39 free body diagram constant velocity
PDF Free Body Diagram PRACTICE PROBLEMS - Yola 8. A skydiver is descending with a constant velocity. Consider air resistance. A free-body diagram for this situation looks like this: 9. A force is applied to the right to drag a sled across loosely packed snow with a rightward acceleration. A free-body diagram for this situation looks like this: 10. Free Body Diagram - Definition, Examples, Solved Problems ... A free-body diagram is a diagram that is modified as the problem is solved. Normally, a free body diagram consists of the following components: The number of forces acting on a body depends on the specific problem and the assumptions made. Commonly, air resistance and friction are neglected.
Physics Simulation: Free-Body Diagrams The Free Body Diagram Interactive is shown in the iFrame below. There is a small hot spot in the top-left corner. Clicking/tapping the hot spot opens the Interactive in full-screen mode. Use the Escape key on a keyboard (or comparable method) to exit from full-screen mode. There is a second hot-spot in the lower-right corner of the iFrame.
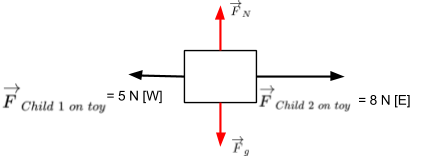
Free body diagram constant velocity
Solved A skier of mass 63 kg skis straight down a 140 ... A skier of mass 63 kg skis straight down a 140 slope at constant velocity. Draw a free-body diagram of the skier with the various external forces acting on her. Include the force of air resistance, which is directed opposite the velocity. (Do this on paper. Your instructor may ask you to turn in this work.) (a) Find the value of the normal force. Free Body Diagrams 1 Constant Velocity - YouTube About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ... PDF 3-3 Constant Velocity, Acceleration, and Force Figure 3.7: Motion diagram and free-body diagram for an object drifting to the right through space. Figure 3.8: Motion diagram and free-body diagram for a box being dragged to the right, by means of a string, across a flat surface.
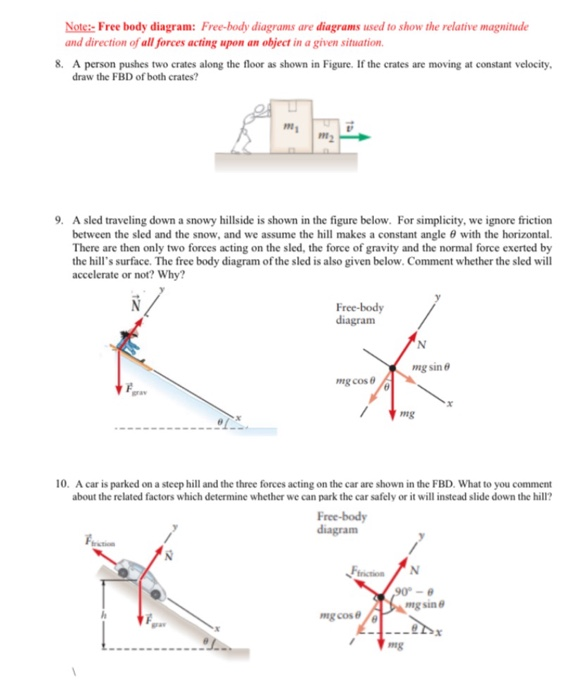
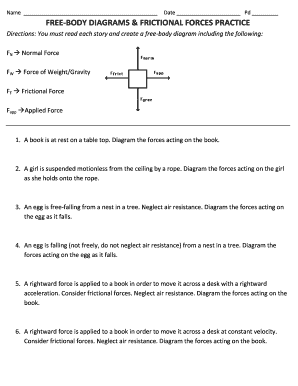
Free body diagram constant velocity. Askler of mass 62 kg skis straight down a 12 slope at ... Askler of mass 62 kg skis straight down a 12 slope at constant velocity. Draw a free-body diagram of the skier with the various external forces acting on her. Include the force of air resistance, which is directed opposite the velocity (Do this on paper. Your instructor may ask you to turn in this work.) (a) Find the value of the normal force. Drawing Free-Body Diagrams - University Physics Volume 1 Explain the effects with the help of a free-body diagram. Use free-body diagrams to draw position, velocity, acceleration, and force graphs, and vice versa. Explain how the graphs relate to one another. Given a scenario or a graph, sketch all four graphs. Answered: Which free-body diagram is correct for… | bartleby Which free-body diagram is correct for an object moving at constant velocity to the right on a frictionless surface? select the letter of your answer a. A • b. B c. C d. D. Question. fullscreen Expand. Transcribed Image Text. Which free-body diagram is correct for an object moving at constant velocity to the right on a frictionless surface ... PDF Free Body Diagrams Practice Problems Free Body Diagrams Practice Problems Construct free-body diagrams for the various situations described below. Use the following forces. 1. A book is at rest on a table top. Diagram the forces acting on the book. 2. A girl is suspended motionless from a bar which hangs from the ceiling by two ropes. Diagram the forces acting on the girl. 3.
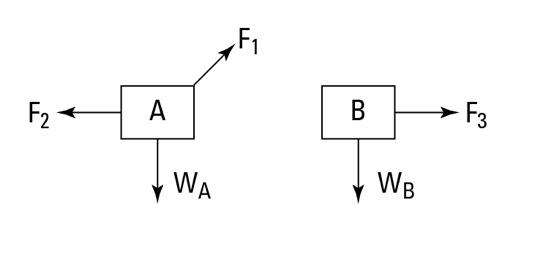
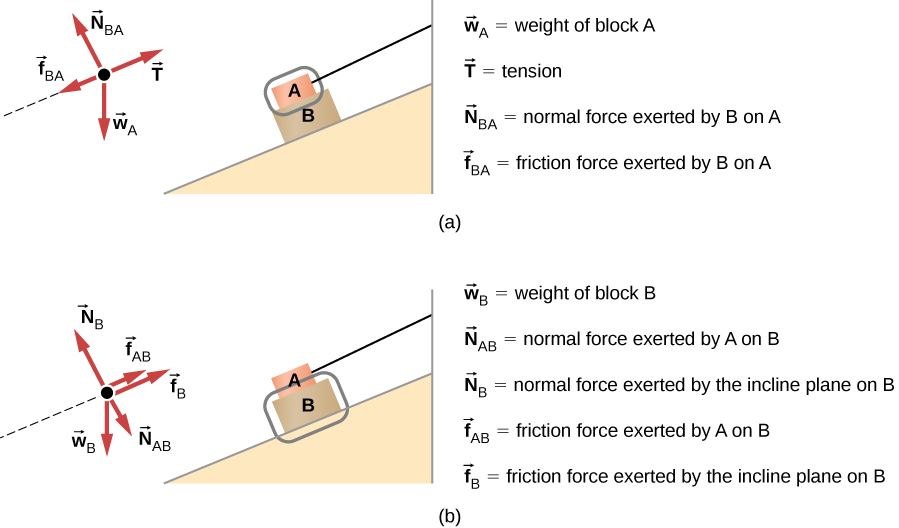
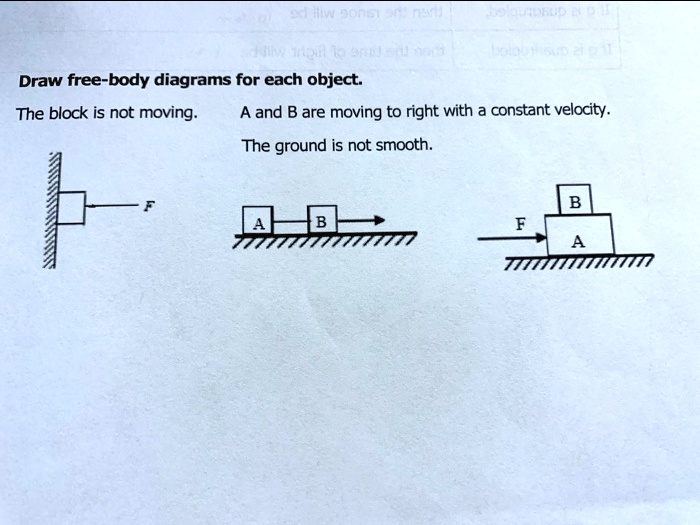
Identifying Free-Body Diagrams for Systems in Equilibrium ... Practice Identifying Free-Body Diagrams for Systems in Equilibrium with practice problems and explanations. ... Suppose that the car below is moving at a constant velocity, identify the free-body ... 5.7 Drawing Free-Body Diagrams - General Physics Using ... Figure 5.32 (a) The free-body diagram for isolated object A. (b) The free-body diagram for isolated object B. Comparing the two drawings, we see that friction acts in the opposite direction in the two figures. Because object A experiences a force that tends to pull it to the right, friction must act to the left. Because object B experiences a component of its weight that pulls it to the left ... PDF Free-Body Diagrams - Ms. Poulton's Science & Math Class ... Construct free-body diagrams for the following physical situations. Label all forces (e.g, Fgrav, Fnorm, Fapp, Ffrict, Fair, Ftens, etc. ). a. A physics book rests upon a level table. b. A skydiver is falling and has reached a terminal velocity. c. A large crate is being pushed leftward at a constant velocity. d. A sledder has reached Free body diagrams - Forces - Edexcel - GCSE Physics ... Free body diagram. Weight, reaction force and friction for an object moving at constant speed down a hill. Drawing of situation. Free body diagram. Weight, upthrust, thrust and air resistance for ...
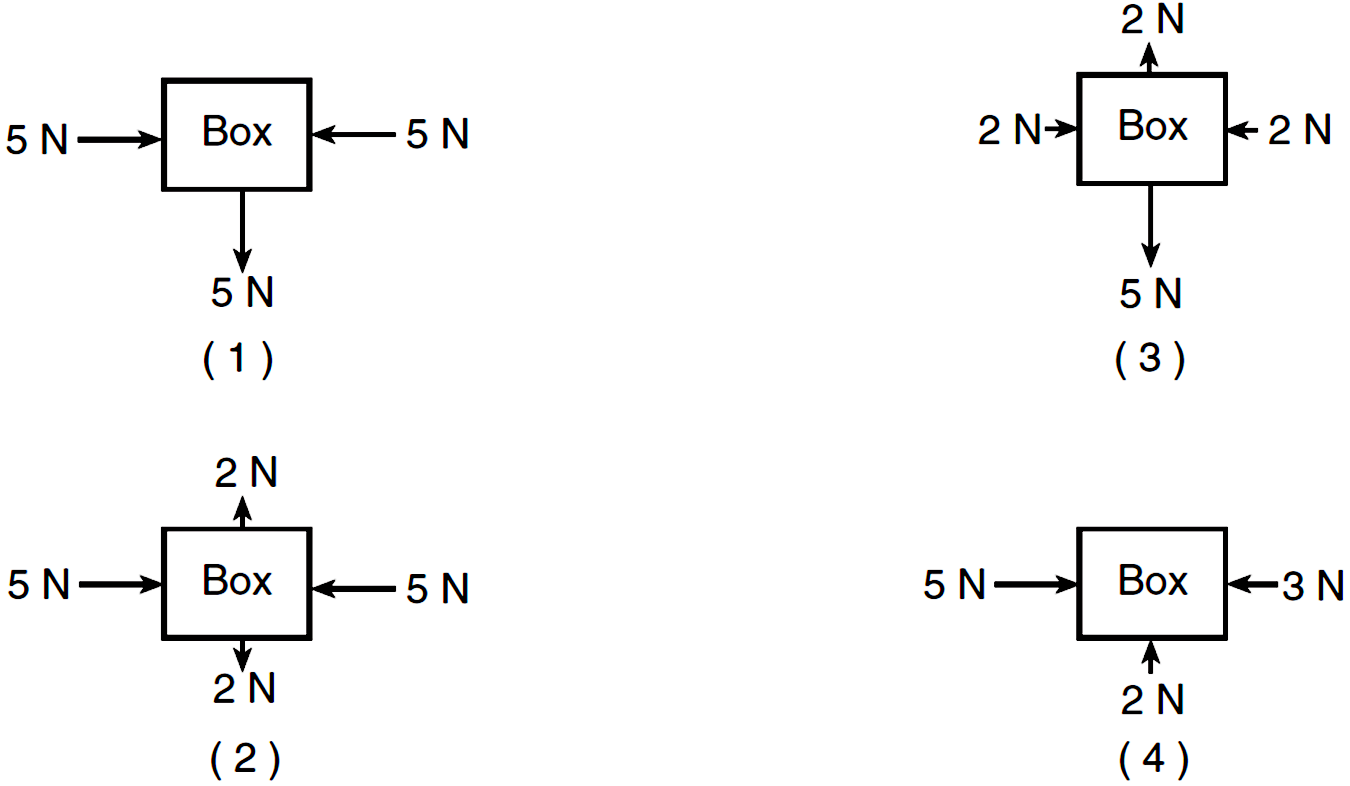
Dynamics/Kinetics - physics of mountain biking The velocity going up the incline is constant. free body diagram of a mountain biker down hill (5 % grade) As you can see of the free body diagram of the biker going down hill, the magnitude of each force remains the same (angle of slope is the same) compared to the up hill free body diagram. 5.7 Drawing Free-Body Diagrams - University Physics Volume 1 Figure 5.32 (a) The free-body diagram for isolated object A. (b) The free-body diagram for isolated object B. Comparing the two drawings, we see that friction acts in the opposite direction in the two figures. Because object A experiences a force that tends to pull it to the right, friction must act to the left. Because object B experiences a component of its weight that pulls it to the left ... PDF Notes: Free Body Diagrams - Weebly Level 3: Drawing Free Body Diagrams When we are working with forces, we often need to find the net force acting on an object. To do this, we first start by sketching a picture of the forces acting on it. We call this picture a free body diagram. There are a few rules we should follow when drawing a free body diagram. 1. Free-body diagram: simple cases - Boston University Physics Constant Velocity: A box is moving at constant velocity to the right. Which free-body diagram is correct? mg down and N up mg down, N up, some other force F to the right mg down, N up, equal-and-opposite forces left and right could be 1 or 3 In both cases above, mg and N are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction.
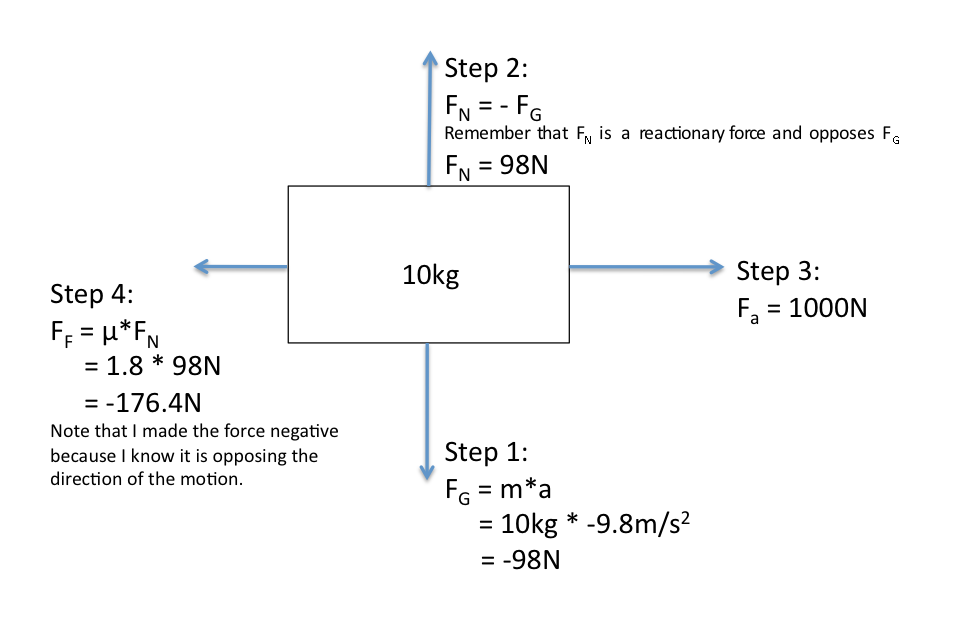
Problem: Object moving at constant velocity over a ... Problem: Object moving at constant velocity over a horizontal surface. Hanna is pulling an object of 20 kg over a horizontal plane. The force Hanna is exerting makes an angle of 30 ° with the horizontal. The coefficient of sliding friction μ, between the object and the plane, is 0.57.. If the object is moving at constant velocity, what is the magnitude of the force provided by Hanna?
Answered: Illustrate the free-body diagram of an… | bartleby Illustrate the free-body diagram of an object moving at constant velocity to the right on a frictionless surface. Expert Solution.
Solved An airplane is flying horizontally at a constant ... An airplane is flying horizontally at a constant velocity. Draw a free-body diagram for this airplane. Question: An airplane is flying horizontally at a constant velocity. Draw a free-body diagram for this airplane.
PDF Free-Body (Force) Diagrams - Monroe Township School District Free-Body (Force) Diagrams 1. A book is at rest on a table top. Diagram the forces acting on the book. 2. An egg is free-falling from a nest in a tree. Neglect air resistance. Diagram the forces acting on the egg as it falls. 3. A piece of paper is falling to the ground at constant velocity. Consider air resistance. Diagram the forces acting on ...
Free Body Diagrams ...Basics - mrwaynesclass.com The trucks drift to the right at a constant velocity. Draw a free body digram for each truck and the rope. To develop the math model a set of equations will be created. The set of equations varies from problem to problem. To create a equation the force will be added in one or more directions.
Drawing Free-Body Diagrams - Physics Classroom Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams that were discussed in an earlier unit. These diagrams will be used throughout our study of physics.
On a free body diagram, how can I tell the difference ... A free body diagram is a sum total depiction of all of forces acting upon the body inclusive of the resulting or causative shears, moments and reactions - keeping the body in resultant equilibrium. There is nothing that is amiss. The free body diagram can be that of a member, multiple members or segment of a member.
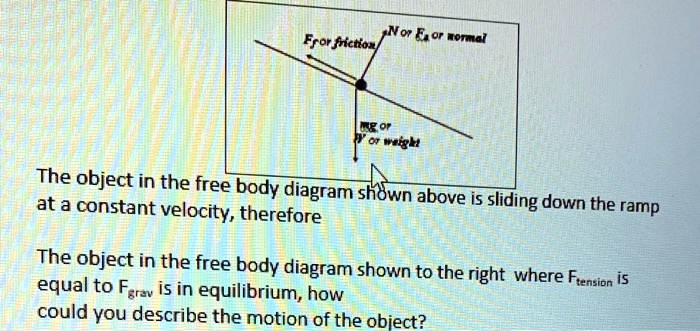
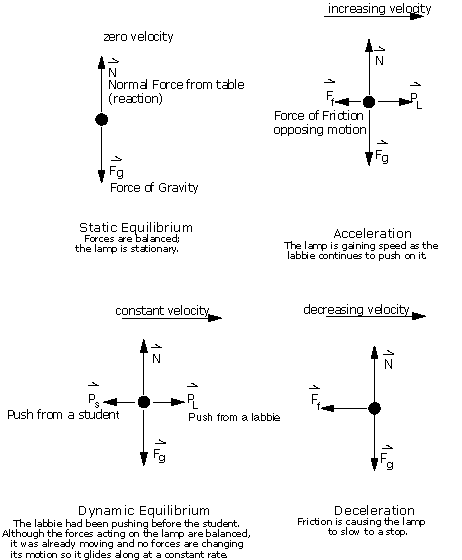
PDF Forces and Free-Body Diagrams - pnhs.psd202.org Free-body diagrams Free-body diagrams are used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting on an object. This diagram shows four forces acting upon an object. There aren't ... constant velocity, meaning a net force of 0N, the F app will equal the F f.
DOC Free Body Diagrams - erhsnyc.org Drawing a free body diagram involves at least the first two of the following steps: Draw a dot to represent the center of gravity of the object. Draw and label arrows extending outward from the dot to represent the forces acting on the object. Drawing the arrows at least approximately to scale and correct angles helps.
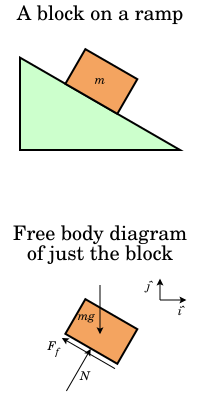
What is a Free-Body Diagram and How to Draw it (with ... A free-body diagram is a representation of an object with all the forces that act on it. The external environment (other objects, the floor on which the object sits, etc.), as well as the forces that the object exerts on other objects, are omitted in a free-body diagram. Below you can see an example of a free-body diagram:
An Easy Guide to Understand Free Body Diagrams in Physics ... The free body diagram of a car traveling at a constant speed consists mainly of five forces, when considered in an actual situation. These vectors are that of friction, gravity, normal force, air resistance, and engine driving force.
PDF 3-3 Constant Velocity, Acceleration, and Force Figure 3.7: Motion diagram and free-body diagram for an object drifting to the right through space. Figure 3.8: Motion diagram and free-body diagram for a box being dragged to the right, by means of a string, across a flat surface.
Free Body Diagrams 1 Constant Velocity - YouTube About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ...
Solved A skier of mass 63 kg skis straight down a 140 ... A skier of mass 63 kg skis straight down a 140 slope at constant velocity. Draw a free-body diagram of the skier with the various external forces acting on her. Include the force of air resistance, which is directed opposite the velocity. (Do this on paper. Your instructor may ask you to turn in this work.) (a) Find the value of the normal force.














0 Response to "39 free body diagram constant velocity"
Post a Comment