37 pathway of light through the eye diagram
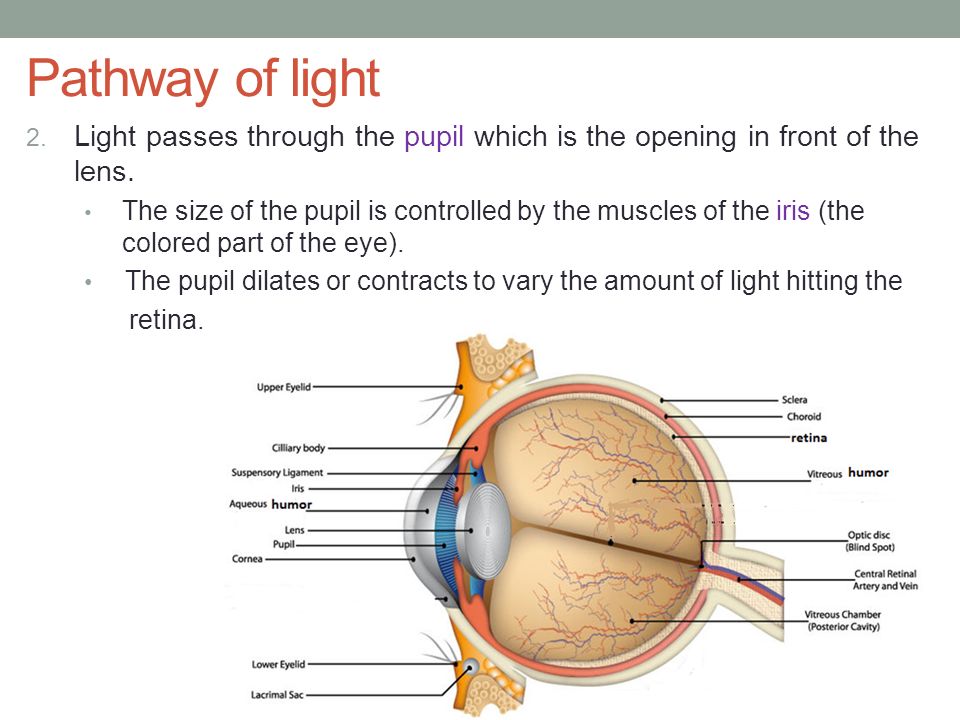
Brain. (Visual Cortex) Bend/focuses light rays onto the lens. It travels through the aqueous humour. allows the light into the eye. Controls amount of light travelling through the pupil by expanding and contracting. Bend light rays to focus them onto the retina. Expands and contracts to help bend and focus these light rays. The Sensing Eye and the Perceiving Visual Cortex. As you can see in Figure 4.7 "Anatomy of the Human Eye", light enters the eye through the cornea, a clear covering that protects the eye and begins to focus the incoming light. The light then passes through the pupil, a small opening in the center of the eye.The pupil is surrounded by the iris, the colored part of the eye that controls the ...
1. Light rays enter the eye through the cornea, the clear front "window" of the eye. The cornea's refractive power bends the light rays in such a way that they pass freely through the pupil the opening in the center of the iris through which light enters the eye. The iris works like a shutter in a camera.

Pathway of light through the eye diagram
Light reflex - The light reflex is mediated by the retinal photoreceptors and subserved by four neurones A. Afferent limb 1. First (sensory) connects each retina with both pretectal nuclei in the midbrain at the level of the superior colliculi. Ø Pupillary fibers travel along with the other fibres transmitting through the optic nerve. Pupil Iris Light enters the eye through the pupil. The iris opens or closes depending on how much light needs to be let into the pupil. The iris is a muscle around your pupil that opens and closes depending on how much light needs to be let in. It is the colored part of your eye. Cornea Light enters your eye through the cornea Light enters and travels through the cornea. 2. Goes throught the aqueous humor behind the cornea to the pupil. 3. Goes through the lens which is controlled in thickness by the muscles. 5. Goes through the vitreous humor and hits the retina. 6. The rods and cone cells of the retina are stimulated sending the information out through the optic nerve.
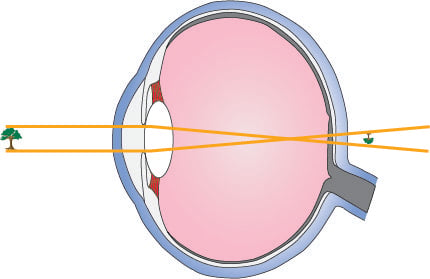
Pathway of light through the eye diagram. The visual pathway's primary task of converting light information into a picture of the outside world is moderated by neurons of the visual cortex. The optic nerve transmits the signals of the eye to the brain. In the eye, the visual pathway begins when light passes through the cornea, pupil, and lens, where it is inverted and projected onto ... The path of light through the eye begins with the objects viewed and how they produce, reflect or alter light in various ways. When your eyes receive light, it begins a second journey through the eye's optical parts that adjust and focus light to the nerves that carry images to your brain. Standing outdoors, for example, a night scene may be lit by streetlights, light from passing cars and the ... What is normal vision? · Light enters the eye through the cornea. · From the cornea, the light passes through the pupil. · From there, it then hits the lens. · Next ... Transcribed image text: In vertebrate animals, the eye is a complicated structure that contains the photoreceptors necessary to gather visual Information about the surrounding environment. In the following image, examine the yellow path entering the eye. This path should represent the passage of light through the eye, but it is slightly incorrect.
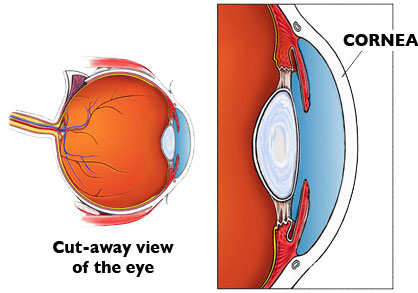
The Cornea refracts and converge the light. It also protects the inside of eye from outer dirt. The light after passing through the Cornea first, travels through a transparent liquid called Aqueous Humor. 2) Aqueous Humor- It is a transparent liquid that maintains internal eye pressure remaining in front and behind Irish. 15 Jun 2018 — Explanation: · 1. Cornea · 2. Aqueous Humor · 3. Pupil · 4. Lens · 5. Vitreous Humor · 6. Retina. Here's a diagram of the eye to follow along: https:/ ...1 answer · See below. Explanation: Light's path through the eye from the outside to the retina is as follows: 1. Cornea 2. Aqueous Humor 3. Pupil 4. ... through it. NOTE: The mirrors will fall out if you turn your periscope upside down. Object 0" 2" 3" 2" 3" 45° 45° 45° 45° Cut-out square of cardboard Observations, Data, and Conclusions Junior Home Scientist 1. Draw a diagram of the path a ray of light follows as it travels from an object, through the periscope, and into your eye. 2. The visual pathway is the pathway over which a visual sensation is transmitted from the retina to the brain. This includes a cornea and lens that focuses images on the retina, and nerve fibers that carry the visual sensations from the retina through the optic nerve. Optic nerve fibers travel through the optic chiasma to the lateral geniculate ...
Question: Concept Map: The Pathway of Light through the Eye Complete the Concept Map to trace the pathway of light through the eye to the retina and explain how light is focused for distant or close vision. This problem has been solved! See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading. Videos (1) The structures and functions of the eyes are complex. Each eye constantly adjusts the amount of light it lets in, focuses on objects near and far, and produces continuous images that are instantly transmitted to the brain. The orbit is the bony cavity that contains the eyeball, muscles, nerves, and blood vessels, as well as the ... Light is refracted by the cornea, passes through the anterior chamber, through the aqueous, through the pupil, is again refracted by the lens and goes through ...4 answers · 9 votes: The lens of our eye is a convex lens. So it basically converges the light to focus the object ... Start studying Pathway of light through the eye. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
The refraction of light through the human eye. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter. Email. Chemical and physical sciences practice passage questions. Practice: Understanding cardiac pressure-volume curves. Practice: Imaging tissue structures using muon tomography.
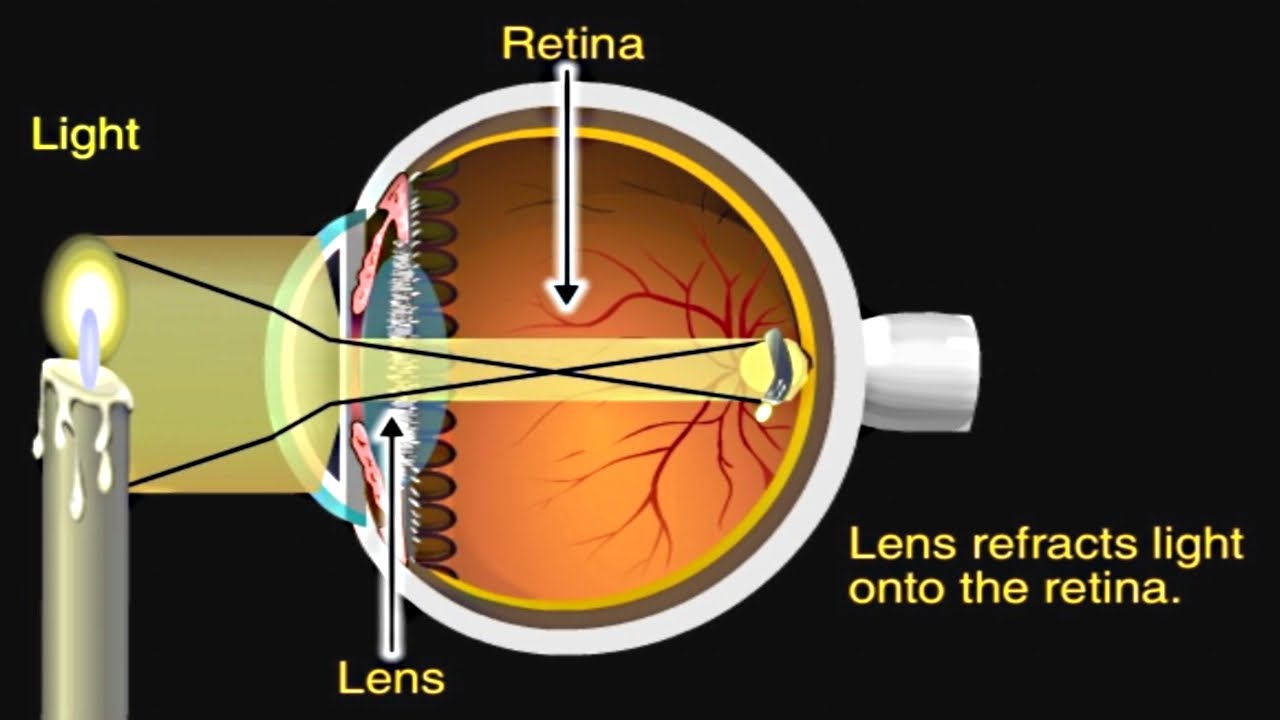
How the Eyes Work. All the different parts of your eyes work together to help you see. First, light passes through the cornea (the clear front layer of the eye). The cornea is shaped like a dome and bends light to help the eye focus. Some of this light enters the eye through an opening called the pupil (PYOO-pul).
The pathway of light from the light source to the eye is a simple path. Lsm 700 light pathways the lsm 700 laser scanning confocal microscope from carl zeiss is designed for ease of use when investigating complex phenomena. It is the light source diaphragm stage slide objective lens body eyepiece and then eye. The light path of specimen to the eye.
Different visual problems will occur depending on where the damage is. The black bars (labeled 1 through 5) indicate where damage may occur and the chart to the right of the pathway indicates the resulting "blind" area (gray shading) of the visual field. Damage at site #1: this would be like losing sight in the left eye.
What Is the Path of Light Through the Eye? According to The Merck Manual Home Health Handbook, light travels through the sclera, cornea, pupil and lens before stopping at the retina, respectively. Once at the retina, the information from the light is converted to electrical impulses for the brain to interpret.
After refraction by the optical system of the eye a real image of the intermediate real image formed by the lens is formed on the retina of the eye. In order that the eye produces a sharp focus of the intermediate onto the retina the distance between the eye must be greater than the least distance of distinct vision which is about 250 m m for ...
The Light Path through the Microscope. Rather than attempting to illustrate all ray paths using a single optical diagram, the distribution of light in a Köhler-illuminated microscope is here represented as four light paths of practical importance to the microscopist: The path taken by light emanating from the lamp filament,
Path of Light. cornea --> pupil --> ciliary muscle/iris --> lens (accomodate!!) --> retina/fovea --> optic nerve --> optic chiasm --> optic tract --> occipital lobe ... - clear opening - helps allow light to pass through. Iris - colored part of eye - allows for amount of light let into eye - controlled by ciliary muscles. Ciliary Muscles ...
Light passes through the front of the eye (cornea) to the lens. The cornea and the lens help to focus the light rays onto the back of the eye (retina). The cells in the retina absorb and convert the light to electrochemical impulses which are transferred along the optic nerve and then to the brain.
The eyes act as the initial point of contact through which photons pass to access the visual pathway. The visual pathway refers to the anatomical structures responsible for the conversion of light energy into electrical action potentials that can be interpreted by the brain. It begins at the retina and terminates at the primary visual cortex ...
Eyes That Capture Light The human eye is made up of various parts (continued) •Pupil: The dark circular opening at the center of the iris in the eye, where light enters the eye. •Iris: The colored part of the eye, a muscular diaphragm, that regulates light entering the eye by expanding and contracting the pupil.
the reflected ray is the light coming away from the mirror A ray diagram for reflection at a mirror In the ray diagram: the hatched vertical line on the right represents the mirror the dashed line...
The cornea has the dual purpose of protecting the eye and refracting light as it enters the eye. After light passes through the cornea, a portion of it passes through an opening known as the pupil. Rather than being an actual part of the eye's anatomy, the pupil is merely an opening. The pupil is the black portion in the middle of the eyeball.
2 trace the path of light through the eye as it. 2. Trace the path of light through the eye as it enters the cornea, is transduced into neural energy, and ends in the visual cortex of the occipital lobe. a. Light enters the eye through the cornea, which protects the eye and bends lights provide focus. b.
The eye The eye is a sense organ that responds to light. The retina Light passes through the eyeball to the retina. There are two main types of light receptors - rods and cones. Rods are more...
Draw a diagram of the human eye as seen in a vertical section and label the parts which suits the following descriptions relating to the : (i) photosensitive layer of the eye. (ii) structure which is responsible for holding the eye lens in its position. (iii) structure which maintains the shape of the eye ball and the area of no vision.
Light enters and travels through the cornea. 2. Goes throught the aqueous humor behind the cornea to the pupil. 3. Goes through the lens which is controlled in thickness by the muscles. 5. Goes through the vitreous humor and hits the retina. 6. The rods and cone cells of the retina are stimulated sending the information out through the optic nerve.
Pupil Iris Light enters the eye through the pupil. The iris opens or closes depending on how much light needs to be let into the pupil. The iris is a muscle around your pupil that opens and closes depending on how much light needs to be let in. It is the colored part of your eye. Cornea Light enters your eye through the cornea
Light reflex - The light reflex is mediated by the retinal photoreceptors and subserved by four neurones A. Afferent limb 1. First (sensory) connects each retina with both pretectal nuclei in the midbrain at the level of the superior colliculi. Ø Pupillary fibers travel along with the other fibres transmitting through the optic nerve.



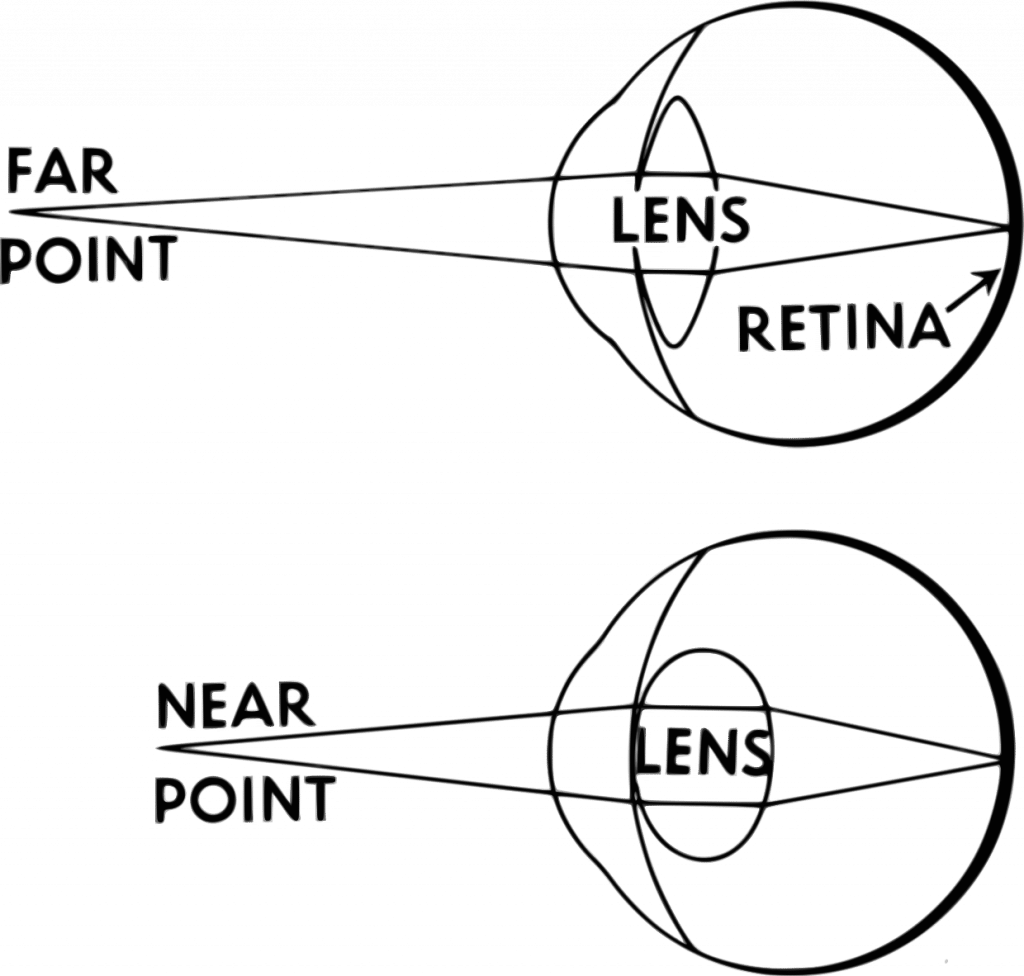

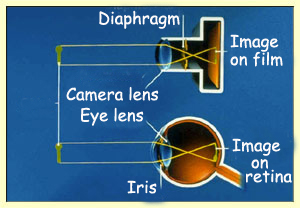
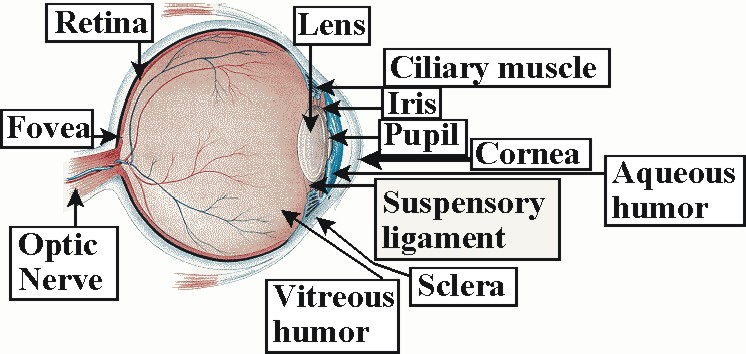


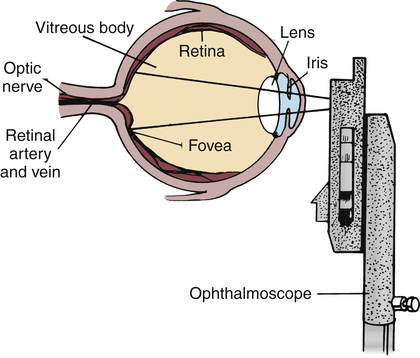








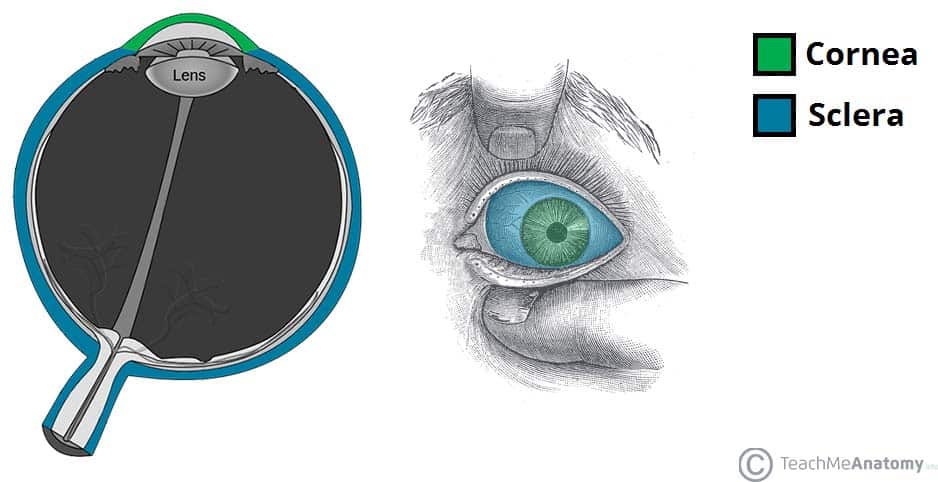


0 Response to "37 pathway of light through the eye diagram"
Post a Comment