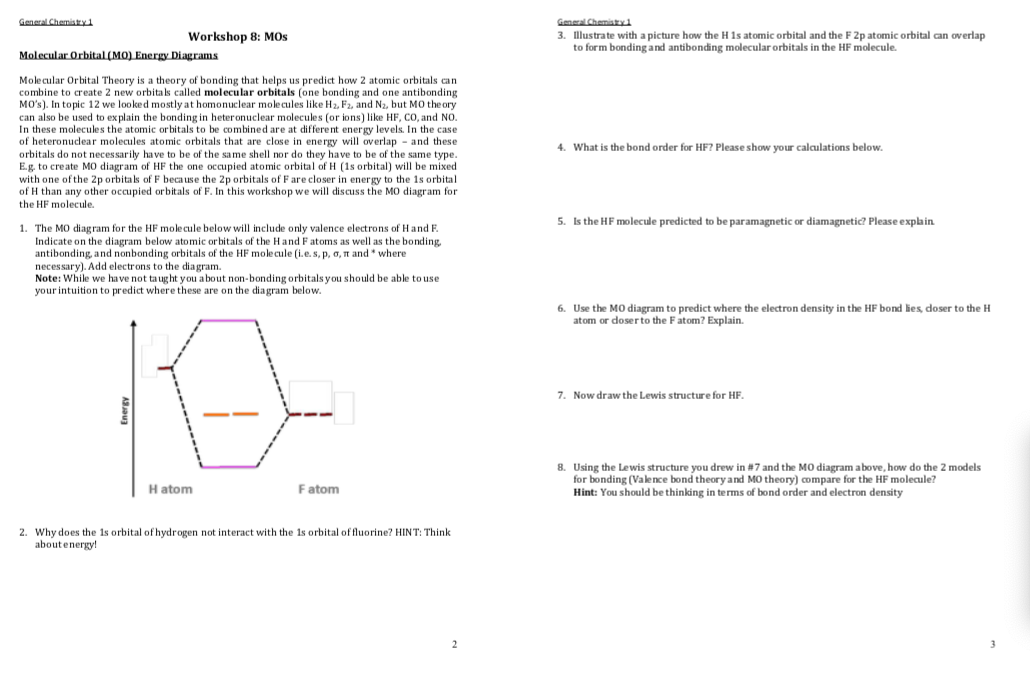
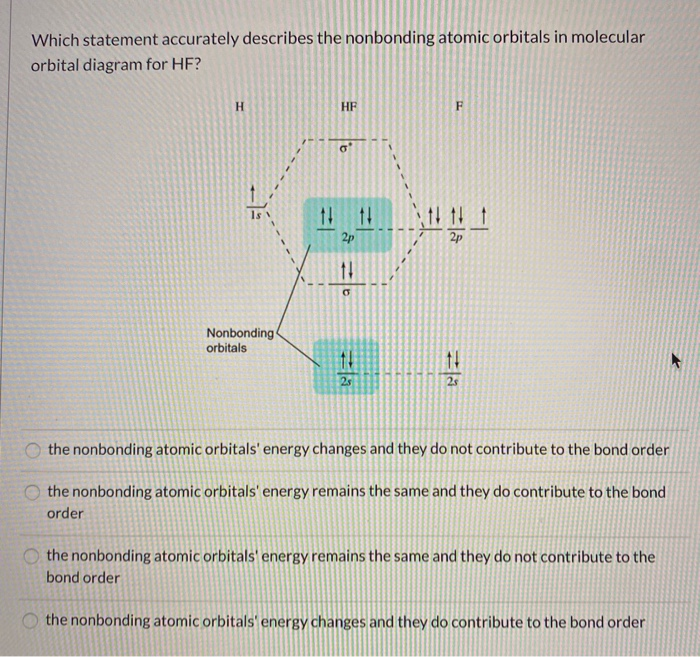
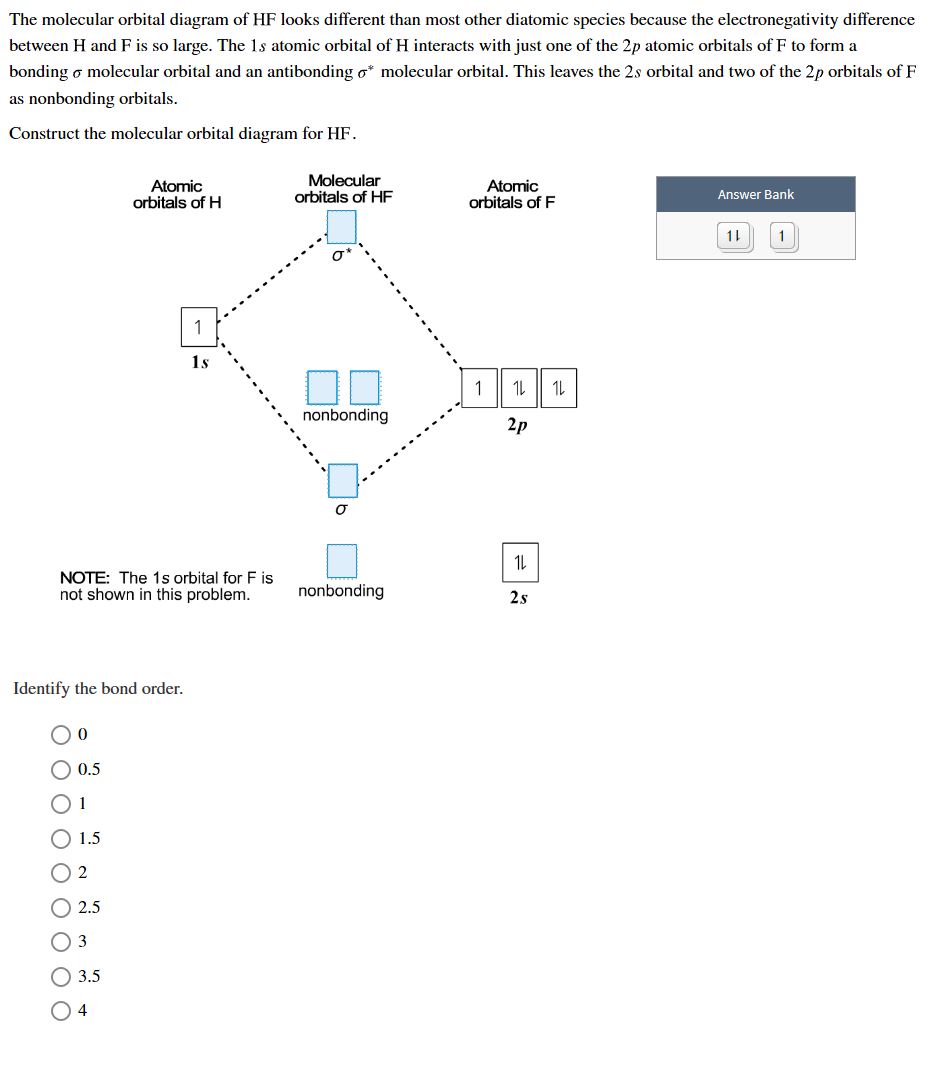
38 hf molecular orbital diagram
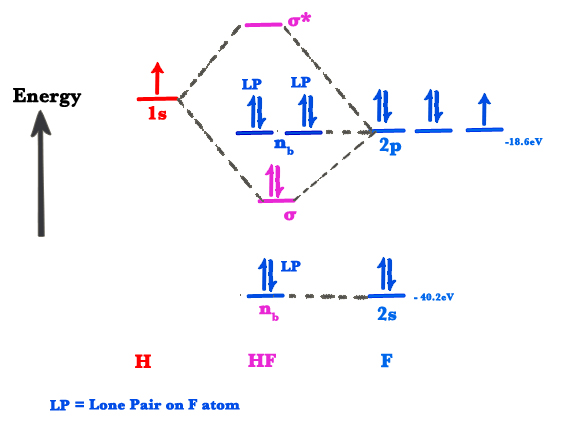
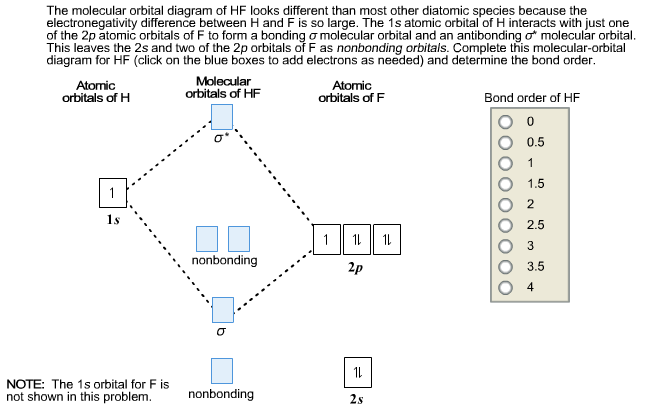
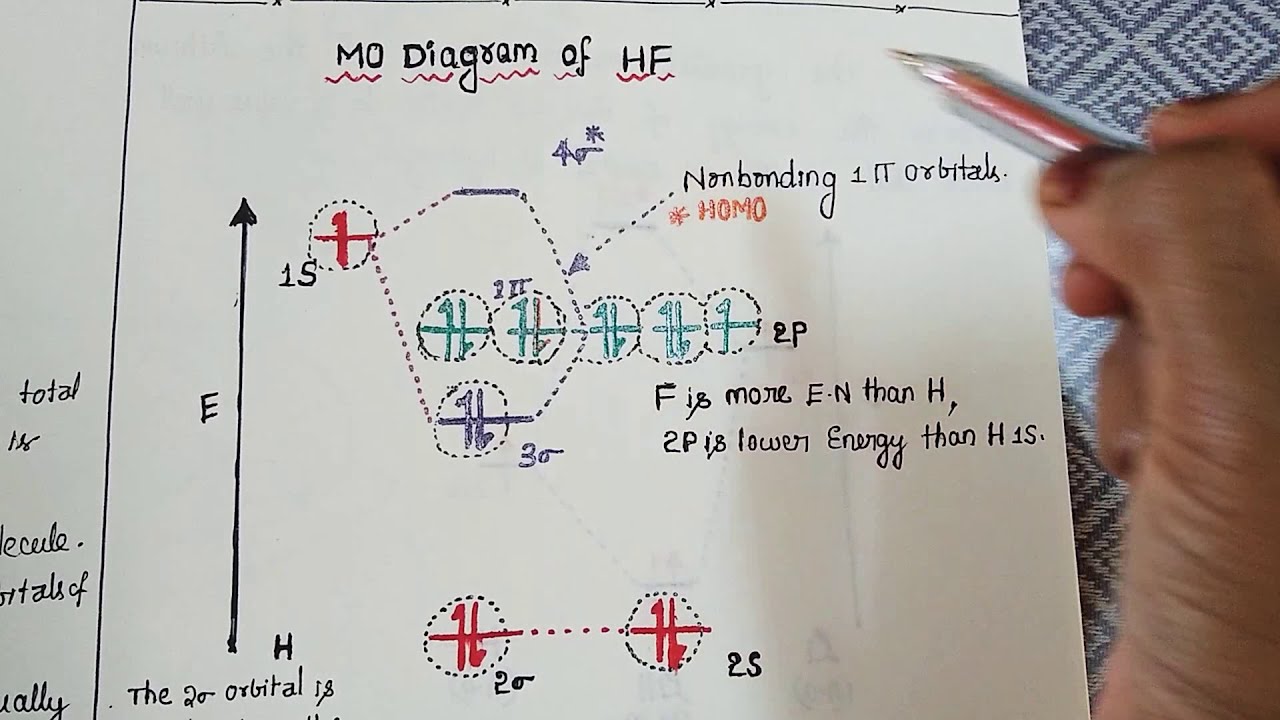
Hf Molecular Orbital Diagram - 15 Luxury Hf Molecular Orbital Diagram molecular orbital theory build f2 video molecular orbital theory build f2 for the ion f2 a draw the molecular orbital diagram b calculate the bond order c would this ion exist Orbital Diagram For Oxygen - Quiz & Worksheet Practice Drawing Electron Orbital Diagrams The molecular orbital diagram of HF looks different than most other diatomic species because the electronegativity difference between H and F is so large. The Is atomic orbital of H interacts with just one of the 2p atomic orbitals of F to form a bonding sigma molecular orbital and an antibonding sigma* molecular orbital.
Molecular orbital surfaces can be viewed to understand how atomic orbitals overlap to make molecular orbitals. Better overlap makes for stronger bonding. To judge if an orbital is sigma or pi type, we look at the direction of overlap of the p orbitals on the two atoms, Figure 2. Sigma bonds are usually stronger because the atomic p-

Hf molecular orbital diagram
Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified. Megan Lim. Oct 26, 2016 · 3 min read. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding ... Molecular Orbital Diagram for the HF Molecule. Interaction occurs between the 1s orbital on hydrogen and the 2p orbital in fluorine causing the formation of a sigma-bonding and a sigma-antibonding molecular orbital, as shown below. Figure 1: Molecular orbitals of HF. (CC BY-SA-NC 2.0 UK: England & Wales License; Nick Greeves). Molecular Orbitals of Hydrogen Fluoride (HF) Ask Question Asked 5 years, 6 months ago. Active 5 years, 2 months ago. Viewed 8k times 1 1 $\begingroup$ This source states that the three s-orbitals of hydrogen and fluorine interact to form three new molecular orbitals, while other sources say that the 2s orbital is non-bonding. Which one is more correct? Also, if they indeed form three new ...
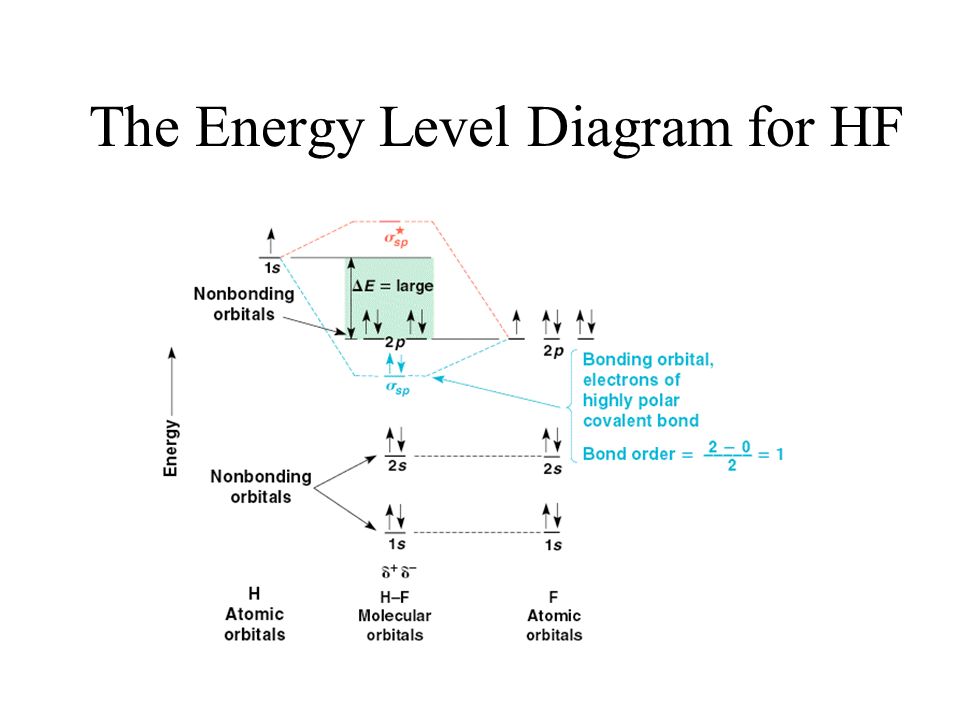
Hf molecular orbital diagram. Figure 1: LCAO MO Diagram for HF (Author: LeeAnn Sager. Used with permission.) The purpose of this activity is to use Hartree-Fock self-consistent-field approach to calculate the molecular orbitals of HF in the minimal atomic basis (STO-3G) and to compare the molecular orbitals to the qualitative LCAO approach. In this screencast, Andrew Burrows walks you through how to construct the MO energy level diagram of HF. http://ukcatalogue.oup.com/product/9780199691852.do#... Answer (1 of 3): The electronic of hydrogen and fluorine are 1s¹ and 1s²2s²2p⁵ respectively. In the formation of HF molecule ,only 2p electrons of fluorine atom would combine effectively with the solitary electron of hydrogen atom. As has been already explained ,only a pz orbital is able to combi... Answer (1 of 2): Here is a useful MO diagram of HCL found on the internet: The Cl electrons residing up to 3s orbital (1s, 2s, 2px,2py,2pz,3s) are largely stabilized than H electron in 1s orbital and therefore they cannot mix and form bond. The 3p electrons of Cl have comparable energy with the ...
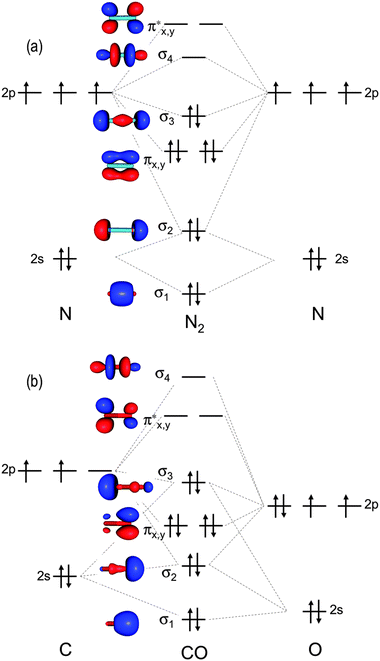
Molecular orbital theory describes the distribution of electrons in molecules in much the same way that the distribution of electrons in atoms is described using atomic orbitals. Using quantum mechanics, the behavior of an electron in a molecule is still described by a wave function, Ψ, analogous to the behavior in an atom.Just like electrons around isolated atoms, electrons around atoms in ... Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in The molecular orbital diagram for HF is given below. Become a member and unlock all Study Answers. Try it risk-free for 30 days Try it risk-free Ask a question. Our experts can answer your tough ... Molecular orbitals were first introduced by Friedrich Hund and Robert S. Mulliken in 1927 and 1928. The linear combination of atomic orbitals or "LCAO" approximation for molecular orbitals was introduced in 1929 by Sir John Lennard-Jones. His ground-breaking paper showed how to derive the electronic structure of the fluorine and oxygen molecules from quantum principles.
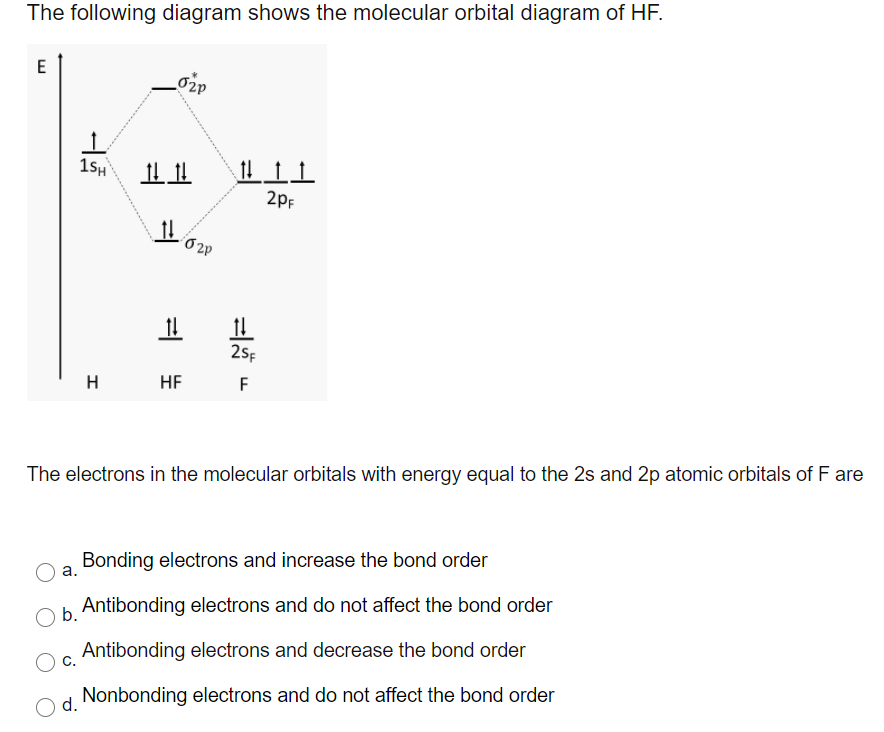
Hf molecular orbital diagram hydrofluoric acid is another example of a homogeneous molecule. Molecular orbital diagram for the hf molecule interaction occurs between the 1s orbital on hydrogen and the 2p orbital in fluorine causing the formation of a sigma bonding and a sigma antibonding molecular orbital as shown below. The molecular orbitals formed in the case of hf molecule will not be ... The energy of the nonbonding HBr molecular orbitals is essentially the same as the 4p atomic orbitals in Br. Constructing the HF molecular orbital energy level diagram - YouTube. Energy Aa Energy Bt 0000 Ooo Energy Energy. 4 13 Draw the MO diagram for HBr Assume the atomic orbitals for each element from CHM 101 at Health and Science School. The molecular orbital diagram of HF looks different than most other diatomic species because the electronegativity difference between H and F is so large. The 1s atomic orbital of H interacts with just one of the 2p atomic orbitals of F to form a bonding o molecular orbital and an antibonding o molecular orbital. The molecular orbitals formed in the case of HF molecule will not be symmetrical. The symmetry occurs because the energies of H(1s) and F(2pz) atomic orbitals are not the same.Molecular orbital diagram for HF molecule is given as.
Molecular Orbital Diagram Of Lih. We shall consider the molecular orbitals in LiH, CH and HF to illustrate how molecular orbital theory describes the bonding in heteronuclear molecules, and to. and 2p orbitals, but that is not how sodium chloride is made. Sodium atoms are Construct an MO diagram for LiH and suggest what type of bond it might have.
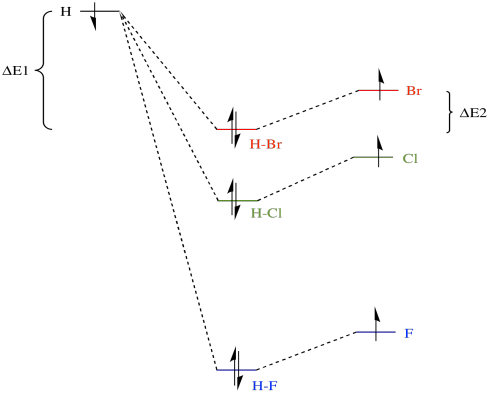
Download scientific diagram | Molecular orbital diagrams for HBr and HF. from publication: Total energy partitioning within a one-electron formalism: A Hamilton population study of surface-CO ...
Click on the HF molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals. Explore bonding orbitals in other small molecules. Hydrogen | Fluorine | Nitrogen | Hydrogen Fluoride | Carbon Monoxide | Methane | Ammonia | Ethylene | Acetylene | Allene | Formaldehyde | Benzene. 213. 49. 3.1 (7) How useful was this page? Click on a star to rate it! Submit Rating . Average ...
HF HOMO Orbital. The HOMO orbital is the highest energy molecular orbital occupied by electrons. In HF, the HOMO orbitals are the double degenerate pi 2px and 2py and pi orbitals. To get a 3-D model you can manipulate, click here. Download time may be significant the first time the applet is loaded.
A molecular orbital diagram that can be applied to any homonuclear diatomic molecule with two identical alkali metal atoms (Li 2 and Cs 2, for example) is shown in part (a) in Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\), where M represents the metal atom. Only two energy levels are important for describing the valence electron molecular orbitals of these species: a σ ns bonding molecular orbital and a σ * ns ...
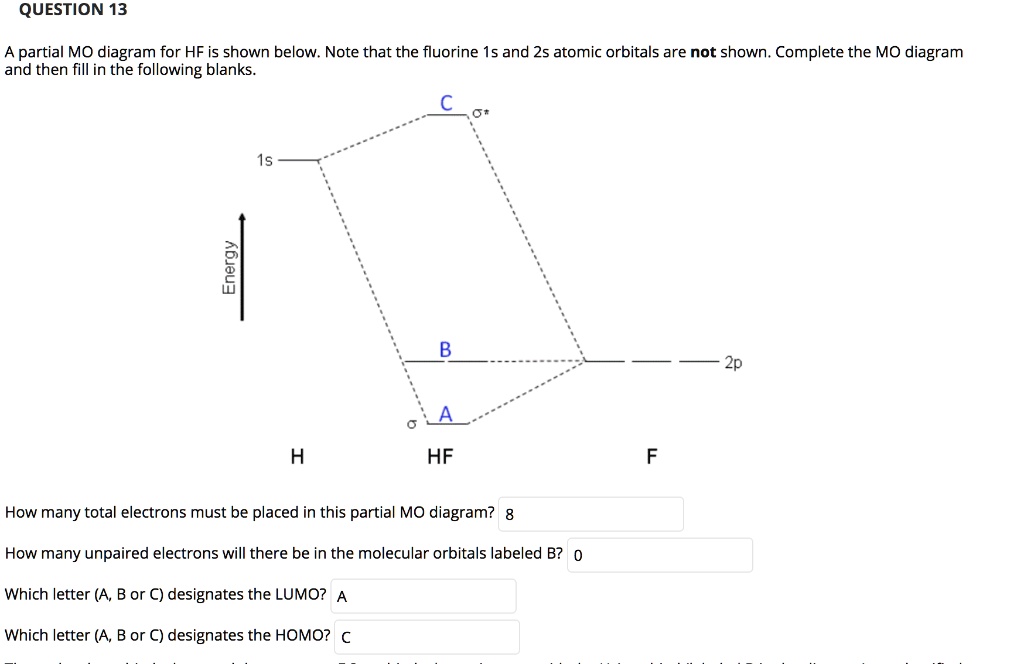
The molecular orbital diagram for the HF molecule is given below. This shows the formation of the bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals (sigma...
Molecular orbital diagram for hf. A molecular orbital diagram or mo diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals lcao method in particular.
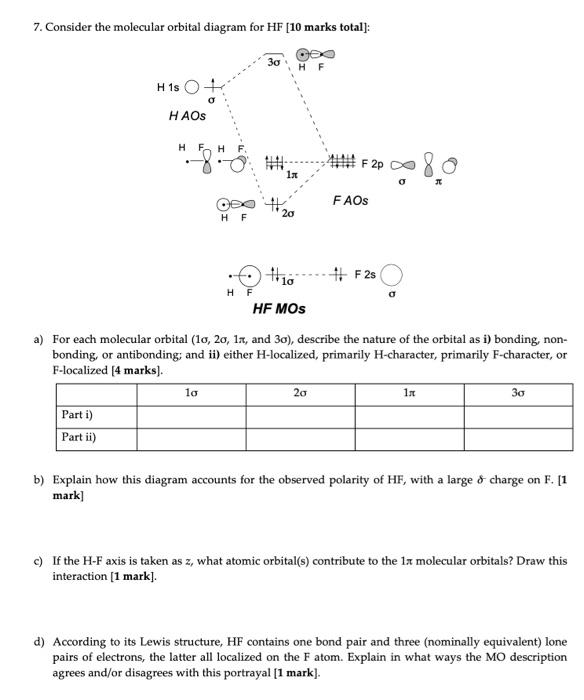
Example 2: hydrogen fluoride When atoms are of different energies, one must be concerned with the relative energies and symmetries of orbitals Orbitals of same symmetry and approximately similar energy combine most effectively Can estimate approximate HF molecular orbitals Energies calculated with Gaussian Gives filling order of orbitals
#MOT #BMO #ABMO #HF #CO #NO #CN #OHHello everyoneThis is shivam here To follow me on instagram search - Sshivam898To join telegram group click on the given l...
Answer (1 of 3): The electronic of hydrogen and fluorine are 1s¹ and 1s²2s²2p⁵ respectively. In the formation of HF molecule ,only 2p electrons of fluorine atom would combine effectively with the solitary electron of hydrogen atom. As has been already explained ,only a pz orbital is able to combi...
HF Molecular Orbital Diagram. Hydrogen fluoride is another example of a heteronuclear molecule. It is slightly different in that the π orbital is non-bonding, as well as the 2s σ. From the hydrogen, its valence 1s electron interacts with the 2p electrons of fluorine. This molecule is diamagnetic and has a bond order of one.
Molecular Orbitals of Hydrogen Fluoride (HF) Ask Question Asked 5 years, 6 months ago. Active 5 years, 2 months ago. Viewed 8k times 1 1 $\begingroup$ This source states that the three s-orbitals of hydrogen and fluorine interact to form three new molecular orbitals, while other sources say that the 2s orbital is non-bonding. Which one is more correct? Also, if they indeed form three new ...
Molecular Orbital Diagram for the HF Molecule. Interaction occurs between the 1s orbital on hydrogen and the 2p orbital in fluorine causing the formation of a sigma-bonding and a sigma-antibonding molecular orbital, as shown below. Figure 1: Molecular orbitals of HF. (CC BY-SA-NC 2.0 UK: England & Wales License; Nick Greeves).
Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified. Megan Lim. Oct 26, 2016 · 3 min read. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding ...















0 Response to "38 hf molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment