36 maximum solubility phase diagram
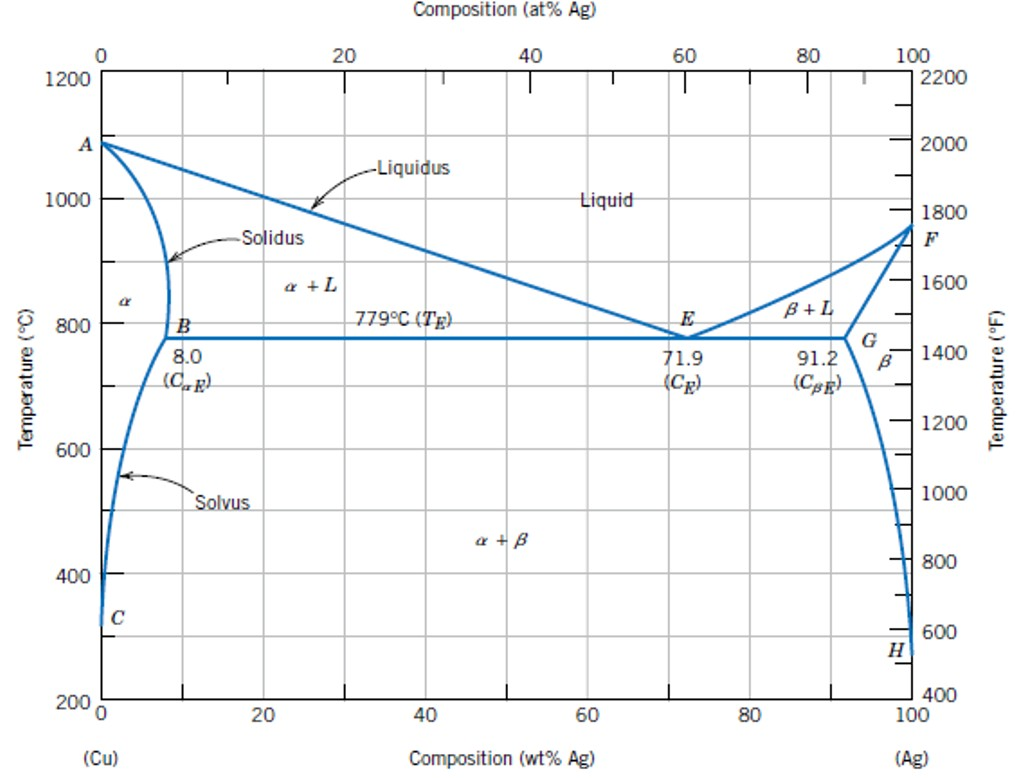
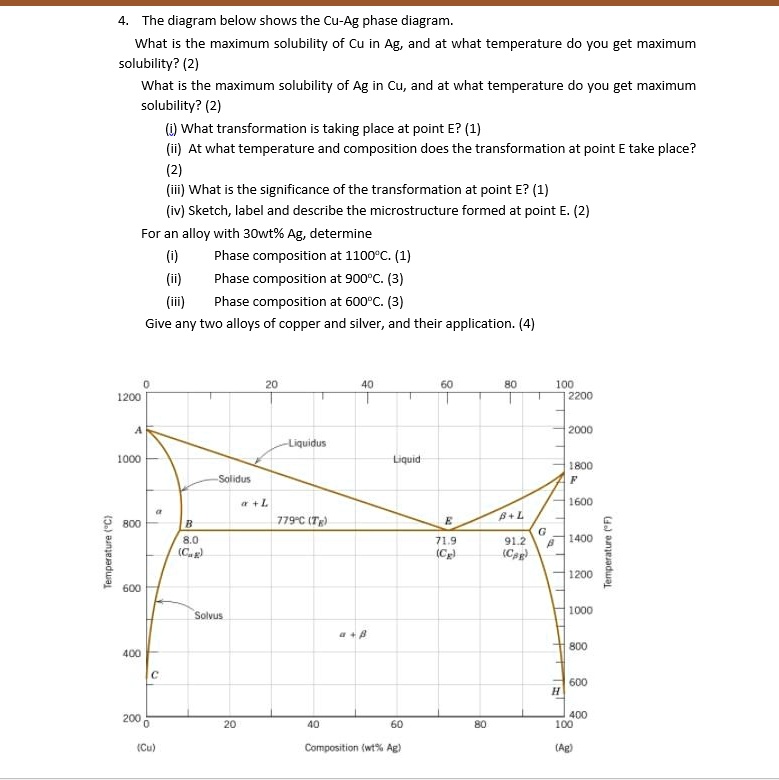
Using the Ag-Cu equilibrium phase diagram The maximum solubility of Cu in Ag is A) 0% Cu B) 8.8% Cu C) 28.1% Cu D) 92% Cu E) Unlimited. 8.8% Cu. Using the Ag-Cu equilibrium phase diagram The eutectic composition is _____ and the temperature of the eutectic reaction is _____ Thinking of binary phase diagrams in terms of solubility limits.
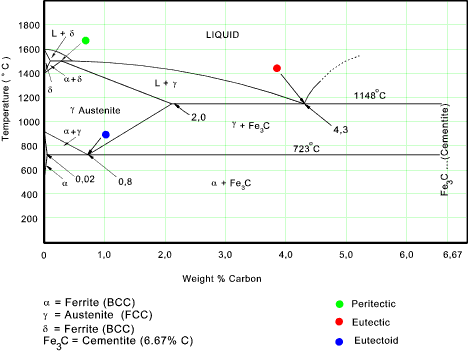
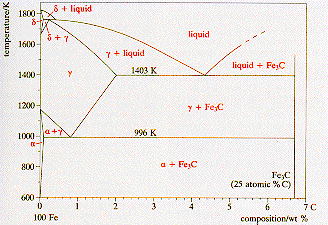
Phases in Fe-Fe3C Phase Diagram ¾α-ferrite - solid solution of C in BCC Fe • Stable form of iron at room temperature. • The maximum solubility of C is 0.022 wt% • Transforms to FCC γ-austenite at 912 °C ¾γ-austenite - solid solution of C in FCC Fe • The maximum solubility of C is 2.14 wt %. • Transforms to BCC δ-ferrite at ...
Maximum solubility phase diagram
13.2 Phase Diagrams: Binary Systems. As explained in Sec. 8.2, a phase diagram is a kind of two-dimensional map that shows which phase or phases are stable under a given set of conditions. This section discusses some common kinds of binary systems, and Sec. 13.3 will describe some interesting ternary systems. How to read the phase diagram. ... The solvus line shows that the host substance A has its maximum solubility at a temperature of 700 °C and can store 20 % B atoms. At this temperature, the entire B atoms of the alloying element remain dissolved in the lattice structure of the host material A. Use the following silver-copper phase diagram for Problems 5-9. 5. What are the solubility limits of Ag in (Cu) and Cu in (Ag)? Recall that (Cu) and (Ag) are the same as α and β, respectively. The solubility limit of Ag in (Cu) is 7.9 wt. % Ag. The solubility limit of Cu in (Ag) is 8.8 wt.% Cu. Note that these
Maximum solubility phase diagram. MSE 2090: Introduction to Materials Science Chapter 9, Phase Diagrams 3 Solvent - host or major component in solution,solute- minor component. Solubility Limitof a component in a phase is the maximum amount of the component that can be dissolved Phase Diagrams This common tangent construction can be extended to quite complicated situations, with several minima, which then give rise to quite complicated free energy curves and hence phase diagrams. For plotting a phase diagram we need to know how solubility limits (as determined by the common tangent construction) vary with temperature. + β) phase boundary at this temperature, or to about 2 wt% Cu. (b) From this same figure, the maximum solubility of Ag in Cu corresponds to the position of the α–(α + β) phase boundary at this temperature, or about 1.5 wt% Ag. 9.8 Cite the phases that are present and the phase compositions for the following alloys: Answer (1 of 4): Before it's answer you must know about that carbon present in Fe combine with it to form Fe3C. Means we can add carbon as much as possible until all Fe is converted into Fe3C. Thus weight %of C in Fe when all Fe converted into Fe3C will be max wt% of C in Fe. For this Let us as...
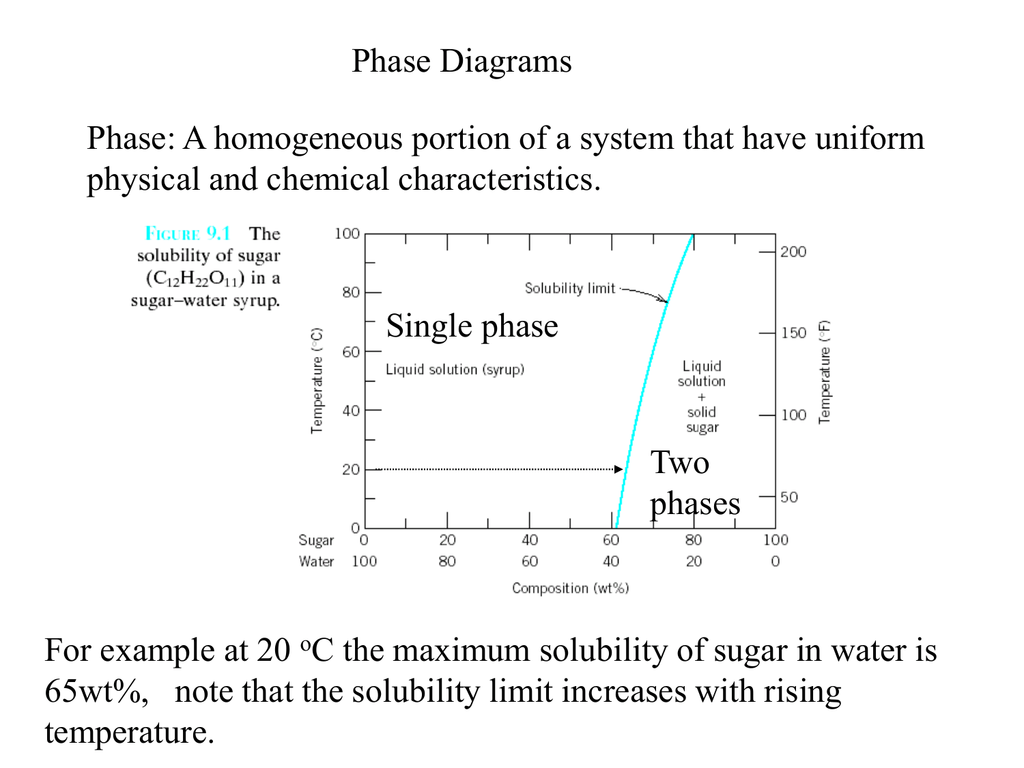
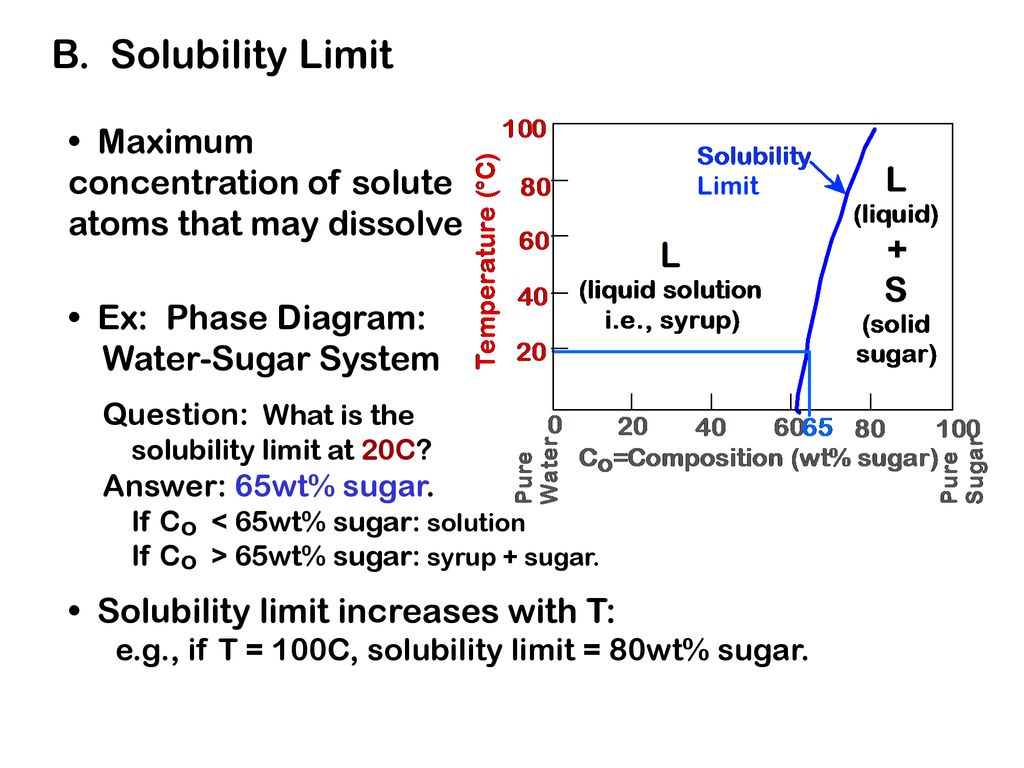
Max. solubility of C in ferrite=0.022% in austenite=2.11%. Phases in Fe-Fe 3 C Phase Diagram The Solubility Limit • Max. concentration for which only a solution occurs. -if Co < 65wt% sugar: syrup-if Co > 65wt% sugar: syrup + sugar • Solubility limit increases with T -e.g ... Phase Diagrams • Information about phases as function of T, Co, P • For this course: According to Murray the assessed Mg-Al phase diagram consists of liquid, -solid solution with hexagonal crystal structure, -solid solution with the αMn structure type, R phase with rhombohedral structure at 42 at.% Mg, Al solid solution with a maximum solubility of 18.9 at.% Solubility Limit: Max concentration for. which only a solution. occurs. • Ex: Phase Diagram: Water-Sugar System. Question: What is the. solubility limit at 20C? Answer: 65wt% sugar. If C. o < 65wt% sugar: sugar. If C. o > 65wt% sugar: syrup + sugar. • Solubility limit increases with T: e.g., if T = 100C, solubility limit = 80wt% sugar. Pure Sugar. Temperature (°C)
2.6 Structural analysis of Mg-RE alloys containing Gd. The maximum solid solubility of Gd in Mg is 23.5 wt.%. When added to Mg, Gd forms a Mg 5 Gd phase with a high melting point of 548 °C. Figure 2.1024 shows the as-cast microstructure (a) and the solution-treated micro-structure (b) of the Mg-14Gd binary alloy. This phase is a solid solution of carbon in FCC Fe with a maximum solubility of 2.14% C. On further heating, it converts into BCC δ-ferrite at 1395°C. γ-austenite is unstable at temperatures below eutectic temperature (727°C) unless cooled rapidly. At 100 C, what is the maximum solubility (a) of Pb in Sn? (b) of Sn in Pb? The lead-tin phase diagram is shown below. Round to the nearest whole number. Question: At 100 C, what is the maximum solubility (a) of Pb in Sn? (b) of Sn in Pb? The lead-tin phase diagram is shown below. Round to the nearest whole number. Phase Diagrams Phase A Phase B Nickel atom Copper atom Chapter 9 - 2 Phase Equilibria: Solubility Limit • Introduction – Solutions – solid solutions, solute atoms dissolve in the solvent to form a solid solution – a single phase – Mixtures – more than one phase • Solubility Limit: Max concentration for which only a single phase ...
The phase solubility profile of Zaleplon with βCD was classified as A L-type. Stability constant with 1:1 molar ratio was calculated from the phase solubility diagram and the aqueous solubility of zaleplon was found to be enhanced by 714% (p < 0.001) for βCD. Binary systems of ZPN with βCD were prepared by kneading method. The solid-state ...
Cellulose solubility phase diagram (shaded areas) in EmimAc–DMSO (line corresponds to 2.5 EmimAc molecules bound to 1 AGU) and in EmimAc–water (line corresponds to experimental results) with dashed line being a possible continuation of C cell max in EmimAc–water. Concentrations are in wt%.
Full Solubility (Cigar shaped diagram) In Cigar shape diagram there are three different regions: 1. Liquid (single phase) 2. Liquid + solid (double phase) 3. Solid solution (single phase) •Liquidus- the boundary line between the liquid region and the double phase region. •Solidus- the boundary line between the solid solution region and the double phase
Full Solubility (Cigar shaped diagram) In Cigar shape diagram there are three different regions: 1. Liquid (single phase) 2. Liquid + solid (double phase) 3. Solid solution (single phase) •Liquidus- the boundary line between the liquid region and the double phase region. •Solidus- the boundary line between the solid solution region and the double phase
Definition of structures: Austenite is an interstitial solid solution of Carbon dissolved in (F.C.C.) iron. Maximum solubility is 2.0 % C at 1130°C. High formability, most of heat treatments begin with this single phase. It is normally not stable at room temperature. But, under certain conditions it is possible to obtain austenite at room temperature.
At 70°C, what is the maximum solubility (a) of Pb in Sn and (b) of Sn in Pb? The lead-tin phase diagram is shown in the Animated Figure 9.8 (a) wt% Pb (b) [The tolerance is +/- 20%. wt% Sn Composition = Composition = Temperature Temperature Composition (at% Sn) 40 60 100 327 °C 600 300 Liquid 500 Liquid 232 °C a L 400 200 183 °C B+L 18.3 61 ...
https://goo.gl/nMe9J1 For 60+ videos on Engineering Materials
–Mixtures – more than one phase • Solubility Limit: Max concentration for which only a single phase solution occurs. Question: What is the solubility limit at 20°C? Answer: 65 wt% sugar. If C o < 65 wt% sugar: syrup If 4C o > 65 wt% sugar: syrup + sugar. 65 Sucrose/Water Phase Diagram P u r e S u g a r T e m p e r a t u r e ...
Hardness of pure material is very poor and maximum strength will be at the point of maximum solid solubility. Influence of Alloying Elements on Phase Diagram: Alloys elements addition always reduces eutectoid composition i.e.% of C while they may increase or decrease the eutectoid temperature.
The maximum temperature at which the two phase region exists is called the critical solution temperature. The critical solution temperature in this experiment is 70˚C. During this experiment, the temperature of the phenol-water system at miscible and temperature at which two phases separated is measured.
The maximum solubility of Cu in Al is equal to 2.5 at. pct at the eutectic temperature of 550 °C.[] The θ-phase (Al 2 Cu) was described for the first time by Owen and Preston[] and also by Friauf.[] The phase was characterized using XRD (single-crystal rotational method), and a tetragonal symmetry was found.
The Al-Si Phase Diagram The binary Al-Si phase diagram was initially studied by Fraenkel of Germany in 1908. It is a relatively simple binary diagram where there is very little solubility at room temperature for Si in Al and for Al in Si. Thus, the terminal solid solutions are nearly pure Al and Si under equilibrium conditions.
Chapter 9: Phase Diagrams Phase A Phase B Nickel atom Copper atom. Chapter 9 - 2 Phase Equilibria: Solubility Limit Introduction – Solutions – solid solutions, single phase – Mixtures – more than one phase • Solubility Limit : Max concentration for which only a single phase solution occurs. Question: What is the solubility limit at 20°C?
Phase equilibria: solubility limit Introduction -Solutions - solid solutions, single phase -Mixtures - more than one phase • Solubility Limit: Max concentration for which only a single phase solution occurs. Sucrose/Water Phase Diagram Sugar) 0 20 40 60 80 100 C o=Composition (wt% sugar) L (liquid solution i.e., syrup) Solubility ...
Use the following silver-copper phase diagram for Problems 5-9. 5. What are the solubility limits of Ag in (Cu) and Cu in (Ag)? Recall that (Cu) and (Ag) are the same as α and β, respectively. The solubility limit of Ag in (Cu) is 7.9 wt. % Ag. The solubility limit of Cu in (Ag) is 8.8 wt.% Cu. Note that these
How to read the phase diagram. ... The solvus line shows that the host substance A has its maximum solubility at a temperature of 700 °C and can store 20 % B atoms. At this temperature, the entire B atoms of the alloying element remain dissolved in the lattice structure of the host material A.
13.2 Phase Diagrams: Binary Systems. As explained in Sec. 8.2, a phase diagram is a kind of two-dimensional map that shows which phase or phases are stable under a given set of conditions. This section discusses some common kinds of binary systems, and Sec. 13.3 will describe some interesting ternary systems.













0 Response to "36 maximum solubility phase diagram"
Post a Comment