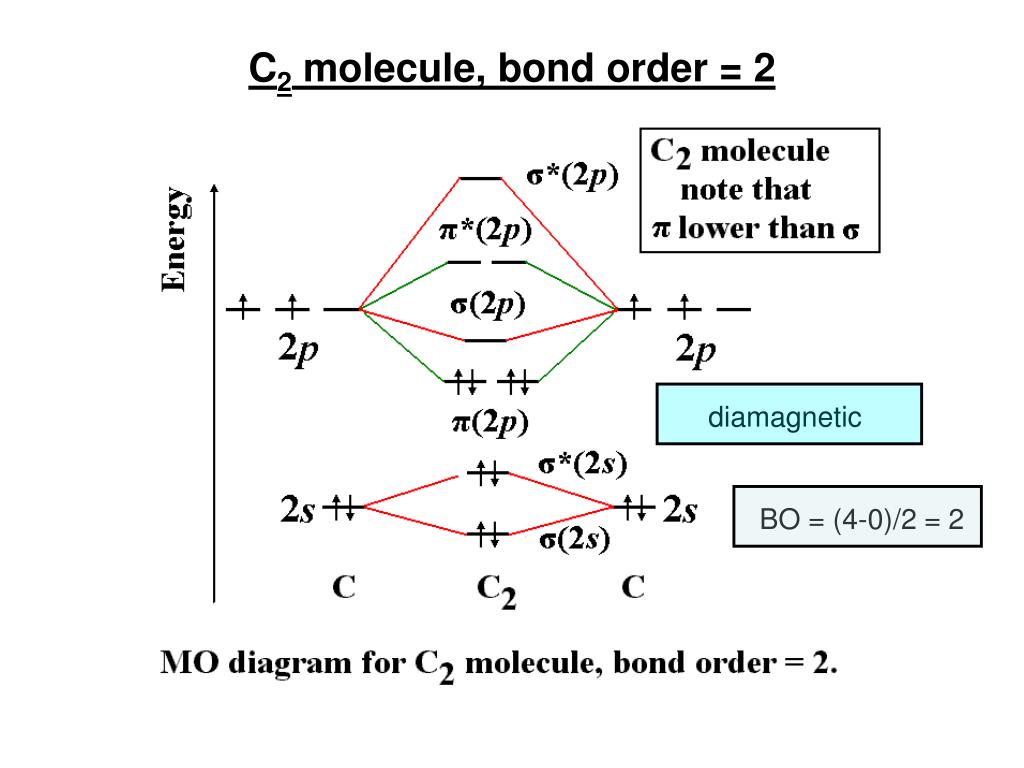
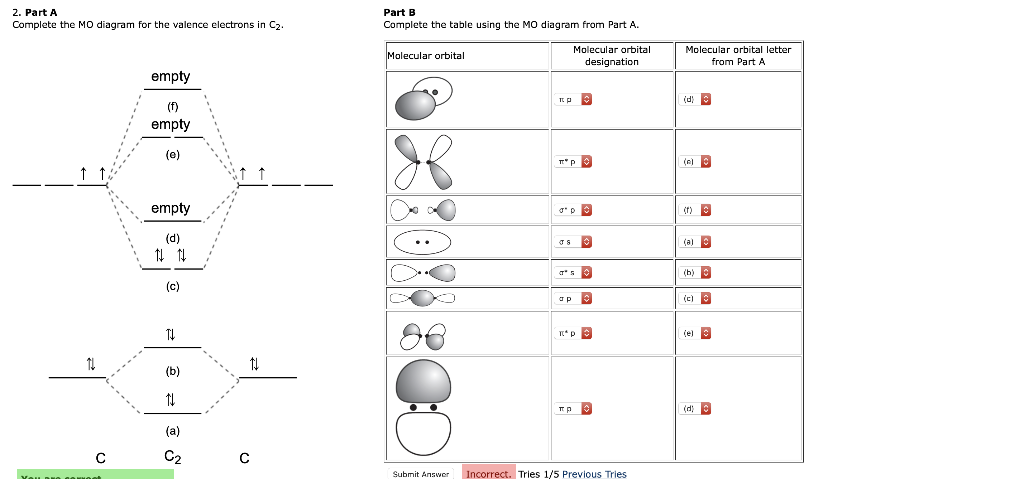
39 mo diagram of c2
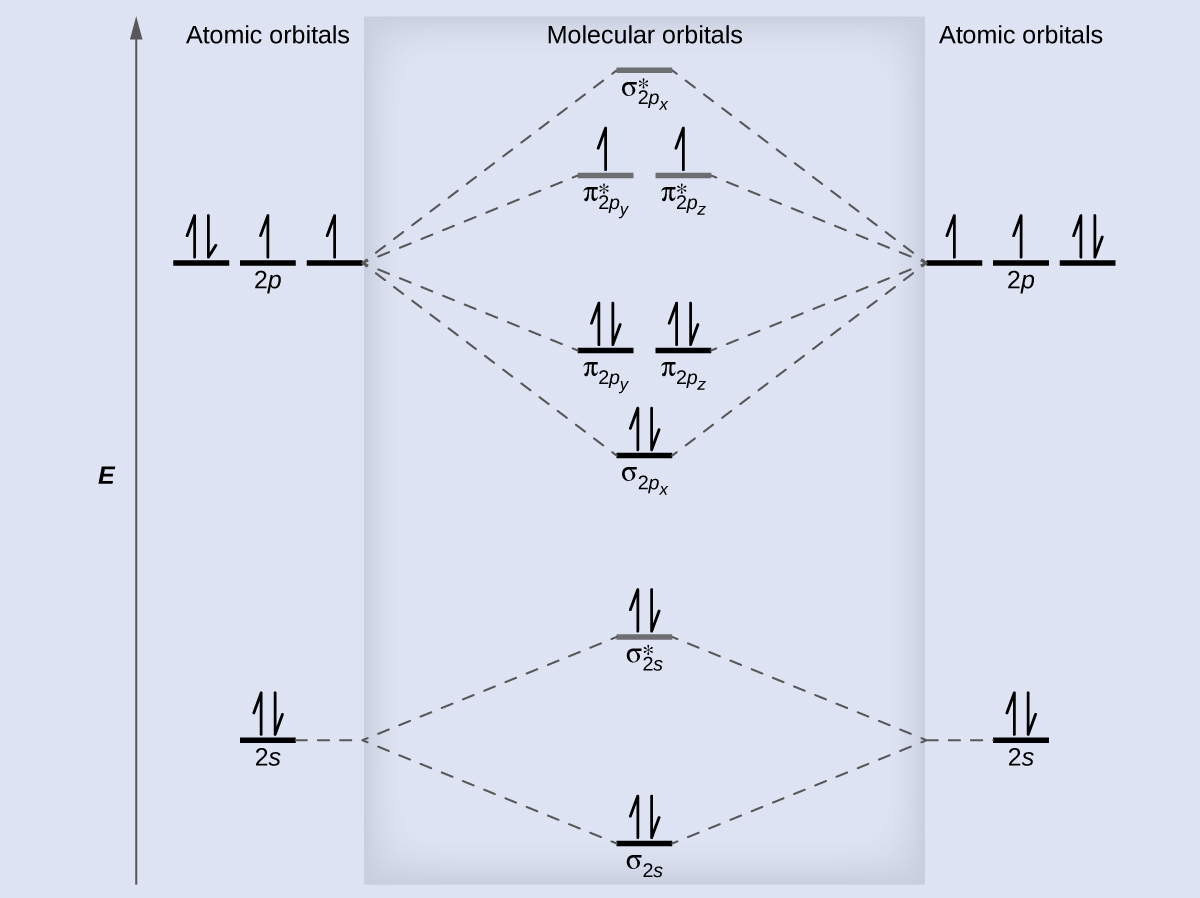
Answer. Use molecular orbital theory to describe the bonding in the following. For each one, find the bond order and decide whether it is stable.4 answers · Top answer: So here we're looking at the molecular orbital theory to describe bonding. So the first example, ... Example \(\PageIndex{3}\): Ion Predictions with MO Diagrams. Give the molecular orbital configuration for the valence electrons in \(\ce{C2^2-}\). Will this ion be stable? Solution. Looking at the appropriate MO diagram, we see that the π orbitals are lower in energy than the σ p orbital. The valence electron configuration for C 2 is
Use MO diagram to place C2-,C2 and C2+ in order of decreasing bond energy? Use MO diagram to place C 2- ,C 2 and C 2+ in order of decreasing bond energy? Q. Using the molecular orbital model, write electronic configurations for the following diatomic species and calculate the bond orders. a.
Mo diagram of c2
If you see the MO diagram , there are two unpaired electrons in the p-pi BO. This is what makes C2 unstable. In order to stabilize, it needs to share these ...5 answers · 8 votes: C2 exists, but only above 3,642 °C (6,588 °F) i.e. in vapor state Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ... Use MO diagrams to place C2^- ,C2, C2^+ in order of the following properties: (b) Increasing bond length a) C2^- C2 C2^+ b) C2^- C2^+ C2 c) C2 C2^- C2^+ d) C2 C2^+ C2^- e) C2^+ C2 C2^- f) C2^+ C2^- C2. Learn this topic by watching MO Theory: Bond Order Concept Videos. All ...
Mo diagram of c2. Molecular orbital diagram for n2 o2 c2 f2 also h2o. Molecular orbital diagram for carbon dimer c2. Mo diagram s can be used to deduce magnetic properties of a molecule and how they change with ionization. Molecular orbital diagram for n2 o2 c2 f2 also h2o. Electronic configuration of c2 molecule is σ 1s2 σ1s2 σ2s2 σ2pz 2 2px 1 2py orbital s ... Exercise 3.3.4. 3. Construct a qualitative molecular orbital diagram for chlorine, Cl 2. Compare the bond order to that seen in the Lewis structure (remember that an electron in an antibonding orbital cancels the stabilization due to bonding of an electron in a bonding orbital). Answer. Question: Draw the molecular orbital (MO) electron diagram for the C2 molecular ion. Be sure your diagram contains all of the electrons in the ion, including any core electrons Energy Explanation Check . This problem has been solved! See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading. Answer (1 of 5): C2 exists, but only above 3,642 °C (6,588 °F) i.e. in vapor state
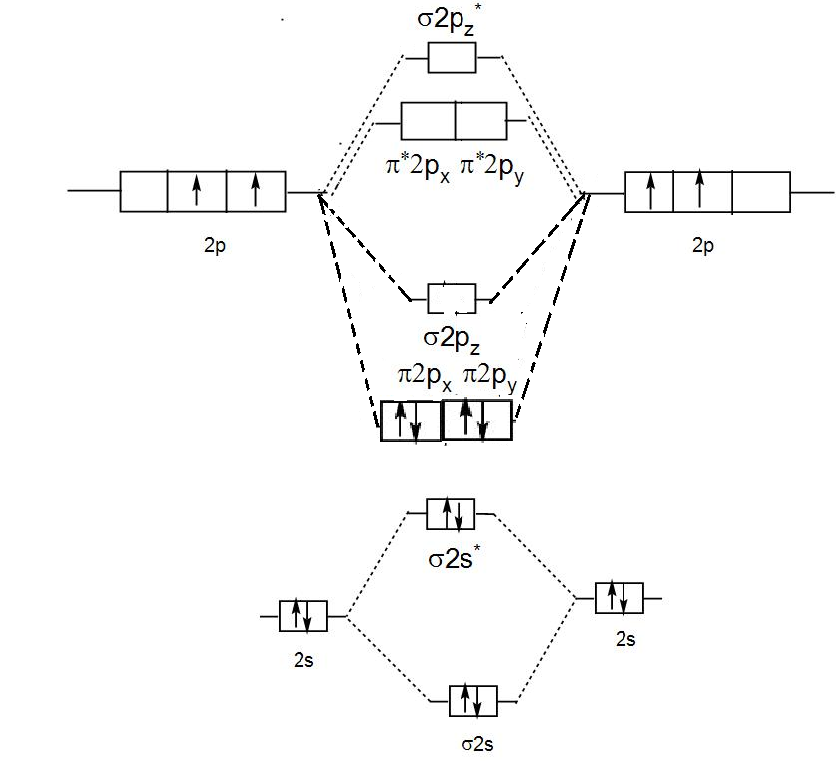
When two carbons atoms bond, the pi(2p) bonding molecular orbitals are lower in energy than the sigma(2p) bonding orbitals.C2(2-) has a bond order of 3, so i... A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ... C22- Molecular Orbital Diagram. The problem provides you with the MO diagram for the C2 molecule, so all you really have to do here is add an electron to that diagram. It is sigma2s (2)sigma2s* (2)sigma2p (2)pi2p (4)pi2p* (4) Bond order 1. It is stable. Bond order of C2- = 1/2 (7 - 2) = 5/2 = 2.5 Bond order of C2 = 1/2 (6 - 2) = 2 Highest bond order means highest bond energy and shortest bond length. So, the highest bond order with highest bond energy and the shortest bond length is found in C2-. So, the order starting with the highest bond order is = C2- > C2 > C2+.
Compare this to the MO diagram of C2 with sp mixing. Calculate bond order for both Mo diagrams and designate if C2 would be considered diamagnetic or paramagnetic in each case (MO diagram with sp mixing and MO diagram without sp mixing) Question: Question 1 (10 points) Draw the complete MO diagram for C2 - Assume NO sp mixing of orbitals when ... This is the molecular orbital diagram for the homonuclear diatomic Be2+, . electrons would be in a bonding orbital, we would predict the Li2 molecule to be . Explain why the relative energy levels diagrams for Li2, Be2, B2, C2, N2 are different The molecular orbital theory of Li2 to F2 gives a graphical explanation. Draw the MO diagram for acetylide ion C2^2- and calculate its bond order. asked Dec 18, 2020 in Chemical Bonding by Aashi01 (13.0k points) chemical bonding; class-11; 0 votes. 1 answer. Draw MO diagram of CO and calculate its bond order. asked Dec 17, 2020 in Chemical Bonding by Panna01 (47.2k points) chemical bonding; Determine the bond order for each molecule b. Determine whether each of the molecules is paramagnetic or diamagnetic. c. Determine which molecule has the ...1 answer · 0 votes: 646 -12 es IS IS LS IS 一4 Bond.ng-anhtond.ra elachroro Dia mame 12-1)ニ1 Peoamagnefr Anamngnetて
(a) Use the MO diagram from Figure 2.18 from the textbook: The electron configuration for O 2 - is 1σ g 2 1σ u 2 2σ g 2 2π u 4 2π g 3. This leaves 1 unpaired electron and gives a bond order of 1.5. (b) Use the same MO diagram as in (a), giving an electron configuration for O 2 + of: 1σ g 2 1σ u 2 2σ g 2 2π u 4 2π g 1.
MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
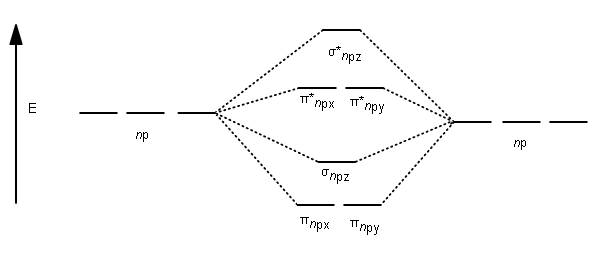
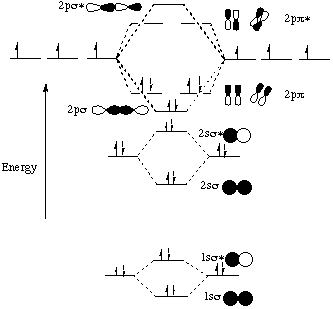
The diagram below shows the two $ 2p\pi $ orbitals, let's say $ 2p\pi x $ and $ 2p\pi y $ , are the highest energy occupied molecular orbitals. The lowest energy unoccupied molecular orbital is $ 2p\sigma $ , so that is where extra electrons will be added.
By drawing molecular orbital diagrams for b2 c2 n2 o2 and f2 predict which of these homonuclear diatomic molecules are magnetic. How to graph a mo molecular orbital diagram for f2. This video shows the mo diagrams of the c2 n2 o2 and f2 molecules.
Use the MO diagram provided below to answer the following questions: What is the bond order for C2? Is C2 paramagnetic or diamagnetic? What is the bond order for C2-? Is C2- paramagnetic or diamagnetic? What is the bond order for C2+? Is C2+ paramagnetic or diamagnetic? Which of the three has the longest bond? Which of the three has the ...
#3. Draw the MO diagram for `O_2^+` This is a bit of a curveball, but a perfectly valid problem. Recall that a cation indicates a loss of `1` electron. `O_2^+` is just the ionized form of `O_2`; that is, it's `O_2` with `1` missing electron. The MO diagram will be the same as the MO diagram of `O_2`, except with `1` less electron.
Re: C2+ C2- Therefore, the 8 electrons would fill up both outer orbitals, the s and p orbitals, while for C2- it would only fill up the 1s orbital and have 2 electrons in the 2s orbital. Therefore, C2- has a stronger bond as it is more stable and harder to pull an electron away from it.
What is the molecular orbital configuration of C2? Looking at the appropriate MO diagram, we see that the π orbitals are lower in energy than the σ p orbital. The valence electron configuration for C 2 is (σ2s)2(σ∗2s)2(π2py,π2pz)4 ( σ 2 s ) 2 ( σ 2 s ∗ ) 2 ( π 2 p y , π 2 p z ) 4 .
Molecular orbital diagram for c2. This video shows the mo diagrams of the c2 n2 o2 and f2 molecules. Molecular orbitals are formed combining similar atomic orbitals. Just because some chemical species shows integral value of bond order doesnt mean that it should exist. Molecular orbital diagram for the molecule oxygen o2.
The answer is C2- because of bond orders. When we draw the C2 MO, we have everything up till the PiPy Orbitlal filled, and the next orbital tht would be filled would be the sigma2Pz orbital. As for bond orders it is 1/2* [ (#e- in bonding orbitals)- (#e- in antibonding orbitals)] Doing this, normally just C2 is 1/2* [ (8)-4]=2.
The lowest energy unoccupied molecular orbital is 2pσ, so that is where the extra electron will be added. The electron configuration of the neutral C2 molecule is -- I'll use the notation given to you in the diagram. C2:(1sσ)2(1s* σ)2(2sσ)2(2s* σ)2(2pπ)4. The electron configuration of the C− 2 ion will be.
The molecular orbital diagram for C 2 molecule is :. The electronic configuration of C 2 is K K (σ2s) 2 (σ * 2s) 2 n(2px) 2 n(2py) 2. The C 2 molecule is diamagnetic because all electrons are paired there are no unpaired electrons.
Answer (1 of 6): Bond order is the number of Chemical bonds between a pair of atoms and indicates the stability of a bond. In a Covalent Bond ( as in case of C2 ) between two atoms, a single bond has a bond order of one, a double bond has a bond order of two, a triple bond has a bond order of th...
Use MO diagrams to place C2^- ,C2, C2^+ in order of the following properties: (b) Increasing bond length a) C2^- C2 C2^+ b) C2^- C2^+ C2 c) C2 C2^- C2^+ d) C2 C2^+ C2^- e) C2^+ C2 C2^- f) C2^+ C2^- C2. Learn this topic by watching MO Theory: Bond Order Concept Videos. All ...
Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ...
If you see the MO diagram , there are two unpaired electrons in the p-pi BO. This is what makes C2 unstable. In order to stabilize, it needs to share these ...5 answers · 8 votes: C2 exists, but only above 3,642 °C (6,588 °F) i.e. in vapor state






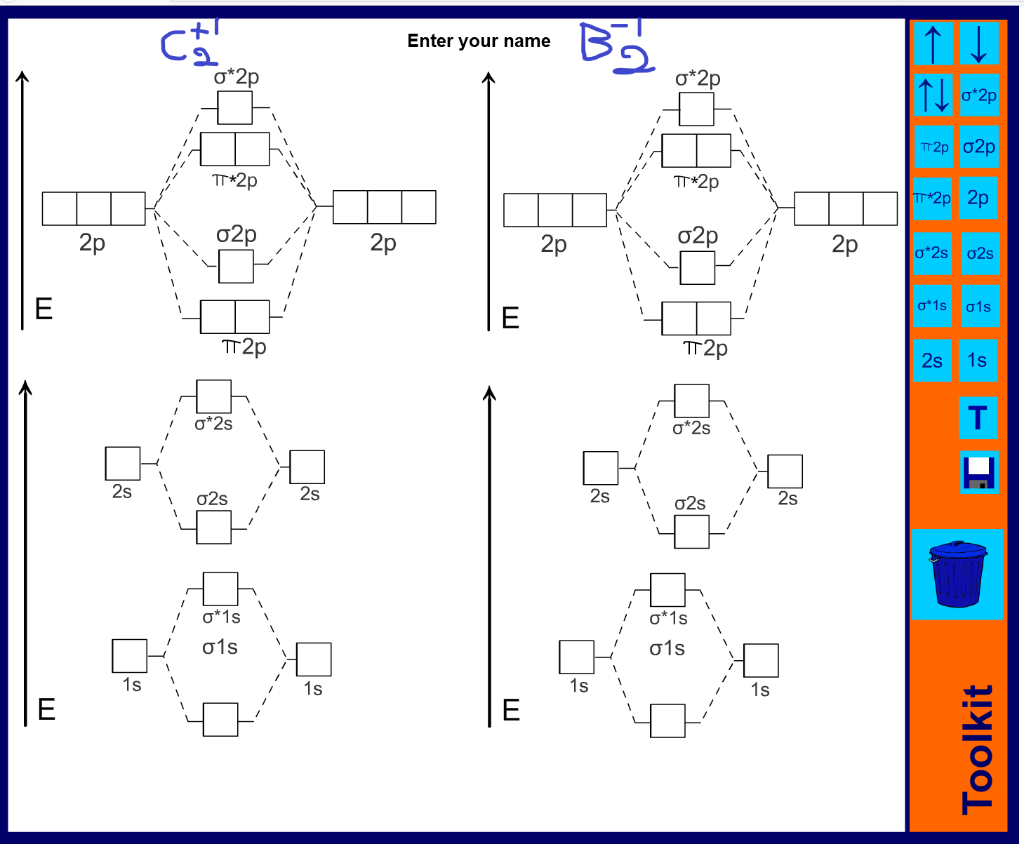
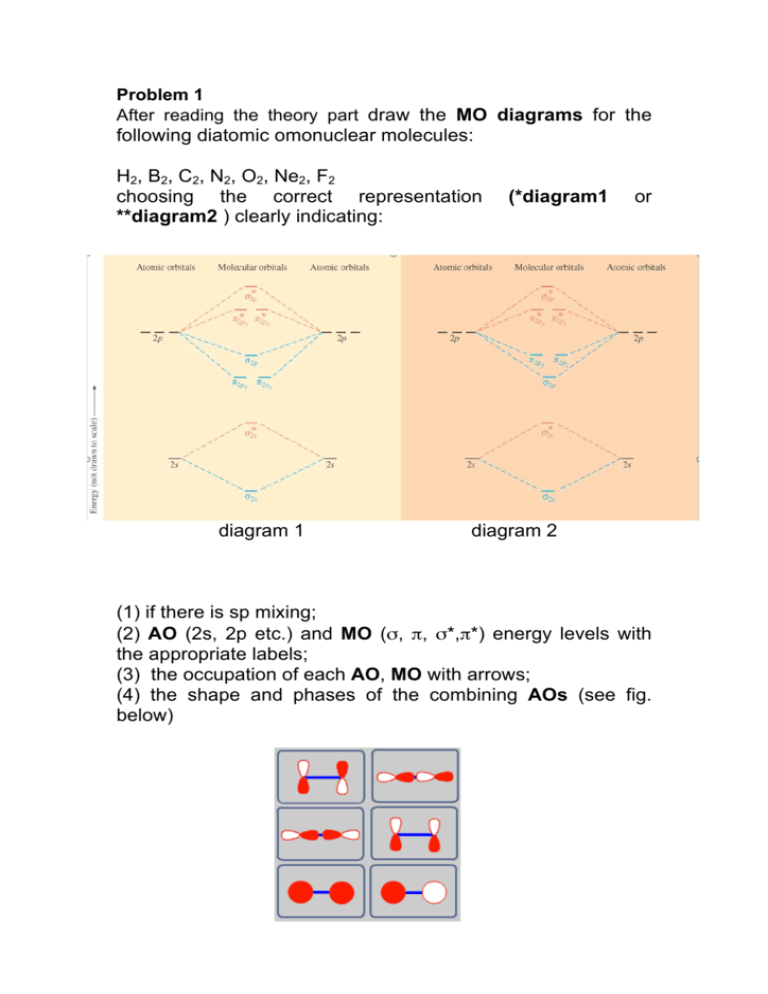



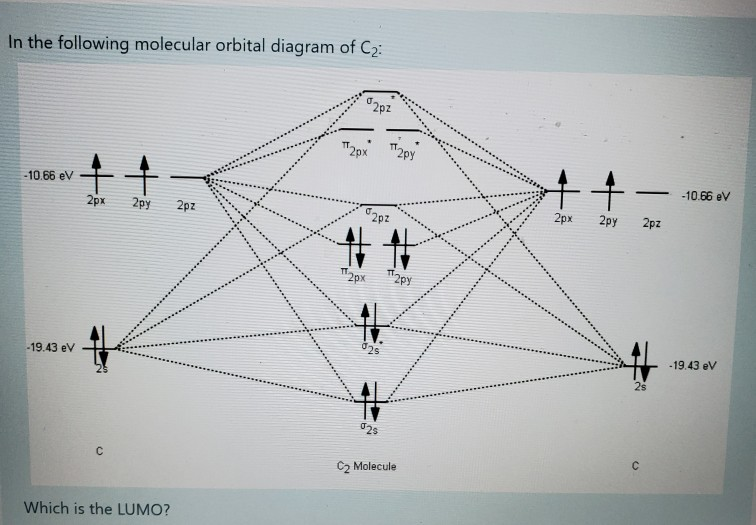

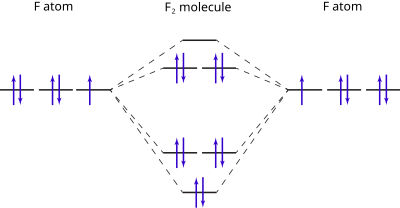


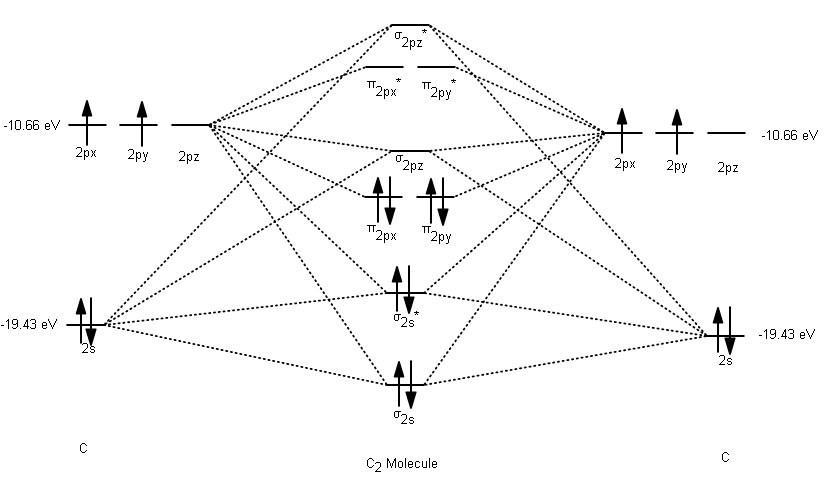

0 Response to "39 mo diagram of c2"
Post a Comment