38 sf6 molecular orbital diagram
Molecular orbitals in SF6. Close. 3. Posted by 7 years ago. Archived. Molecular orbitals in SF6. Hi all, I am trying to work out some molecular orbitals for SF6. I know that we do not need to involve the d orbitals and so I am just looking at the sulfur s and p and then the orbitals from the fluorines .
Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified. Megan Lim. Oct 26, 2016 · 3 min read. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding ...
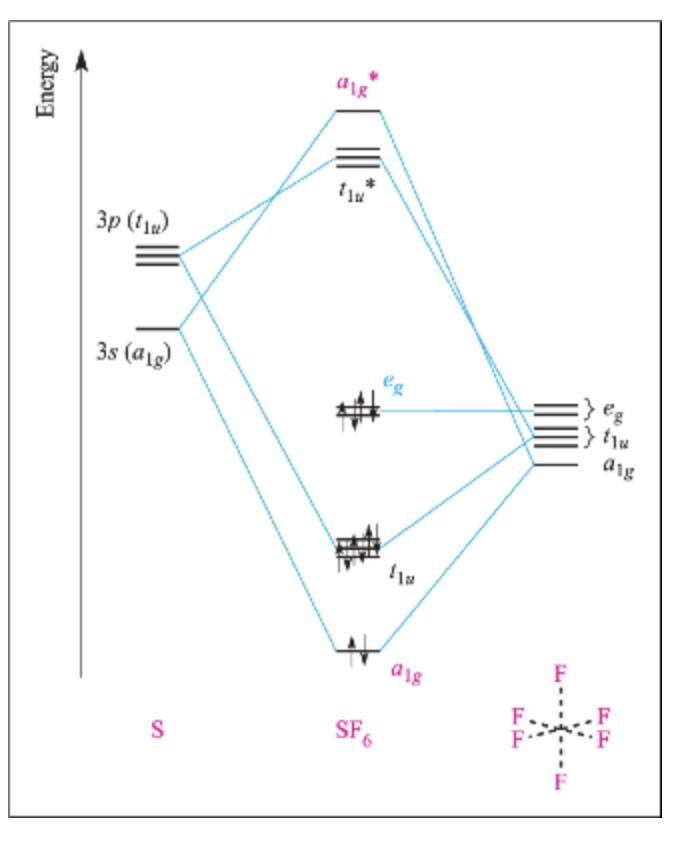
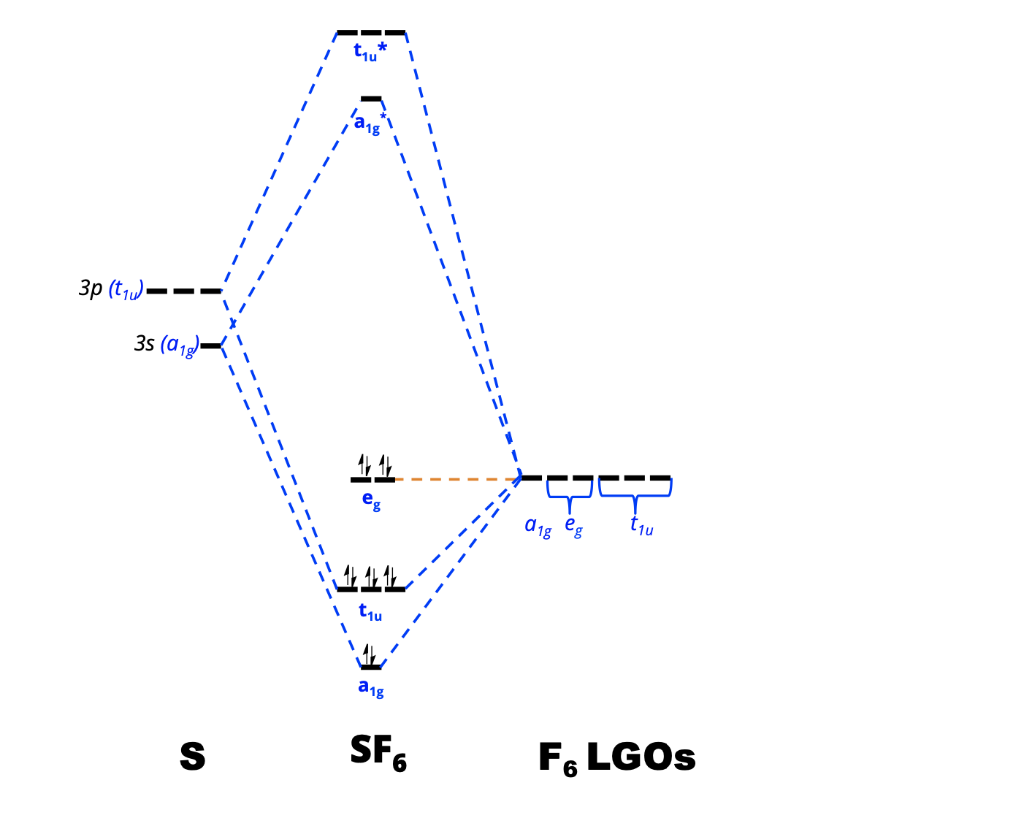
View Notes - 4_MO Diagrams with LGOs_SF6_KEY from CHEM 312 at University of Washington. Names: _ CHEM 312 1. Consider the octahedral compound SF6. a. Assign the symmetry labels to the sulfur 3s and
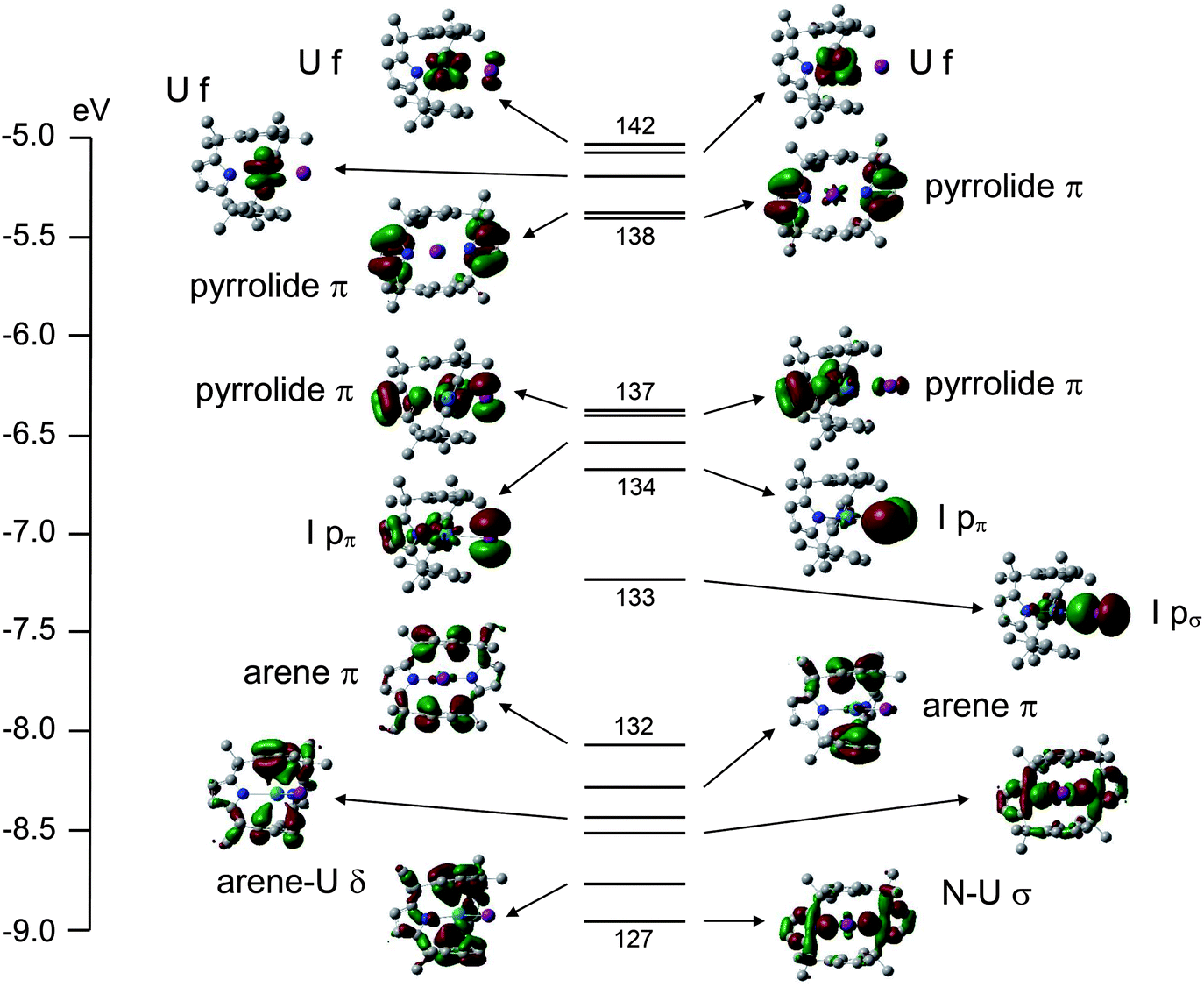
Sf6 molecular orbital diagram
The molecular orbital diagram representing this order of energy levels is shown in fig. Fig. No. 5 Order of Energy Levels for Boron, Carbon, Nitrogen etc. This kind of energy reversal is due to mixing of 2s and 2p orbitals where the energy difference is very close, that is, for B, C, and N atoms. According to the symmetry interactions, the two ...
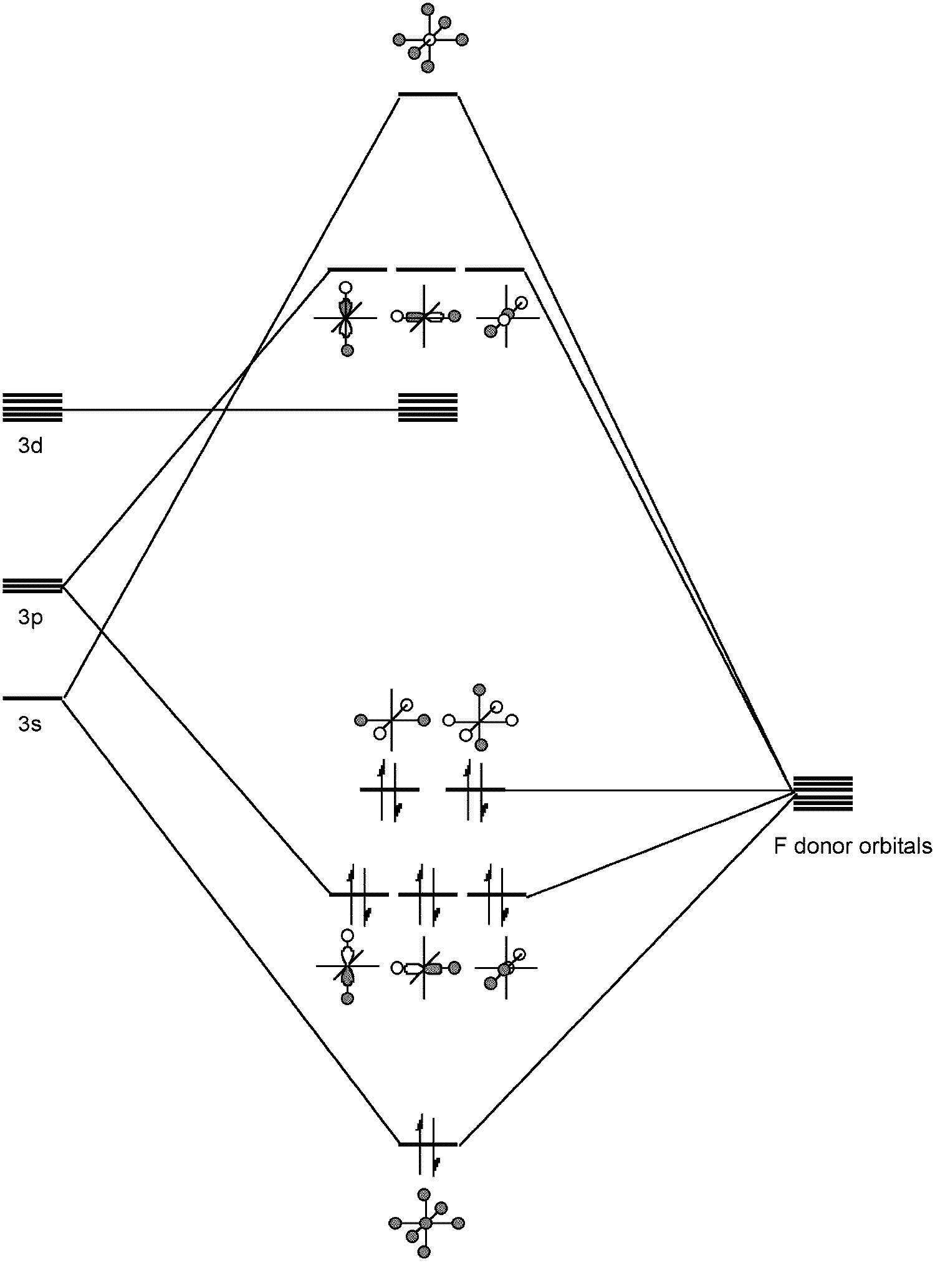
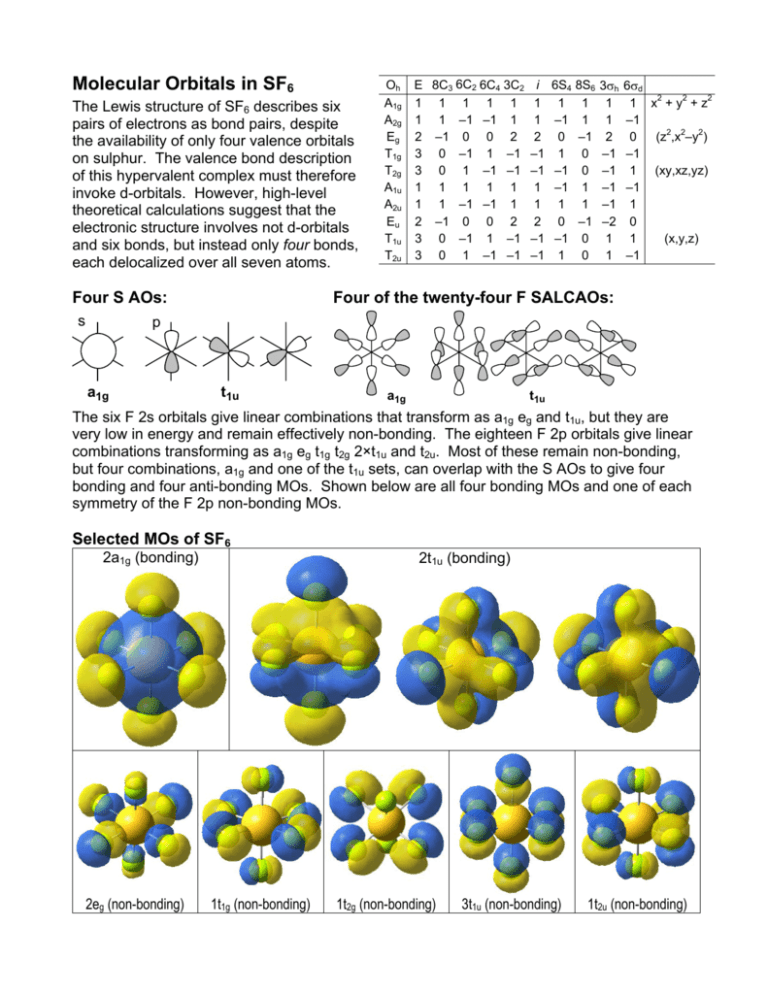
If you limit consideration to hybridization of atomic orbitals, a good reference to see is On the role of d orbitals in sulfur hexafluoride J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1986, 108 (13), pp 3586-3593.. First, it is found that of the 6 valence electrons that atomic sulfur has (two 3s and four 3p), in SF6 a total of 3.1 electrons worth of electron probability density remain in sulfur atomic orbitals.
The new orbitals thus formed are known as hybrid orbitals. More significantly, hybrid orbitals are quite useful in explaining atomic bonding properties and molecular geometry. Let us quickly look at the example of a carbon atom. This atom forms 4 single bonds wherein the valence-shell s orbital mixes with 3 valence-shell p orbitals.
Sf6 molecular orbital diagram.
Figure 9.7. 3: Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules with Only 1 s Atomic Orbitals. (a) The H 2+ ion, (b) the He 2+ ion, and (c) the He 2 molecule are shown here. Figure 9.7. 3 a shows the energy-level diagram for the H 2+ ion, which contains two protons and only one electron.
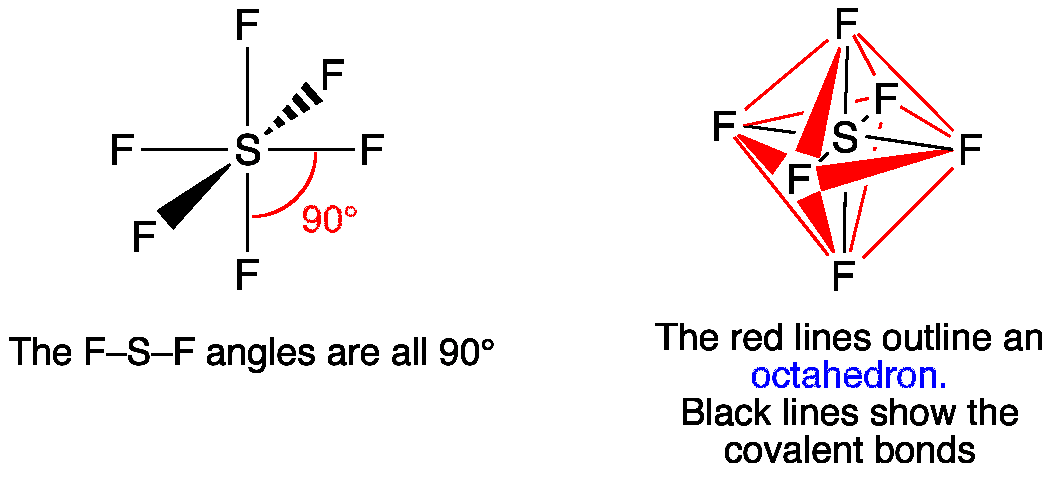
SF6 Molecular Geometry, Lewis Structure, Shape, and Polarity. Sulfur hexafluoride or SF6 is an inorganic, greenhouse gas. It is non-flammable, odourless, and colourless, and is an excellent insulator. It is a hypervalent octahedral molecule that has been an interesting topic of conversation among chemistry enthusiasts.
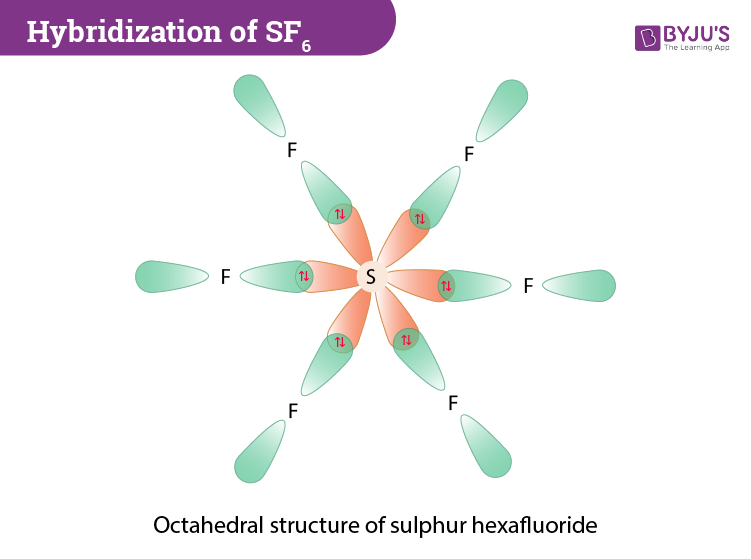
The orbitals involved are 3s, 3p y, 3p y, 3p z and 3dx 2 - y2 and 3d z2. During the formation of SF 6, the sulphur atom which is the central atom in its ground state will have 3s 2 3p 4 configuration.
Molecular Orbitals for Larger Molecules 1. Determine point group of molecule (if linear, use D2h and C2v instead of D∞h or C∞v) 2. Assign x, y, z coordinates (z axis is principal axis; if non-linear, y axes of outer atoms point to central atom)3. Find the characters of the reducible representationfor the combination of
Molecular orbital theory posits the notion that electrons in molecules likewise exist in different orbitals that give the probability of finding the electron at particular points around the molecule. To produce the set of orbitals for a molecule, we add together the valence atomic wavefunctions for the bonded atoms in the molecule.
Molecular Orbitals. Just like the atomic orbitals, molecular orbitals(MO) are used to describe the bonding in molecules by applying the group theory. The basic thought of what is molecular orbitals can be the organized combinations of the atomic orbitals according to the symmetry of the molecules and the characteristics of atoms.
Answer (1 of 6): Here is the solution, > * For O2 molecule, > * For F2 molecule, Thanks for reading.
These hybrid orbitals also influence the molecular geometry, reactivity, and bonding traits of a compound. Hybridization, in tandem with quantum mechanics, is a widely researched topic of modern science. The new hybrid orbitals are different from the original ones on account of energy and arrangement of the outermost orbit of electrons in a ...
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ...
SF6 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization, and MO Diagram SF6 or sulfur hexafluoride is an inorganic and one of the most stable gases that are known in chemistry. This gas has more density than air. The general identification of the gas can't be done because it is odorless and colorless in nature.
Polyatomic Molecular Orbital Theory Transformational properties of atomic orbitals Atomic orbital Transforms as s x2+y 2+z 2 px x py y pz z dz2 z2, 2z 2-x2-y2 dx2-y2 x2-y2 dxy xy dxz xz dyz yz S py • When bonds are formed, atomic orbitals combine according to their symmetry. • Symmetry properties and degeneracy of orbitals and bonds can be ...
O h point group contains 3 C 4, 4 C 3, 9 C 2, 4 S 6, 3 S 4, 3 σ h, 6 σ d and a centre of inversion. Inversion operation is a reflection through the centre of the molecule. In this case, the centre of the molecule is the Sulfur atom. Click the arrow to show an animation of the inversion in 3D. Pointgroup Flow Chart.
(b) These orbitals combine to form a trigonal bipyramidal structure with each large lobe of the hybrid orbital pointing at a vertex. As before, there are also small lobes pointing in the opposite direction for each orbital (not shown for clarity). The sulfur atom in sulfur hexafluoride, SF 6, exhibits sp 3 d 2 hybridization. A molecule of ...
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ...
Answer (1 of 8): Edit for clarity as my original answer was a bit misleading. It's important to note that scientists don't talk about d orbital hybridization in the context of hypervalence anymore. It was a controversial issue for a while but sulfur does not need to use it's d orbitals (in a sig...
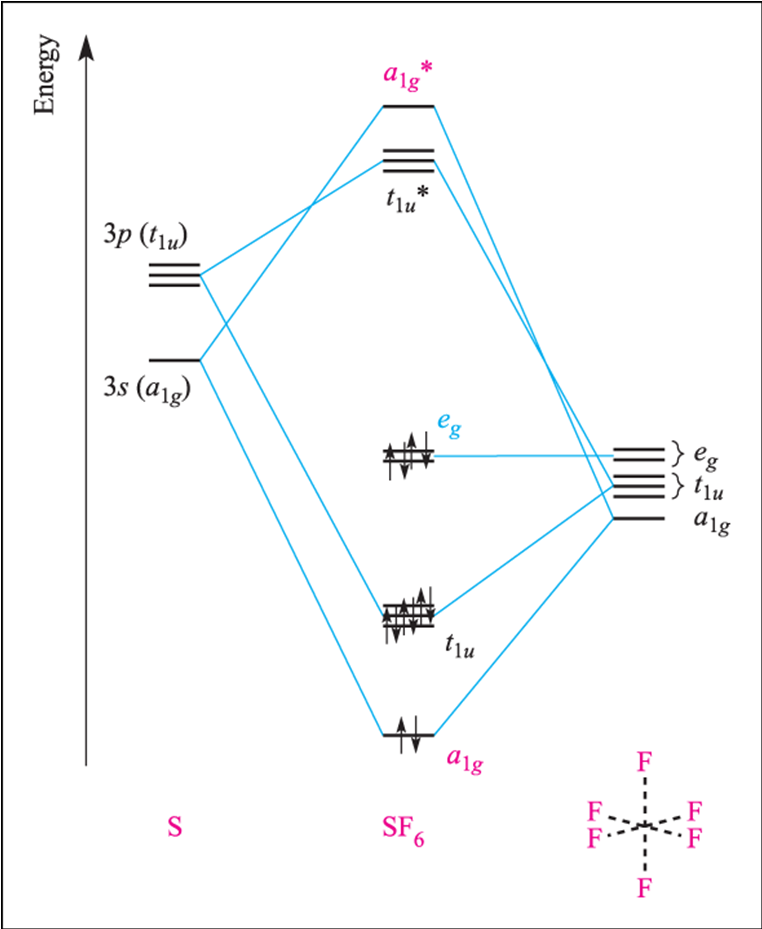
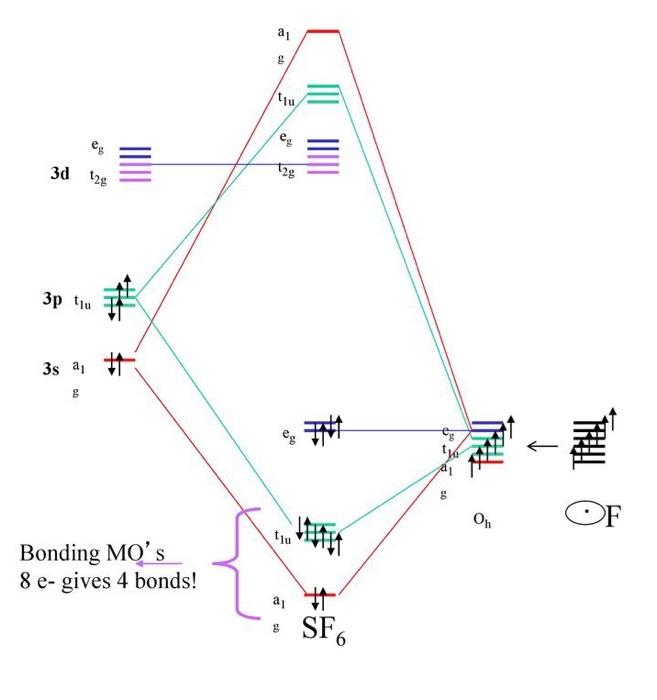
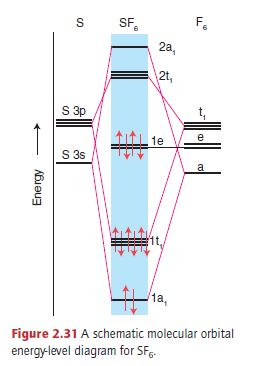
In the construction of the molecular orbital diagram of a polyatomic molecule (SF6), 12 valence electrons are used to occupy 10 MO; account for the origin of the 12 electrons and the 10 MOs.
Molecular Orbital Diagram for polyatomic molecules BeH2 ... Molecular orbital theory(mot) of SF6/CO2/I3-/B2H6 hybridization - Why is the F-F bond in fluorine a p-p ...
SF4 < SF6 < SiH4 c. SF6 < SiH4 < SF4 d. SF6 < SF4 <SiH4 e. SiH4 < SF6 < SF4. SF6 <SF4 < SiH4. Which statement is true? a. The total number of molecular orbitals formed doesn't always equal the number of atomic orbitals in the set. b. When two atomic orbitals come together to form two molecular orbitals, one molecular orbital will be lower in ...
Simple Molecular Orbitals - Sigma and Pi Bonds in Molecules An atomic orbital is located on a single atom. When two (or more) atomic orbitals overlap to make a bond we can change our perspective to include all of the bonded atoms and their overlapping orbitals. Since more than one atom is involved, we refer to these orbitals as molecular orbitals.
1. Generate and reduce a representation with a basis set of the fluorine 2s orbitals of TeF4 and SF6. 2. Construct quantitative molecular orbital diagrams for N2, O2, and F2 using the valence orbital ionization energies (VOIE) taken from photoelectron spectroscopic data. The data for O2 have been "averaged" to eliminate complexities arising ...
From the LCAO point of view this can be viewed as the contribution of higher atomic orbitals (d-orbitals, for example) to the bonding molecular orbitals. In the case of $\ce{SF6}$ the contribution of sulfur atomic orbitals to the bonding states is lower (because most of the electrons are localized on fluorines).
Molecular Orbitals in SF6 The Lewis structure of SF6 describes six pairs of electrons as bond pairs, despite the availability of only four valence orbitals on sulphur. The valence bond description of this hypervalent complex must therefore invoke d- orbitals.
Question: In the Molecular Orbital diagram of SF6 , these sulfur orbitals are non-bonding: px , py , pz dxy , dxz. This problem has been solved! See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading. In the Molecular Orbital diagram of SF 6, these sulfur orbitals are non-bonding: p x, p y, p z. d xy, ...
In the construction of the molecular orbital diagram of a polyatomic molecule sf612 valence electrons are used to occupy 10 mo account for the origin of the 12 electrons and the 10 mos if u 55208


![How is the bonding in the [Au6C(PPh3)6]2+ cluster explained ...](https://i.stack.imgur.com/Y1psc.png)









0 Response to "38 sf6 molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment