45 myosin and actin diagram
Fresh Diagram Of A Sarcomere - Glaucoma Template Diagram Of Sarcomere Wiring Diagram Third Level. Myosin bonds with actin to ratchet the tropomyosin down the length of the myosin. Give the appreance of striations on skeletal and cardiac muscle. Thin filaments composed of actin are anchored at the Z line and form transient sliding interactions with thick filaments composed of myosin molecules. Mechanism of Muscle Contraction: Definition, Diagram, Muscle Fatigue, In this mechanism, an actomyosin complex is formed that results in muscular contraction. It includes three stages: Excitation-Contraction Coupling Role of Troponin and Tropomyosin Sliding Mechanism 1. Excitation-Contraction Coupling Excitation-contraction coupling is the process that takes place between the excitation and contraction of the muscle.
Function of the Left Heart | SpringerLink The myosin head (in its short conformation, bound to actin) can cleave ATP which then detaches the myosin head from actin and fully extends the myosin head to its greatest length. The extended myosin head can now bind further along on the actin filament and, when bound, the myosin head undergoes reverse conformational change resulting in ...
Myosin and actin diagram
Actin - Wikipedia Actin takes part in the regulation of chromatin structure, interacting with RNA polymerase I, II and III. In Pol I transcription, actin and myosin ( MYO1C, which binds DNA) act as a molecular motor. For Pol II transcription, β-actin is needed for the formation of the preinitiation complex. Pol III contains β-actin as a subunit. Physiological Significance of the Force-Velocity Relation in Skeletal Muscle and ... (A) Diagram showing a myosin head (M) connected to a myosin filament via springs S1 and S2, and a myosin-binding site (A) on an actin filament. Arrows indicate directions of relative sliding between actin and myosin filaments. (B) Diagram showing the rate constants (fand g)as functions of distance (x) of M from its equilibrium position (0). Sarcomere Coloring Sheet Answer Key → Waltery Learning Solution for Student In this human muscles worksheet students are given a diagram of the human muscles on the front side of the body. Mitochondria B are dispersed through the muscle fibers color all mitochondria pink. Diagram in model 2 and describe possible reasons why there is a limit to the amount of shortening that.
Myosin and actin diagram. Actin vs Myosin- Definition, 14 Major Differences, Examples Actin filaments in the muscles are short in length ranging from 2-2.6 µm and thin with a diameter of about 0.005 µm. The actin filaments in muscles are separated by actin-binding proteins, α-actinin that binds two actin filaments while leaving space for myosin. The α-actin is the significant component of the contractile apparatus of muscles. Difference between Myosin and Actin No. Myosin : Actin. Definition. 1. A super family which include motor proteins and has function in muscle contraction is known as Myosin. A proteins which is multifunctional protein forms microfilaments and present in the eukaryotic cells, this is known as Actin. Types of Skeletal Muscle Contraction - Learn Insta The process of muscular contraction occurs over a number of key steps, including: Depolarisation and calcium ion release. Actin and myosin cross-bridge formation. Sliding mechanism of actin and myosin filaments. Sarcomere shortening (muscle contraction) Myosin-based regulation of twitch and tetanic contractions in mammalian skeletal ... (A) Schematic diagram of the sarcomere for the best-fit model parameters at peak force in the twitch. The sarcomere is delimited by Z-disks (black) and contains overlapping actin (dark grey) and myosin (white) filaments.
Ultrastructure of Muscle - Skeletal - Sliding Filament - TeachMeAnatomy Ultrastructural Appearance of Skeletal Muscle. The striated appearance of skeletal muscle fibres is due to the organisation of two contractile proteins: actin (thin filament) and myosin (thick filament).. The functional unit of contraction in a skeletal muscle fibre is the sarcomere, which runs from Z line to Z line.A sarcomere is broken down into a number of sections: Sarcomere Coloring Worksheet Answers → Waltery Learning Solution for Student Lightly color the myosin and actin molecules. Mitochondria B are dispersed through the muscle fibers color all mitochondria pink. Sarcomere coloring worksheet sarcomere coloring worksheet key sarcomere coloring worksheet answers sarcomere coloring worksheet answer key Color the following parts on the diagrams below. Describe the structure of myosin and actin filaments, with the help of neat and ... 1. Each myosin filament is a polymerized protein. Many meromyosins (monomeric proteins) constitute one thick filament. 2. Myosin molecule consists of two heavy chains (heavy meromyosin / HMM) coiled around each other forming a double helix. One end of each of these chains is projected outwardly is known as cross bridge. Diagrammatology - Michael Whittle 'Model for the origins of movement' depicts the branching, diagrammatic lineages of actin and myosin as fragile interlinked tori floating in an empty white space (figure 2). Figure 2: Model for the origins of movement (Myosin and Actin molecular family trees as linked, punctured tori) 2017, 124 x 124 cm, Ink and watercolour on paper
The Early History of the Biochemistry of Muscle Contraction Myosin B was renamed actomyosin (Szent-Györgyi, 1942b). Straub (1943)showed that the newly discovered protein existed in two forms: globular actin (G-actin) that was stable in the absence of salt, and in the presence of ions it polymerized to form fibrous actin (F-actin). Week 2 Diagram | Quizlet Voluntary muscle pulls on bones and causes body movements. Epimyosium Connective tissue covering the entire muscle Perimyosium Connective tissue covering around a fascicle (bundle of muscle fibers) Fascicles Bundles of muscle fibers wrapped in perimysium Myofibrils Microscopic protein filaments that makeup muscle cells. Myosin Discovery of ultrafast myosin, its amino acid sequence, and structural features ... Based on this crystal structure and the recently published cryo-electron microscopy structure of acto-myosin XI at low resolution (4.3-Å), it appears that the actin-binding region contributes to the fast movement of Chara myosin XI. Mutation experiments of actin-binding surface loops support this hypothesis. Sign up for PNAS alerts. What is a Sarcomere? - Parts & Contraction - Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com Only the periphery of the A-band contains the protein myosin. The I-band is made up of actin. It is the sliding movement of A-band myosin along I-band actin that allows sarcomere to length and...
Integrin-dependent phagocytosis – spreading from microadhesion to new concepts | Journal of Cell ...
CSCS Chapter 1: Structure and Function of Body Systems - Personal Trainer Pioneer Myosin and Actin. Myosin and Actin give skeletal muscles its striated appearance. The action potential discharging from a motor nerve is the signal that releases calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. This goes into the myofibril and causes tension to develop within the muscle.
Chapter 9: Skeletal Muscle (A) Diagram | Quizlet Start studying Chapter 9: Skeletal Muscle (A). Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Discovery of ultrafast myosin, its amino acid sequence, and structural features - PMC We also report an atomic structure (2.8-Å resolution) of myosin XI using X-ray crystallography. Based on this crystal structure and the recently published cryo-electron microscopy structure of acto-myosin XI at low resolution (4.3-Å), it appears that the actin-binding region contributes to the fast movement of Charamyosin XI.
Muscle Contraction: Actin and Myosin Bonding - Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com It consists of a head and a tail region. Together, the tails of approximately three hundred myosin molecules form the shaft of the thick filament. The myosin heads of these molecules project...
Differences Between Actin and Myosin - Actin vs Myosin Myosin is an ATPase which is able to move along filaments of actin by linking the hydrolysis process of ATP to changes in conformation. Myosins consist of one or two chains of heavy chain as well as a number of light chains. A genomic analysis has revealed 13 distinct myosins.
Structure and Function of Cardiomyocyte | SpringerLink The myosin globular head and the G-actin monomer interact in the presence of ATP, resulting in the formation of a crossbridge and the sarcomere shortens. Tropomyosin on either side of actin engages the actin-myosin cleft, averts Ca 2+ binding and thus impacts formation of the actin-myosin crossbridge . The troponin complex, which is part of the ...
The Mystery of Muscle -- A tale of actin and myosin Myosin. Like actin, myosin isn't just one protein, but a massive family of them. In fact, the human genome encodes more than 40 different myosin proteins. [40] Berg JM, Tymoczko JL, Stryer L. Biochemistry. 5th edition. New York: W H Freeman; 2002. Section 34.1, Most Molecular-Motor Proteins Are Members of the P-Loop NTPase Superfamily.
Sarcomere Coloring Sheet Answer Key → Waltery Learning Solution for Student In this human muscles worksheet students are given a diagram of the human muscles on the front side of the body. Mitochondria B are dispersed through the muscle fibers color all mitochondria pink. Diagram in model 2 and describe possible reasons why there is a limit to the amount of shortening that.
Physiological Significance of the Force-Velocity Relation in Skeletal Muscle and ... (A) Diagram showing a myosin head (M) connected to a myosin filament via springs S1 and S2, and a myosin-binding site (A) on an actin filament. Arrows indicate directions of relative sliding between actin and myosin filaments. (B) Diagram showing the rate constants (fand g)as functions of distance (x) of M from its equilibrium position (0).
Actin - Wikipedia Actin takes part in the regulation of chromatin structure, interacting with RNA polymerase I, II and III. In Pol I transcription, actin and myosin ( MYO1C, which binds DNA) act as a molecular motor. For Pol II transcription, β-actin is needed for the formation of the preinitiation complex. Pol III contains β-actin as a subunit.
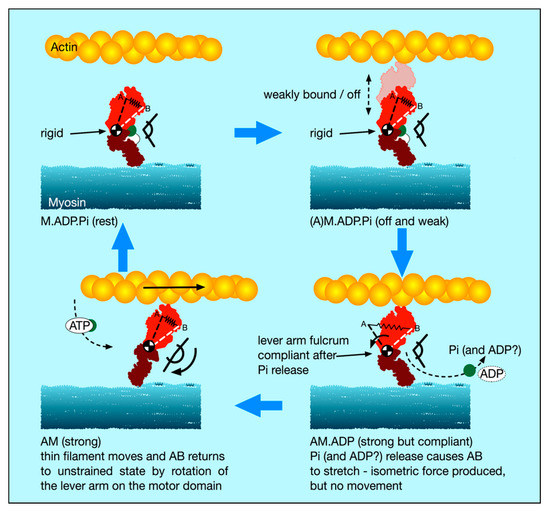

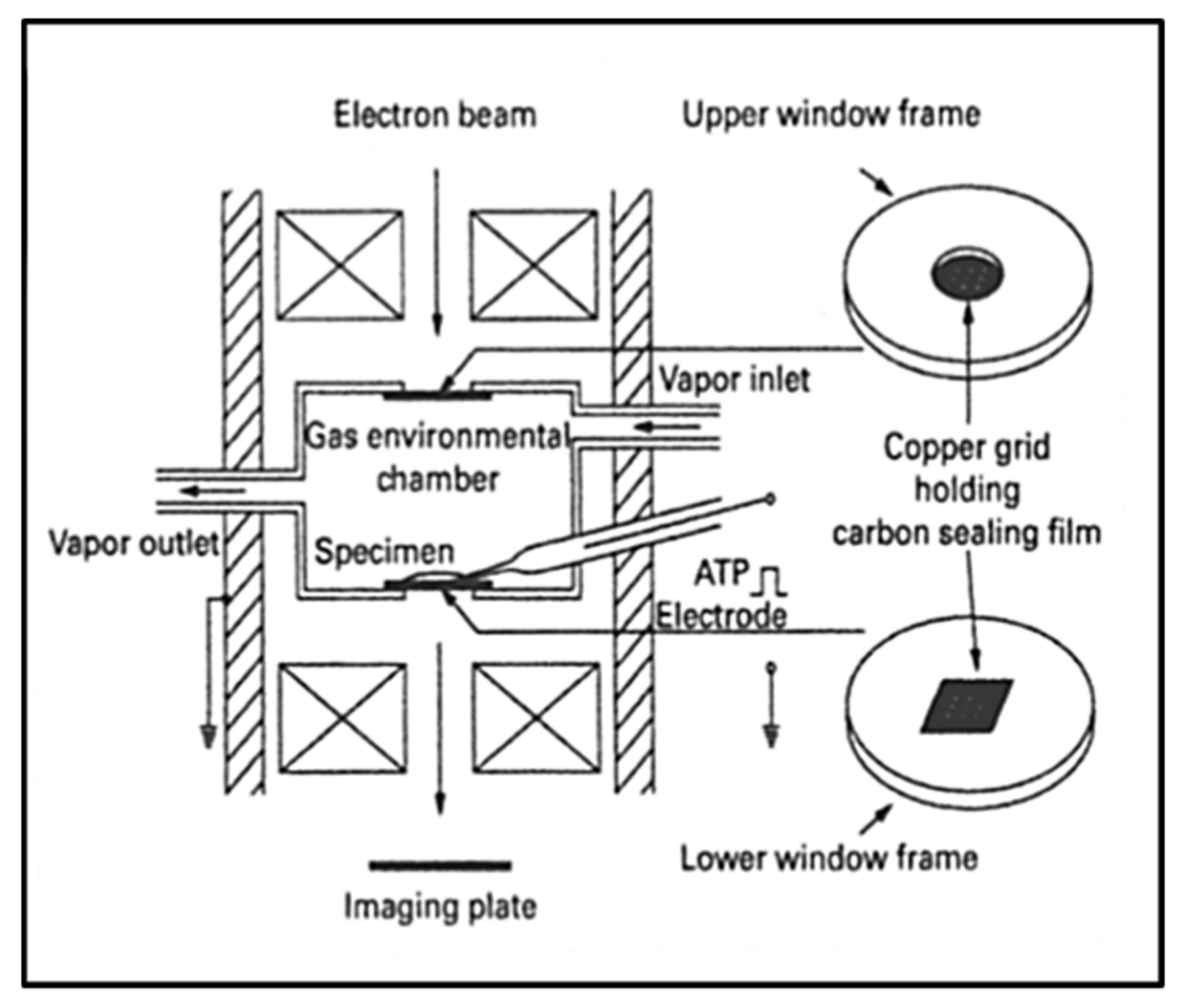

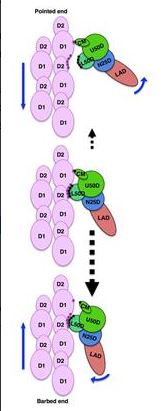
0 Response to "45 myosin and actin diagram"
Post a Comment