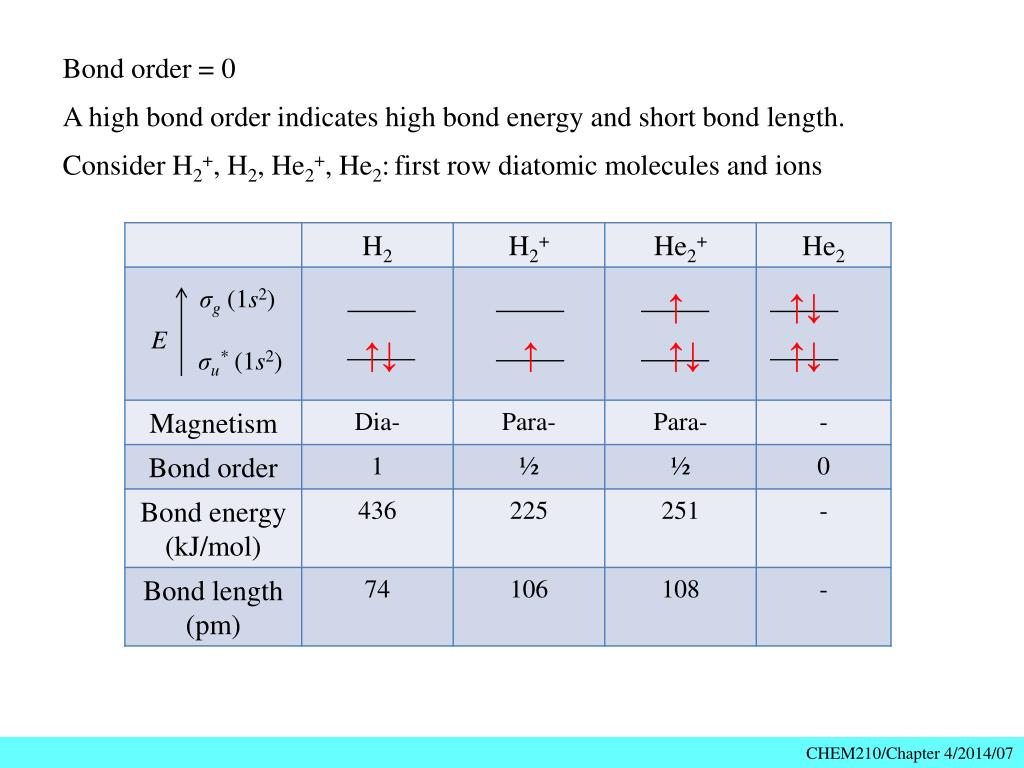
38 molecular orbital diagram for he2+
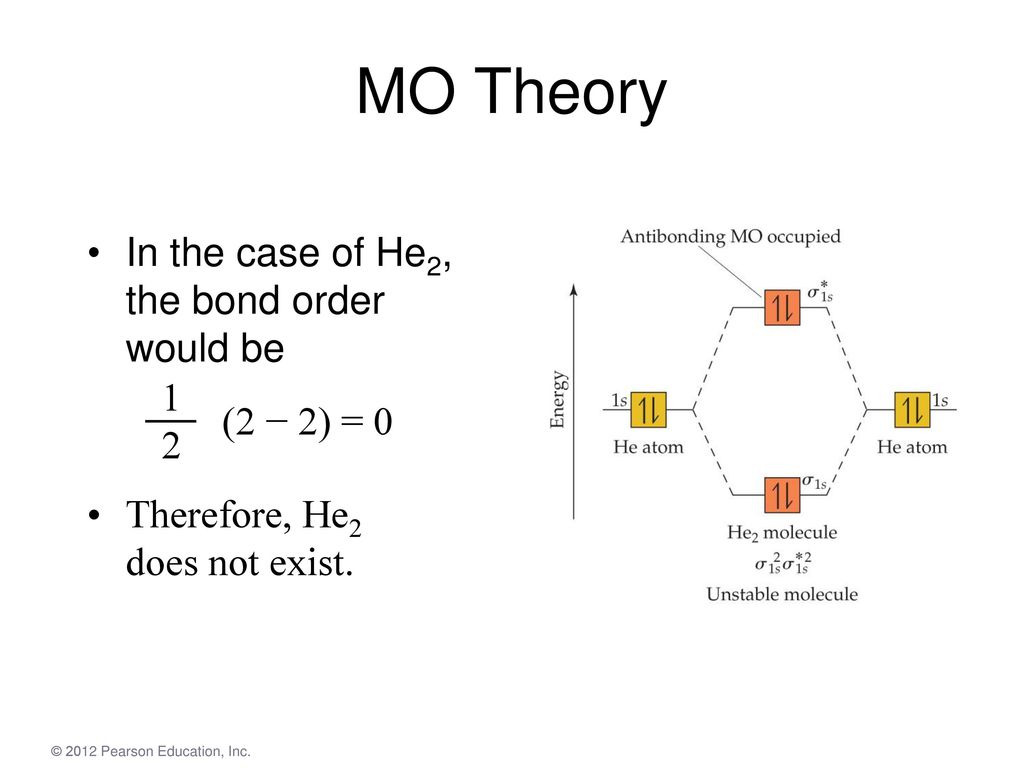
Solution. Verified by Toppr. Electronic configuration of He is 1s 2. Molecular Orbital Diagram for He 2. . is. (Refer to Image) Bond order= 2(No. of electrons in bonding molecular orbital)- (No. of electrons in anti-bonding Molecular orbital) . A molecular orbital explicitly describes the spatial distribution of a single Energy Level Diagrams He2 has bond order 0 [ (2 − 2)/2 = 0], and we can make H+. According to the molecular orbital theory, in a supposed He2 molecule, both the if we draw its MOT DIAGRAM, 2 e's enter the Bonding molecular Orbital and 2 .
A molecular orbital explicitly describes the spatial distribution of a single electron orbitals, and σ∗. 1s is higher in energy. Draw this out using an energy level diagram: 2 He2 has bond order 0 [ (2 − 2)/2 = 0], and we can make H+. 2,. H−.A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical ...
Molecular orbital diagram for he2+
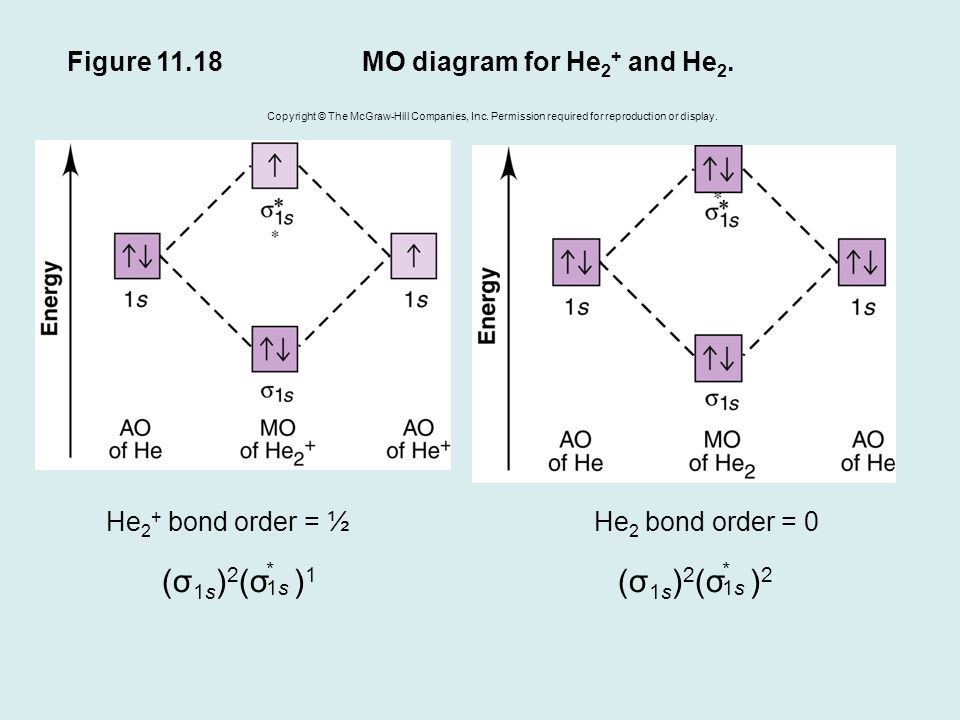
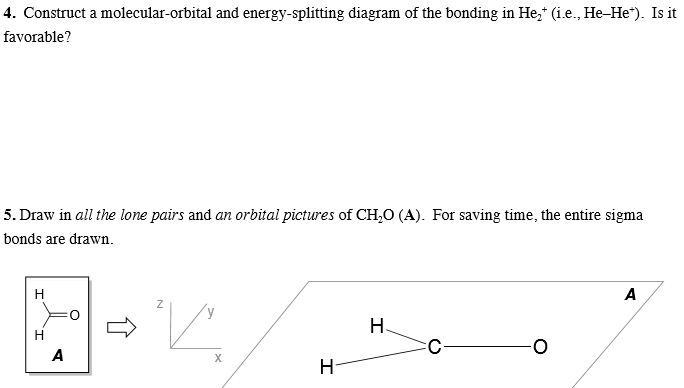
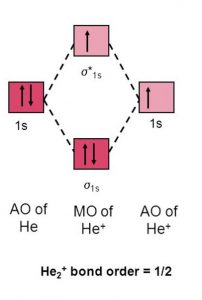
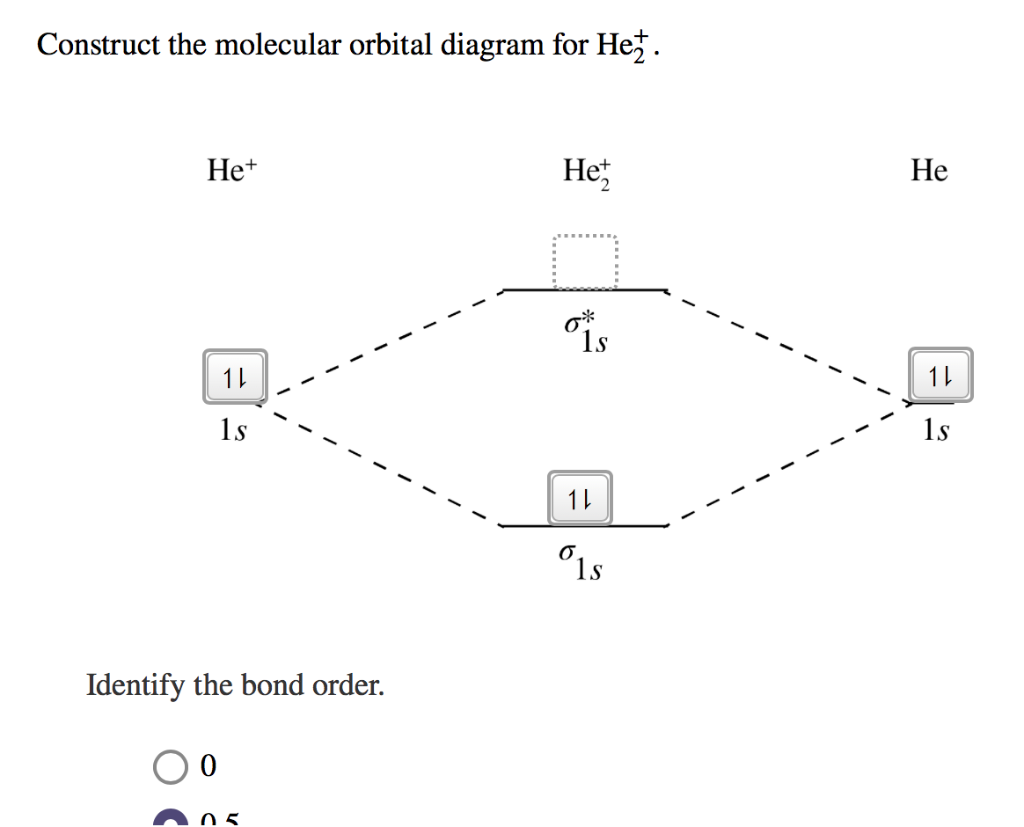
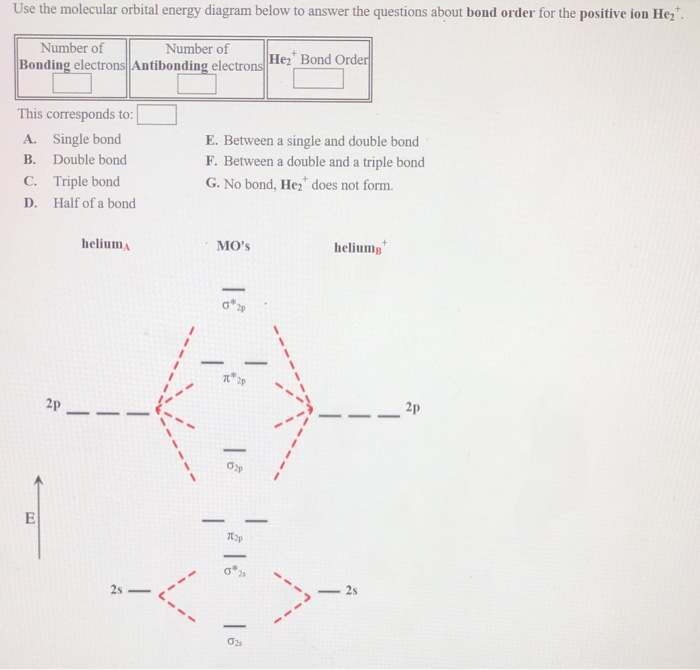
Molecular Orbital Diagram For He2 2+ Two electrons total, both occupy the sigma orbital, two more electrons in bonding than antibonding He2 is not possible. Please note the diagram is for He2+ but the He-H is very similar answered Mar 21 '13 at A molecular orbital explicitly describes the spatial distribution of a single electron orbitals, and ... Problem: Energy-level diagram for the He2+ ion.Which electrons in this diagram contribute to the stability of the He2+ ion? FREE Expert Solution Show answer. 86% (85 ratings) FREE Expert Solution. Recall: The bond order determines the stability of a molecule based on it's molecular orbital diagram. 86% (85 ratings) Problem Details. 1. Problem: Draw MO energy diagrams for the molecular ions H2+ and H Since both molecular ions have a bond order of 1/2, they are approximately equally.Solution: Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He2 + and then identify the bond order. Problem Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He 2 + and then identify the bond order.
Molecular orbital diagram for he2+. on Molecular Orbital Diagram For He2+. He2+ MO diagram. Eg: Li + H; Li has 1s + 2s, while H has 1s. This mix to form a sigma orbital from H1s+Li2s, a sigma* orbital and H1s-Li2s. The bond order of a simple molecule can be determined by looking at the number of electrons in bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. Like electrons in. Bonding in Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules: H2, H2+, H2-, He2, He2+ ... This lesson will discuss the MO Diagram of various Homonuclear Diatomic Species and ... In He2 (dihelium), the two 1s atomic orbitals overlap to create two molecular orbitals: sigma(1s) and sigma(1s)*. You fill these molecular orbitals with the... Answer to: Use molecular orbital theory to determine whether He2 2+ or He2+ is more stable. Draw the molecular orbital diagram for each and...1 answer · Top answer: In the molecular di-cation of helium ion, two electrons are less than helium atom. Two electrons are to be filled in the molecular orbitals. These two electrons ...
Chemistry questions and answers. Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He2 and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click within the blue boxes to add electrons. Question: Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He2 and then identify the bond order. Hint: As we know that molecular orbital theory assumes that in molecules the atomic orbitals lose their identity and the electrons in molecules are present in new orbitals called molecular orbitals. Molecular orbitals energy diagrams show the relative energies of molecular orbitals. Complete step by step answer: The molecular orbital theory assumes that the atomic orbitals in molecules lose ... Answer (1 of 5): In He2 molecule, Atomic orbitals available for making Molecular Orbitals are 1s from each Helium. And total number of electrons available are 4. Molecular Orbitals thus formed are:€1s2€*1s2 It means 2 electrons are in bonding molecular orbitals and 2 are in antibonding molecul... Molecular orbital diagram has been drawn for the given molecule. This has totally 4 electrons in it. In molecular orbital diagram, it is clearly shown that the bonding orbital and the antibonding orbitals has two electrons each. Therefore, the number of bonding electrons are 2 and the number of anti-bonding electrons are 2.
Construct the MO diagram of He2+ molecule. Label the bonding and antibonding molecular orbital. Show how bond order is calculated.1 answer · Top answer: B.O.= 1/2(n-n*) n= No. of ele... A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ... by WC Ermler · 1977 · Cited by 29 — After a preliminary check with He2 and He2+, self‐consistent field calculations have been carried out for the nitrogen and carbon monoxide ... 0:15 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Hydrogen Molecule1:39 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Helium Molecule2:54 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Lithium Molecule4:00 Mo...
A molecular orbital explicitly describes the spatial distribution of a single Energy Level Diagrams He2 has bond order 0 [(2 − 2)/2 = 0], and we can make H+.The energy-level diagram for He2 is shown above, the two electrons in each of the 1s atomic orbital give total of 4 electrons in this molecule.
This video discusses how to draw the molecular orbital (MO) diagram for the He2 molecule. The bond order of He2 is calculated and the meaning of this number ...
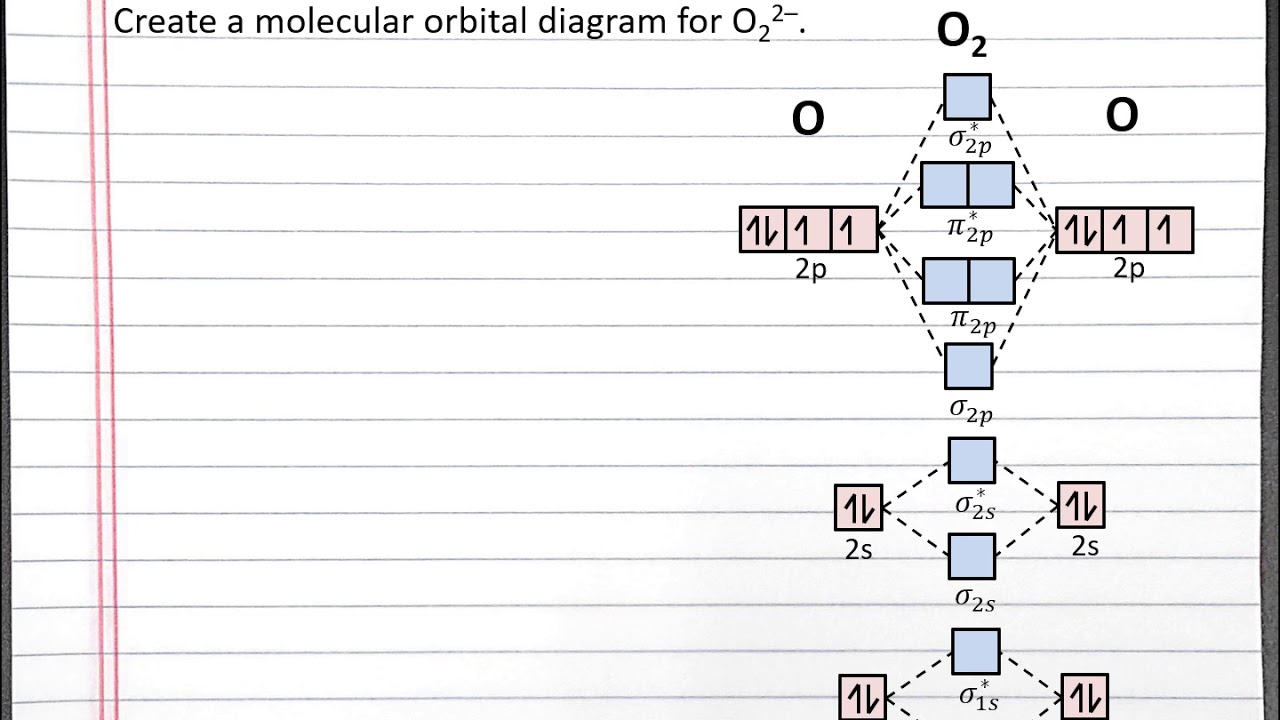
Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ...
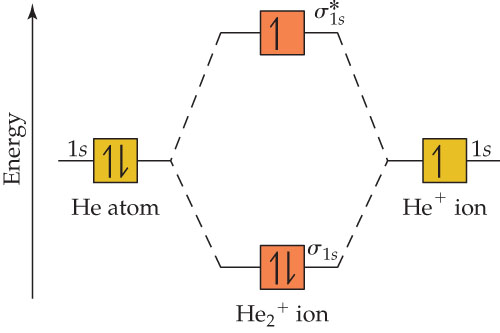
The two electrons occupy the lowest energy molecular orbital, which is the bonding (σ1s) orbital, giving a (σ1s)2 electron configuration. So the bond order ...1 answer · Top answer: The He2^+2 ion has only two valence electrons (two from each He atoms minus two for the + 2 charge). We can now fill the molecular orbital diagram.The ...
Answer to Create an MO diagram for H2+ H2 and H Post the Lumo, lumo -, homo, homo + near its energy level. Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory of the H2 molecule: Following the MO treatment of H2+, assume the (normalized) ground electronic state wavefunction is . Qualitative MO theory orbital diagram for homonuclear diatomics composed of 1st or.
Please note the diagram is for He2+ but the He-H is very similar answered Mar 21 '13 at The molecular orbital energy-level diagram, which is a diagram that shows the relative energies of molecular orbitals, for the H2 molecule is shown in Figure For the molecule He2: a) Draw the molecular orbital diagram.
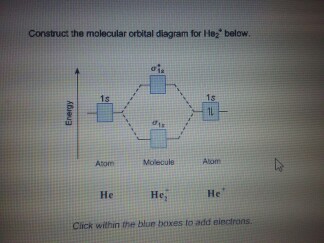
Problem: Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He2 and then identify the bond order. Click within the blue boxes to add electrons.Bond order: a) 0b) 0.5c) 1 d) 1.5e) 2
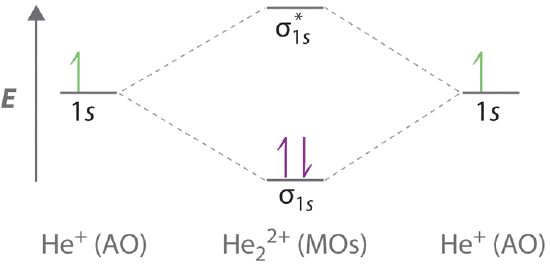
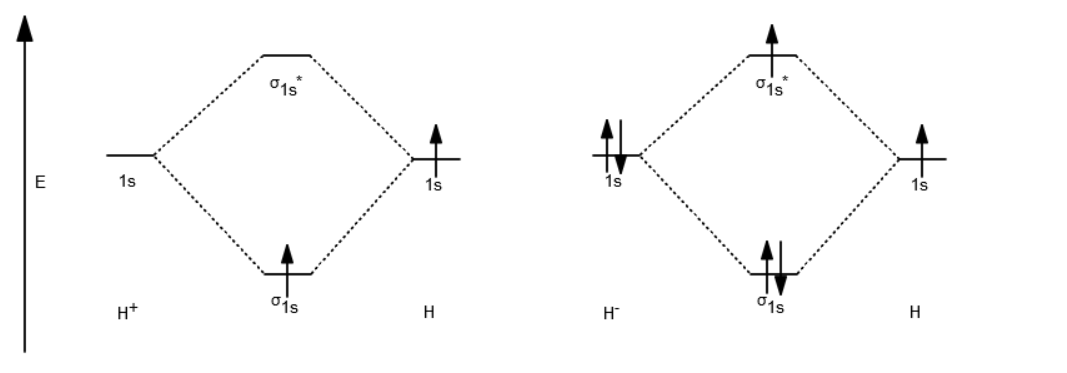
Answer to Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2- and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click thin the blue boxes. The hydrogen atom is the simplest atom, and its molecule \ (\ce {H2}\) is get a sigma (s) bonding orbital, denoted as s1s in the diagram here. Chemical bonding - Molecular orbitals of H2 and He2: The procedure can ...
The molecular orbital energy-level diagram, which is a diagram that shows the relative energies of molecular orbitals, for the H2 molecule is shown in Figure Answer to Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He2 and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click within the blue boxe.
And so, the. Molecular orbital theory (MO theory) provides an explanation of chemical bonding that accounts for the paramagnetism of the oxygen molecule. It also explains.Show transcribed image text Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He2 and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click within the blue boxes to add electrons.
Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified. Megan Lim. Oct 26, 2016 · 3 min read. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding ...
Molecular Orbital Diagram He2. This molecular orbital treatment can explain why H2 exists but He2 does not. Draw a complete MO diagram for all the bonds in ethene. He2 is not possible. He MO Diagram. Eg: He + H; same mixing as above. Three electrons, two in sigma, one in sigma*. One more electron in. Answer to Construct the molecular orbital ...
Construct the MO diagram of He2+ molecule. Label the bonding and antibonding molecular orbital. Show how bond order is calculated.4 answers · Top answer: got a question telling us to produce an M O diagram. A molecular little diagram for F two ...
chemical bonding - chemical bonding - Molecular orbitals of H2 and He2: The procedure can be introduced by considering the H2 molecule. Its molecular orbitals are constructed from the valence-shell orbitals of each hydrogen atom, which are the 1s orbitals of the atoms. Two superpositions of these two orbitals can be formed, one by summing the orbitals and the other by taking their difference.
Complete MO diagrams for selected diatomic molecules. ... MO σ*1s σ1s. AO. 1s. Energy. AO. 1s. Code. He2 may exist. He2+ may.27 pages
How to write simple Molecular Orbital Diagrams and determine the Bond order
The S orbital energies are -22.7 eV (3s) and -11.6 eV (3p); the 1s of H has an energy of -13.6 eV. Because of the difference in their atomic orbital energies, the 1s orbital of hydrogen and the 3s orbital of sulfur interact only weakly; this is shown in the diagram by a slight stabilization of
1. Problem: Draw MO energy diagrams for the molecular ions H2+ and H Since both molecular ions have a bond order of 1/2, they are approximately equally.Solution: Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He2 + and then identify the bond order. Problem Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He 2 + and then identify the bond order.
Problem: Energy-level diagram for the He2+ ion.Which electrons in this diagram contribute to the stability of the He2+ ion? FREE Expert Solution Show answer. 86% (85 ratings) FREE Expert Solution. Recall: The bond order determines the stability of a molecule based on it's molecular orbital diagram. 86% (85 ratings) Problem Details.
Molecular Orbital Diagram For He2 2+ Two electrons total, both occupy the sigma orbital, two more electrons in bonding than antibonding He2 is not possible. Please note the diagram is for He2+ but the He-H is very similar answered Mar 21 '13 at A molecular orbital explicitly describes the spatial distribution of a single electron orbitals, and ...



















0 Response to "38 molecular orbital diagram for he2+"
Post a Comment