39 hr diagram lab answers
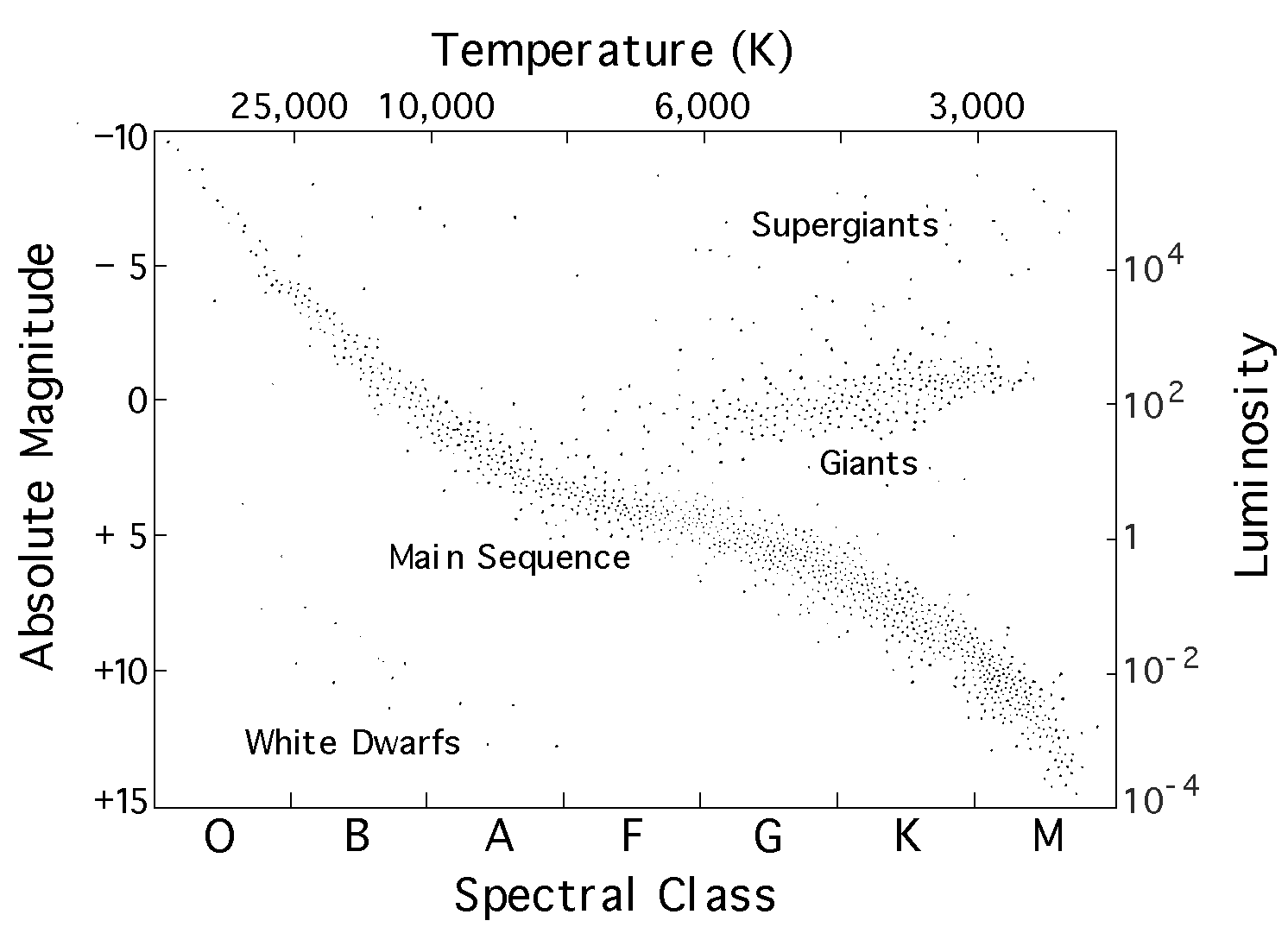
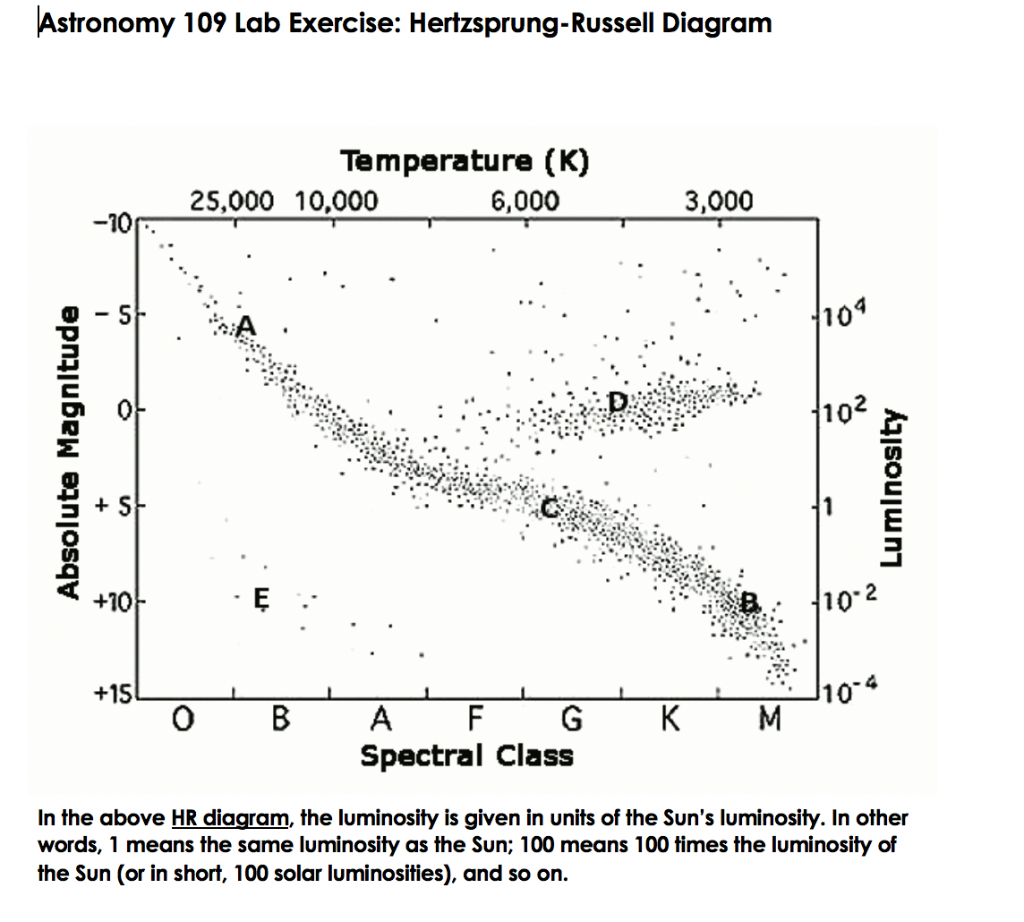
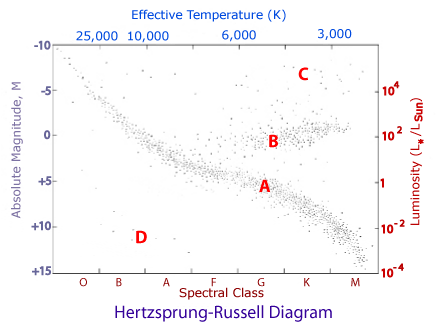
The location of the hottest stars on the HR diagram. The location of the coolest stars on the HR diagram. The location of the brightest stars on the HR diagram. HR Diagram. A graph that shows the relationship between stars temperature…. Left. The location of the hottest stars on the HR diagram. 18 Terms. Earth Sciences questions and answers. Astronomy 109 Lab Exercise: Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Temperature (K) 25,000 10,000 6,000 3,000 4104 o Absolute Magnitude Luminosity 110-2 +15 Spectral Class In the above HR diagram, the luminosity is given in units of the Sun's luminosity. In other words, 1 means the same luminosity as the Sun; 100 means ...
Answer the questions using the above HR Diagram 1. What factor affects the color of a star? 2. What factor affects the luminosity of a star? 3. What is the approximate surface temperature of the sun? 4. Is the surface temperature of white dwarf stars higher or lower than red super giants? Sun

Hr diagram lab answers
5.) Explain in 1-2 sentences what the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram shows (1 point). The HR Diagram shows the relationship between the brightness and temperature of stars. The majority of stars follow a main sequence trend line from red, cold, and dim to blue, hot, and bright with a few outliers like white dwarfs and red giants. The H-R diagram is a graph of star brightness versus star temperature. When many stars are plotted on an H-R diagram, it is found that they fall into groups. These groupings indicate star sizes and are clues to how the stars change during their lifetime. The measure of star brightness used in the H-R diagram is termed absolute magnitude. a line running from the lower right to the upper left of the HR diagram, a region called the main sequence. In this lab, we will explore the relationship between stellar classi cation and stellar properties to develop our own H-R Diagram. We will also use a pre-existing H-R Diagram to explore the properties of the di erent classes of stars.
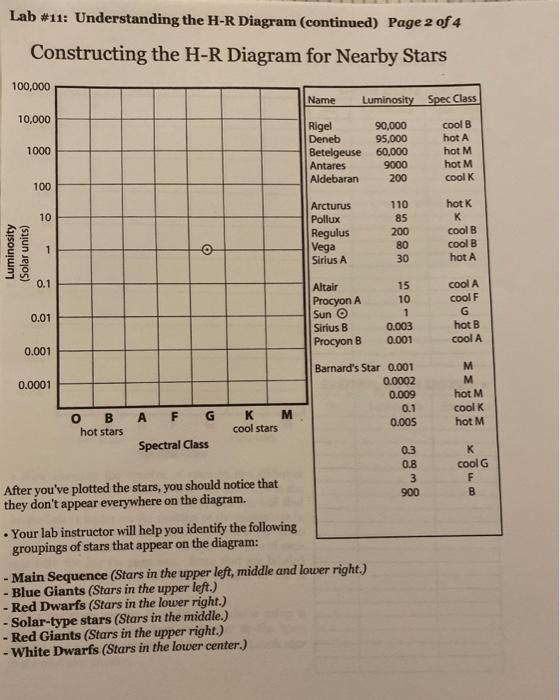
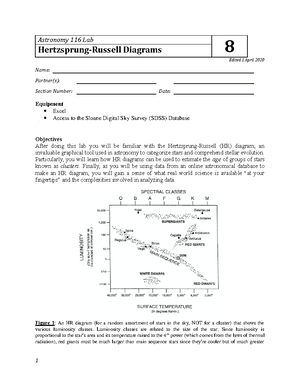
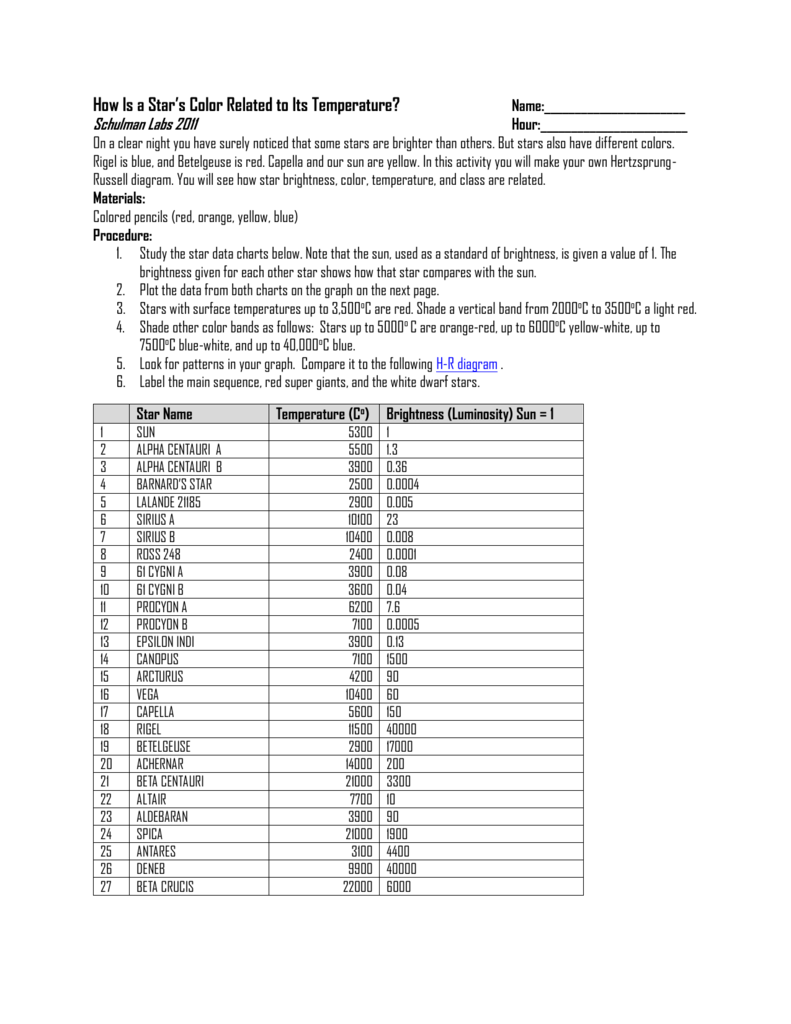
Hr diagram lab answers. Lab: H-R Diagram. Purpose: In this lab we will investigate the relationship between the temperature, brightness and diameter of stars. Introduction. The H-R Diagram is a tool that astronomers use to classify stars based on their luminosity, magnitude, temperature, spectral class and evolutionary stage. Lab # 11: Understanding the H-R Diagram & Stellar Evolution: Purpose: To learn how astronomers classify stars using luminosity & temperature. To construct a H-R Diagram to help understand stellar evolution. Method: Luminosity = Brightness x Distance. Temperature is a measure of heat energy. Select H-R diagram. Introduction: In the early 1900s, two astronomers—Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell—independently made a graph comparing star luminosity and temperature. This graph, now known as a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, or H-R diagram, is still used today to classify stars into groups. The purpose of this lab is to have you identify the main characteristics used to classify stars, and the five main types of stars. You will also become familiar with the use of the Hertzsprung-Russell (HR) diagram used for the classification of stars.
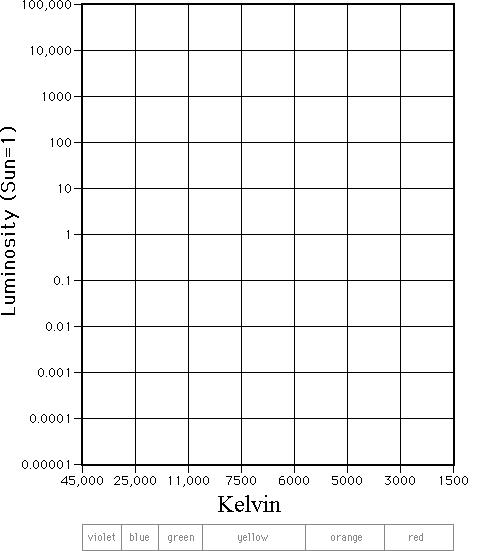
HR DIAGRAM ACTIVITY. NAME _____ DATE _____ HOUR ___ The Hertzsprug- Russel diagram (H-R) is a graph where a star's temperature is plotted against its brightness. From this diagram you can determine star properties as well as its life stage. Purpose. To classify stars. Material. s. Star chart, graph, colored pencils. Procedure Astronomy Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Lab study guide by Savkingham includes 23 questions covering vocabulary, terms and more. Quizlet flashcards, activities and games help you improve your grades. H. R. Diagram Lab Directions Step #1: Look at the chart on the next page to identify each star's temperature and luminosity. Plot the characteristics of each star on the chart titled, "Characteristics of Stars". Be sure to label each star's name next to its data point on the chart. Step #2: The color that a star appears is based upon its ... 7. According to the HR diagram, a massive star with a surface temperature of 20,000 K that is nearly a million times brighter than the sun would mostly likely be classified as a _____ 8. Which type of star is dimmer than the Sun? _____ 9.
Unformatted text preview: Answer Sheet ASTR 100 - Spring 2016 Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Online Lab • Print out this answer sheet, and use it to record your work for the online lab.• Save a copy of your answer sheet as a pdf file or as jpeg images, and upload your work on Compass2g by clicking on the title Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Online Lab as it appears under the Online Labs tab. Transcribed image text: HR Diagram 106 1000 R6 100 RG) blue giants 10 5 10 R Supergiants (I) 104 Instability Strip red giants Dwarfs (V) 103 1 RO Giants (III) 102 Luminosity (Lo) 101 0.1 RG 100 10 -14 0.01 Re 10-24 red dwarfs 10-30.001 R White Dwarfs 10-4 40000 20000 10000 5000 2300 Temperature (K) Options x-axis scale: temperature y-axis scale: luminosity show main sequence show isoradius ... Lab #6. The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram and Stellar Evolution . Students explore the basic phases of stellar evolution on and beyond the Main Sequence, and learn to utilize a Hertzsprung-Russell (color-magnitude) diagram to understand the relationship between fundamental parameters for stars such as mass, luminosity, temperature, and age. 4. Measure the diameter of each star and place them in the H-R Diagram Graph according to their size and color. 5. Tape or glue the stars to the diagram. 6. If you have more than one star that looks alike in diameter and color, group them in a small area on the graph. 7. Use the graph to answer the questions. Teaching Module developed by Karri ...
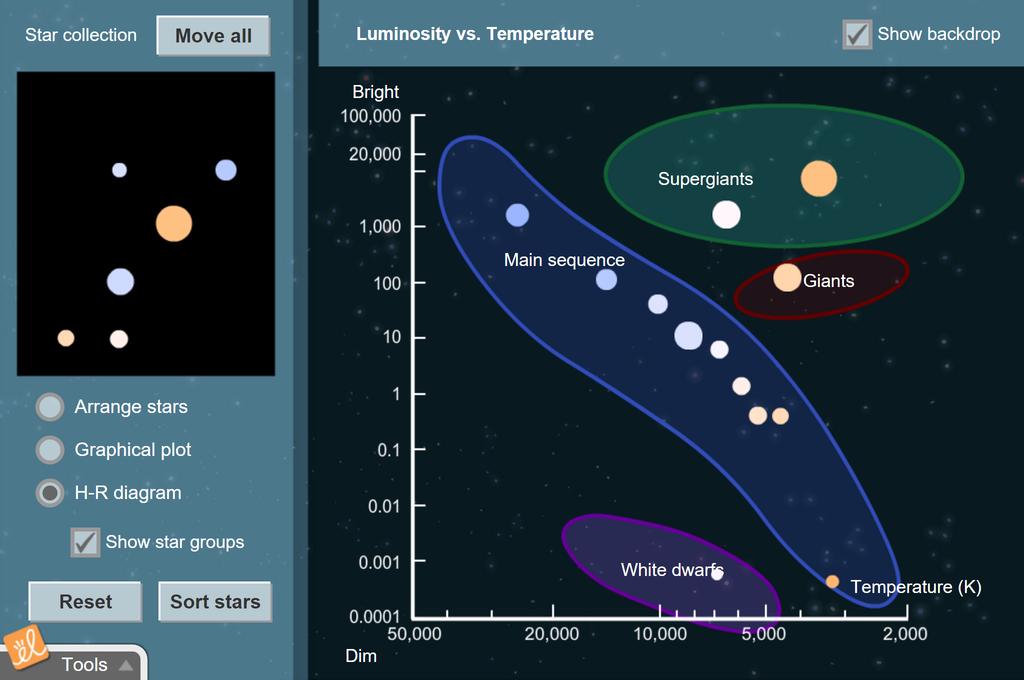
A collection of stars visible from Earth can be arranged and classified based on their color, temperature, luminosity, radius, and mass. This can be done using one or two-dimensional plots, including a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram of luminosity vs. temperature. Time's Up! As a guest, you can only use this Gizmo for 5 minutes a day.
Created Date: 5/4/2015 9:15:33 AM
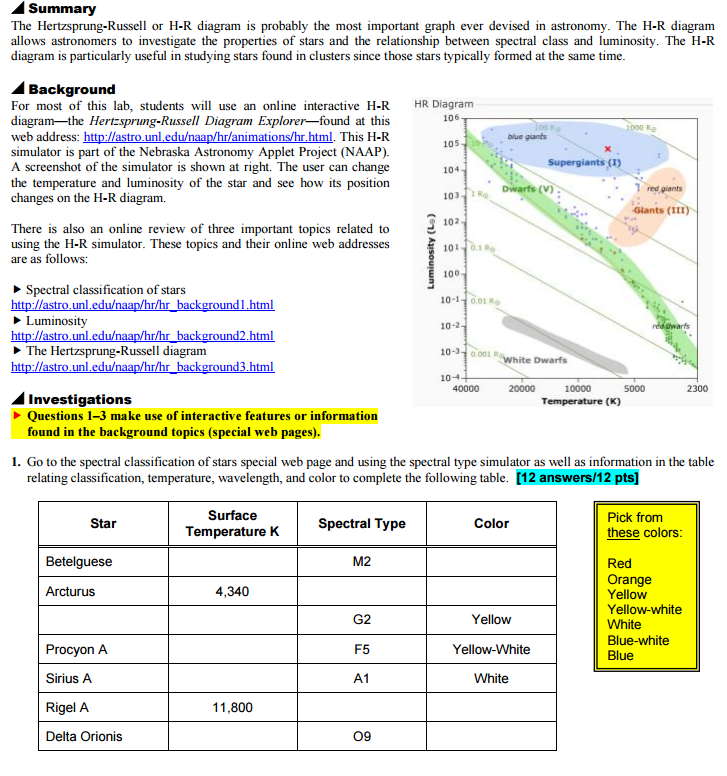
Video assists students with navigating the HR Diagram simulator used in completing the Module 7 lab activity. This focuses on the HR Diagram simulator.
HR Diagram Lab. Course: Astronomy Of Stars And Galaxies (AST 132) Name: Adele Harris. HR Diagram - Student Gui de. Background Information. W ork through the background sections on Spec tral Classification, Luminosi ty, a nd the. Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram. Then complete the following questions related to the background.
Lab 6 The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram and Stellar Evolution 6.1 Introduction On a clear, dark night, one might see more than two thousand stars. Unlike our distant ancestors, we recognize that each one is a huge ball of hot gas that radiates energy, like our own (very nearby) star, the Sun. Like the Sun, the stars shine by converting hydrogen
The short video explains how to read the different axes of the H-R diagram. There are 3 questions related to the H-R diagram which students will answer on their lab sheet. RESEARCH IT! The research station will allow students to go online and interact by categorizing stars on an H-R diagram according to brightness and temperature.
People also ask hr diagram lab answer key. What two criteria is the HR diagram based on? The two primary characteristics of the HR diagram are temperature and luminosity. What relationship is shown on the HR diagram? The Hertzsprung\u2013Russell diagram, abbreviated as H\u2013R diagram, HR diagram or HRD, is a scatter plot of stars showing the ...
7. $1.75. PDF. This is a bingo game activity for students to play while reviewing the HR Diagram. This download includes 25 different bingo cards for students, 2 HR Diagrams for reference during the game, and 24 questions with answers. Throughout the game students will practice looking at a stars spectral class, t.
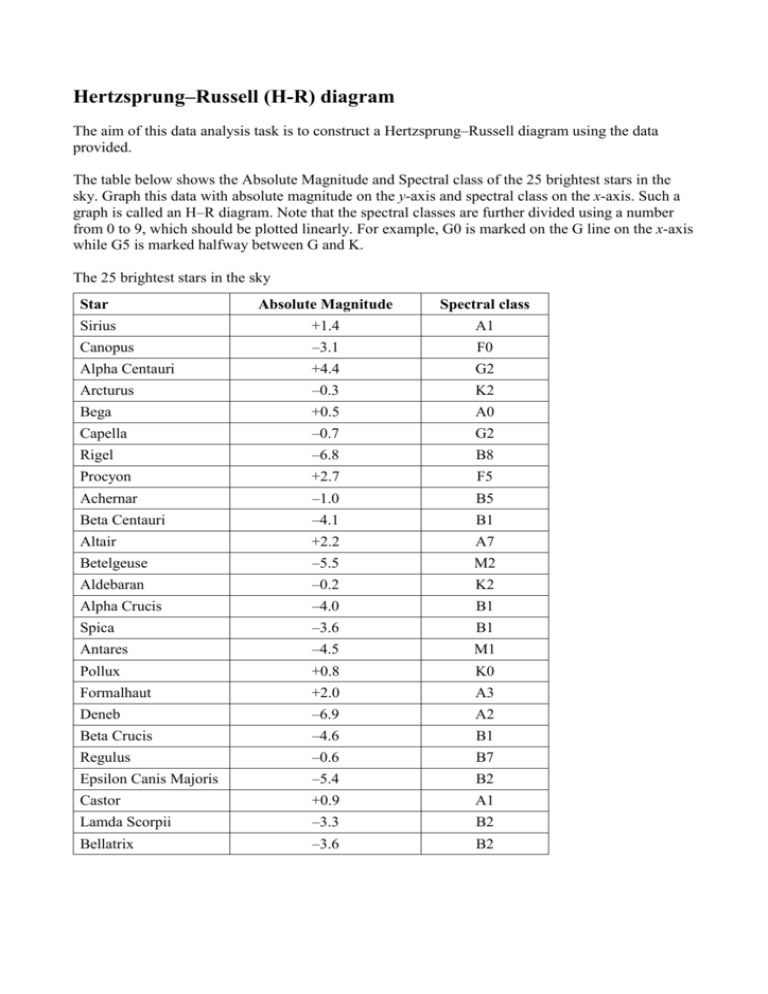
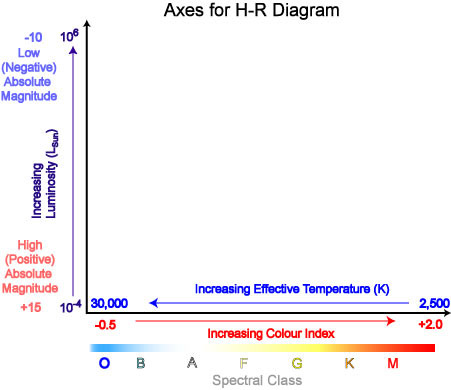
The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is one of the most important tools in the study of stellar evolution.Developed independently in the early 1900s by Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell, it plots the temperature of stars against their luminosity (the theoretical HR diagram), or the colour of stars (or spectral type) against their absolute magnitude (the observational HR diagram, also known ...
The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram (or HR diagram) is constructed in logarithmic coordinates. In this graphic construction, each star is a point marked on the ordinate by its brightness (luminosity or absolute magnitude) and on the abscissa by its spectral type (or surface temperature). By making such a graph for a cluster of stars, H.N. Russell publishes an article in Nature in 1914 where he ...
2019 H-R Diagram Answer Key Vocabulary: giant, H-R diagram, luminosity, main sequence, star, supergiant, white dwarf Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) [Note: The purpose of these questions is to activate prior knowledge and get students thinking. Students are not expected to know the answers to the Prior Knowledge Questions.] 1. ...
a line running from the lower right to the upper left of the HR diagram, a region called the main sequence. In this lab, we will explore the relationship between stellar classi cation and stellar properties to develop our own H-R Diagram. We will also use a pre-existing H-R Diagram to explore the properties of the di erent classes of stars.
The H-R diagram is a graph of star brightness versus star temperature. When many stars are plotted on an H-R diagram, it is found that they fall into groups. These groupings indicate star sizes and are clues to how the stars change during their lifetime. The measure of star brightness used in the H-R diagram is termed absolute magnitude.
5.) Explain in 1-2 sentences what the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram shows (1 point). The HR Diagram shows the relationship between the brightness and temperature of stars. The majority of stars follow a main sequence trend line from red, cold, and dim to blue, hot, and bright with a few outliers like white dwarfs and red giants.



















0 Response to "39 hr diagram lab answers"
Post a Comment