36 to locate the lower airway on a diagram, you would point to the area:
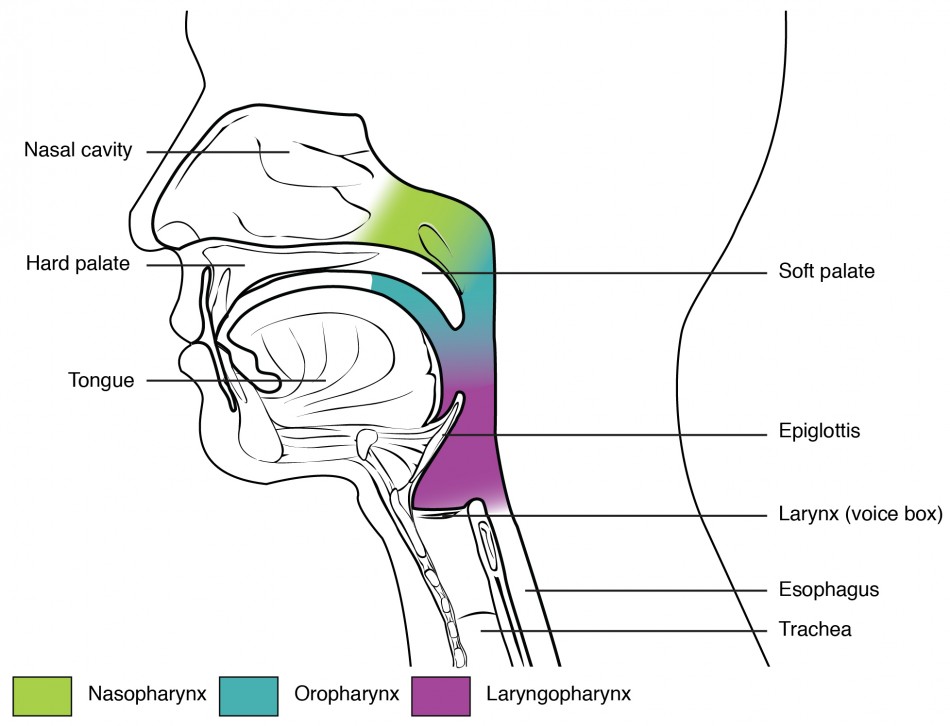
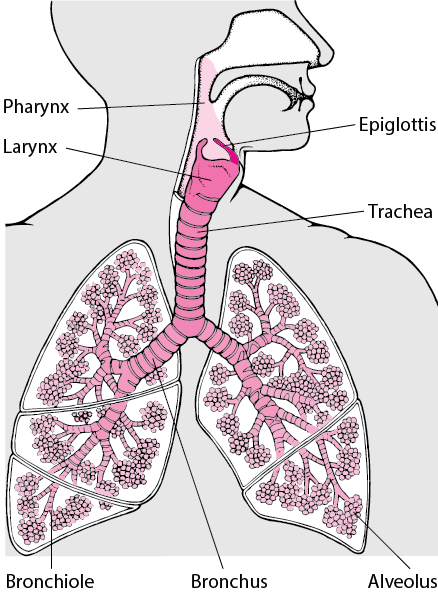
What is the Epiglottis. The epiglottis is a cartilaginous flap covering the opening of the windpipe during swallowing to prevent food from entering the lungs [1].. Where is the Epiglottis Located. The flat, leaf-like structure is attached to the superior end of the larynx (voice box), protruding into the pharynx, just behind the root of the tongue, in its relaxed state [2].
Consider the phase diagram for carbon dioxide shown in Figure 5 as another example. The solid-liquid curve exhibits a positive slope, indicating that the melting point for CO 2 increases with pressure as it does for most substances (water being a notable exception as described previously). Notice that the triple point is well above 1 atm, indicating that carbon dioxide cannot exist as a liquid ...
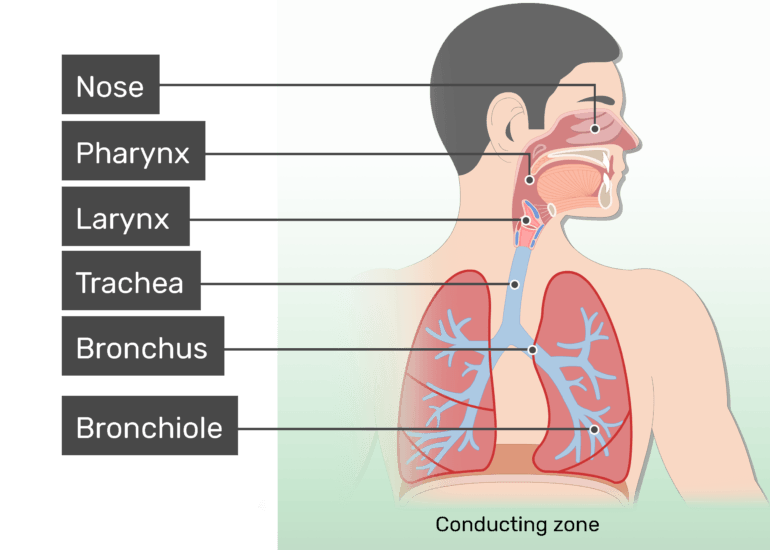
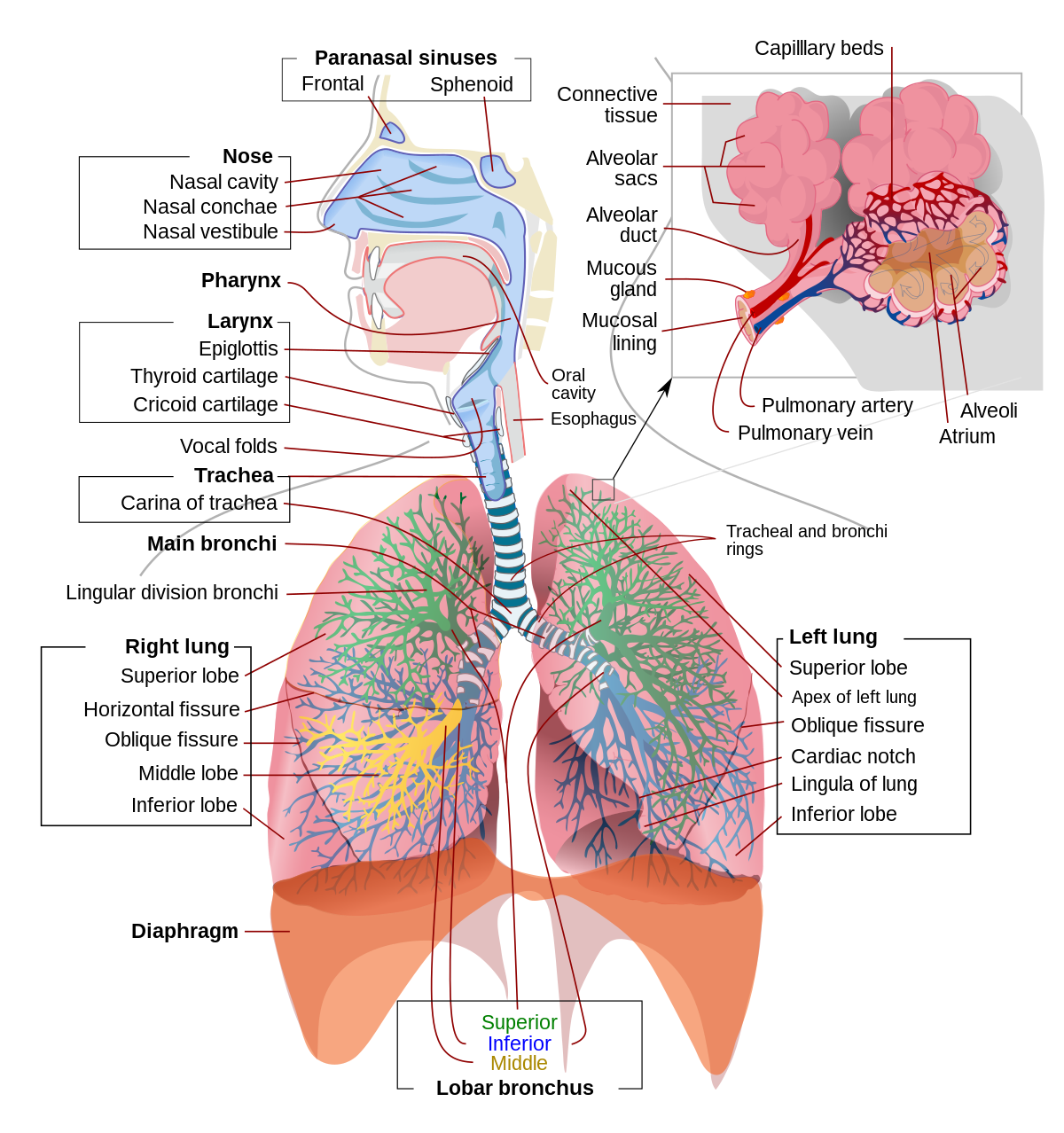
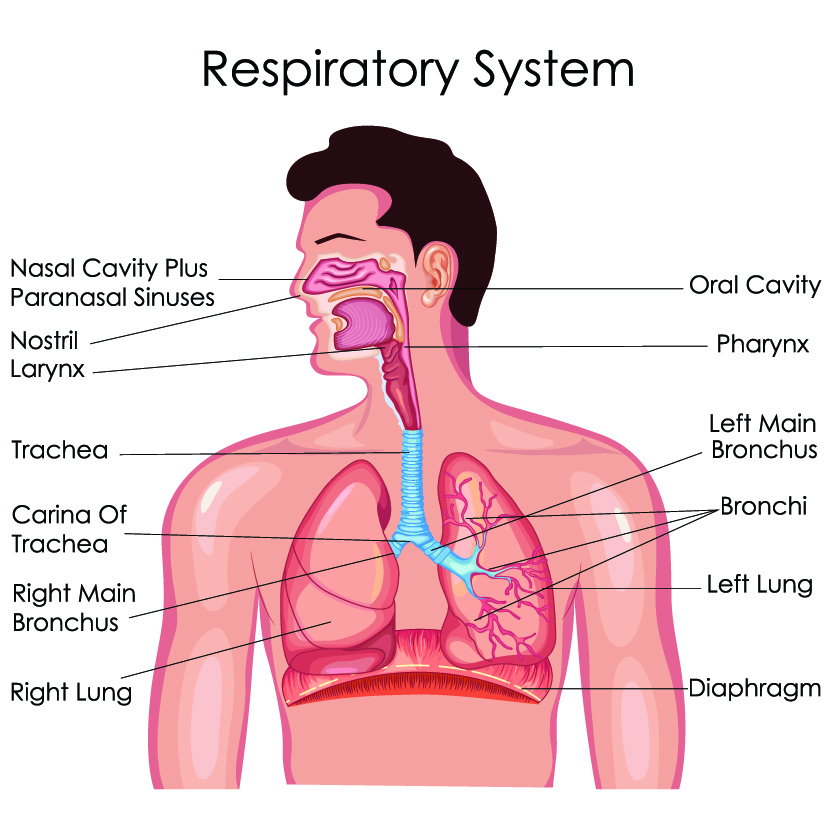
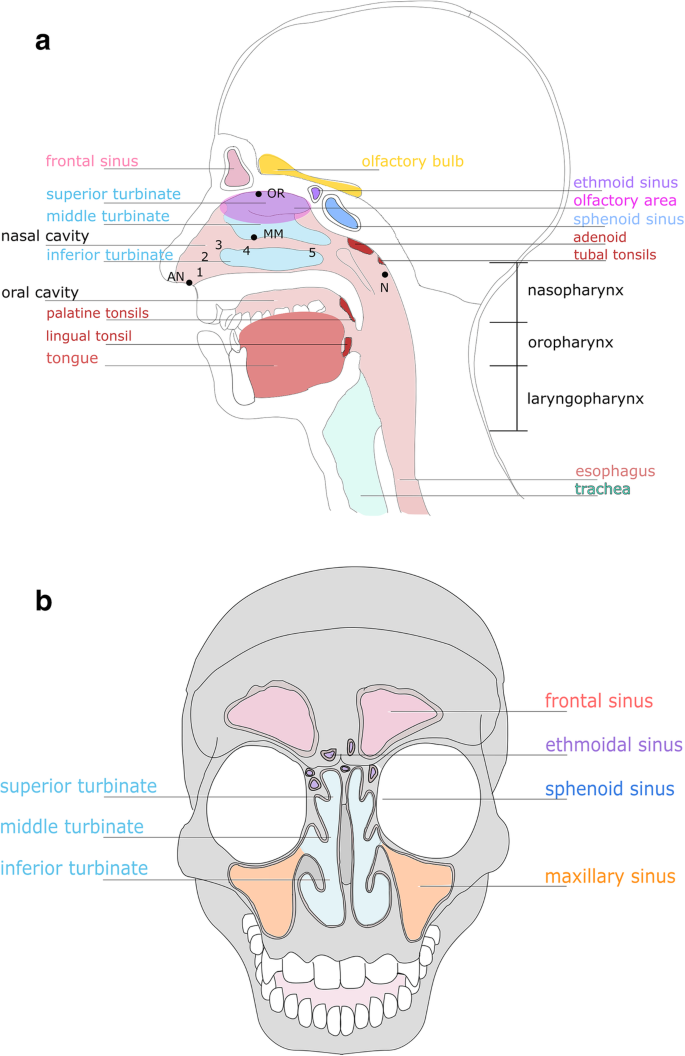
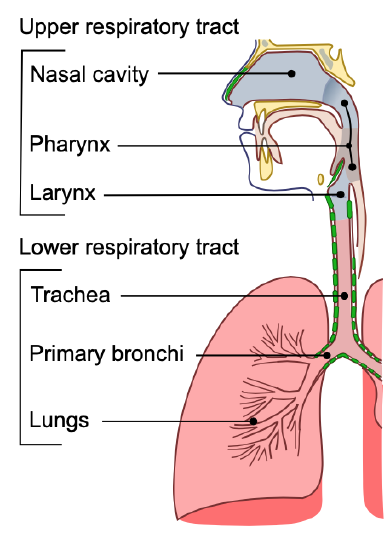
From a functional perspective, the respiratory system can be divided into two major areas: the conducting zone and the respiratory zone. The conducting zone consists of all of the structures that provide passageways for air to travel into and out of the lungs: the nasal cavity, pharynx, trachea, bronchi, and most bronchioles.
To locate the lower airway on a diagram, you would point to the area:
(e) At the temperature and pressure at point 2, Y(l) Y(g) 12. Where on a phase diagram can you locate conditions under which only one phase exists? (a) at an intersection of two lines (b) at the normal boiling point (c) at an intersection of three lines (d) in an area bounded by lines (e) at the triple point 13.
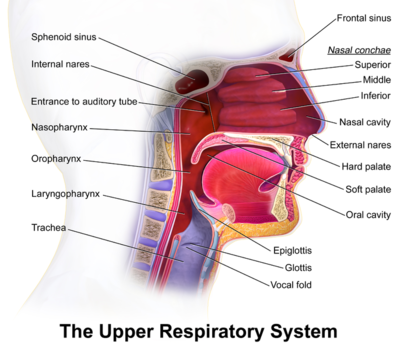
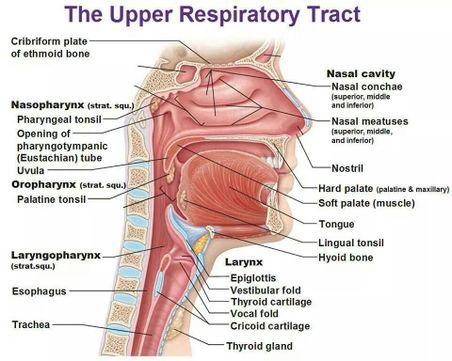
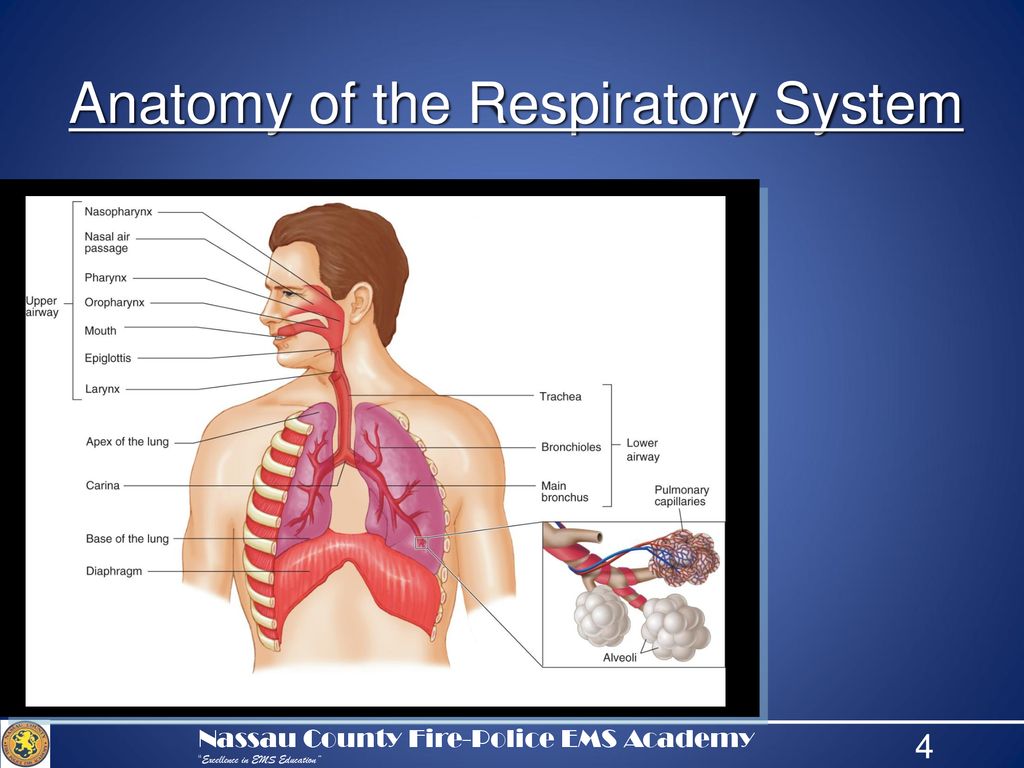
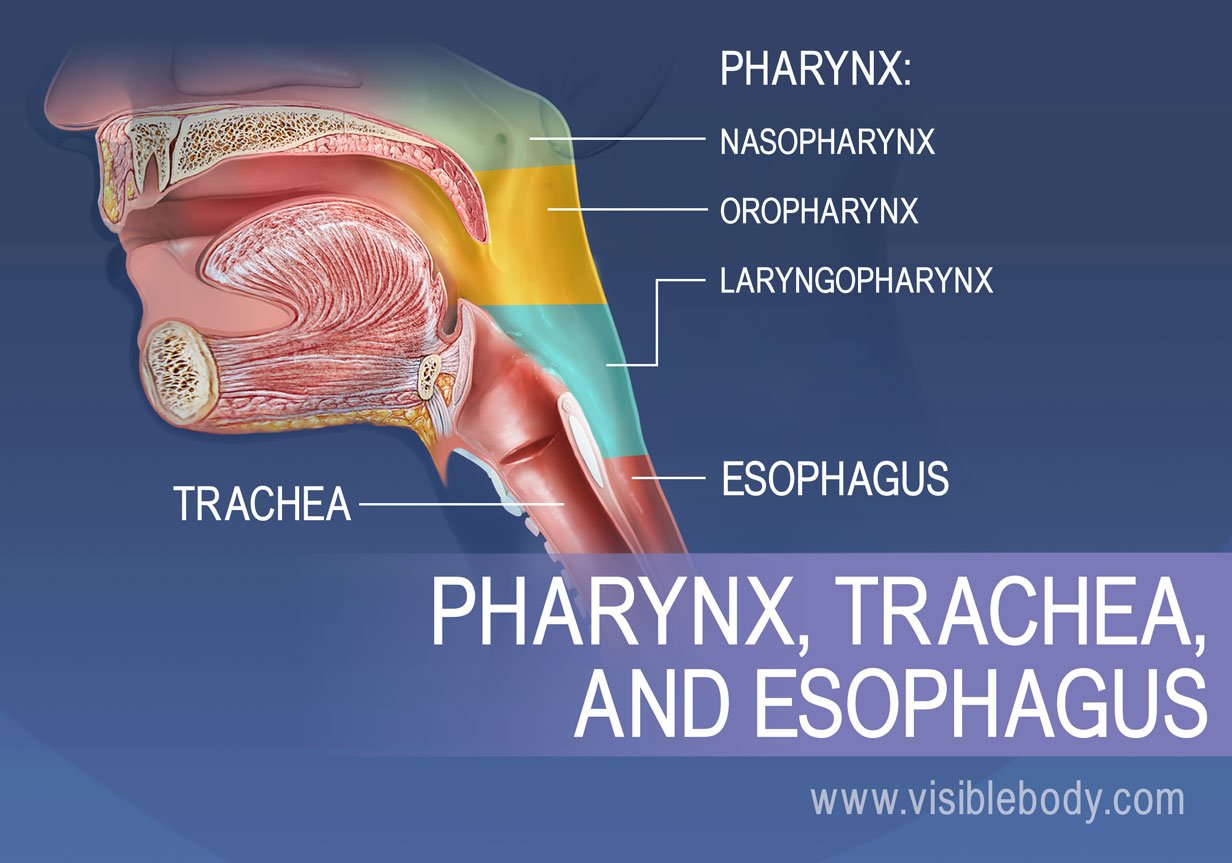
The upper respiratory tract, can refer to the parts of the respiratory system lying above the sternal angle (outside of the thorax), above the vocal folds, or above the cricoid cartilage. The larynx is sometimes included in both the upper and lower airways. The larynx is also called the voice box and has the associated cartilage that produces sound. The tract consists of the nasal cavity and ...
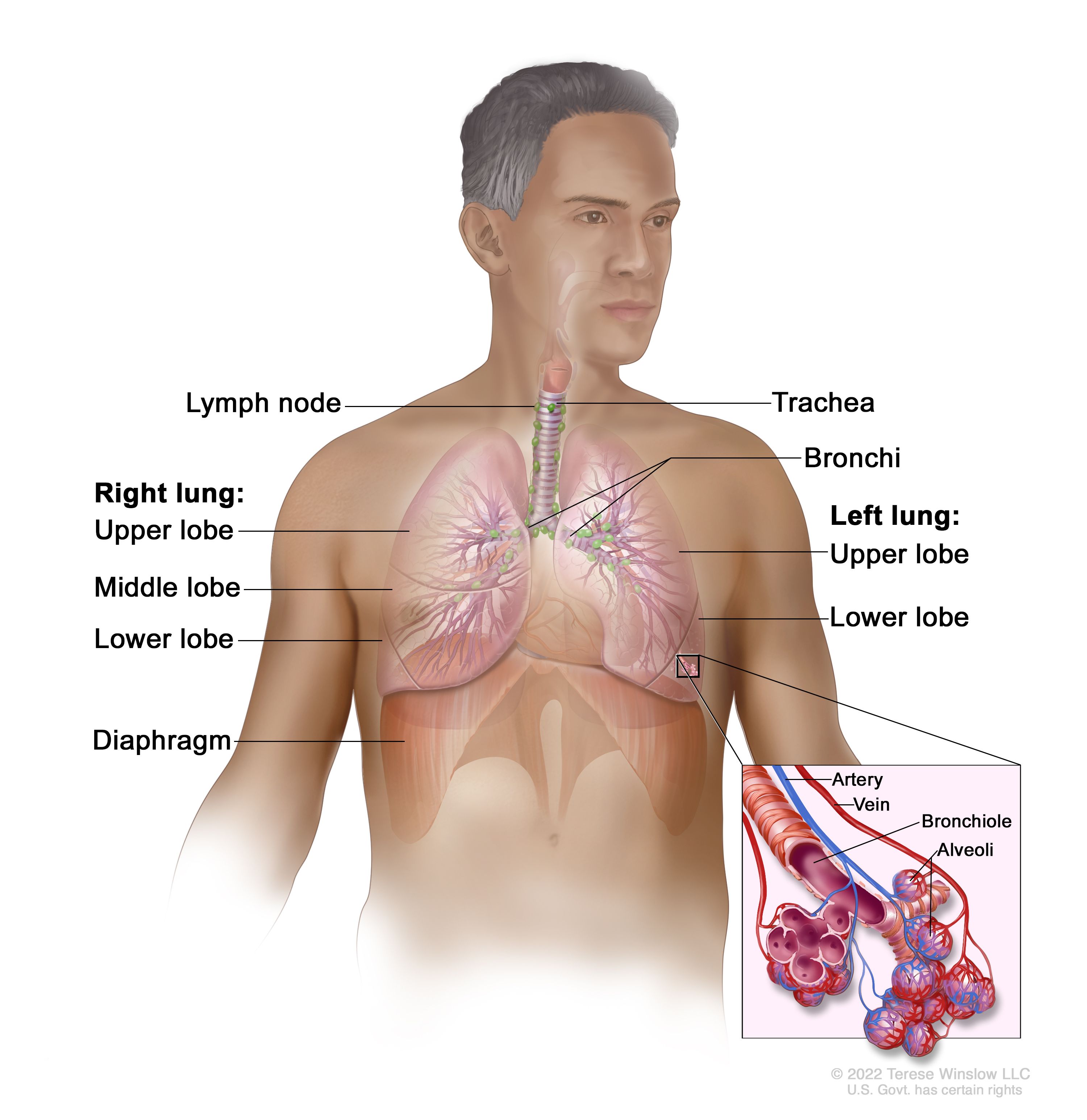
All the respiratory passages from the trachea to the respiratory bronchioles are called the tracheobronchial tree. The trachea divides at the sternal angle into right and left primary bronchus which goes into the right and left lungs. Each bronchus enters the lung at a notch called the hilum. Blood vessels and nerves also connect with the lungs ...
To locate the lower airway on a diagram, you would point to the area:.
When suctioning a child's airway, the EMT must take care not to: touch the back of the airway. ... You are suctioning the oral cavity of a patient who is vomiting profusely. You are using a soft (French) catheter to help clear the oral cavity, but it keeps getting clogged. ... To locate the lower airway on a diagram, you would point to the area ...
Step 5: To determine the domain of consideration, let's examine .Certainly, we need Furthermore, the side length of the square cannot be greater than or equal to half the length of the shorter side, 24 in.; otherwise, one of the flaps would be completely cut off. Therefore, we are trying to determine whether there is a maximum volume of the box for over the open interval Since is a ...
Correct answer:square units. Explanation: The area of rectangle can be found by multiplying the width and length of the rectangle. To find the length of the rectangle compare the x values of two of the coordinates: Since the length is . To find the width of the rectangle we need to look at the y coordinates of two of the points.
If you look at the M3 cluster H-R diagram (figure 6b), you see that the main sequence only extends part way to the upper-left, and then the stars appear off the main sequence to the upper right, in the Red Giant area of the H-R diagram.
Basic Airway Anatomy Upper Airway. The upper airway is the "A" of the ABC's. As the entry point for oxygen any damage to, or blockage of, the structures in the upper airway can rapidly result in unconsciousness or death. The anatomy of the upper airway can be broken down into the nose, mouth, and throat.
An Overview of Airway Anatomy. Airway, ventilation and respirations are a big part of emergency medicine and they make up 18-22% of the NREMT exam. This page will focus on airway anatomy and function for emergency medical technicians (EMT). Students can use it as an NREMT study guide or as a reminder to help brush up on basic skills if you are ...
To locate the lower airway on a diagram, you would point to the area: A. in the hypopharynx. B. below the larynx. C. at the alveoli. D. ... You arrive on the scene of a partially collapsed building and need to assess a patient who was in the area of the collapse. A sign that the patient has an adequate airway would be: ... Which of the ...
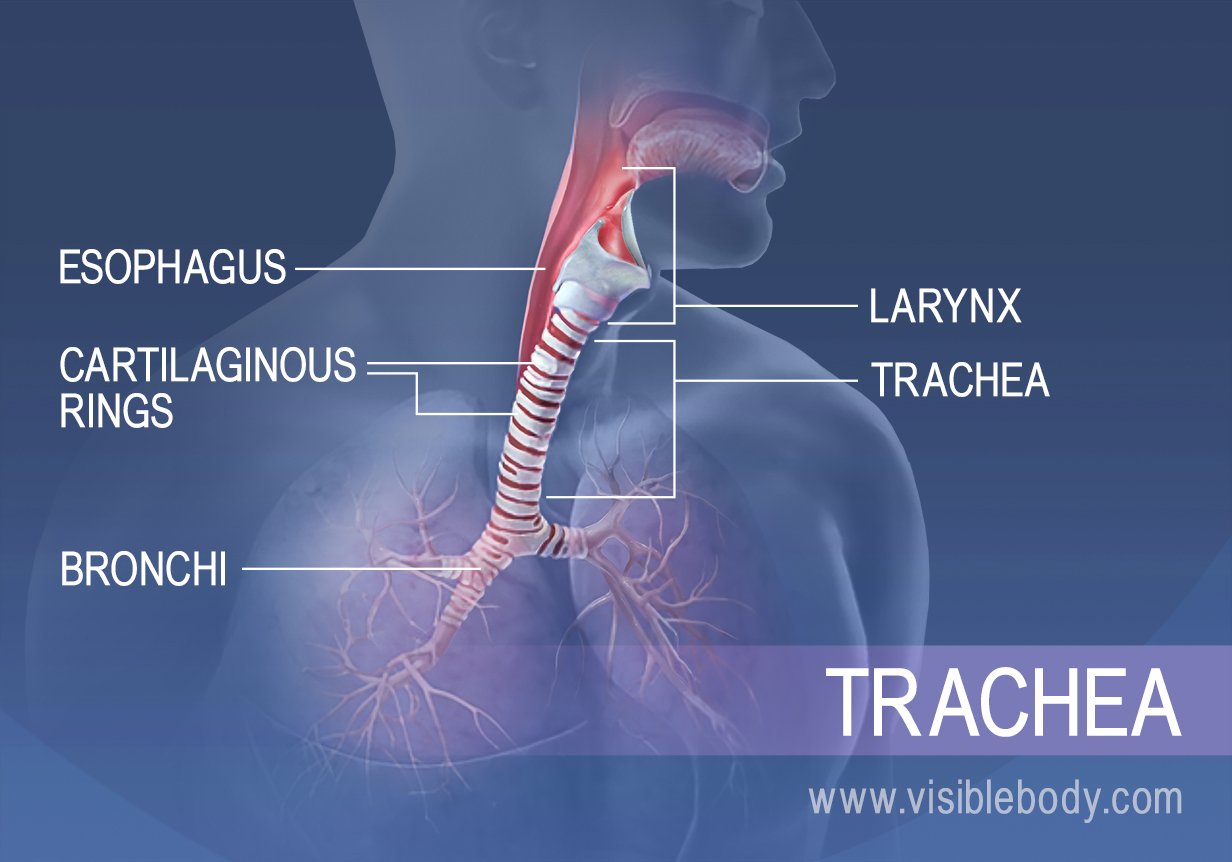
Trachea is the medical name for the windpipe, the largest airway in the respiratory system, about 4-5 inches in length and 1 inch in diameter that extends from the lower end of the larynx or voice box [1]. An integral part of the human airway, the trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli together make up the lower respiratory tract [2, 3].
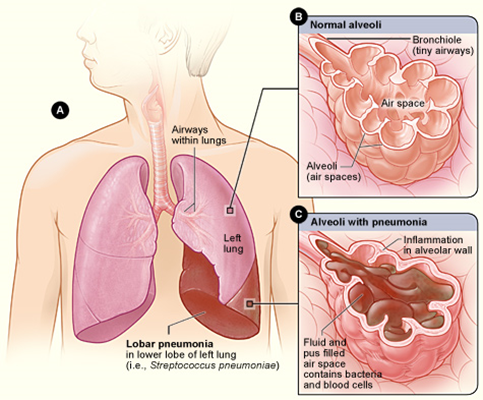
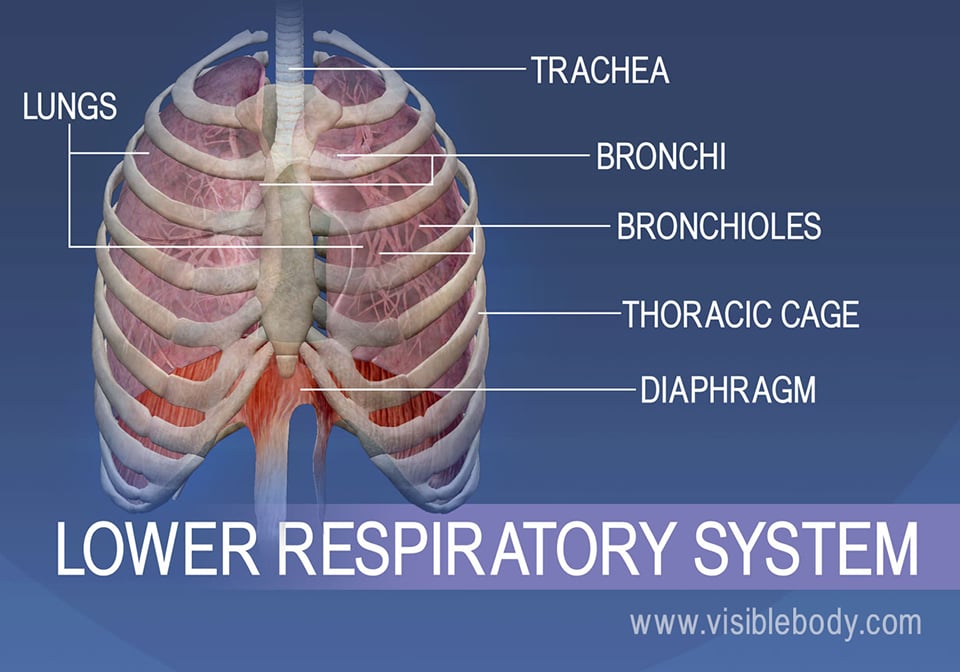
The lower respiratory system, or lower respiratory tract, consists of the trachea, the bronchi and bronchioles, and the alveoli, which make up the lungs. These structures pull in air from the upper respiratory system, absorb the oxygen, and release carbon dioxide in exchange. Other structures, namely the thoracic cage (or rib cage) and the diaphragm, protect and support these functions.
Airway routing occurs along pre-deined pathways called airways. [Figure 2-2] Airways can be thought of as three- dimensional highways for aircraft. In most land areas of the world, aircraft are required to ly airways between the departure and destination airports. The rules governing airway routing, Standard Instrument Departures (SID)
The ultimate pulmonary unit from respiratory brochiole to alveoli is called Acinus. There are about 28 orders of division of tracheo-bronchial tree. Total no. of alveoli has been estimated to be between 200 - 600 million, with a total surface area of 40 - 80 meter square.
The respiratory tract in humans is made up of the following parts: External nostrils - For the intake of air.; Nasal chamber - which is lined with hair and mucus to filter the air from dust and dirt.; Pharynx - It is a passage behind the nasal chamber and serves as the common passageway for both air and food.; Larynx - Known as the soundbox as it houses the vocal chords, which are ...
Lower Respiratory Tract Structural and Functional Anatomy. The organs making up the lower respiratory tract are all protected and kept in place by the rib cage, and the sternum, while the diaphragm and the intercostal muscles are vital to their functioning as well [3].. Trachea
Lower respiratory system Larynx, trachea, bronchi and lungs Functionally Conducting zone - conducts air to lungs Nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles and terminal bronchioles Respiratory zone - main site of gas exchange Respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveolar sacs, and alveoli
Phase Diagrams. The figure below shows an example of a phase diagram, which summarizes the effect of temperature and pressure on a substance in a closed container. Every point in this diagram represents a possible combination of temperature and pressure for the system. The diagram is divided into three areas, which represent the solid, liquid ...
Federal Aviation Administration
To locate the lower airway on a diagram, you would point to the area: A. Below the larynx. B. At the alveoli. C. Above the glottis. D. In the hypopharynx. A. Below the larynx. The lower Airway begins below the larynx. Your patient presents with burns to the face, nose, and mouth and with noticeable soot in his mouth. This patient is predisposed to:
To locate the lower airway on a diagram, you would point to the area: A. above the glottis. B. in the hypopharynx. C. below the larynx. D. at the alveoli.
The area under the curve from x = 0 to x = 0.5 is denoted by B. (iv) Draw a diagram to show rectangles which could be used to find lower and upper bounds for B, using not more than three rectangles for each bound. (You are not required to find the bounds.) 0.5 0.7 0.9
21.1 OVERVIEW OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM • Classified anatomically into upper and lower tracts: § _____- passageways from nasal cavity to larynx § Lower - passageways from trachea alveoli o Alveoli - tiny air sacs, site of gas exchange o _____- »Each is a collection of millions of alveoli and their blood vessels embedded in elastic
You arrive on the scene of a partially collapsed building and need to assess a patient who was in the area of the collapse. A sign that the patient has an adequate airway would be: ... To locate the lower airway on a diagram, you would point to the area: below the larynx.
Alveolar Epithelium. The one-cell thick walls of the alveoli are composed of two distal airway epithelium cell types (pneumocytes) [7]. Type-1 squamous alveolar epithelial cells: Constituting 95% of the alveolar surface area [8], the type 1 cells are extremely thin and flexible to help in the process of gas diffusion so the oxygen-carbon dioxide exchange can occur between the alveoli and the ...
Suctioning helps to remove fluid from the upper airway. It is not effective for bronchoconstriction or stridor, and it can cause hypoxia if it is too prolonged. To locate the lower airway on a diagram, you would point to the area: A. below the larynx. B. in the hypopharynx. C. at the alveoli. D. above the glottis. below the larynx
The compliance of a system is defined as the change in volume that occurs per unit change in the pressure of the system. In layman terms, compliance is the ease with which an elastic structure stretches. Compliance is, therefore, basically a measurement of the elastic resistance of a system. Pulmonary compliance (C) is the total compliance of both lungs, measuring the extent to which the lungs ...





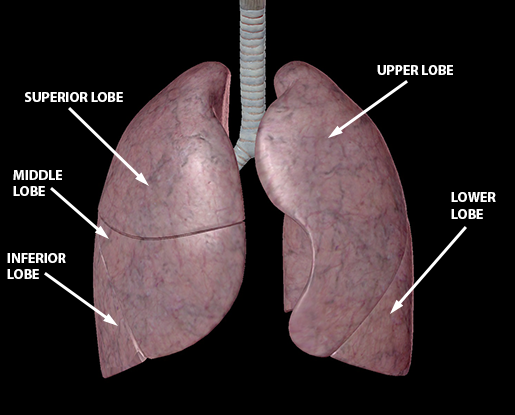
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/fissura-horizontalis-pulmonis-dextri/DvEowfn02rWTcROzUgq5Kw_Fissura_horizontalis_pulmonis_dextri_01.png)

:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/lung-4/7rJXUAkQZMuLSa4vnR9g_RackMultipart20180207-1462-vrc81e.png)









0 Response to "36 to locate the lower airway on a diagram, you would point to the area:"
Post a Comment