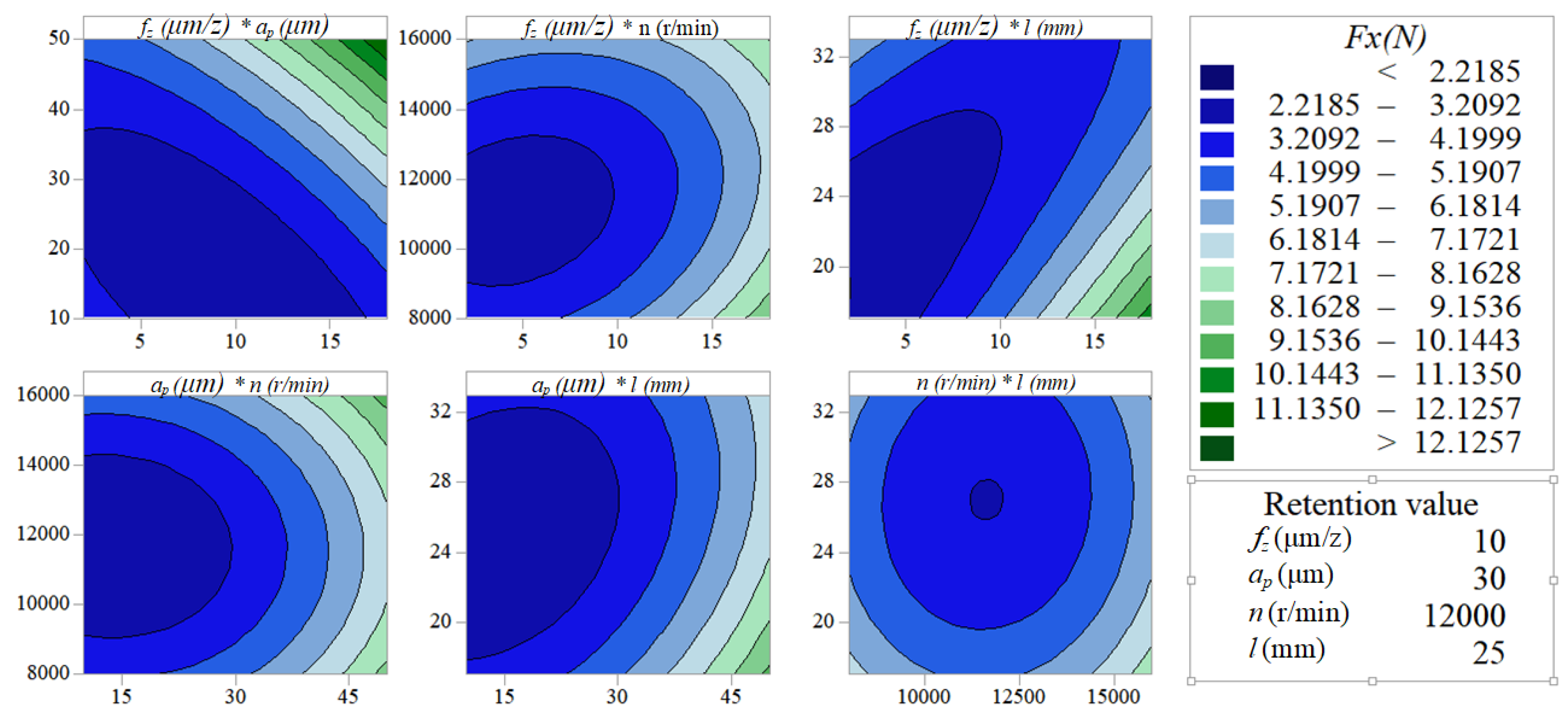
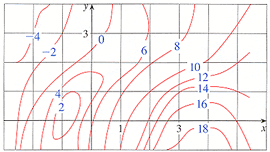
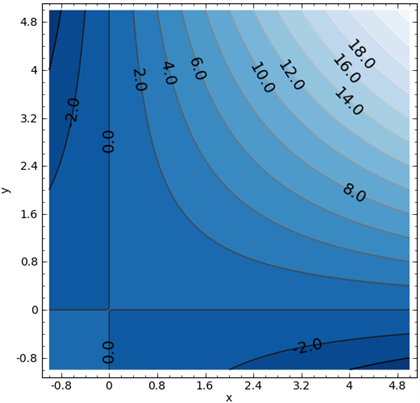
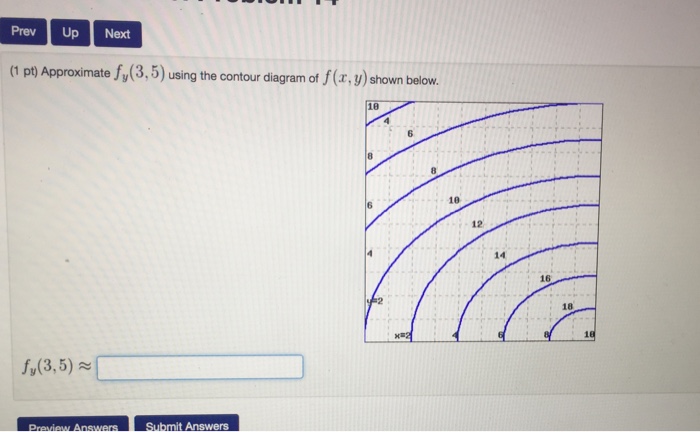
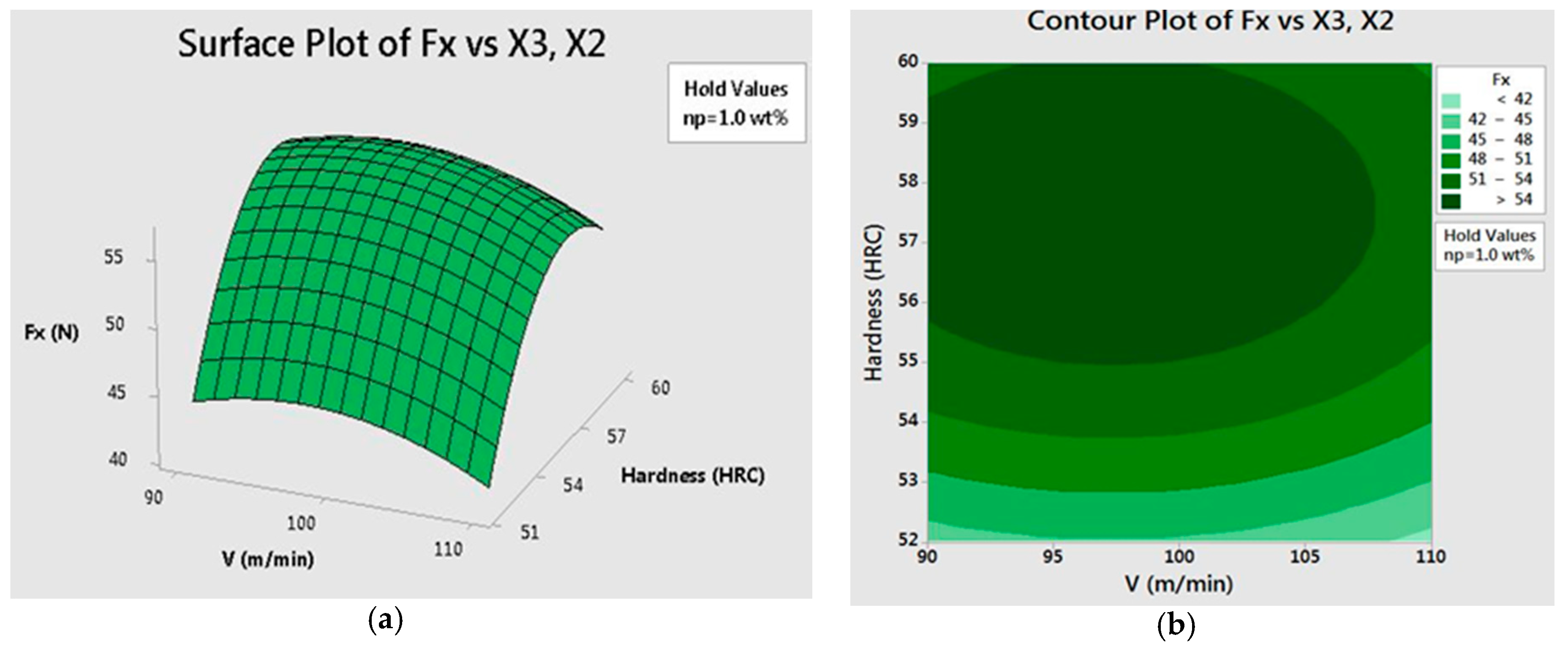
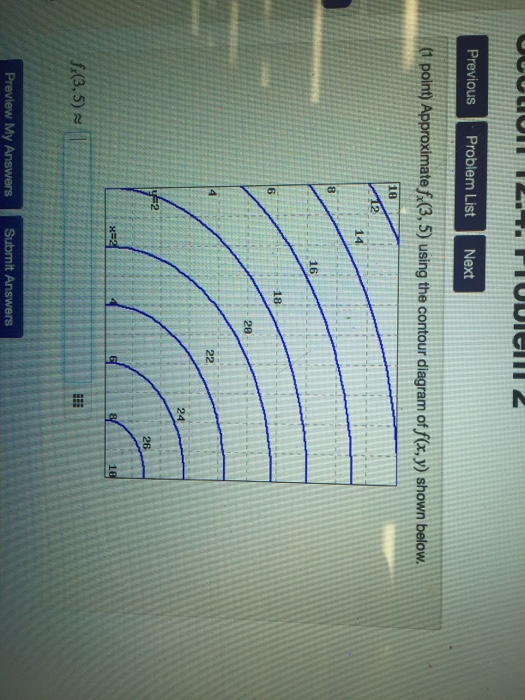
35 approximate fx(3,5) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below.
x 2+ y = 5. (c)Use the graph to approximate the points at which fhas a maximum or a minimum ... fare straight lines with slope 2 (in xyterms), as shown below. (b)Overlaying the constraint, we are allowed to move on a circle of radius p 5. (c)From the graph, the maximum values occurs where the constraint circle just touches the f= 5 contour line ... This video explains how to use the slope of a secant line to determine the value of a partial derivative using a contour map.Site: http://mathispower4u.com
Curves in R2: Three descriptions (1) Graph of a function f: R !R. (That is: y= f(x)) Such curves must pass the vertical line test. Example: When we talk about the \curve" y= x2, we actually mean to say: the graph of the function f(x) = x2.That is, we mean the set
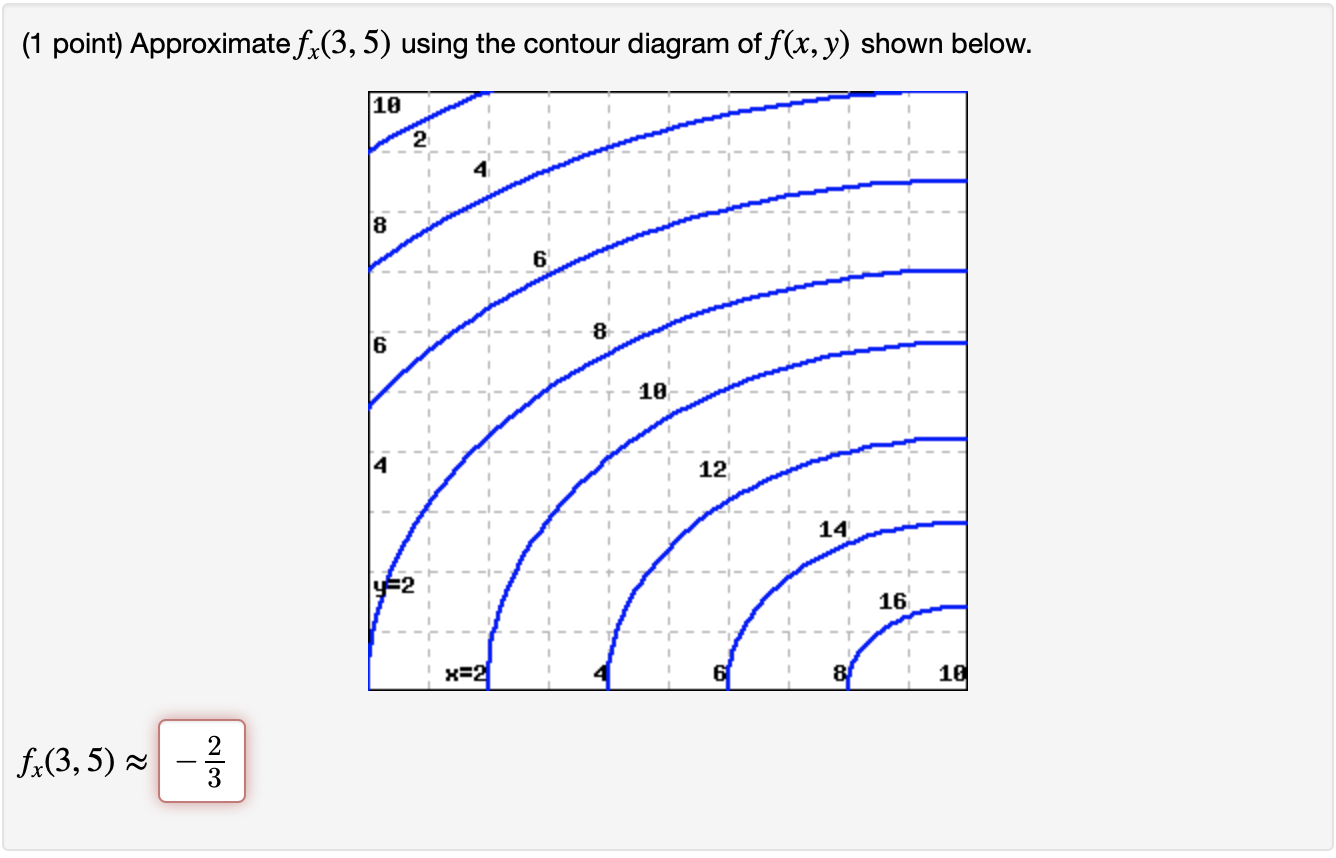
Approximate fx(3,5) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below.
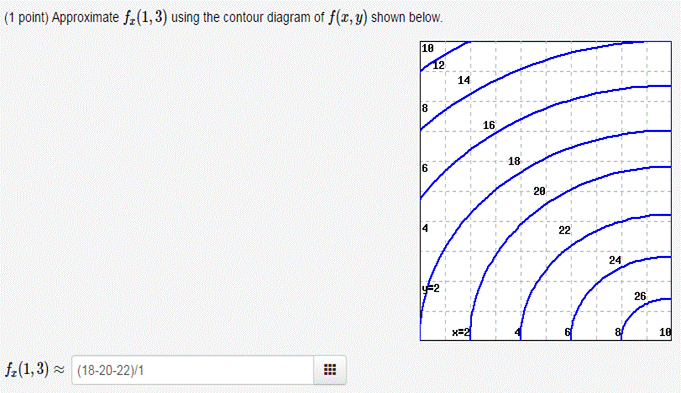
Answer to 16. (1 point) Approximate fr(3,5) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below. 10 14 12 10 2 *=2 of 10 fx (3, 5) ~ Solution for Approximate fx(1,3) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below. If f(x,y)=3x^2−2y^2, find the value of the directional derivative at the point (−4,4) in the direction given by the angle θ=2π/5 -22.63 (1 point) For each of the following functions, find the maximum and minimum values of the function on the circular disk: x^2+y^2≤1.
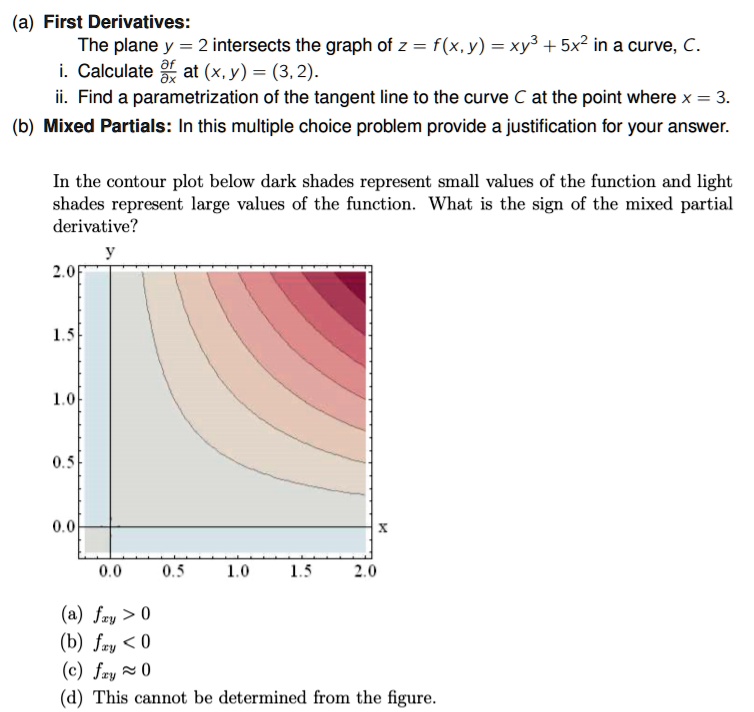
Approximate fx(3,5) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below.. Ask about how fx changes in the y-direction and about fy. 6. Figure 9.7 is a contour diagram for f(x,y) with the x and y axes in the usual directions. At the point P, if x increases, what is true of fx(P)? If y increases, what is true of fy(P)? (a) Have the same sign and both increase. (b) Have the same sign and both decrease. Graphs of Surfaces and Contour Diagrams - 1 Picturing f(x;y): Contour Diagrams (Level Curves) We saw earlier how to sketch surfaces in three dimensions. However, this is not always easy to do, or to interpret. A contour diagram is a second option for picturing a function of two variables. 3 3. Determine the sign of f x and f y at the point using the contour diagram of f in the gure below. (a) P (b) Q (c) R (d) S 4. Approximate f x(3;5) using the contour diagram of f(x;y) shown in the gure below. MATH 165 Precalculus Fall 2016 MATH 165 COURSE REVIEW Page 2 of 14 25 mi B 7 mi cable cable x x y 3 7 2 0 0 3 1 5 3 9 5 0 4. If f 3 5 8xx x 2, evaluate and simplify , 0 h h f x h f x. 5. Given f (x) 35x4 25x2, use your graphing calculator to approximate the following.Round your
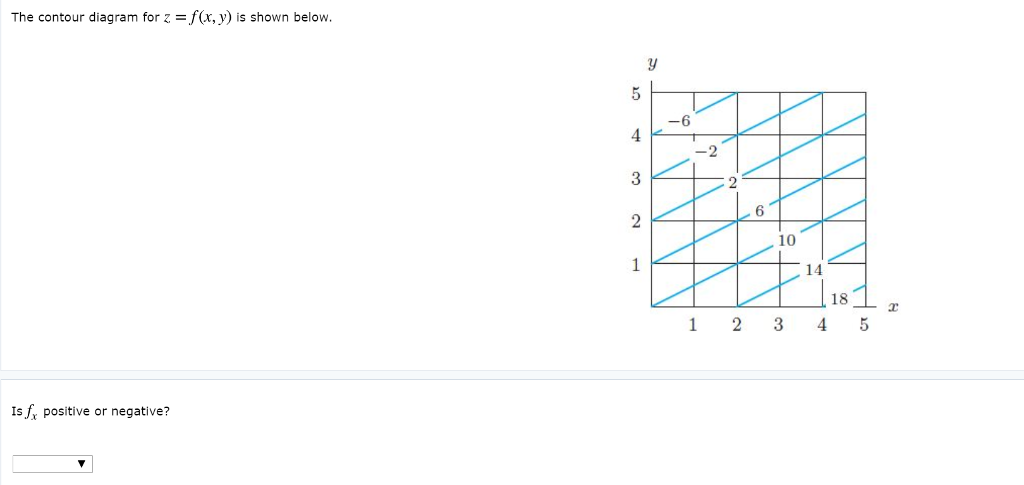
fullscreen Expand. Transcribed Image Text. Approximate f (3, 5) using the contour diagram of f (x, y) shown below. 18 12 10 6 X=2 10. check_circle. Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. from contour map., f (3,5) = 10 now …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Approximate f_y (3, 5) using the contour diagram of g (x, y) shown below. F (x, y) approximate. See the answer See the answer done loading. Approximate f x (1,3) using the contour diagram of f (x,y) shown below. Solve for f x (1,3) = ????? Expert Answer. Who are the experts? Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 100% (21 ratings) 3. Let the figure below be the contour diagram of f (x,y ). Find an approximate x derivative at (2, 2) by using the centered difference quotient. Ans:1/2 4. Figure 11 shows the graph of the function P(x, 2) of x that is obtained from P(x, y) b y setting y = 2, and figure 12 shows the graph of the function P(3, y) of y that is obtained from P(x ...
27 Tangent Planes to Level Surfaces Suppose S is a surface with equation F(x, y, z) = k, that is, it is a level surface of a function F of three variables, and let P(x 0, y 0, z 0) be a point on S. Let C be any curve that lies on the surface S and passes through the point P.Recall that the curve C is described by a continuous vector function r(t) = 〈x(t), y(t), z(t)〉. If the following is a contour diagram for f(x,y) with the z = 0 contour at the origin, going up by 1 for each concentric circle, approximate the rate of change of f(x,y) at (1,1) in the direction of Approximate fx(3,5) using the contour diagram of fx(x,y). I am very confused full credit for right answer. Show transcribed image text (1 point) Approximate fx(3, 5) using the contour diagram of f(x, y) shown below. Best Answer. This is the best answer based on feedback and ratings. Transcribed image text: Approximate fx (3,5) using the contour diagram of f (x,y) shown below. Previous question Next question.
Approximate fx(3,5) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below. fx(3,5)? ... What happens next? After payment, your answer will be immediately delivered to your email (so don't forget to check your spam folder in case you don't see anything!)
We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 100% (1 rating) Transcribed image text : Approximate f_x(3, 5) using the contour diagram of f(x, y) shown below.
Pt approximate f x 3 5 using the contour diagram of f. This preview shows page 4 - 5 out of 5 pages. Suppose that f(x,y)is a smooth function and that its partial derivatives have the values, fx(- 1,- 8) =4 andfy(- 1,- 8) = 3. Given thatf(- 1,- 8) = - 9, use this information to estimate the following values: Estimate of (integer value) f(- 1,- 7 ...
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Transcribed image text: (1 point) Approximate fx (3, 5) using the contour diagram of f (x, y) shown below. Fx (3,5).
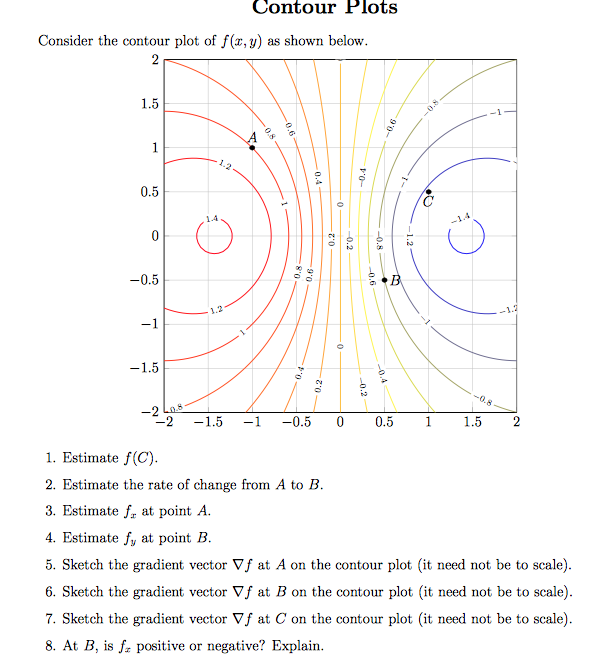
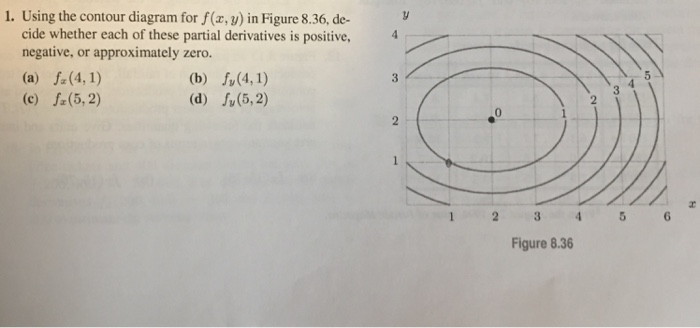
Math 205 HWK 11 Solns continued §14.7 p687 Problem 19, §14.7, p687. Use the given level curves of the function z = f(x,y) to decide the sign (positive, negative, or zero) of each of the following partial derivatives at the point P indicated
ASSIGNMENT 6 SOLUTION JAMES MCIVOR 1. Stewart 14.3.10 [3 pts] A contour map for a function fis given. Use it to estimate f x(2;1) and f y(2;1). Solution: We can estimate f
(1 point) Approximate f x (3, 5) using the contour diagram of f (x, y) shown below. f x (3, 5) ≈ Answer(s) submitted: •-2/3 (correct) 17. (1 point) If z = f (x)+ yg (x), what can we say about z yy? Correct Answers: • C 4
4 Gradients and directional derivatives in the plane Remark 4.1. The partial derivatives f x and f y tell us the rate of change of f parallel to the coordinate axes. In this section, we consider partial derivatives
Determine the sign of fxfx and fyfy at each indicated point using the contour diagram of ff shown below. (The point PP is that in the first quadrant, at a positive xx and yy value; QQ through TT are located clockwise from PP, so that QQ is at a positive xx value and negative yy, etc.)
20. Use the contour diagram for f (x, y) f(x,y) shown below to estimate the directional derivative of f f in the direction v ⃗ v→ at the point P. 1. The function f has continuous second derivatives, and a critical point at (− 3,− 2) Suppose 2. The function f f has continuous second derivatives, and a critical point at (6,− 9) (6,−9 ...
Let P vary along the region of the x-axis shown in the gure below. How does df dx (P) ... Approximate f x (3, 5) using the contour diagram of f (x,y ) in Figure 14.9. 24 68 10 2 4 6 8 10 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 x y Figure 14.9 ... and the sign of fy(P)? Example. Approximate the instantaneous rate of change fx(P) using an average rate of change.
If f(x,y)=3x^2−2y^2, find the value of the directional derivative at the point (−4,4) in the direction given by the angle θ=2π/5 -22.63 (1 point) For each of the following functions, find the maximum and minimum values of the function on the circular disk: x^2+y^2≤1.
Solution for Approximate fx(1,3) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below.
Answer to 16. (1 point) Approximate fr(3,5) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below. 10 14 12 10 2 *=2 of 10 fx (3, 5) ~

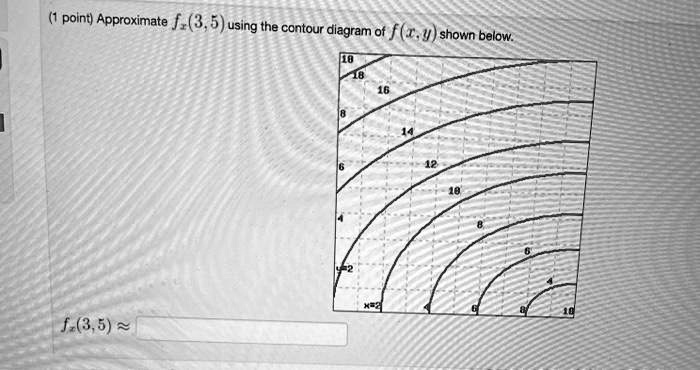













0 Response to "35 approximate fx(3,5) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below."
Post a Comment