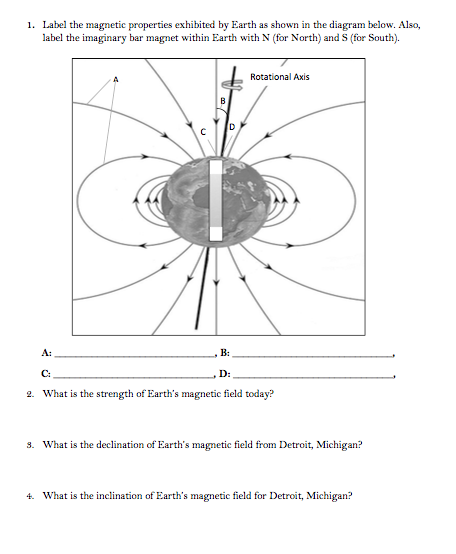
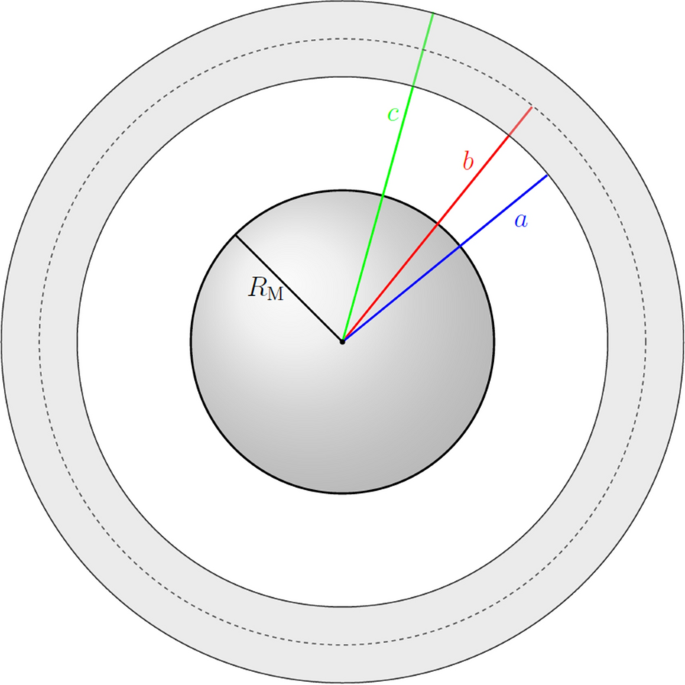
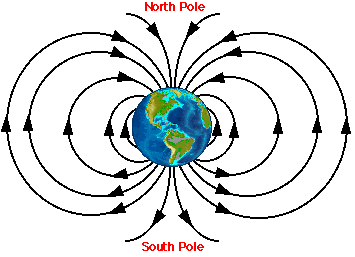
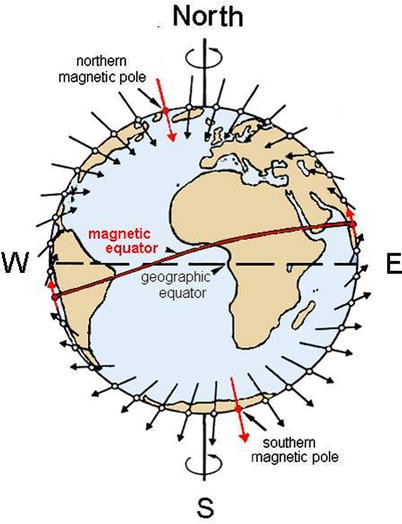
40 label the diagram of earth's magnetic field appropriately.
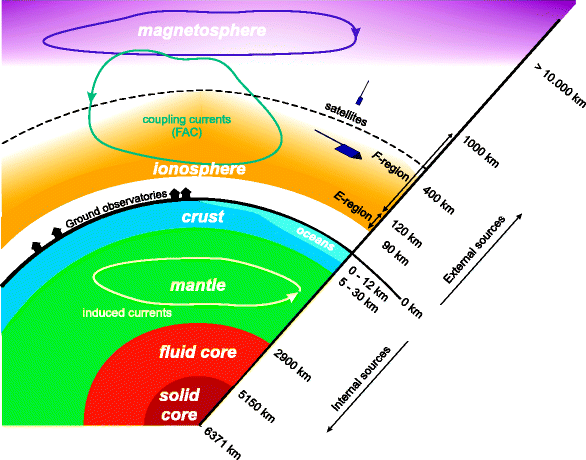
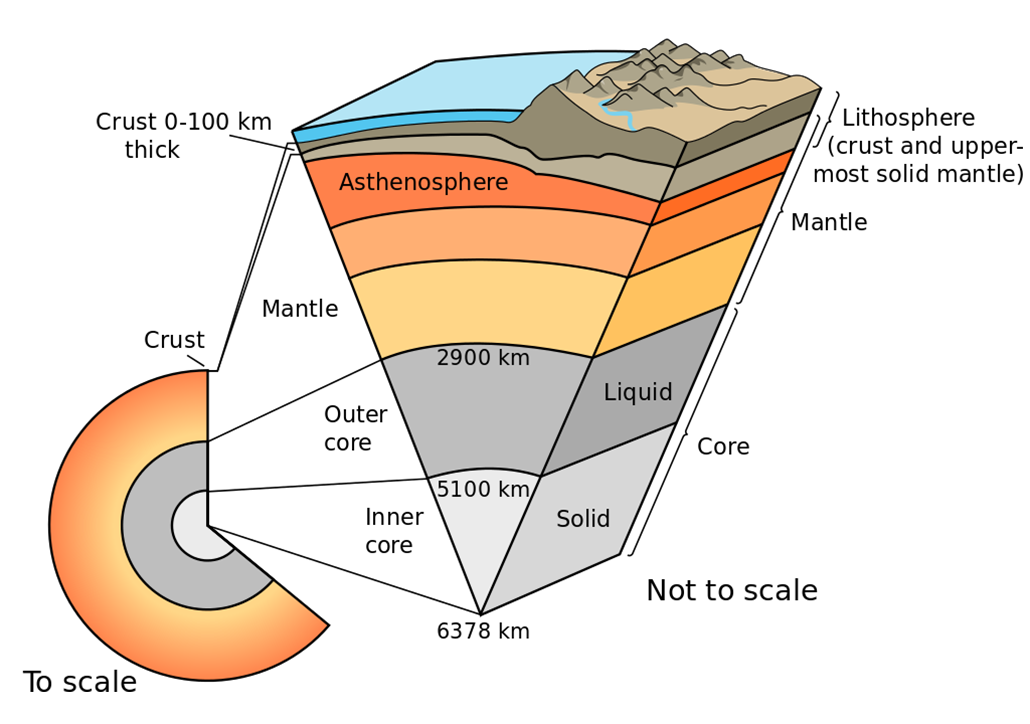
The Earth's magnetic field The behaviour of a compass shows that the Earth has a magnetic field. Scientists believe that this field is produced by convection currents in the Earth's core, which ... The Earth's outer core is in a state of turbulent convection as the result of radioactive heating and chemical differentiation. This sets up a process that is a bit like a naturally occurring electrical generator, where the convective kinetic energy is converted to electrical and magnetic energy. Basically, the motion of the electrically conducting iron in the presence of the
Because the Earth is made of magnetic elements such as Iron, Nickel, and Cobalt, the Earth acts as an extremely large magnet, which attracts these charged particles, among other things. In concurrence with that, as the Earth rotates, its hot core generates strong electric currents that produce the magnetic field, a.k.a. magnetosphere.

Label the diagram of earth's magnetic field appropriately.
The area around a magnet is called the magnetic field. (a) The Earth has a magnetic field. What causes the Earth's magnetic field? Tick one box. The movement of liquid iron in the Earth's outer core The gravitational field of the Earth The permanent magnet in the Earth's core (1) (b) Look at Figure 1. Figure 1 Right: a schematic diagram of Earth's interior. The outer core is the source of the geomagnetic field. [Larger image] Earth's magnetic field comes from this ocean of iron, which is an electrically conducting fluid in constant motion. Sitting atop the hot inner core, the liquid outer core seethes and roils like water in a pan on a hot stove. 3 0625/03/M/J/05 [Turn over (b) On Fig. 1.2, draw arrows to show the directions of the forces acting on the sphere when it is at the position shown by point S on the graph. Label your arrows with the names of the forces. [2] Fig. 1.2 (c) Explain why the sphere is moving with constant speed at S. [2] (d) Use the graph to calculate the approximate distance that the sphere falls
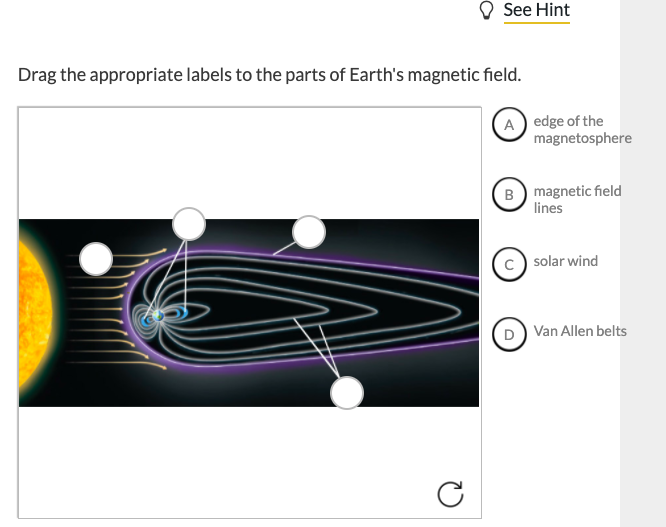
Label the diagram of earth's magnetic field appropriately.. 9.3 Earth's Magnetic Field. Heat is also being transferred from the solid inner core to the liquid outer core, and this leads to convection of the liquid iron of the outer core. Because iron is a metal and conducts electricity (even when molten), its motion generates a magnetic field. Earth's magnetic field is defined by the North and South ... Drag the Appropriate labels to the parts of Earth's magnetic field. (from left to right) ... Label the block diagram of the lithosphere (left to right) Moho, continental crust, athenospheric mantle, oceanuc crust, lithosphere. Label the of Earth's magnetic field (left to right) lines of magnetic force, magnetic equator, north magnetic pole ... body diagrams. The student will be able to: S3P-4-01: Define the gravitational field qualitatively as the region of space around a mass where another point mass experiences a force. S3P-4-02: Diagram the Earth's gravitational field, using lines of force. S3P-4-03: Define the gravitational field quantitatively as a force per unit mass. According to the current understanding of Earth's magnetic field and how magnetic fields are generated, which two components in Earth's internal structure are required in order to generate a magnetic field? ... compose the inner regions of the magnetosphere and directly affect the auroral events seen on Earth. Label the appropriate regions of ...
The secular variation of the magnetic field causes declination to change with time. Changes in declination can be quite large. At Yellowknife, NWT, for example, the declination is changing by more than one degree every three years.On the other hand, at Ottawa, the yearly change in declination is almost zero. The diagram shows the change in declination at several locations in Canada. Label the magnetic properties exhibited by Earth as shown in the diagram below. Also label the imaginary bar magnet within Earth with N (for North) and S (for South). Rotational Audis 2. What is the strength of Earth's magnetic field today? 3. What is the declination of Earth's magnetic field from Detroit, Michigan? 4. Label the diagram of Earth's magnetic field appropriately. D,C,A,B. Label the polarity chrons with the appropriate title and polarity. Note that some of the chrons contain short-duration subchrons. The boundaries between the chrons are indicated by the heavy black lines. The thickness of layers on this diagram represents the duration of time ... Magnetic force decreases as the distance from the magnet increases. Magnetic force can travel through non-magnetic materials such as air and water. Compass needles point north and south in response to the Earth's magnetic field. You can also use them to detect magnetic fields of other objects. Think Quick!
Label the polarity chrons with the appropriate title and polarity. Note that some of the chrons contain short-duration subchrons. The boundaries between the chrons are indicated by the heavy black lines. The thickness of layers on this diagram represents the duration of time during which the layer accumulated. An 'Earth inductor' consists of a 500 turn coil. Figure 2 and Figure 3 shows it set up to measure the horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic field. When the coil is rotated an induced emf is produced. € Figure 2 € Figure 3 € The mean diameter of the turns on the coil is 35 cm. Figure 4 shows the output recorded The separation of earth's magnetic field and the smart rock's magnetic strength is avoided through localization based on the magnetic gradient tensors, and the convergence and the accuracy of ... B. Positive magnetic anomalies occur where seafloor basalt has the same polarity as Earth's present-day magnetic field. C. All polarity chrons are the same length of time; they differ only in the magnetic strengths they represent. D. The width of each rock stripe is a measure of how long the polar direction took to change.
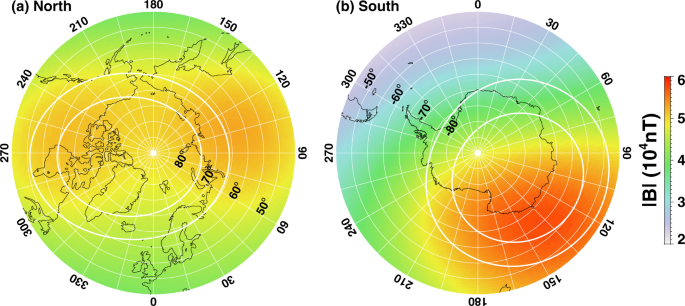
The positions of the magnetic poles can be defined in at least two ways [5].. Often, a magnetic (dip) pole is viewed as a point on the Earth's surface where the magnetic field is entirely vertical. Another way of saying this is that the inclination of the Earth's field is 90° at the North Magnetic Pole and -90° at the South Magnetic Pole. At a magnetic pole, a compass held in the horizontal ...
Faraday's law can be used to work out the size of an induced e.m.f. such as that across the wingtips of an aircraft flying in the Earth's magnetic field. In Britain the Earth's field makes an angle of 20° with the vertical, see the following diagram. Unlike that of a bar magnet, the Earth's magnetic field is from South to North.
To examine the magnetic field associated with a bar magnet and construct the magnetic field lines. 2. To measure the magnitude and approximate orientation of the Earth's magnetic field in classroom. INTRODUCTION In these exercises, you will study the magnetic field of bar magnets and the earth. You will draw field lines and analyze their meaning.
100% (8 ratings) Answer: { If you find it helpful pleas …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: O See Hint Drag the appropriate labels to the parts of Earth's magnetic field. edge of the magnetosphere magnetic field lines (c) solar wind D) Van Allen belts. Previous question Next question.
Example 1: Calculate the vertical component of the earth's magnetic field at the equator if the horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field is at B and the angle of dip is 60०. Solution: The horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field, H = B e cos 60० = B. B e х ½ = B.
Magnetic declination / magnetic variation: the Earth's magnetic axis is not parallel to its geographic axis (axis of rotation) a compass reading deviates from geographic north. Magnetic inclination: the magnetic field is not horizontal at most of earth's surface, its angle up or down. The magnetic field is vertical at magnetic poles.
7. Draw a diagram of the Planet Earth and its Magnetic Field Lines. Be sure to indicate the direction of the field lines. Label the poles of the Earth's Magnetic Field. Also indicate in your diagram the true geographic North of the planet. [K5] Question: 7. Draw a diagram of the Planet Earth and its Magnetic Field Lines.
Label the diagram of Earth's magnetic field appropriately. (Left to Right) Lines of Magnetic Force, Magnetic Equator, North Magnetic Pole, North Geographic Pole. Label the polarity chrons with the appropriate title and polarity. Note that some of the chrons contain short-duration subchrons. The boundaries between the chrons are indicated by the ...
A magnetic field is a picture that we use as a tool to describe how the magnetic force is distributed in the space around and within something magnetic. [Explain] Most of us have some familiarity with everyday magnetic objects and recognize that there can be forces between them.
Experiment 18: Earth's Magnetic Field 99 A typical compass is constrained to 2 dimensions and rotates to point to Earth's magnetic south pole, which is (approximately) geographic north. Earth's magnetic field, however, is a 3 dimensional phenomenon. It has components that point into and out of the earth, not just along the surface.
3 0625/03/M/J/05 [Turn over (b) On Fig. 1.2, draw arrows to show the directions of the forces acting on the sphere when it is at the position shown by point S on the graph. Label your arrows with the names of the forces. [2] Fig. 1.2 (c) Explain why the sphere is moving with constant speed at S. [2] (d) Use the graph to calculate the approximate distance that the sphere falls
Right: a schematic diagram of Earth's interior. The outer core is the source of the geomagnetic field. [Larger image] Earth's magnetic field comes from this ocean of iron, which is an electrically conducting fluid in constant motion. Sitting atop the hot inner core, the liquid outer core seethes and roils like water in a pan on a hot stove.
The area around a magnet is called the magnetic field. (a) The Earth has a magnetic field. What causes the Earth's magnetic field? Tick one box. The movement of liquid iron in the Earth's outer core The gravitational field of the Earth The permanent magnet in the Earth's core (1) (b) Look at Figure 1. Figure 1






















0 Response to "40 label the diagram of earth's magnetic field appropriately."
Post a Comment