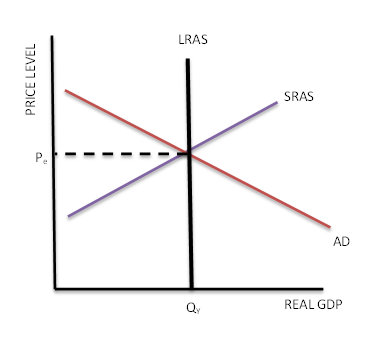
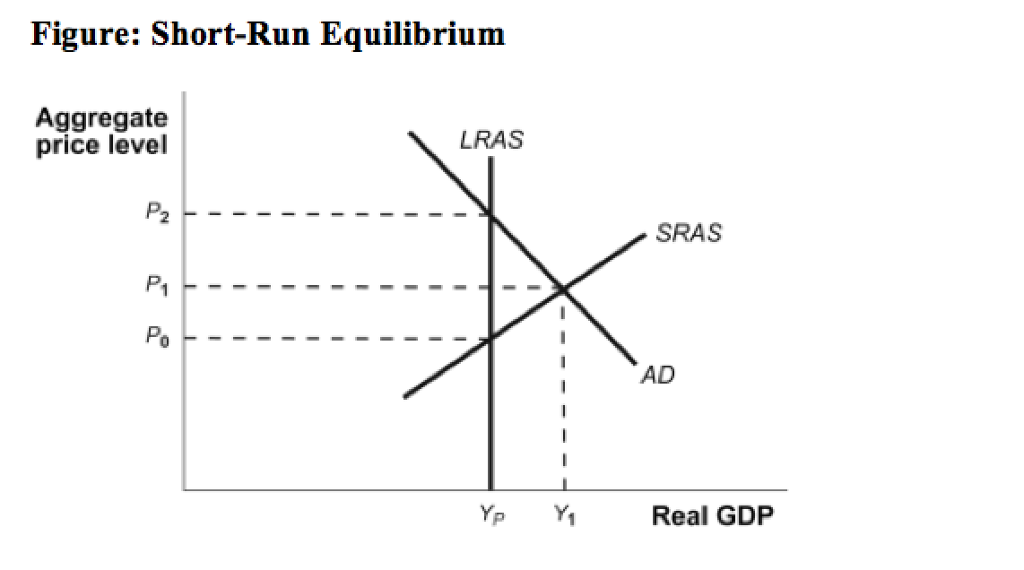
38 consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point a.
Consider the following diagram, in which the current shortrun equilibrium is at point A. a. At point A, the economy has. an inflationary gap b. If the marginal propensity to consume equals, to eliminate the gap, the government should decrease spending by $ trillion. (Round your answer to two decimal places. We offer assignment help in more than 80 courses. We are also able to handle any complex paper in any course as we have employed professional writers who are specialized in different fields of study. From their experience, they are able to work on the most difficult assignments. The following are some of the course we offer assignment help in ...
Short-run equilibrium. An economy is in short-run equilibrium when the aggregate amount of output demanded is equal to the aggregate amount of output supplied. In the AD-AS model, you can find the short-run equilibrium by finding the point where AD intersects SRAS. The equilibrium consists of the equilibrium price level and the equilibrium output.
_r3amyt.jpg)
Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point a.
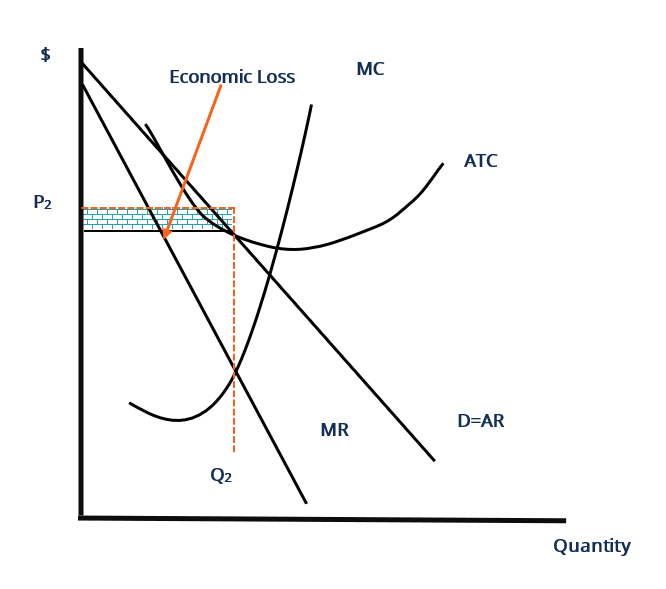
4. Shut down point in the short run When a firm suffers from losses in the short run (P<ATC), it has two choices: 1) Continue to run the firm: Loss1= (P-ATC)*Q 2) Stop production by shutting down temporarily. Under this choice, firm still need to pay its fixed cost since fixed cost is kind of sunk cost in the short run. Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point A. Please answer part B. Text Problem 13-10 Consider the following ... Economics questions and answers. Xx Text Problem 13-10 : Question Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point A. LRAS SRAS a. At point A, the economy has an inflationary gap b. If the marginal propensity to consume equals 0.9, to eliminate the gap, the government should decrease spending by $ trillion.
Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point a.. Get 24⁄7 customer support help when you place a homework help service order with us. We will guide you on how to place your essay help, proofreading and editing your draft – fixing the grammar, spelling, or formatting of your paper easily and cheaply. Suppose that an economy begins at the short-run equilibrium shown as point A in the figure to the right. Identify which of the other points on the diagram-points B , C, D, or E-could represent a new short -run equilibrium after the described events given below take place and move the economy away from point A. Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point A. a. At point A, the economy has an inflationary gap. b. If the marginal propensity to consume equals 0.5 , to eliminate the gap, the government should decrease spending by $.58. 8 trillion. (Round your answer to two decimal places. ) There is an inflationary gap, because at point A equilibrium real GDP of ... there be when this industry is in long-run equilibrium? 13) All firms in a competitive industry have the following long-run total cost curve: C(q) = q3 - 10q2 + 36q where q is the output of the firm. a. Compute the long run equilibrium price. What does the long-run supply curve look like if this is a
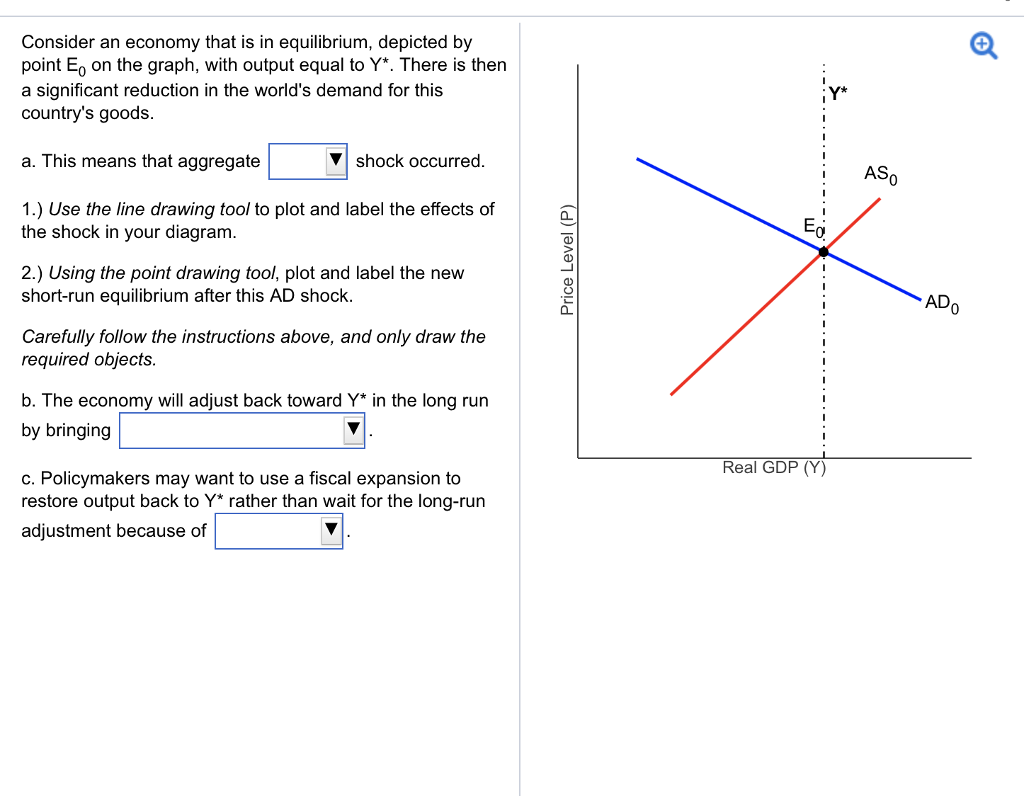
b. Suppose that Macroland experiences a negative demand shock. Graph the short-run changes in the original equilibrium that will occur because of this demand shock. On your graph, identify the new short-run equilibrium level of output (Y 2) and the new short-run equilibrium aggregate price level (P 2). Label any shifts in AD or AS clearly. c. short-run AND long-run impact of this decline on output and prices. A decline in energy prices shifts the SRAS curve down, so the new short-run equilibrium moves from 1 to 2. Over the long run, however, prices will rise back up to their original level and the long-run equilibrium reverts back to 1. b. We always make sure that writers follow all your instructions precisely. You can choose your academic level: high school, college/university, master's or pHD, and we will assign you a writer who can satisfactorily meet your professor's expectations. A Decrease in Demand. Panel (b) of Figure 3.10 "Changes in Demand and Supply" shows that a decrease in demand shifts the demand curve to the left. The equilibrium price falls to $5 per pound. As the price falls to the new equilibrium level, the quantity supplied decreases to 20 million pounds of coffee per month.
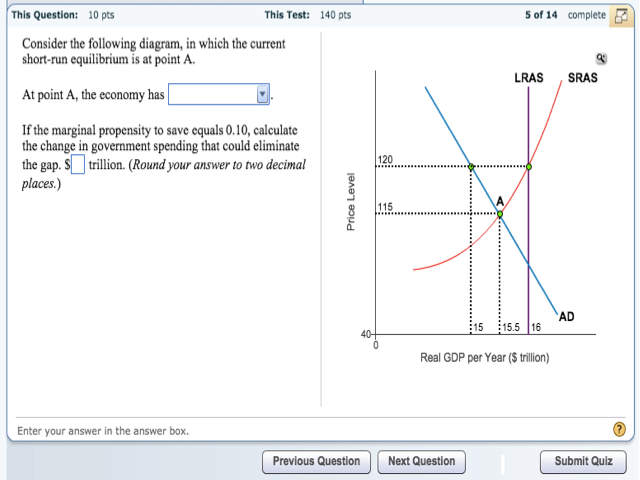
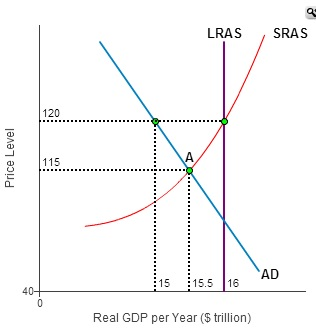
Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point A. At point A, the economy has a recessionary gap . LRAS SRAS If the marginal propensity to save equals 0.20, calculate the change in government spending that could eliminate the gap. $0.1 trillion. The initial equilibrium point is shown by X on the aggregate demand, AD, and aggregate supply, AS, diagram. What would be the new equilibrium point in the short run if the forecasts prove to be accurate and Question: Text Problem 13-10 EQuestion Help Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point A. Q LRAS SRAS a. Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point A. At point A, the economy has (an expectation gap / an inflationary gap / a recessionary gap) . If the marginal propensity to save equals 0.20 , calculate the change in government spending that could eliminate the gap. $____ trillion. (Round your answer to two decimal places. ) This economy is currently ...
Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point A. At point A, the economy has a recessionary gap. (This is my answer, I think it's right). If the marginal propensity to save equals 0.20, calculate the change in governemtn spending that could eliminate the gap. $ ____ trillion.
Transcribed image text: Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point A LRAS SRAS At point A, the economy has a ...
The interaction of SRAS and AD determine national income. We can compare that national income to the full employment national income to determine the current phase of the business cycle. An economy is said to be in long-run equilibrium if the short-run equilibrium output is equal to the full employment output.
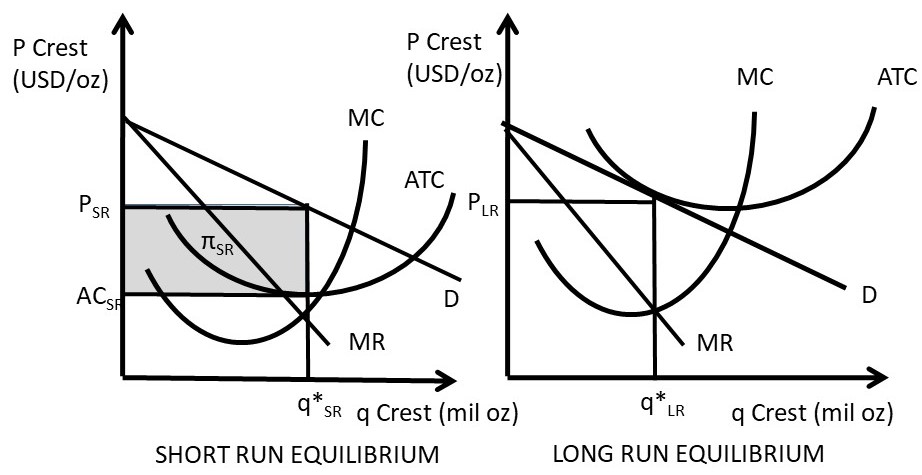
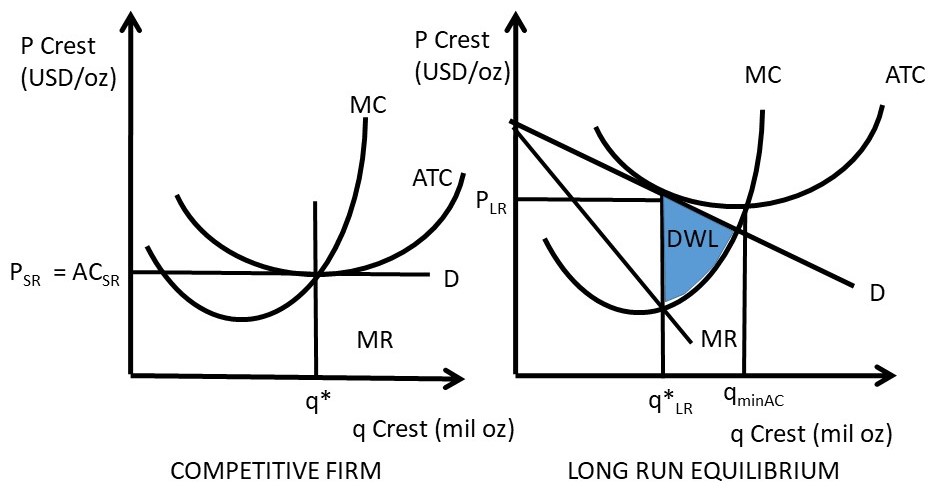
A purely competitive firm is currently in short-run equilibrium and its MC exceeds its ATC at its current output level. It can be concluded that. A. Firms will leave the industry in the long run. B. The firm is realizing an economic profit. C. The firm is suffering an economic loss. D. The firm will shut down in the short run.
We provide solutions to students. Please Use Our Service If You’re: Wishing for a unique insight into a subject matter for your subsequent individual research;
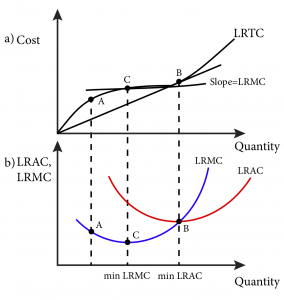
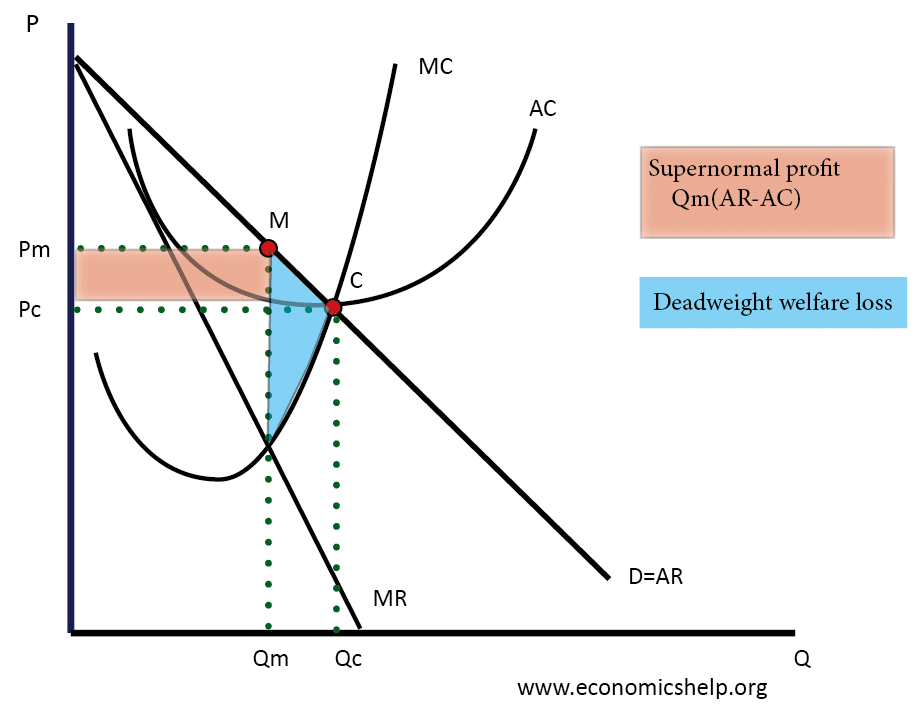
In long-run equilibrium under perfect competition, the price of the product becomes equal to the minimum long-run average cost (LAC) of the firm. In monopoly, on the other hand, long- run equilibrium occurs at the point of intersection between the monopolist's marginal revenue (MR) and long-run marginal cost (LMC) curves.
1. Assume that the United States economy is currently in a recession in a short-run equilibrium. (a) Draw a correctly labeled graph of the short-run and long-run Phillips curves. Use the letter A to label a point that could represent the current state of the economy in recession.
At this point, equilibrium price is OP 1 and industry supply is OQ 1. This is also long run equilibrium, to begin with. Hence, e 1 will be a point on the long run supply curve. ii. An upward shift in demand curve (D 3 D 4) will push the short run price to OP 2 at which the industry will supply OQ 2.
Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point A. At point A, the economy has a recessionary gap. (This is my answer, I think it's right).
Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point A. At point A, the economy has a recessionary gap. If the marginal propensity to save equals 0.25 , calculate the change in government spending that could eliminate the gap. $.25 trillion. (Round your answer to two decimal places.
approach money market equilibrium in the short run (here) and the way we approached it in the long run (chapter 14). • In Chapter 14 we made the following long-run assumptions: In the long run the price level P is fully flexible and adjusts to bring the money market to equilibrium;
38 consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point a. Written By Christine J. Bell . Thursday, November 18, 2021 Add Comment Edit. 3. Use the sticky-wage model of the short-run aggreg at e supply curve to work out the effects of the following changes on th at curve: a. An in crease in the target real wage, ω . Ans: The equ at ion th at we derived for the ...
A) At point A, the economy has a(n) ____ Get the detailed answer: Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point A. 🏷️ LIMITED TIME OFFER: GET 20% OFF GRADE+ YEARLY SUBSCRIPTION →
(f) Draw the short-run Phillips curve that you found, labeling the coordinates of the points on it that correspond to points A and B above. Using point B, and the long-run equilibrium point we get the following short-run Phillips curve. Inflation rate . 1% Unemployment rate 2% B 5% 0% A
Suppose that an economy begins at the short-run equilibrium shown as point A in the figure to the right. Identify which of the other points on the diagram−points B , C, D, or E−could represent a new short -run equilibrium after the described events given below …
7. Short-run supply and long-run equilibrium Consider the competitive market for titanium. Assume that, regardless of how many firms are in the industry, every firm in the industry is identical and faces the marginal cost (MC), average total cost (ATC), and average variable cost (AVC) curves shown on the following graph. 8. Short-run and long ...
Consider an economy described by the following short run model. C = c 1(Y-T) I = b 0 + b 1Y- b 2i Md/P = C-a*i G = G 0 T = T 0 Ms = M 0 All the parameters (a, b 0,b 1, b 2, c 1) in the model are positive, and b 1+ c 1<1. We assume for simplicity that P=1. Important: Note that unlike in the short run model we have seen in class, money demand
9-2 MyEconlab Module Nine Homework-Jennifer Brown Instruetor: Allyson Clarke Gource: M BA-502-Q 3225-17TW3-Clarke htps://xlitemprod.pearsoncm g.coml apilv l/print/en-us/econ Assignment: 9-2 MyEconlab Module i Nine Homework i Jennifer Brown 2t10t17 Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point A.
equilibrium price level and equilibrium level of real domestic output will fall to: A) 250 and $200, respectively. C) 150 and $300, respectively. B) 200 and $300, respectively. D) …
(a) Consider a simple Keynesian model where C = 50 + 0.6Y and I = 30 + 0.2 Y. The country is closed without government. Determine the equilibrium national income of the country. (b) Suppose that in this country last year’s aggregate demand determines this year’s production.
Transcribed image text: Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point A. LRAS SRAS a. At point A, the economy has ...
rises even more than in the short run. This process continues until the long-run level of output is again reached. At the new equilibrium, point C, interest rates have risen to r3, and the price level is permanently higher. Note that, like monetary policy, fiscal policy cannot change the long-run level of output.
7 Firms and markets for goods and services 7.1 Introduction. Technological and cost advantages of large-scale production favour large firms. Firms producing differentiated products choose price and quantity to maximize their profits, taking into account the product demand curve and the cost function.
3. Following a real depreciation, the trade balance improves. Uncertain. We need to distinguish between what happens in the short-run vs. what happens in the long-run. If we look at the effects of a real depreciation over time, we see that it initially increases the trade deficit, because ε rises, but neither IM nor X changes right away.
We offer assignment help in more than 80 courses. We are also able to handle any complex paper in any course as we have employed professional writers who are specialized in different fields of study. From their experience, they are able to work on the most difficult assignments. The following are some of the course we offer assignment help in ...
consider the following diagram in which the current short run equilibrium is at point A. consider the following diagram in which the curren ...
(a) Using a correctly labeled graph with both the short-run and long-run Phillips curves and the relevant numbers from above, show the current long-run equilibrium as point A. (b) Calculate the real interest rate in the long-run equilibrium. (c) Assume now that the Federal Reserve decides to target an inflation rate of 3 percent. What open-market
Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point A. a. At point A, the economy has _____. b. If the marginal propensity to save equals 0.25 , calculate the change in government spending that could eliminate the gap. $____ trillion. a. a recessionary gap b. .25. Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point A. a. At ...
equilibrium point, point 1, has higher output than the original equilibrium at point 0. Over time, prices rise when output exceeds its long-run level, causing a shift in the asset market equilibrium curve from AʹAʹ to AʺAʺ, which returns output to its long-run level. Figure 17(6)-6 12.
Question: Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point A. At point A, the economy has a recessionary gap.
Consider the following occurrences. Use the AA-DD model to determine the impact on the variables (+, −, 0, or A) from the twin-deficit identity listed along the top row. Consider only short-run effects (i.e., before inflationary effects occur) and assume ceteris paribus for all other exogenous variables.
Economics questions and answers. Xx Text Problem 13-10 : Question Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point A. LRAS SRAS a. At point A, the economy has an inflationary gap b. If the marginal propensity to consume equals 0.9, to eliminate the gap, the government should decrease spending by $ trillion.
Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point A. Please answer part B. Text Problem 13-10 Consider the following ...
4. Shut down point in the short run When a firm suffers from losses in the short run (P<ATC), it has two choices: 1) Continue to run the firm: Loss1= (P-ATC)*Q 2) Stop production by shutting down temporarily. Under this choice, firm still need to pay its fixed cost since fixed cost is kind of sunk cost in the short run.



















0 Response to "38 consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point a."
Post a Comment