application: usage, Examples. Derivations for a mirror formula with a ray diagram
PDF Spherical Mirror Ray Diagram Worksheet Draw a ray diagram to show the image formed by the mirror. Calculate the object and image distances. C F 4. The mirror shown below has a radius of curvature of 1,2m. For an object placed 0.3m from the mirror, draw a ray diagram to show the image formed by the mirror. Describe the characteristics of the image.
Sign Convention for Spherical Mirrors - GeeksforGeeks The sign conventions followed for any spherical mirror are given as: 1) All distances are measured from the pole of a spherical error. 2) Distances measured in the direction of incident light are taken as positive, while distances measured in a direction opposite to the direction of the incident light are taken as negative.
Spherical Mirrors - GeeksforGeeks The following is the diagram showing the concave as well as the convex mirror. Concave Mirror A spherical mirror of which the reflecting surface is curved inwards which means that it faces towards the centre of the sphere is known to be a concave mirror.
Use of Spherical Mirrors: Check Definition - Embibe Use of Spherical Mirrors: Check Applications, definitions, different types, examples, and other important details here at Embibe ... ii. convex mirror, the reflected ray appears to emerge from the focal point behind the mirror on the principal axis. ... We consider the following points for representing images by ray diagrams in both concave and ...
Physics Tutorial: Ray Diagrams - Concave Mirrors Yet the same method works for drawing a ray diagram for any object location. 1. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw two incident rays traveling towards the mirror. Using a straight edge, accurately draw one ray so that it passes exactly through the focal point on the way to the mirror.
Image formation by Spherical Mirrors: Meaning, Sign Convention - Embibe Ray Diagrams of Image Formation by Spherical Mirrors. Image formation by spherical mirrors can be represented by ray diagrams. The ray diagrams of a concave mirror for different object positions and their corresponding image positions are as mentioned below: (a) Object Position: At Infinity. Image Position: At the Principal Focus
Spherical mirrors; and Refraction - Boston University Step 1 - Draw a ray diagram. The more careful you are in constructing this, the better idea you'll have of where the image is. Step 2 - Apply the mirror equation to determine the image distance. (Or to find the object distance, or the focal length, depending on what is given.) Step 3 - Make sure steps 1 and 2 are consistent with each other.







0 Response to "38 spherical mirror ray diagram"
Post a Comment