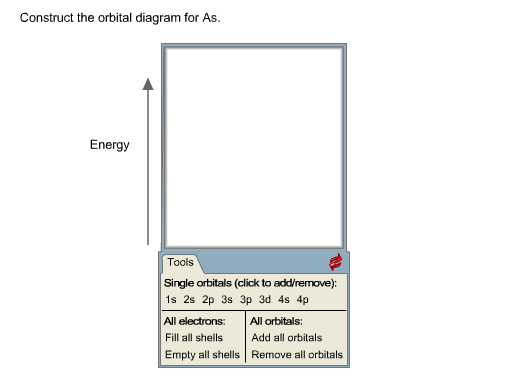
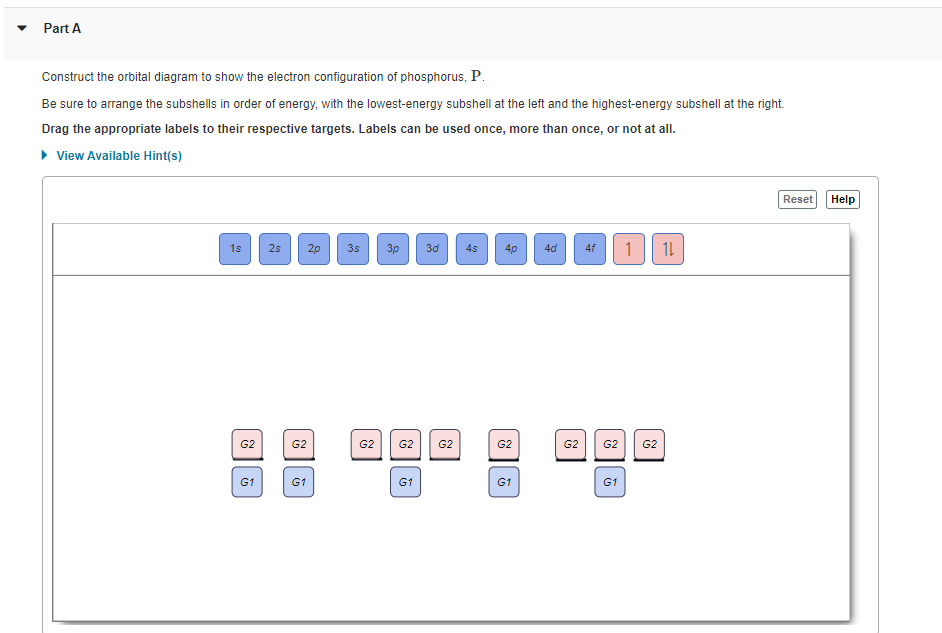
37 construct the orbital diagram for as
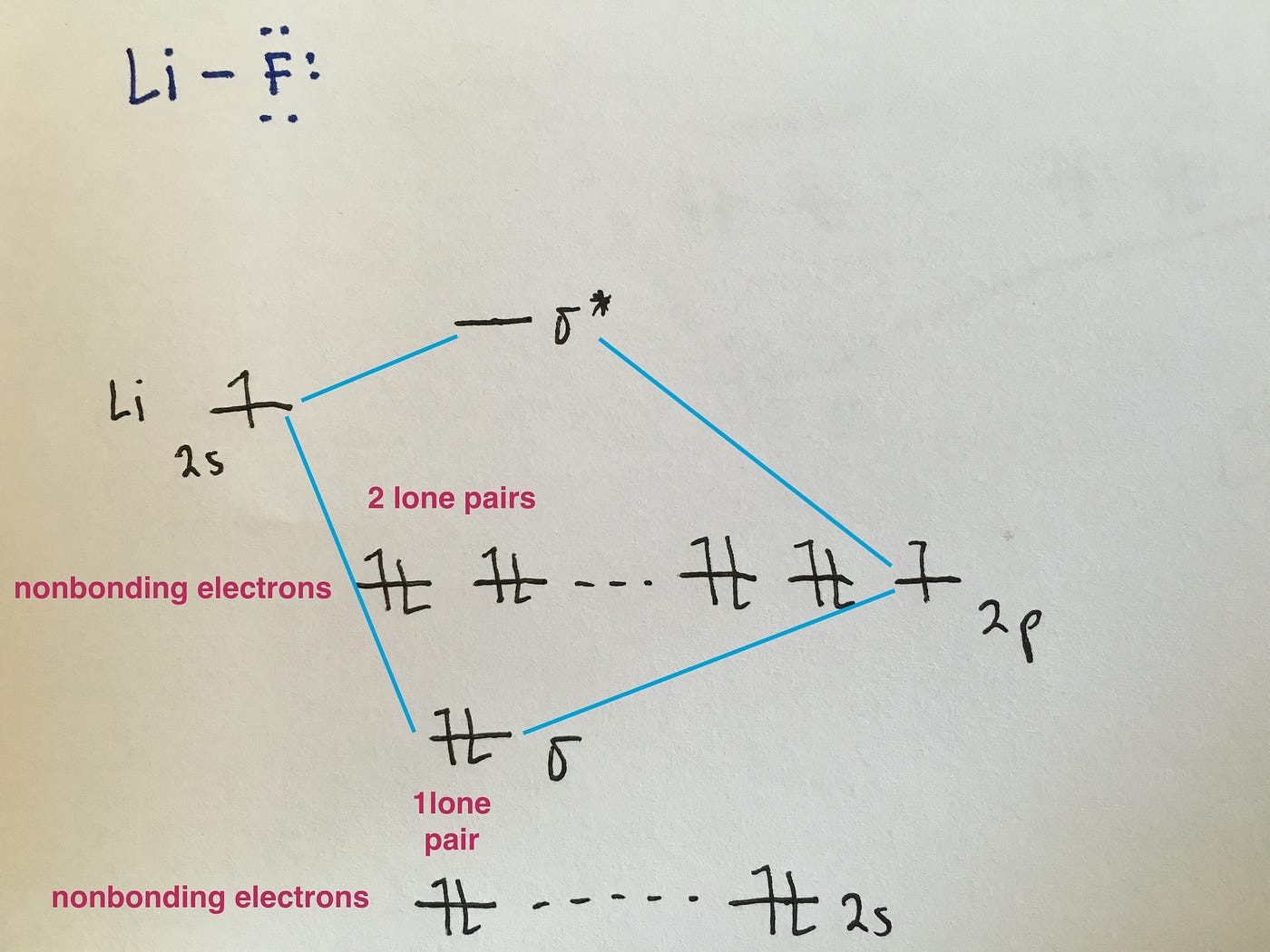
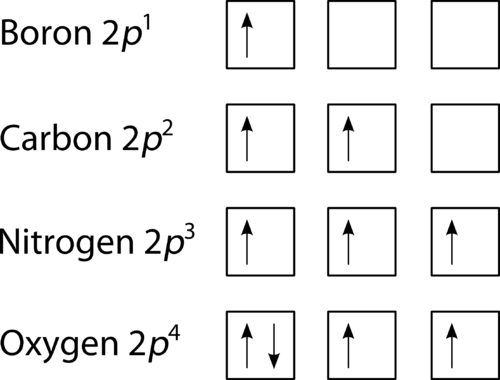
The orbital diagram shows how the electrons are arranged within each sublevel. The maximum number of electrons allowed in an orbital is #2# , each with opposite spins (Pauli's exclusion principle). In a neutral carbon atom, the #"1s"# sublevel has one orbital with two electrons with opposite spins, represented by the arrows pointing in opposite ... Construct the orbital Diagram Of the F- Ion. construct construct the orbital diagram the f- ion chem 120a november 8 2005 fall 2004 8 00 - 9 20 am exam ii name prepare a molecular orbital energy level diagram for no construct a solved construct the orbital diagram the f ion a ne answer to construct the orbital diagram of the f ion a neutral fluorine atom has 9 electrons how many ...
Orbital Diagram For Aluminum.They consist of the symbol for the element in the. It explains how to write the orbital diagram. Electron Dot Diagram For Aluminum — UNTPIKAPPS (Millie Bailey) Here are some orbital diagrams of elements with more electrons to help you understand the rules, electron configuration, orbital diagrams, and quantum numbers. . They consist of the symbol for the element in

Construct the orbital diagram for as
Construct a molecular orbital diagram using the 2s and 2p orbitals for each atom as your basis set. Use the D2h character table to determine and label the SALCS of the oxygen and carbon orbitals ... Answer to: Draw and explain the orbital diagram for copper (Z = 29). By signing up, you'll get thousands of step-by-step solutions to your homework... Mo is element 42 so for the 3+ ion you draw the configuration for . It is not the same orbital diagram as Y this is because it is a transition metal. The electron added would go into the 3pz orbital and is the second electron in that orbital. The element is Ga. b) The orbital diagram shows the 2s and 2p orbitals .
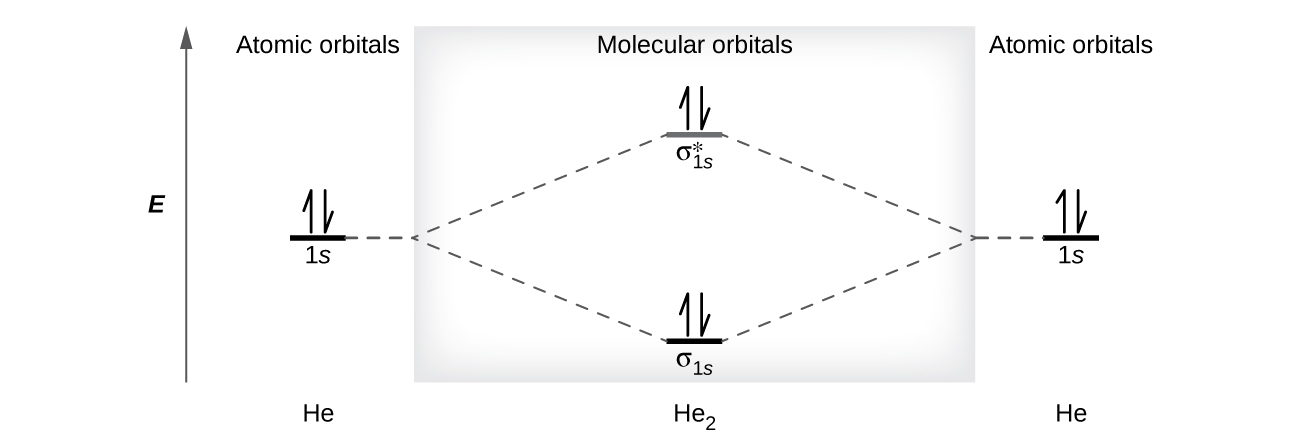
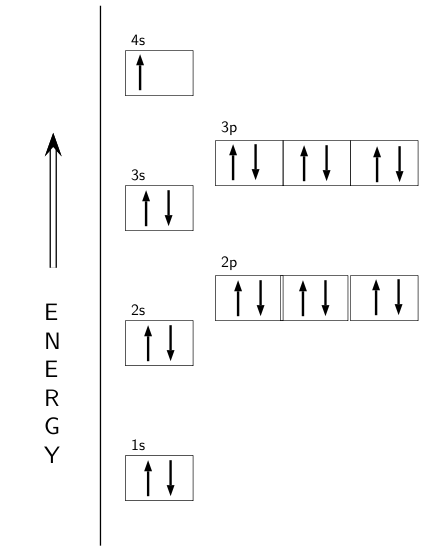
Construct the orbital diagram for as. Construct the molecular orbital diagram for dichlorine. x y z z y 3 x y z z y 4 Showing the p orbitals. Showing the s and p orbitals. ORBITALS AND MOLECULAR REPRESENTATION 11. CARBON ORBITALS Methane Ethane METHANE AND ETHANE C H H H H CH4 C C H H H H H H C2H6 1 2 Color conventions: Hydrogen atoms are shown in gray. 36 construct the orbital diagram of the f- ion. Construct the orbital diagram of each atom or ion. In writing the electron configurat ion for fluorine the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. The 24 electrons of a. Ion electron confugurat ion s. A neutral fluorine atom has 9 electrons. Asked for: molecular orbital energy-level diagram, bond order, and stability. Strategy: Combine the two He valence atomic orbitals to produce bonding and antibonding molecular orbital; s. Draw the molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the system. Determine the total number of valence electrons in the He 2 2 + ion. Fill the molecular ... An orbital diagram, or orbital box diagram, is a way of representing the electron configuration of an atom. A box, line, or circle, is drawn to represent each orbital in the electron configuration. (using the Aufau Principle to order the orbitals and hence the boxes, lines or circles, as shown below) 1s. →. 2s.
Question: Construct the orbital diagram for Ni. Construct the orbital diagram for Ni. see more. Best answer. Atomic orbital diagrams are also known as electron-in-a-box diagrams. These are simplified diagrams of how electrons are arranged within the orbitals for a. Answer to Construct the orbital diagram for Ni. Start by adding the appropriate ... Electron orbital diagrams and written configurations tell you which orbitals are filled and which are partially filled for any atom. The number of valence electrons impacts on their chemical properties, and the specific ordering and properties of the orbitals are important in physics, so many students have to get to grips with the basics. Electronic structure of oxygen atom is Leaving out the 4 electrons in the 1s orbitals of two oxygen atoms constituting the molecule (represented as KK), the molecular orbital energy diagram for remaining 12 electrons of oxygen as molecule is shown:(i) Electronic configuration:(ii) Bond order: Here Nb = 8; Na = 4The two oxygen atoms in a molecule of oxygen are united through two covalent bonds ... Problem: Construct the orbital diagram for As.HintStart by adding the appropriate subshells. For example, carbon is in the 2p block of the periodic table, and so you need to show the 2p subshell and everything below it.Next, click the orbitals to add electrons (represented as arrows).
Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. Construct the orbital diagram for the phosphide ion, p-. 3p 3s Answer Bank Energy 2p 11 2s Is. Procedure for Constructing Molecular Orbital Diagrams Based on Hybrid Orbitals 1. Begin with the Lewis structure. 2. Decide how many orbitals each atom needs to make its sigma bonds and to hold its non-bonding electrons. Draw the atomic and hybrid orbitals on on side of the page. 3. For each sigma bond, take a hybrid (or atomic) orbital from ... Orbital diagrams are a visual way to show where the electrons are located within an atom. Orbital diagrams must follow 3 rules: The Aufbau principle, the Pau... Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 90% (29 ratings) Transcribed image text: Construct the orbital diagram for arsenic. Answer Bank Energy.
The rules for orbital filling diagrams. If you want to learn how to draw orbital filling diagrams, you need to follow these handy rules. They probably won't make sense right now, but I'll explain them when the time is right. For now, trust me that these rules are handy ones: Electron configurations list the orbitals from lower to higher ...
Electron orbital diagram s and written configurations tell you which orbital s are filled and which are partially filled for any atom. The number of valence electrons impacts on the ir chemical properties, and the specific ordering and properties of the orbital s are important in physics, so many students have to get to grips with the basics. Construct the orbital Diagram for as.
Construct the orbital diagram for As. First, we need to determine the electron configuration for As (arsenic). The electron configuration depends on the number of electrons an atom or ion has. Since As is neutral (uncharged), we can say that Z (atomic number) = number of protons = number of electrons. Arsenic has an atomic number of 33, so it ...
Potassium's atomic number is 19. This means that every atom of potassium has 19 protons in its nucleus. In a neutral atom, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons. So the electron configuration of potassium will involve 19 electrons. The full electron configuration of potassium is "1s"^2"2s"^2"2p"^6"3s"^2"3p"^6"4s"^1". The noble gas notation is "[Ar]4s"^1".
This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into orbital diagrams and electron configuration. It explains how to write the orbital diagram n...
Answer to Construct the orbital diagram for Ni. Start by adding the appropriate subshells. For example, carbon is in the 2p block.1. Describe the two differences between a 2p x orbital and a 3p y orbital. The 2px orbital lies on the x-axis. The 3py orbital lies on the y-axis and is larger than the 2px orbital. 2.
Construct SALCs and the molecular orbital diagram for NH\(_3\). This is the first example so far that has more than two pendant atoms and the first example in which the molecule has atoms that lie in three dimensions (ie it is not flat). Ammonia is a trigonal pyramidal molecule, with three pendant hydrogen atoms.
Step 3: Construct the orbital diagram for the ion. 82% (439 ratings) Procedure for Construct ing Molecular Orbital Diagram s B as ed on Hybrid Orbital s 1. Begin with the Lewis structure. 2. Decide how many orbital s each atom needs to make its sigma bonds and to hold its non-bonding electrons.
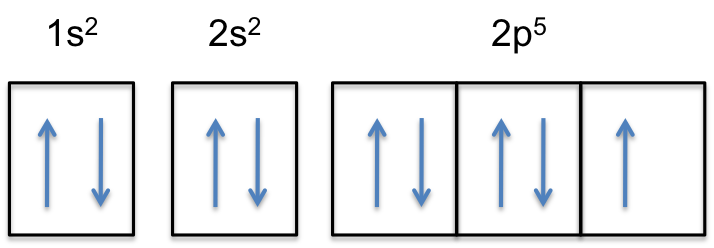
Orbital Diagram For Arsenic. Because the 4p section has 3 orbitals, but Arsenic ends with 4p3. It'll want to leave as few orbitals empty, so you have three arrows pointing up. The orbital diagram of arsenic can be written as 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s23p6 4s2 3d10 4p3. Arsenic has 33 electrons, including 3 in itsoutermost shell. schematron.org!
Construct the orbital Diagram for as. construct construct the orbital diagram for as a b a b 2 be same symmetry i e transform as the same construct a "relative" molecular orbital energy diagram f interpret the construct the orbital diagram for as imageresizertool construct the orbital diagram for as thanks for visiting our site this is images about construct the orbital diagram for as posted ...
Mo is element 42 so for the 3+ ion you draw the configuration for . It is not the same orbital diagram as Y this is because it is a transition metal. The electron added would go into the 3pz orbital and is the second electron in that orbital. The element is Ga. b) The orbital diagram shows the 2s and 2p orbitals .
Answer to: Draw and explain the orbital diagram for copper (Z = 29). By signing up, you'll get thousands of step-by-step solutions to your homework...
Construct a molecular orbital diagram using the 2s and 2p orbitals for each atom as your basis set. Use the D2h character table to determine and label the SALCS of the oxygen and carbon orbitals ...
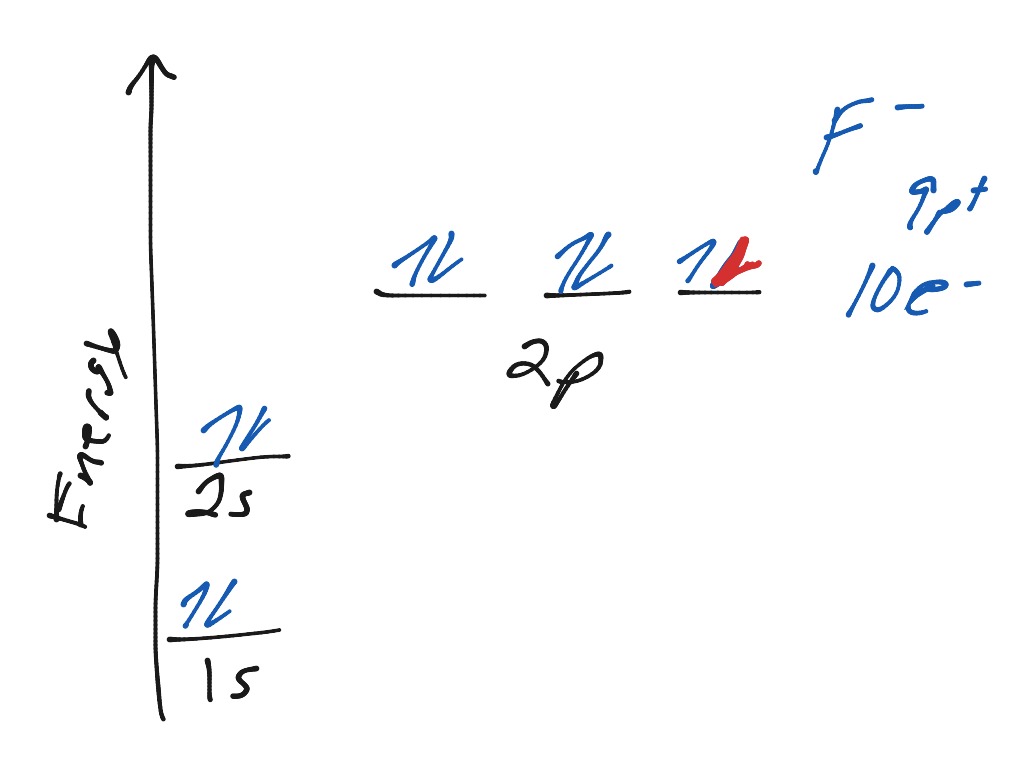




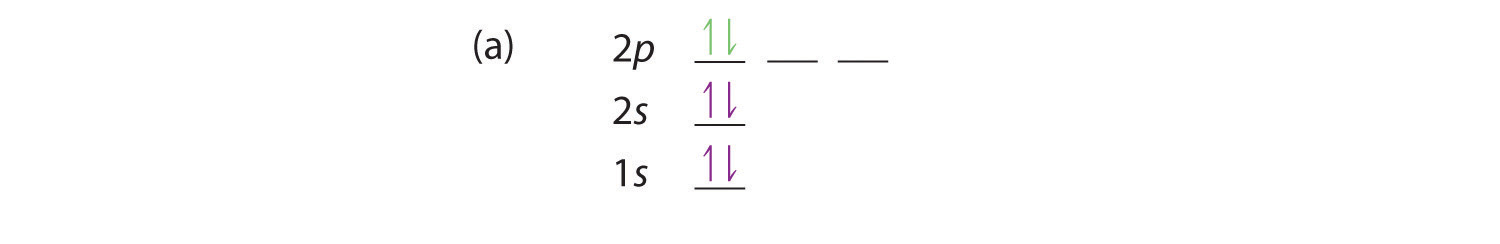


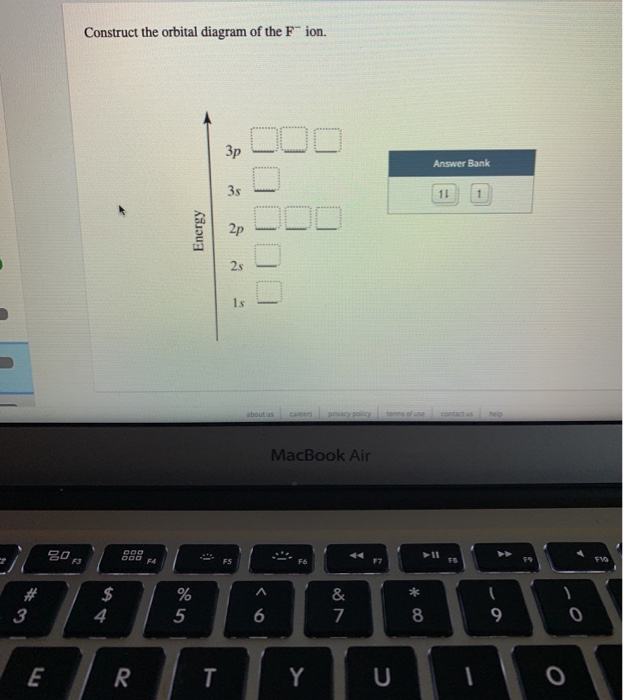

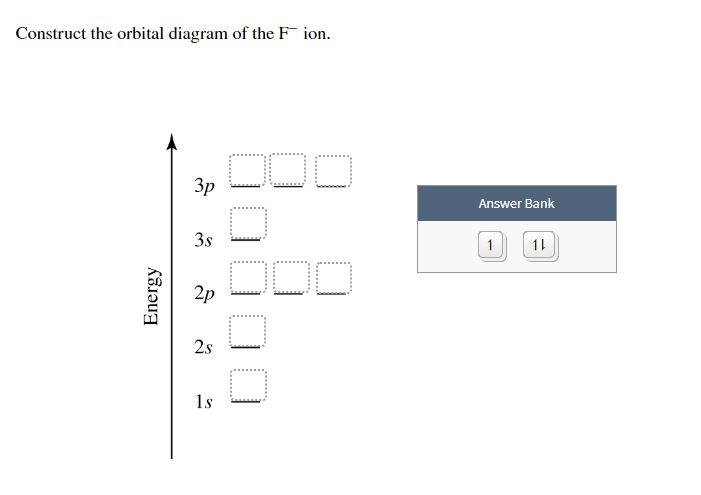













0 Response to "37 construct the orbital diagram for as"
Post a Comment