40 orbital diagram of nitrogen
Nitrogen (N) has an atomic mass of 7. Find out about its chemical and physical properties, states, energy, electrons, oxidation and more. What is the Orbital Diagram For Nitrogen? When we talk about the orbital diagram, we first need to understand what exactly it means. Therefore, during exams, the student can expect questions related to this topic so it is important that the students must go through it.
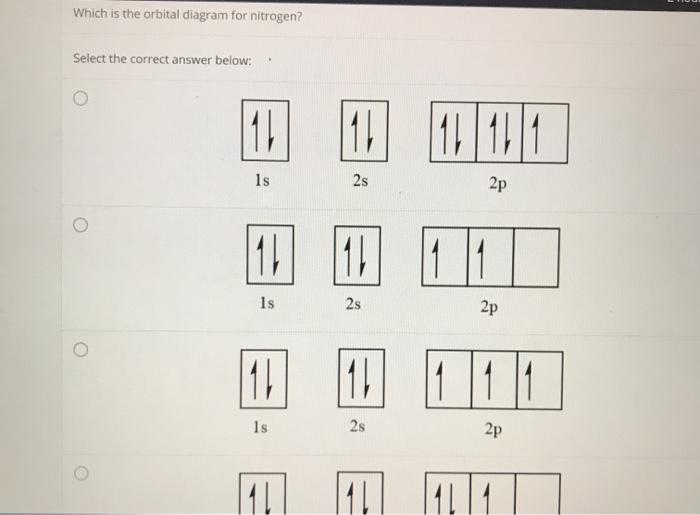
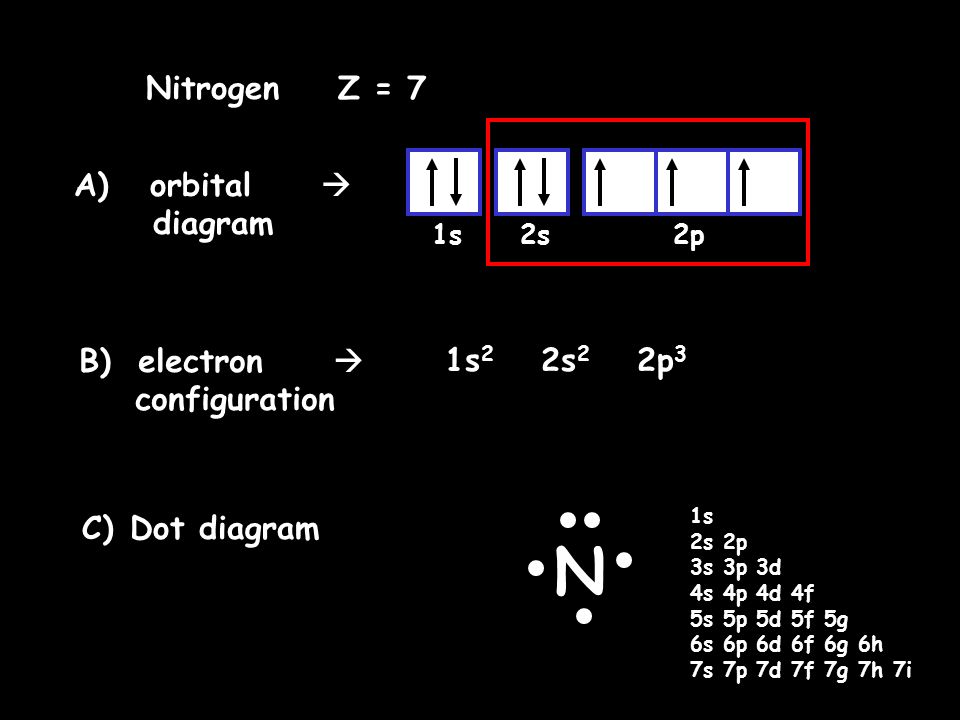
The choice A accurately specifies and illustrates the orbital diagram of a Nitrogen atom with 7 electrons. Based on the number of electrons in a Nitrogen atom, there are two energy levels, the s and p sub-levels: Nitrogen = 2, 5 . The first energy level, S will take up two electrons with opposite spin.
Orbital diagram of nitrogen
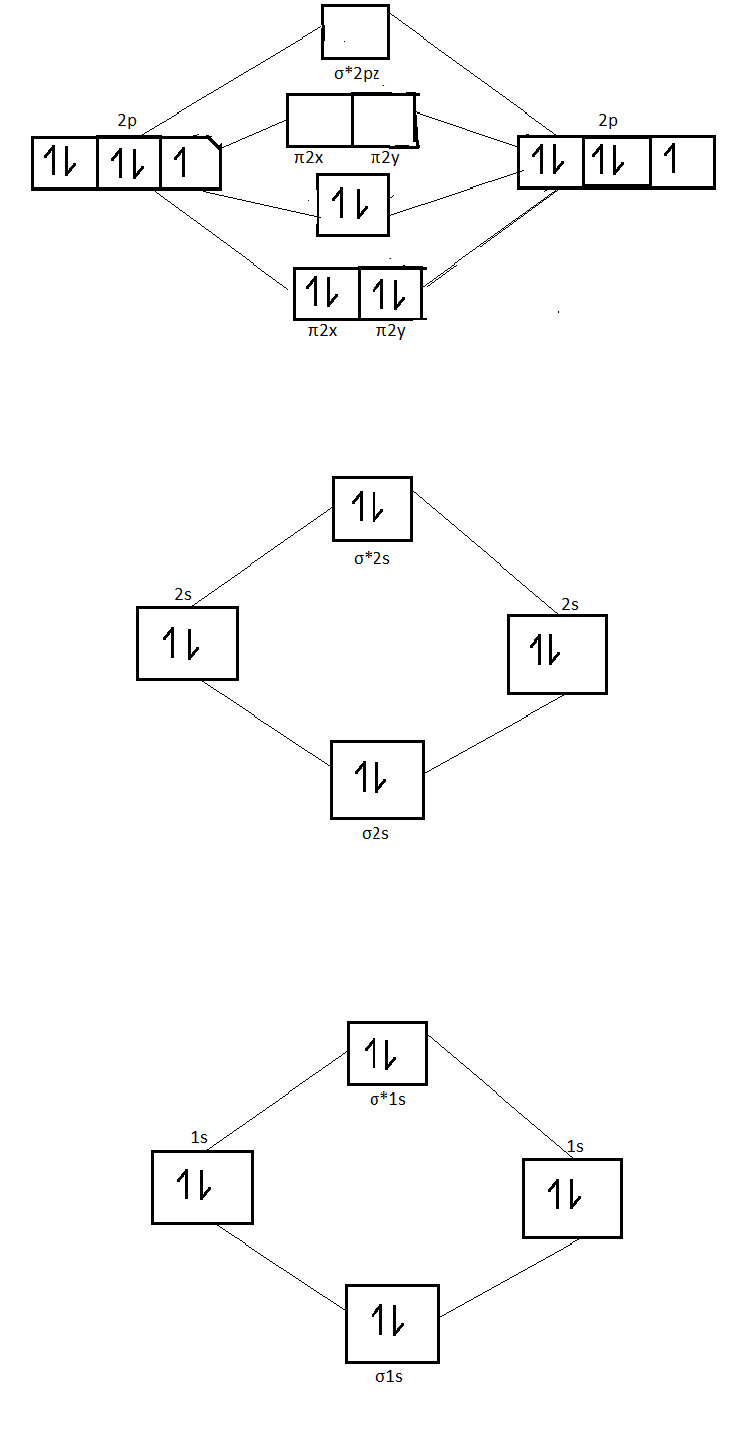
Orbital diagrams are pictorial descriptions of the electrons in an atom. Three rules are useful in forming orbital diagrams. According to the Auf Bau Principle, each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital. You jump up a little bit in energy and we get the 2s orbital that make it the 2p sublevel. 2b2 is the π* 2py antibonding MO. 4a1 is the σ* 2pz antibonding MO. As a further note, the 2s −2s overlap is the same idea as the 1s −1s overlap. So, the molecular electron configuration would be written in a similar manner as the atomic counterpart, but using molecular orbitals instead. We obtain: (σ1s)2(σ* 1s)2(σ2s)2(σ* 2s)2(π2px)2 ... Pressurized nitrogen in the satellite's false body provided the first opportunity for meteoroid detection. Sputnik 1 was launched during the International Geophysical Year from Site No.1/5, at the 5th Tyuratam range, in Kazakh SSR (now at the Baikonur Cosmodrome). The satellite traveled at 29,000 kilometres per hour (18,000 mph), taking 96.2 minutes to complete an orbit, and emitted radio ...
Orbital diagram of nitrogen. Molecular Orbital Diagram of N2. Molecular orbitals exist in molecules where each molecule has its electron configuration in terms of a sigma bond and pi bond. According to molecular orbital theory, it tells about magnetic nature, stability order, and the number of bonds in a molecule. This video tells about how electronic configuration of Nitrogen can be written using s, p, d & f notation, orbital diagram & condensed electronic configurati... When we write the electron configuration of N the first two electrons go in the 1s orbital. As 1s can only hold 2 electrons and the other next ... To see this video, other videos, chemistry education text, and practice problems visit my website. Website is 100% FREE to use.http://scientifictutor.org/
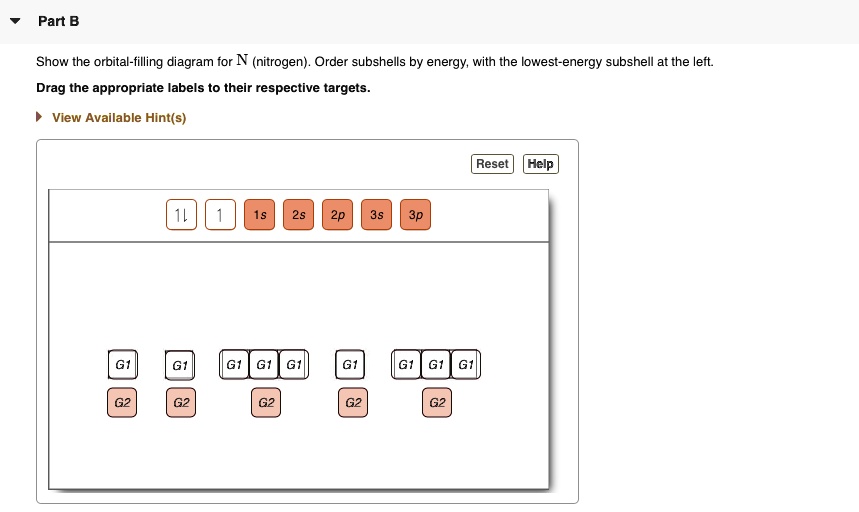
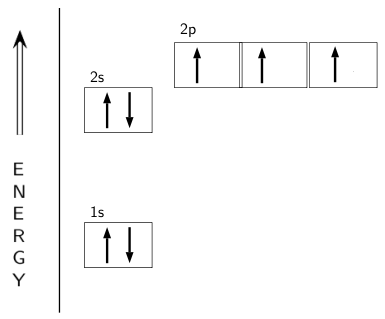
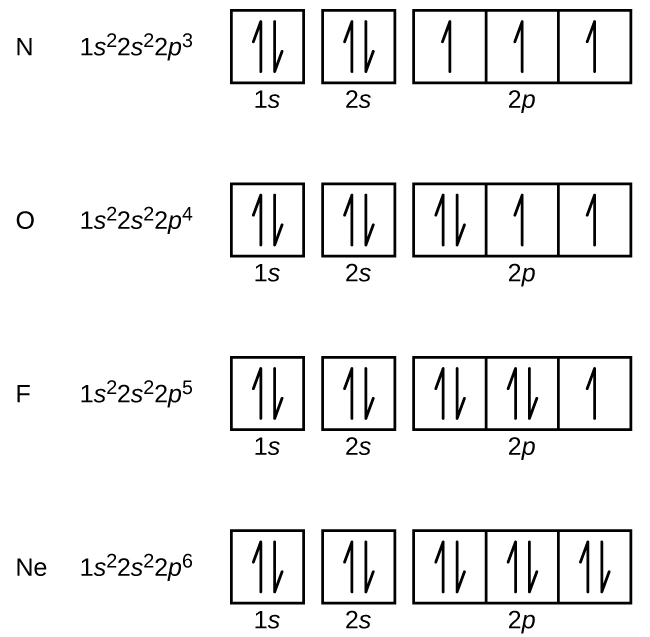
The periodic table shows us that nitrogen (N) has an atomic number of 7. As a result, a neutral nitrogen atom will have 7 electrons. In orbital filling diagrams, s-sublevels have 1 orbital and p ... Here, one sp orbital of C fuses with 1s orbital of H. And the other sp orbital of C fuses with one of the p orbitals of Nitrogen. The px orbitals of both C and N form sigma bonds while the Py and Pz orbitals form perpendicular Pi bonds. Polarity of HCN. Now let us look at whether the compound is polar or nonpolar in nature. A nitrogen atom has seven electrons. In the ground state, they are arranged in the electron configuration 1s 2 2s 2 2p 1 x 2p 1 y 2p 1 z.It therefore has five valence electrons in the 2s and 2p orbitals, three of which (the p-electrons) are unpaired. It has one of the highest electronegativities among the elements (3.04 on the Pauling scale), exceeded only by chlorine (3.16), oxygen (3.44 ... Answer (1 of 2): Nitrogen : Atomic number is 7 Electronic configuration of Nitrogen is 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1 2pz1 Copper: Atomic number is 29 Expected atomic number is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d9 or [Ar] 4s2 3d9 Here, 3d orbital has 9 electrons. Partially filled orbitals are not stable. So, cop...
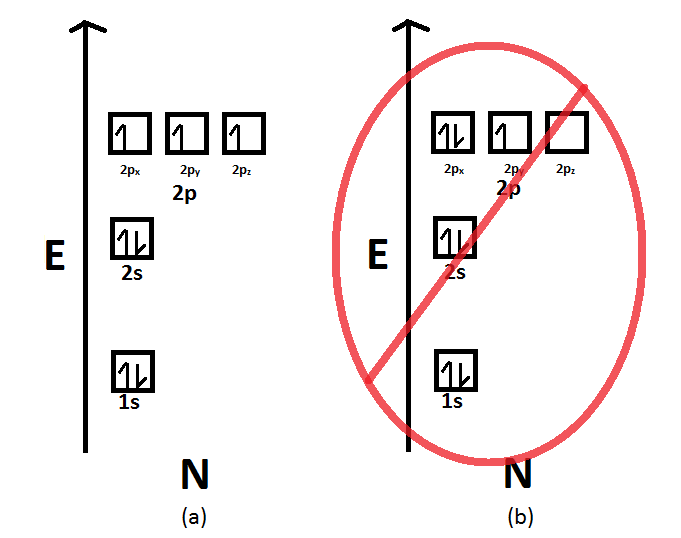
What is the atomic orbital diagram for nitrogen? The remaining three electrons will go in the 2p orbital. Therefore the N electron configuration will be 1s22s22p3. The configuration notation for Nitrogen (N) provides an easy way for scientists to write and communicate how electrons are arranged around the nucleus of the Nitrogen atom. Molecular orbital diagram of nitrogen gas is shown in the image. Since there are 7 electrons present in one nitrogen atom, so 14 electrons are... Electrons of nitrogen are to be filled in this diagram. Left side represents the configuration of one atom of nitrogen molecule and the right side represents ... Orbital Filling Diagrams •Each box represents an orbital which can hold a max of 2 e- •Aufbau principal -each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available; German for "build up" •Electrons are notated with an arrow -Up arrow goes first then, down arrow -Arrows represent the opposing spin of electrons 5.2 Quantum Theory & The Atom
Diagram of Hund's rule in boron, carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen. Figure 1. The 2p . Orbital filling diagrams essentially just turn this big list of electron locations . In the same way, the orbital filling diagram for nitrogen will be.Given the same amount of absorbed solar energy coming in, the amount of IR escaping to space at the top of the ...
Click here to get an answer to your question ✍️ Give orbital diagram of the following:nitrogen.
Orbital filling diagrams essentially just turn this big list of electron locations . In the same way, the orbital filling diagram for nitrogen will be. Nitrogen is the seventh element with a total of 7 electrons. In writing the electron configuration for nitrogen the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s.
The following molecular orbital diagram may be used for the following problems. For oxygen and fluorine, the σ 2p orbital should be lower in energy than the π 2p. However, the diagram will still yield correct bond order and magnetic behavior for these molecules. ____ 29. According to molecular orbital theory, which of the followin g species is the most likely to exist? a. H 2 2-b. He 2 c. Li ...
Orbital Diagram Of Nitrogen. molecular orbital diagram a molecular orbital diagram or mo diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory molecular orbital theory home faculty molecular orbital theory the goal of molecular orbital theory is to describe molecules in a similar way to how we describe atoms that is in
Orbital Filling Diagram for Nitrogen. show the orbital filling diagram for rm n nitrogen best answer the electronic configuration for nitrogen atom is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 3 lowest energy state will have two electrons in s shell which is spherical in shape one spin up and another spin down chemistry problem please help show the orbital filling diagram for nitrogen stack the subshells inorder of energy ...
The correlation diagrams for nitrogen and carbon monoxide and the first are nearly parallel to the corresponding orbital energy curves. Bond order for N2 is 3; bond order for N2- is and bond order for N2+ is I have not included pictures of the MO diagrams that show the orbital energies. N2+ has less bond energy.
To write the orbital diagram for the Nitrogen atom (N) first we need to write the electron configuration for just N. To do that we need to ...
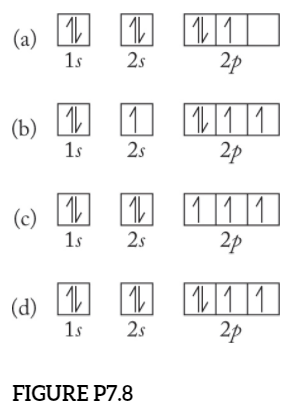
Which one of the following is the correct orbital diagram for nitrogen? ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑ ↑ ... The lowest energy orbital in the quantum-mechanical model is the. 1s orbital. Which orbital would the electron of a ground state hydrogen atom occupy? 1s.
Here is the full molecular orbital diagram for N2. Now we add the 10 electrons, 5 from each nitrogen atom. Note that the bottom sigma symmetry orbital is ...
The orbital diagram for a ground-state nitrogen atom is. 1s (up down) 2s (up down) 2p (up, up, up) Electrons in an orbital with l = 3 are in a/an. f orbital. Transition metal elements have atoms or ions with partially filled. d subshells. Calculate the energy of a photon of light with a wavelength of 360 nm.
Nitrogen electron configuration is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 3.The period of nitrogen is 2 and nitrogen is a p-block element. The electron configuration of nitrogen(N) and the orbital diagram is the main topic of this article.
Orbital diagram of Nitrogen (N) 8. Orbital diagram of Oxygen (O) 9. Orbital diagram of Fluorine (F) 10. Orbital diagram of Neon (Ne) 11. Orbital diagram of Sodium (Na)
Atomic Orbital Diagrams: These are also known as electron-in-a-box diagrams. This is a simplified diagram of how the electrons are arranged within the orbitals ...
Two p-atomic orbitals (one from each nitrogen) atom combine to form two molecular orbitals, the bonding molecular orbital σ2px and antibonding molecular orbital σ*2px. The other four p-atomic orbitals (two from each nitrogen) atom combine to give four molecular orbitals, two bonding molecular orbitals i.e. π2py and π2pz, while two ...
Molecular Orbital Theory is primarily used to explain the bonding in molecules that cannot be explained by Valence Bond Theory. These are molecules that generally involve some form of resonance. Resonance implies that a bond is neither single nor double but some hybrid of the two. Valence bond theory only describes the bonding of single or double or triple bonds. It does not provide an ...
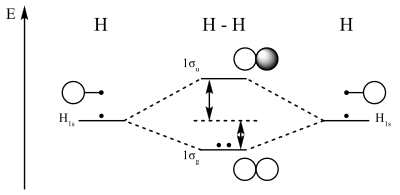
Molecular orbital diagram for hydrogen: For a diatomic molecule, an MO diagram effectively shows the energetics of the bond between the two atoms, whose AO unbonded energies are shown on the sides. The unbonded energy levels are higher than those of the bound molecule, which is the energetically-favored configuration. Linear Combination of Atomic Orbitals. A linear combination of atomic ...
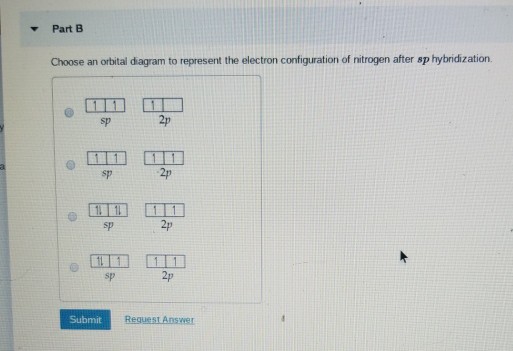
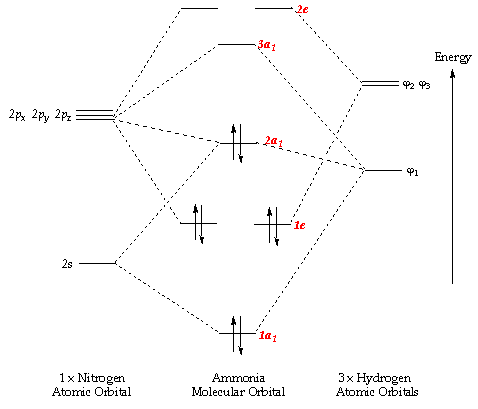
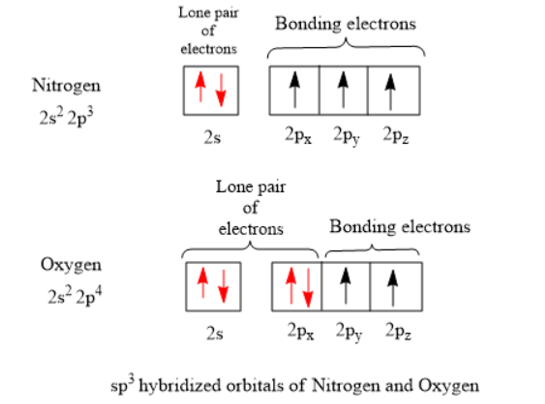
Methyl amine. The nitrogen is sp 3 hybridized which means that it has four sp 3 hybrid orbitals. Two of the sp 3 hybridized orbitals overlap with s orbitals from hydrogens to form the two N-H sigma bonds. One of the sp 3 hybridized orbitals overlap with an sp 3 hybridized orbital from carbon to form the C-N sigma bond. The lone pair electrons on the nitrogen are contained in the last sp 3 ...
3 Unpaired electrons. Nitrogen atom has total 7 electrons. Two will fill up the n=1 level, and then there are five electrons in the n=2 level. Nitrogen can bond three times with other electrons to fill up it's shell with 8, (8-5=3). And these are those 3 unpaired electrons which were residing the 2p sub-shell of the Nitrogen atom , before the formation of 3 bonds.
To book a personalized 1-on-1 tutoring session: Janine The Tutorhttps://janinethetutor.com More proven OneClass Services you might be ...
Molecular orbitals in Nitrogen. Use the buttons to display the 1s and 2p atomic orbitals that make up the molecular orbitals. There are four molecular orbitals derived from the 1s and 2s orbitals. Use the buttons to display the 1s and 2p atomic orbitals that make up the molecular orbitals. The p orbitals combine to produce a sigma and two ...
Nitrogen is the seventh element with a total of 7 electrons. In writing the electron configuration for nitrogen the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for N goes in the 2s orbital. The remaining three electrons will go in the 2p orbital.
Why does oxygen have a different molecular orbital diagram? Hear this out loudPauseS-p mixing is the primary cause of the difference in the molecular orbitals of nitrogen and oxygen, which is influenced by the initial atomic orbital energies. The lighter second period elements (prior to oxygen) have a relatively small difference in energy ...
Pressurized nitrogen in the satellite's false body provided the first opportunity for meteoroid detection. Sputnik 1 was launched during the International Geophysical Year from Site No.1/5, at the 5th Tyuratam range, in Kazakh SSR (now at the Baikonur Cosmodrome). The satellite traveled at 29,000 kilometres per hour (18,000 mph), taking 96.2 minutes to complete an orbit, and emitted radio ...
2b2 is the π* 2py antibonding MO. 4a1 is the σ* 2pz antibonding MO. As a further note, the 2s −2s overlap is the same idea as the 1s −1s overlap. So, the molecular electron configuration would be written in a similar manner as the atomic counterpart, but using molecular orbitals instead. We obtain: (σ1s)2(σ* 1s)2(σ2s)2(σ* 2s)2(π2px)2 ...
Orbital diagrams are pictorial descriptions of the electrons in an atom. Three rules are useful in forming orbital diagrams. According to the Auf Bau Principle, each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital. You jump up a little bit in energy and we get the 2s orbital that make it the 2p sublevel.

















0 Response to "40 orbital diagram of nitrogen"
Post a Comment