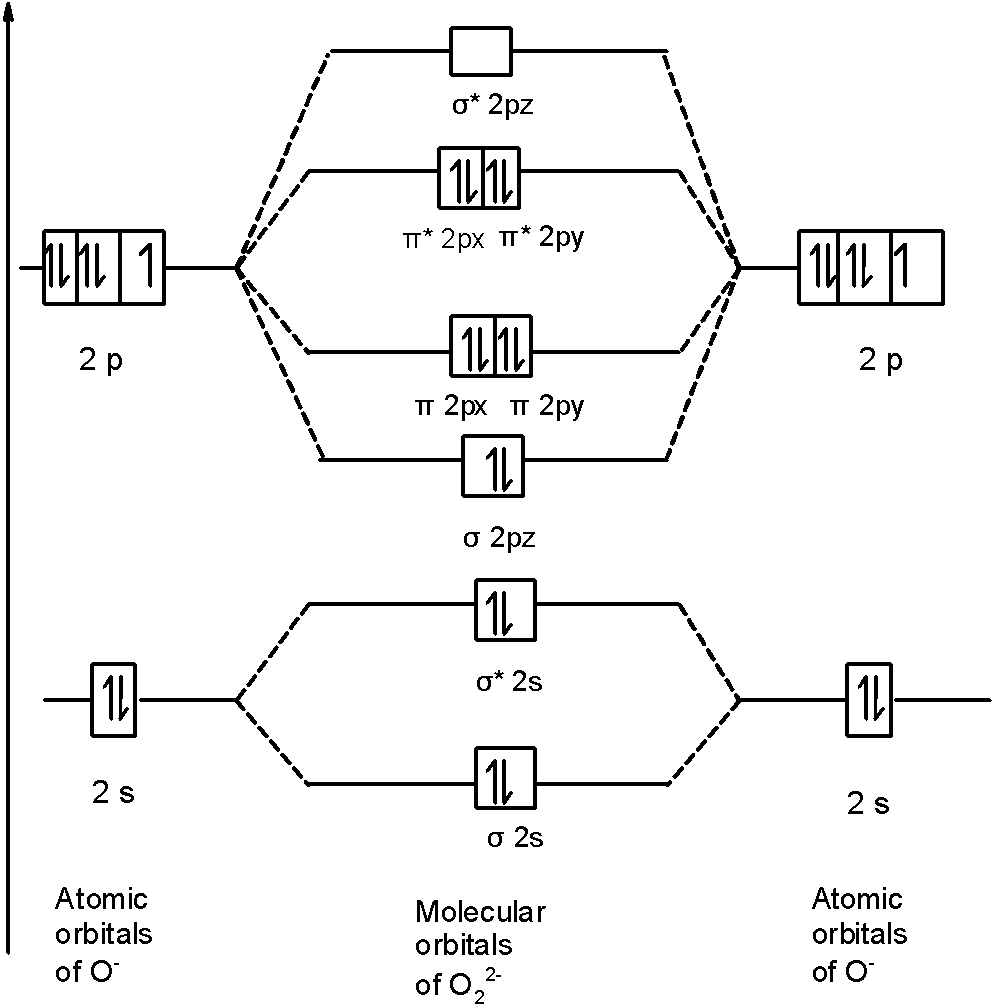
36 o2 2- molecular orbital diagram
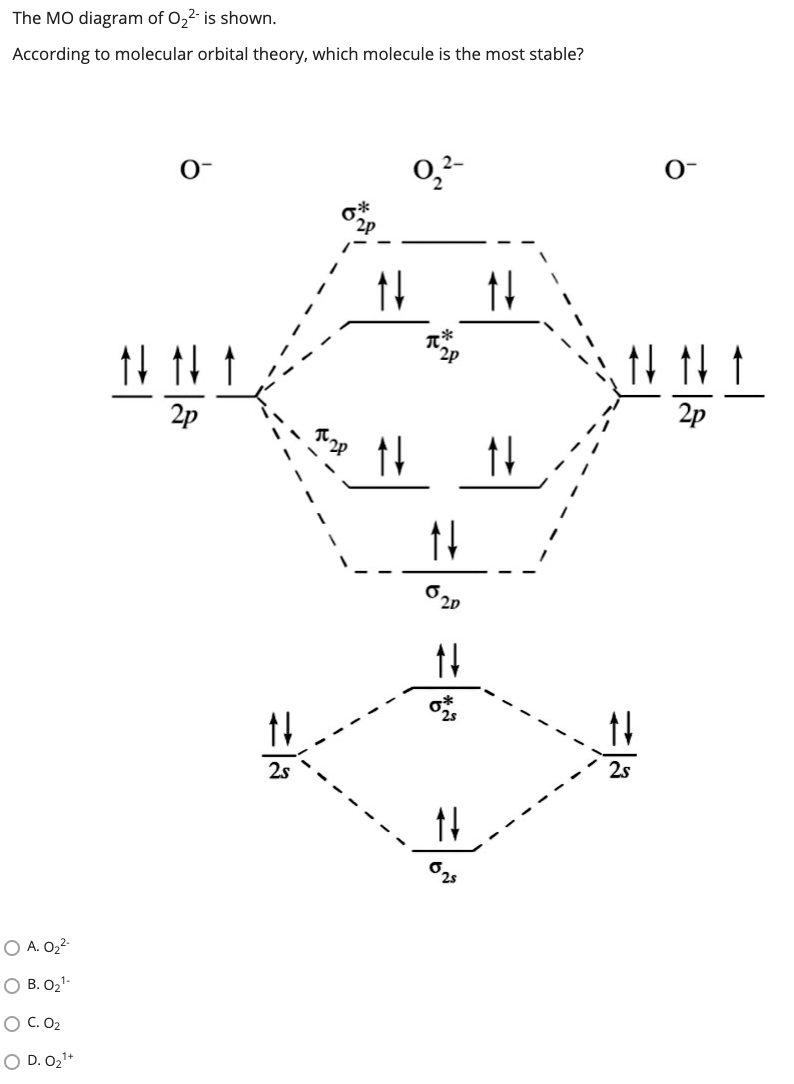
We’re being asked why O22+ ion ... than O2 itself. For this, we need to determine the bond order for each species. · The bond order tells us the stability of a bond: a higher bond order means the bond is more stable and stronger. Step 1: Calculate the total number of valence electrons present. Step 2: Draw the molecular orbital diagram...
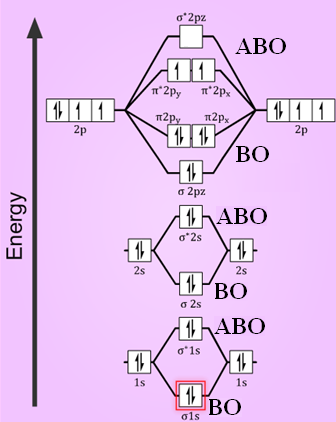
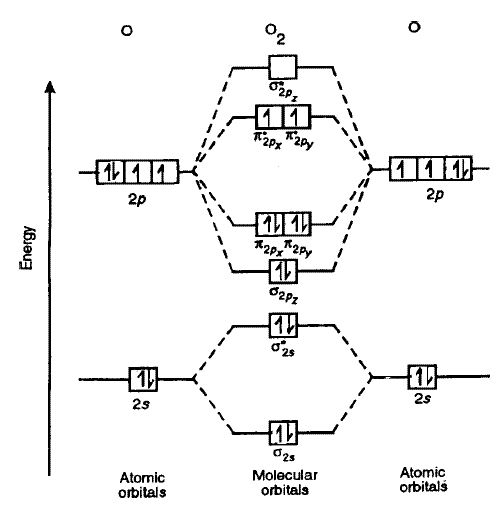
We know that Oxygen has atomic number = 8. Thus, the electronic configuration for an atom of oxygen in the ground state can be given as - $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^4}$ One atom of oxygen has 8 electrons. Thus, two atoms will possess 16 electrons i.e. Oxygen molecules will have 16 electrons. The molecular orbital diagram of an Oxygen molecule is as -
October 28, 2014 - Compare the stabilities of O2 , O2-,O22- . ... Ans: The stabilities of these can be best explained using Molecular orbital theory. (i) Formation Oxygen molecule: Electronic configuration of oxygen atom-1s² 2s² 2p⁴ Atomic orbitals of oxygen combine to form molecular orbitals.
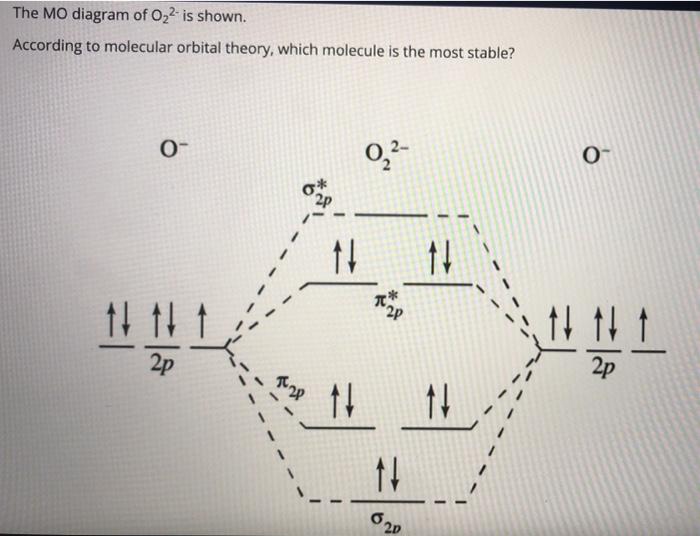
O2 2- molecular orbital diagram
3 Mar 2021 — Molecular#Orbital#Diagram #Oxygen#Molecule#MOdiagram #Chemistry #Class11 #NEET #JEE #MDCAT #ECAT #ChemicalBonding This video is a small ...
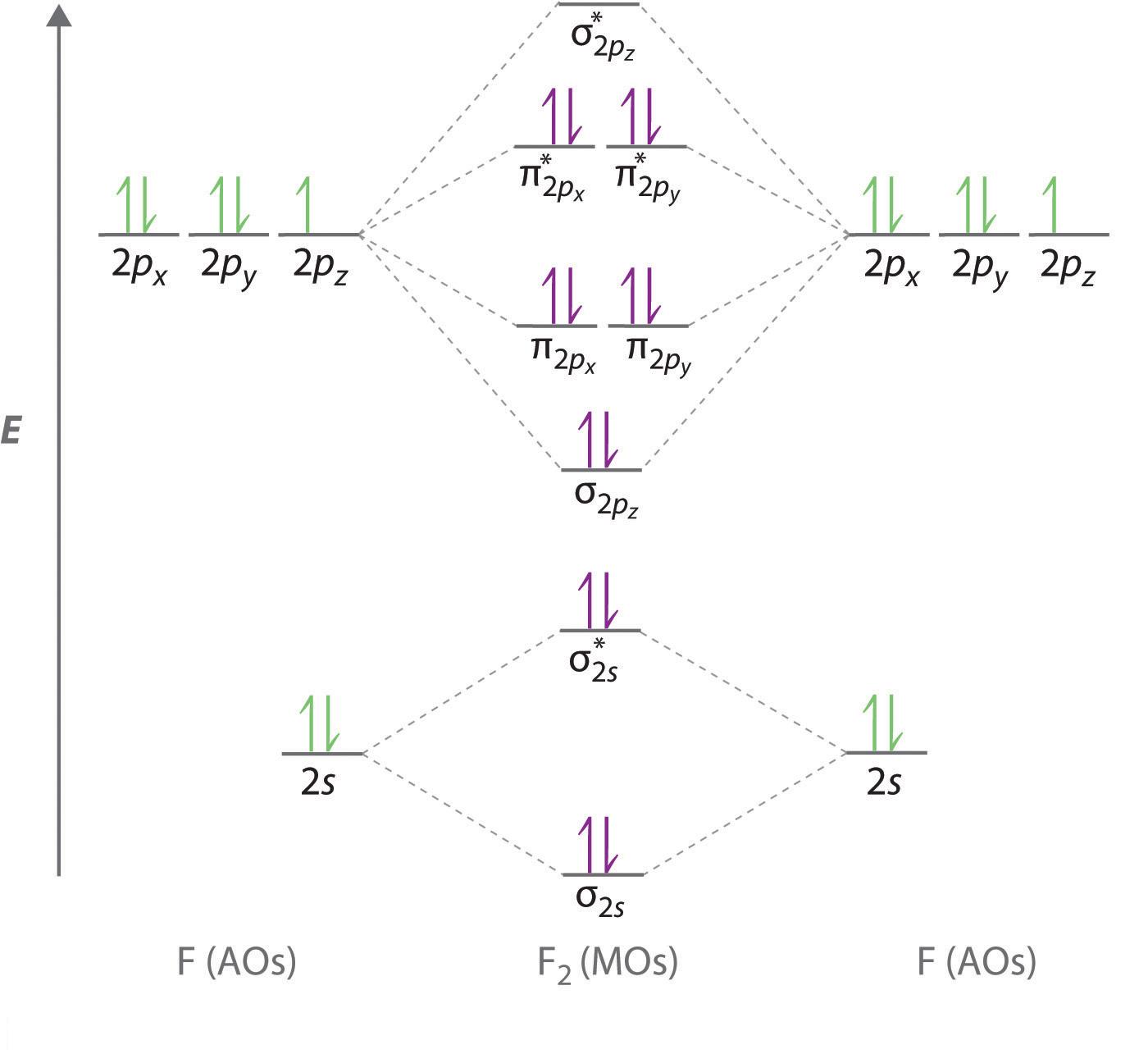
This means that the electron configuration of a neutral oxygen atom must account for 8 electrons. The molecular orbital diagram for an O2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the interactions between the 2s and 2p valence orbitals. image via upload.wikimedia.org image via upload.wikimedia.org
Question: Below is a molecular orbital diagram for O2. Label the atomic and molecular orbitals and fill in the electrons. Sketch two bonding and two antibonding orbitals in the provided boxes and identify which MOs they correspond to in the MO diagram. (8) Is O2 diamagnetic or paramagnetic and is this consistent with the Lewis structure.
O2 2- molecular orbital diagram.
O2 molecular orbital diagram oxygen has a similar setup to h 2 but now we consider 2s and 2p orbitals. This diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of a molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals. Beyard 3.
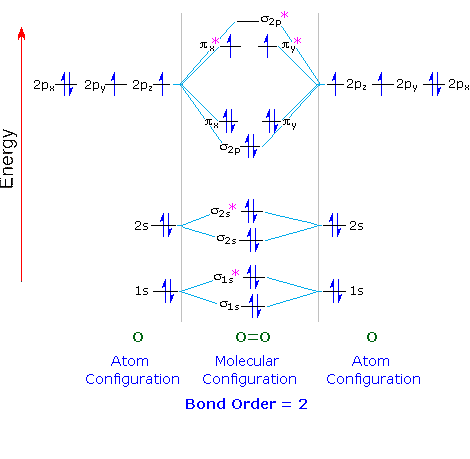
Electronic structure of oxygen atom is Leaving out the 4 electrons in the 1s orbitals of two oxygen atoms constituting the molecule (represented as KK), the molecular orbital energy diagram for remaining 12 electrons of oxygen as molecule is shown:(i) Electronic configuration:(ii) Bond order: Here Nb = 8; Na = 4The two oxygen atoms in a molecule of oxygen are united through two covalent bonds ...
How To make molecular Orbital diagramhttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UYC-ndQ6Lww&t=6s
How to draw molecular Orbital Diagram of Oxygen molecule (O 2) ? Oxygen (O 2) molecule: Oxygen atom has electronic configuration 1s2, 2s2, 2p4 . Two p-atomic orbitals (one from each oxygen) atom combine to form two molecular orbitals, the bonding molecular orbital σ2px and antibonding molecular orbital σ*2px.
Draw a molecular orbital diagram of $ {N_2}$ or $ {O_2}$ with magnetic behavior and bond order. Hint: Generally the molecular orbital diagrams are used to understand the bonding of a diatomic molecule. You should know that molecular orbital diagrams are used to deduce magnetic properties of a molecule; they also help us to find out the bond ...
In order to continue enjoying our site, we ask that you confirm your identity as a human. Thank you very much for your cooperation
The bond length in the oxygen species can be explained by the positions of the electrons in molecular orbital theory. To obtain the molecular orbital energy-level diagram for O 2, we need to place 12 valence electrons (6 from each O atom) in the energy-level diagram shown in Figure 9.10.1 . We again fill the orbitals according to Hund's rules ...
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. Compare the bond order in H 2 + and H 2 using the molecular orbital energy diagram for ...
The Molecular orbital diagram for O2 O 2 is like this: As you can see the oxygen molecule has two unpaired electrons in the lower π π * ant-bonding states. For O2+2 O 22 + basically remove the two unpaired electrons in the π π * anti-bonding states, as they are the most easily removed. 26K views View upvotes Sponsored by Elite Side Lines
A molecular orbital explicitly describes the spatial distribution of a single electron orbitals, and σ∗. 1s is higher in energy. Draw this out using an energy level diagram: 2 He2 has bond order 0 [ (2 − 2)/2 = 0], and we can make H+. 2,. H−.A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical ...
January 4, 2021 - Hund’s rule dictates that one electron occupies each orbital, and their spins are parallel, giving the O2 molecule two unpaired electrons. This diagram shows 8 electrons in bonding orbitals and 4 in antibonding orbitals, resulting in a predicted bond order of 2. We now turn to a molecular orbital ...
You'll need the molecular orbital (MO) diagram of O2. Begin with the atomic orbitals. Oxygen atom has 2s and 2p valence orbitals and 6 valence electrons: Each oxygen contributes 6, so we distribute 12 valence electrons into the molecule to get O2. Two 2s orbitals combine to give a σ2s bonding and σ* 2s antibonding MO.
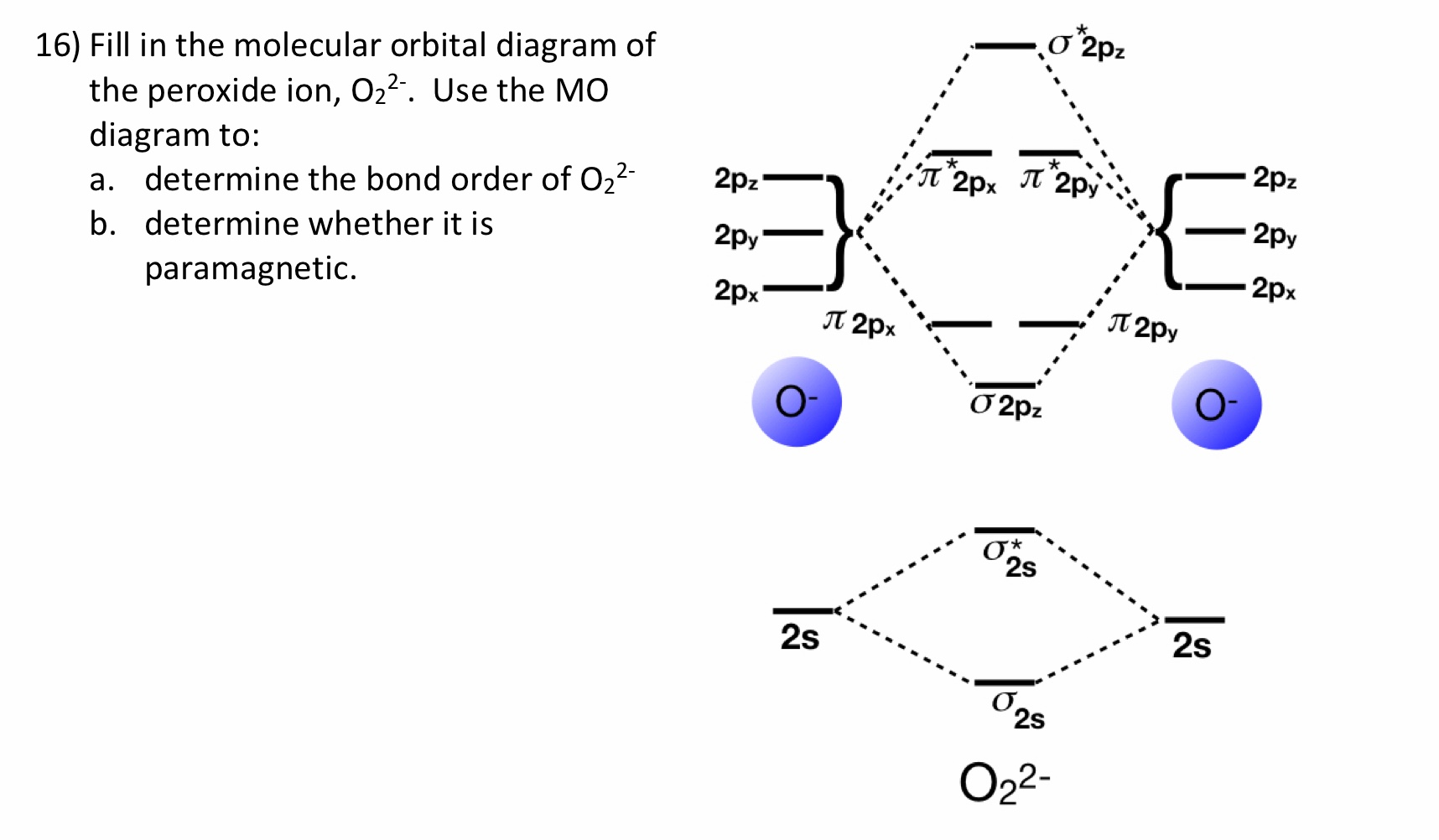
Answer to Draw molecular orbital diagrams for O2-, O22-, and
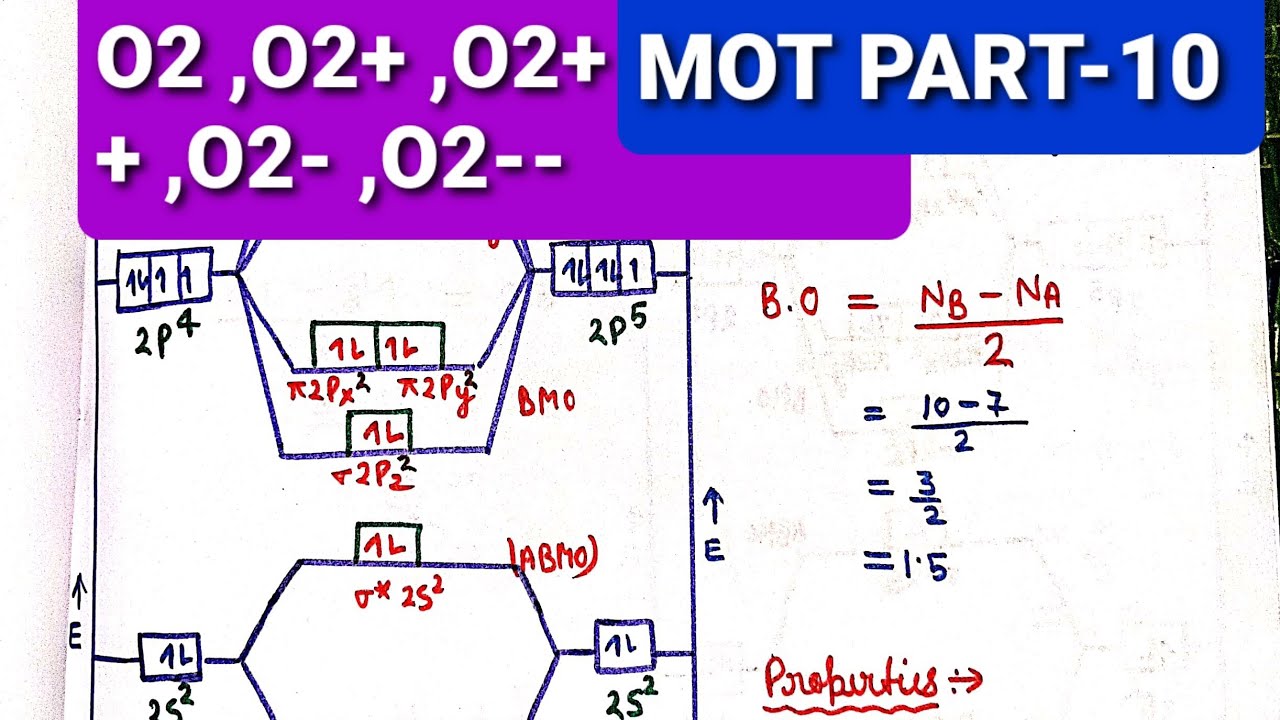
December 30, 2019 - In O2−,O2 and O2−2molecular species, the total number of antibonding electrons respectively are: ... Thus no of electrons in the antibonding orbitals are respectively 7,6,8.
Follow me on instagram- https://www.instagram.com/trickychemistrysuman/?hl=en Follow me on facebook page- https://lm.facebook.com/l.php?u=https://fb.me
January 31, 2018 - First step is to find the total valence electrons for each molecule, O2 will appear to have 12 valence electrons (6+6 =12), O2- has 13 (12 +1) and O22- has 14 (12+2) ... Draw molecular orbital diagrams for O2-, O22-, and O2. Which has the highest bond order? Which would be paramagnetic, and ...
In the molecular orbital diagram for O 2+ ion, the highest occupied orbital is: A σ MO orbital B π MO orbital C π ∗ MO orbital D σ ∗ MO orbital Medium Solution Verified by Toppr Correct option is C) As it can be seen from the given structures that in the molecular orbital diagram for O 2+ ion, the highest occupied orbital is π ∗ MO orbital.
Remember: When two oxygen atoms bond, the pi(2p) bonding molecular orbitals are lower in energy than the sigma(2p) bonding orbitals. They are flipped compare...
The Molecular orbital diagram for O2 O 2 is like this: As you can see the oxygen molecule has two unpaired electrons in the lower π π * ant-bonding states. For O2+2 O 22 + basically remove the two unpaired electrons in the π π * anti-bonding states, as they are the most easily removed. 26K views View upvotes Sponsored by Elite Side Lines
Consider the Molecular orbital diagram for the ion O2 Predict the bond order. 3.0 o 1.5 1.0 2.5 2.0 Submit Answer Incorrect Tries 1/2 Previous Tries Consider the following statements. Which type of orbital will be the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO)?
The molecular orbital diagram for C 2 molecule is :. The electronic configuration of C 2 is K K (σ2s) 2 (σ * 2s) 2 n (2px) 2 n (2py) 2. The C 2 molecule is diamagnetic because all electrons are paired there are no unpaired electrons. Molecular orbital diagram for c2 2-. The bond order of B2, C2, and N2 are 1, 2, and 3, respectively.
molecular orbital diagram of O2+ Electronic configuration of O2+ In the case of O2- 17 electrons are present &3 electrons are present in antibonding orbitals. If number of electrons more in antibonding orbital the molecule become unstable.
AboutPressCopyrightContact usCreatorsAdvertiseDevelopersTermsPrivacyPolicy & SafetyHow YouTube worksTest new features · © 2021 Google LLC
Bond order (B.O) 1/2 × [Number of an electron in antibonding molecular orbitals] - [Number of electrons in bonding molecular orbitals] The higher the order of the bond the greater the pull between the two atoms and the shorter the length of the bond. (1) B.O for O 2 = 1/2 × [10 - 6] B.O for O 2 = 2 (2) B.O for O 2 - = 1/2 × [10 - 7]
December 20, 2019 - Draw molecular orbital diagram of O2 or N2 with magnetic behavior and bond order. ... As it can be seen from the MOT of O2, The electrons in the highest occupied molecular orbital are unpaired therefore it is paramagnetic in nature. Also, the bond order can be calculated as [Nb−Na]/2...
Oxygen's paramagnetism is explained by the presence of two unpaired electrons in the (π 2py, π 2pz)* molecular orbitals. Check Your Learning. The main component of air is N 2. From the molecular orbital diagram of N 2, predict its bond order and whether it is diamagnetic or paramagnetic.
When two oxygen atoms overlap, the sigma(2p) molecular orbital is LOWER in energy than the pi(2p) orbitals. This different from Nitrogen, where it's the othe...
Our videos prepare you to succeed in your college classes. Let us help you simplify your studying. If you are having trouble with Chemistry, Organic, Physics, Calculus, or Statistics, we got your back! Our videos will help you understand concepts, solve your homework, and do great on your exams.
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Transcribed image text: Complete this valence molecular-orbital diagram for oxygen, O2. Click the blue boxes to add electrons as needed.
Printable O2 molecular orbital diagrams are available for you to guide your study in the molecular orbital lesson. This diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of a molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.
To obtain the molecular orbital energy-level diagram for (ce {O2}), we need to place 12 valence electrons (6 from each O atom) in the energy-level diagram shown in Figure (PageIndex {1}). We again fill the orbitals according to Hund’s rules and the Pauli principle, beginning with the orbital that is lowest in energy.
O2has a single bond, with four electrons in the π*orbitals canceling those in the π orbitals. O2 -has three electrons in the π* orbitals, and a bond order of 1.5. The Lewis structures have an unpaired electron and an average bond order of 1.5. O2has two unpaired electrons in its π* orbitals,and a bond order of 2.
Bond order 2 N b − N a = 2 8 − 4 = 2 Thus, oxygen molecule has two bonds. i.e., one is bond and one p bond. The last two electrons in p 2 p x ∙ and p 2 p y ∙ orbitals will remain unpaired. Therefore, oxygen molecule has paramagnetic character due to the presence of two unpaired electrons.
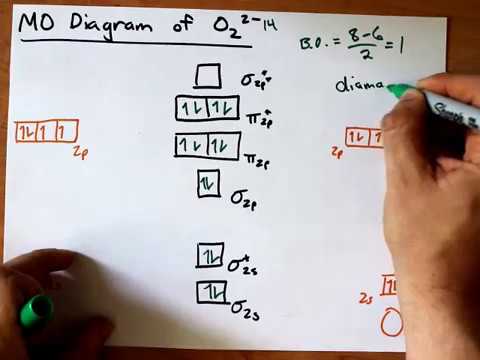
It is sigma2s(2)sigma2s*(2)sigma2p(2)pi2p(4)pi2p*(4)Bond order 1. It is stable. In fact, it's the perioxide ion.Check me out: http://www.chemistnate.com
Answer (1 of 6): Here is the solution, > * For O2 molecule, > * For F2 molecule, Thanks for reading.
The lighter second period elements (prior to oxygen) have a relatively small difference in energy between the 2s and 2p orbitals. This allows sufficient s-p mixing to lower the energy of the σ(2s) and σ*(2s) molecular orbitals, and is energetically offset by an increase in energy of the σ(2p) and σ*(2p) molecular orbitals.
August 15, 2020 - In O2 and F2, there is a crossover of the sigma and the pi ortbials: the relative energies of the sigma orbitals drop below that of the pi orbitals'. Information from the MO diagram justify O2's stability and show that it's bonding order is 2. The LUMO (lowest unoccupied molecular orbital) ...
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ...
are combined. The molecular orbital diagram for an O2molecule would therefore ignore the 1selectrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the interactions between the 2sand 2pvalence orbitals. Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level The 2sorbitals on one atom combine with the 2sorbitals on another to form a 2sbonding and a 2s*
Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the oxygen molecule, O 2. From this diagram, calculate the bond order for O 2. How does this diagram account for the paramagnetism of O 2? Show Solution. We draw a molecular orbital energy diagram similar to that shown in Figure 7.7.12. Each oxygen atom contributes six electrons, so the diagram appears as ...

















0 Response to "36 o2 2- molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment