38 what is the maximum number of electrons that can occupy a box in an orbital filling diagram
Draw the molecular orbital diagram for B2 + (this is not B-B. it has an electron missing, so its B-B cation!) The number of unpaired electrons in the B2+ molecule is 2 (two) 1 (one) 3 (three) zero ; Question: Draw the molecular orbital diagram for B2 + (this is not B-B. it has an electron missing, so its B-B cation!) The number of unpaired ... What is the maximum number electrons that can occupy any d orbital?, An individual d-orbital can hold no more than 2 opposite-spin electrons.Individual orbitals can hold no more than 2 electrons each, regardless of the type of orbital you've got. The d-subshell is comprised of 5 d-orbitals, which means it can hold a maximum of 10 electrons, 2 from each d-orbital.
Answer (1 of 2): Using Hunds rule, aufbau principle and pauli exclusion principle, one can order the electrons in an atom into orbitals in order of lowest energy to highest energy. Determine the number of electrons in an atom by looking at a periodic table. For example, carbon has 6. Aufbau princ...

What is the maximum number of electrons that can occupy a box in an orbital filling diagram
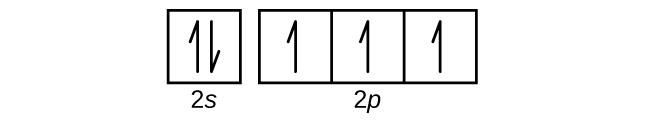
Each box represents one orbital, and an orbital can only have a maximum number of two electrons. There are three 'p' orbitals, and on the left side, it is shown how the 'p' orbitals are filled. The orbital names s, p, d, and f describe electron configuration. These line groups are called sharp, principal, diffuse, and fundamental. The orbital letters are associated with the angular momentum Plasma (from Ancient Greek πλάσμα 'moldable substance') is one of the four fundamental states of matter.It consists of a gas of ions – atoms or molecules which have at least one orbital electron stripped (or an extra electron attached) and, thus, an electric charge.
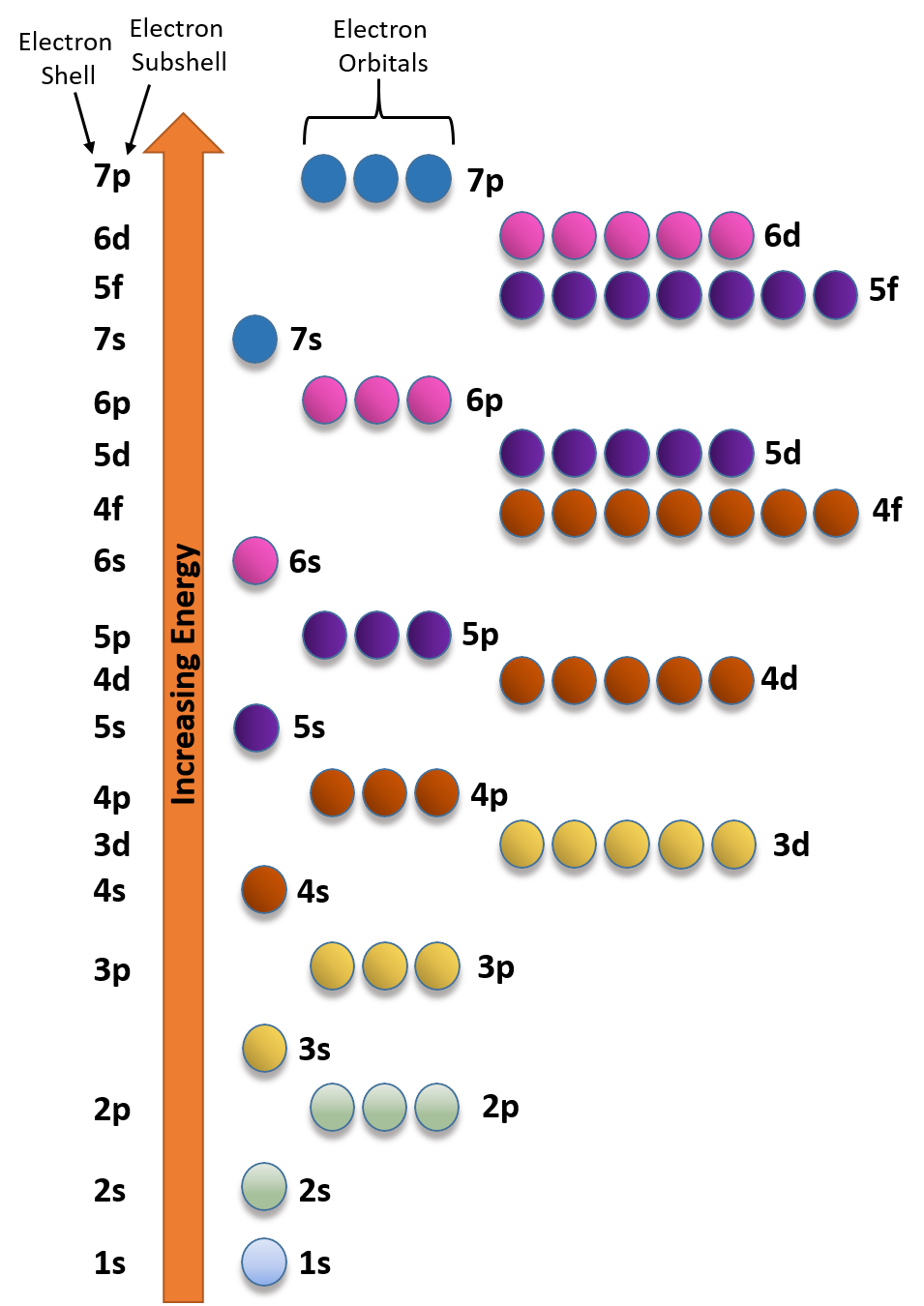
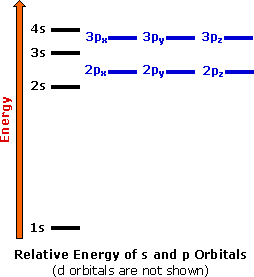
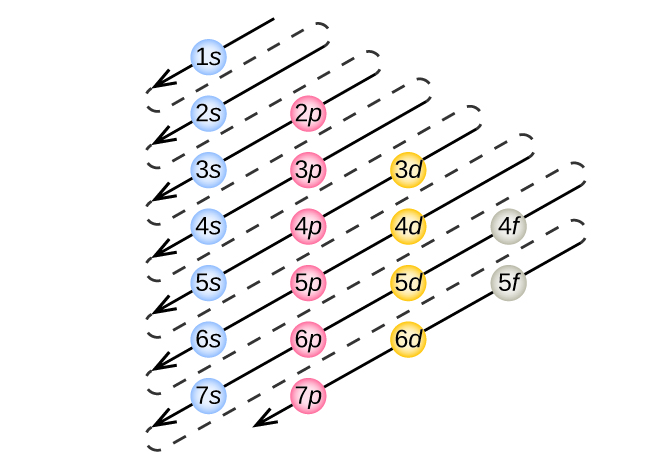
What is the maximum number of electrons that can occupy a box in an orbital filling diagram. However, I was previously taught that the maximum number of electrons in the first orbital is 2, 8 in the second orbital, 8 in the third shell, 18 in the fourth orbital, 18 in the fifth orbital, 32 in the sixth orbital. I am fairly sure that orbitals and shells are the same thing. The three-dimensional space, present around the nucleus of an atom, where the probability of finding an electron is maximum, is called the orbit. Each orbital is associated with a fixed number of electrons. E.g. the maximum number of electrons present in s, p, d, and f subshells are 2, 6, 10, and 14 respectively. Electronic Configuration In this case, the "x" in ns x and nd x is the number of electrons in a specific orbital (i.e. s-orbitals can hold up to a maximum of 2 electrons, p-orbitals can hold up to 6 electrons, d-orbitals can hold up to 10 electrons, and f-orbitals can hold up to 14 electrons). To determine what "x" is, simply count the number of boxes that you come ... That is the electrons first occupy the lowest energy orbital available to them. Once the lower energy orbitals are completely filled, then the electrons enter the next higher energy orbitals. The order of filling of various orbitals as per the Aufbau principle is given in the figure 2.12 which is in accordance with (n+ l) rule.
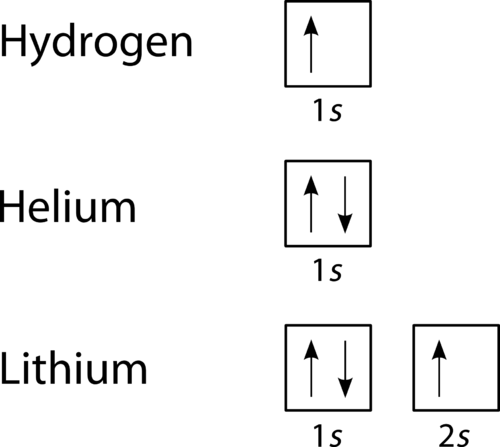
They can also attach to the second type of protein, called the intrinsic proteins. What are 4 methods of transport across the membrane? Simple diffusion - movement of small or lipophilic molecules (e.g. O 2 , CO 2 , etc.) Osmosis - movement of water molecules (dependent on solute concentrations) Facilitated diffusion - movement of large ... A maximum of 2 arrows can be drawn in each box. (because a maximum of 2 electrons can occupy an orbital) When 2 arrows occupy the same box we refer to the electrons as paired, and we must apply the Pauli Exclusion Principle so that these arrows face in opposite directions (one "spin up", one ... What is the next atomic orbital in the series 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p? In order as: 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p… 1s will be filled first, with the maximum of 2 electrons. 2s will be filled next, with the maximum of 2 electrons. 2p will be filled next, with the maximum of 6 electrons. For orbital diagrams, this means two arrows go in each box (representing two electrons in each orbital) and the arrows must point in opposite directions (representing paired spins). The electron configuration and orbital diagram of helium are: The n = 1 shell is completely filled in a helium atom.
Correct answer to the question What is the maximum number of electrons that can occupy a box in an orbital filling diagram at any energy level? a. 2 b. 6 c. 8 d. 14 - hmwhelper.com July 14, 2020 - The 1s orbital and 2s orbital both have the characteristics of an s orbital (radial nodes, spherical volume probabilities, can only hold two electrons, etc.) but, as they are found in different energy levels, they occupy different spaces around the nucleus. Each orbital can be represented by ... Another way to represent an electron configuration is through an orbital diagram. In an orbital diagram, orbitals are represented as boxes and electrons are represented by arrows (↑ or ↓), with two electrons occupying each orbital/box. Orbitals are labeled according to their principle energy levels and sublevels (1s, 2p, etc..). Helium ... You need to fill one shell, starting with shell number one, before filling another. The last shell does not have to be full of electrons. What are the numbers of electrons in each shell? First shell (n = 1) Each energy level may contain a limited number of electrons. the maximum number of electrons ...
The Pauli Exclusion Principle states that, in an atom or molecule, no two electrons can have the same four electronic quantum numbers. As an orbital can contain a maximum of only two electrons, the two electrons must have opposing spins. This means if one electron is assigned as a spin up (+1/2) electron, the other electron must be spin-down ...
The maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated in a sub-shell is 2(2l +1) (where l is orbital quantum number). c) How many maximum number of electrons can that be accommodated in an orbital? Answer: The maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated in an orbital is 2. d) How many sub-shells are present in a principal energy shell?
Chemistry 2.12: Electron Orbitals. What is the maximum number of electrons that can occupy a box in an orbital filling diagram at any energy level? What is the maximum number electrons that can occupy any d orbital? Use an aufbau diagram.
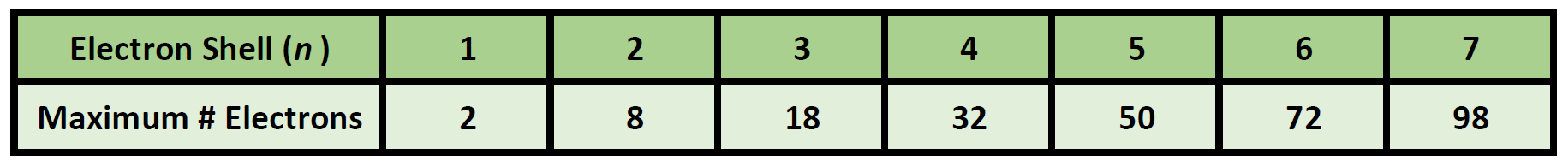
Using the above you can work out the maximum number of electrons that can occupy a shell is 2n 2. Electrons are placed into available shells, starting with the lowest energy level. Each shell must be full before the next starts to fill.
n – Pricipal Quantum Number: represents the energy level the electron is in, linked to the periods of the periodic. Can be 1 to 7 l – Secondary Quantum Number/Orbital Shape Quantum number: represents the shape of the orbital- s, p, f, d. l is a range of n-1. ml – Magnetic quantum number: ...
Find an answer to your question What is the maximum number of electrons that can occupy the hydrogen-like atomic orbitals defined by the quantum numbers: n-3, l… alajahb3812 alajahb3812 01/09/2020 Chemistry High School What is the maximum number of electrons that can occupy the hydrogen-like ...
If #ℓ# is the angular quantum number of subshell then maximum electrons it can hold is #2(2 ℓ + 1)#
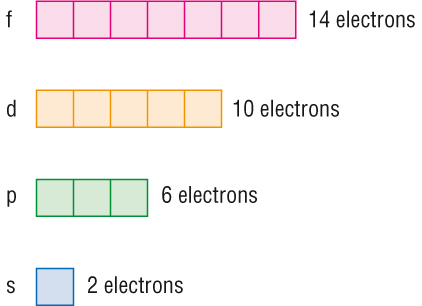
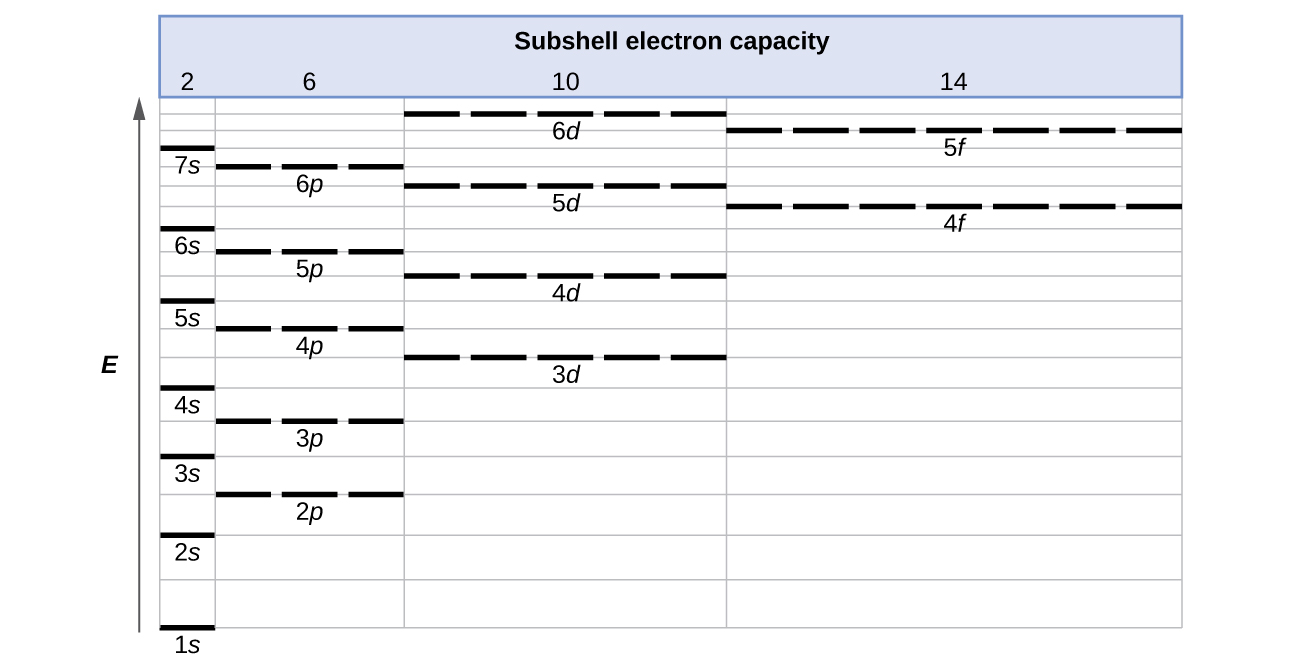
For each principal quantum number, n, there is one s orbital, three p orbitals, five d orbitals and seven f orbitals. Therefore, an s orbital can hold two electrons, a p orbital can hold six electrons, a d orbital can hold ten electrons, and an f orbital can hold 14 electrons. Ground State Electron Configuration. Quantum numbers.
Filling of Electrons in Orbitals. Following rules have to be kept in mind while filling the electrons in orbitals: Rule 1: Each electron shell can only accommodate \(2 \text {n}^{2}\) electrons, where \(\text {n}\) denotes the shell number.
Pauli's Exclusion Principle: no two electrons can have the same spin in one orbital. Hund's Rule: electrons occupy orbitals singly, then, after all orbitals are occupied, pair up in the same sub ...
What is the maximum number electrons that can occupy any d orbital? Use an aufbau diagram. The next two electrons go in to each of p orbital s, with both electrons hav in g the same sp in. Each box represents a s in gle orbital an d the number of sp in s in each box represents the number of electrons in that particular orbital. S-orbital can ...
Electrons fill orbitals starting at the lowest available energy state before filling higher states. Aufbau procedure: Determine number of electrons for the atom of interest. Fill available orbitals starting with the lowest-energy levels first and avoid pairing electrons in a single orbital until it is necessary.
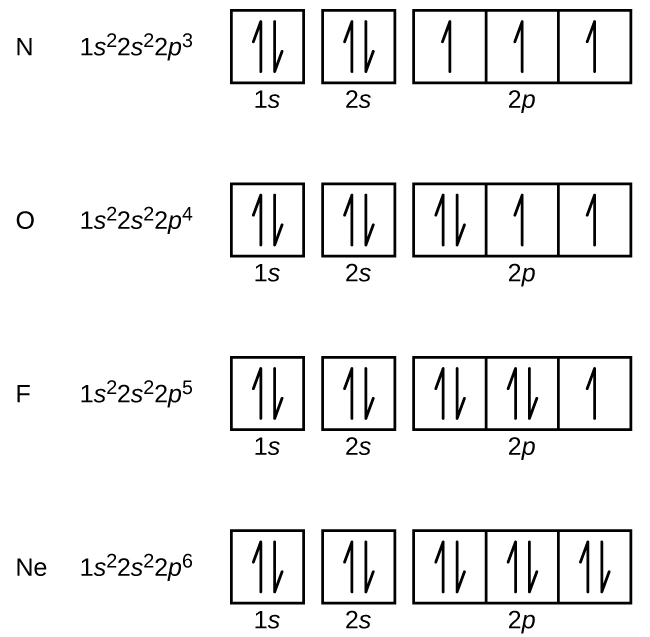
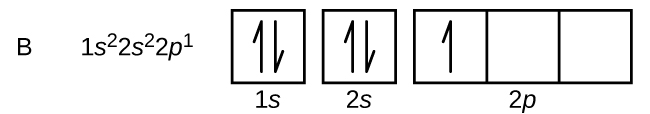
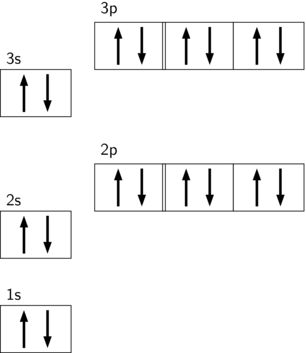
When drawing orbital diagrams, we include empty boxes to depict any empty orbitals in the same subshell that we are filling. Carbon (atomic number 6) has six electrons. Four of them fill the 1s and 2s orbitals. The remaining two electrons occupy the 2p subshell.
where the electrons live. There can be two electrons in one orbital maximum. The s sublevel has just one orbital, so can contain 2 electrons max. The p sublevel has 3 orbitals, so can contain 6 electrons max. The d sublevel has 5 orbitals, so can contain 10 electrons max.
What is the maximum number electrons that can occupy any d orbital? An individual d-orbital can hold no more than 2 opposite-spin electrons. Individual orbitals can hold no more than 2 electrons each, regardless of the type of orbital you’ve got. The d-subshell is comprised of 5 d-orbitals, ...
Oxygen has 8 electrons. The electron configuration can be written as 1s 2 2s 2 2p 4. To draw the orbital diagram, begin with the following observations: the first two electrons will pair up in the 1s orbital; the next two electrons will pair up in the 2s orbital. That leaves 4 electrons, which must be placed in the 2p orbitals.
Start studying CHEM 2.12 QUIZ. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Orbital Diagrams. Electron configuration can be expressed in the form of an orbital diagram, where each orbital refers to a subshell and one-headed arrows are used to depict electrons. Each orbital can accommodate only 2 electrons. s: 1 orbital (2 electrons maximum)
Electrons occupy orbitals in a definite sequence, filling orbitals with lower energies first. But, in the third level the energy ranges of the principal energy levels begin to overlap. As a result, the 4s sublevel is lower in energy than the 3d sublevel, so it fills first.
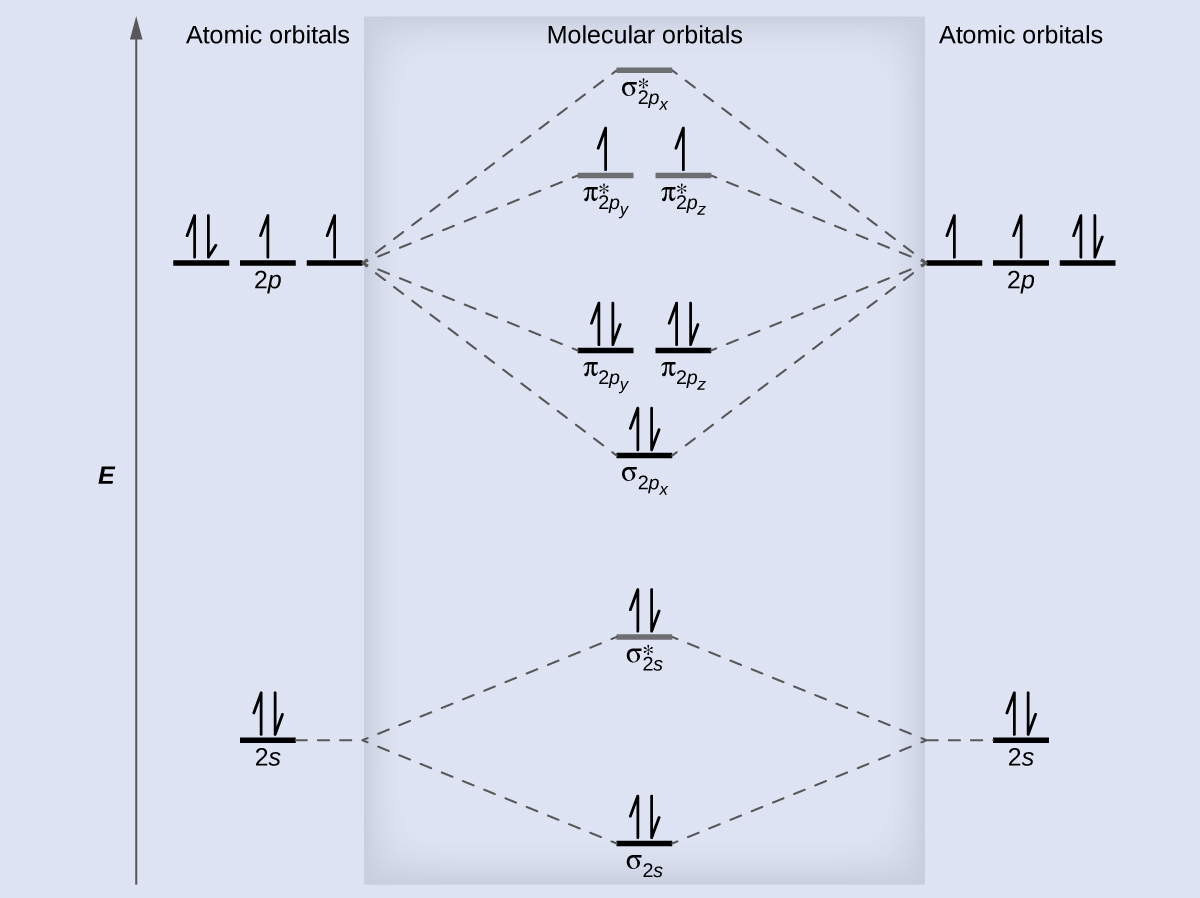
The Molecular orbital can hold two electrons, so both electrons in the H 2 molecule are in 1 s bonding orbital; electron configuration is {matheq}{\left({\text{σ}}_{1s}\right)}^{2}.{endmatheq} We represent this configuration by molecular orbital energy diagram in which a single upward arrow indicates one electron in the orbital, and two arrows ...
Each shell can contain only a fixed number of electrons, up to two electrons can hold the first shell, up to eight (2 + 6) electrons can hold the second shell, up to 18 (2 + 6 + 10) can hold the third shell and so on. The general formula is that the nth shell can hold up to 2(n2) electrons in principle.
The s sublevel has just one orbital, so can contain 2 electrons max. The p sublevel has 3 orbitals, so can contain 6 electrons max. The d sublevel has 5 orbitals, so can contain 10 electrons max. And the 4 sublevel has 7 orbitals, so can contain 14 electrons max.
Both electrons fit into the 1s subshell since s subshells can hold up to 2 electrons; therefore, the electron configuration for helium atoms is 1s2 (spoken together "one-ess-two"). Various subshells host a various maximum number of electrons. Any kind of s subshell can hold as much as 2 electrons; p, 6; d, 10; and f, 14 (Table \(\PageIndex2\)).
The orbitals that have n=2 are 1s, 2s, and 2,p. Both 1s and 2s can have a maximum of 2 electrons while 2p orbital can have a maximum of 6 electrons.
Electron orbitals are the three-dimensional areas around the nucleus of an atom where a particular electron resides. Each orbital can hold two electrons. They are also known as atomic orbitals. Atomic orbitals come in different shapes, depending on the number of electrons the atom has. We will learn about the s orbital, p orbital, d orbital and ...
From here, the third electron shell will have two electrons occupy its 3s orbital (3s 2), followed by another 6 electrons in its 3p orbitals (3p 6). Should a fourth electron shell be required another two electrons can be placed in the 4s orbital (4s 2 ), before adding 10 electrons to the 3d orbital (3d 10 ) as this has a lower energy level than ...
Orbitals are regions within an atom that the electron will most likely occupy. Each subshell has a specific number of orbitals: s = 1 orbital, p = 3 orbitals, d = 5 orbitals, and f = 7 orbitals ...
Only two electrons with different spins can occupy a single orbital. The first of these rules is known as the Pauli exclusion principle , and it states that no two electrons in an atom can have ...
October 22, 2018 - In this, the number of electrons in each shell is continuously written. e.g. Cl (17) = Box method: In this method, each orbital is denoted by a box and electrons are represented by half-headed (↑) or full-headed (↑) arrows. An orbital can occupy a maximum of two electrons. e.g.
Plasma (from Ancient Greek πλάσμα 'moldable substance') is one of the four fundamental states of matter.It consists of a gas of ions – atoms or molecules which have at least one orbital electron stripped (or an extra electron attached) and, thus, an electric charge.
The orbital names s, p, d, and f describe electron configuration. These line groups are called sharp, principal, diffuse, and fundamental. The orbital letters are associated with the angular momentum
Each box represents one orbital, and an orbital can only have a maximum number of two electrons. There are three 'p' orbitals, and on the left side, it is shown how the 'p' orbitals are filled.






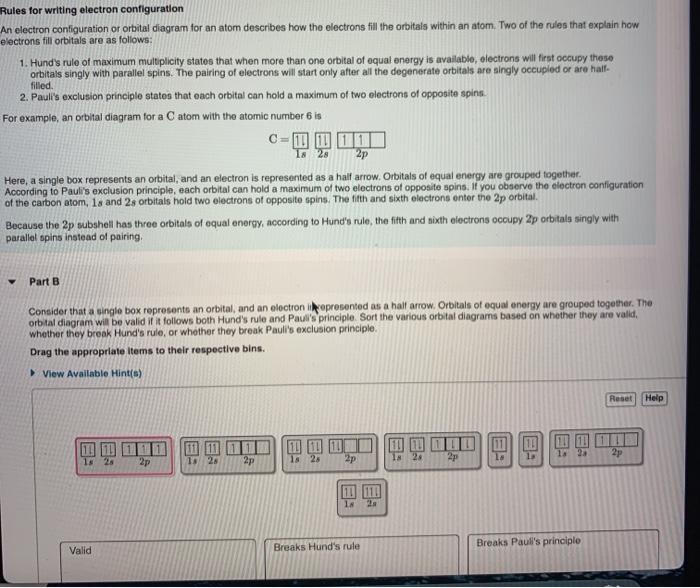
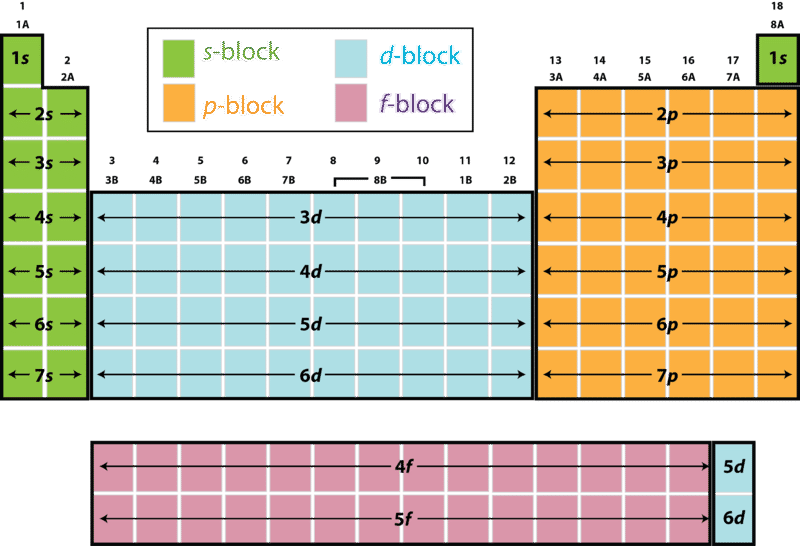
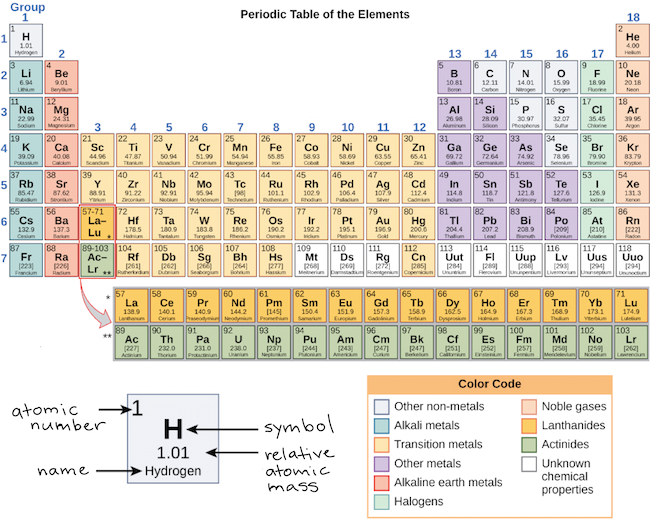
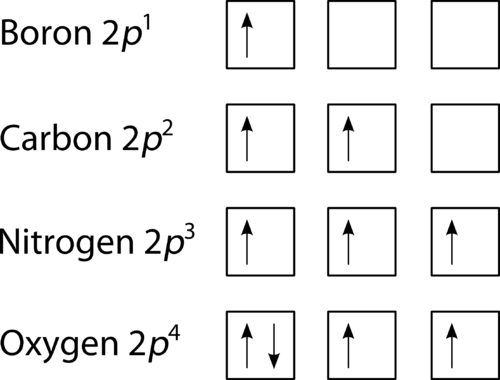










0 Response to "38 what is the maximum number of electrons that can occupy a box in an orbital filling diagram"
Post a Comment