42 the image below shows the reactions of the citric acid cycle. label the enzymes on the diagram
essayhelpp.com › biology-lBIOLOGY L - Essay Help Mar 07, 2022 · During acetyl CoA formation and the citric acid cycle, all of the carbon atoms that enter cellular respiration in the glucose molecule are released in the form of CO2 Use this diagram to track the car… The image below shows the reactions of the citric acid ... The image below shoshone the reactions of the citric acid cycle. Label the enzymes on the diagram. CH-OH WAD + Cos Hc fumarate CHi succinale co
› 10355171 › Molecular_Cell_Biology(PDF) Molecular Cell Biology 5th ed - Lodish et al | 희수 김 ... Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
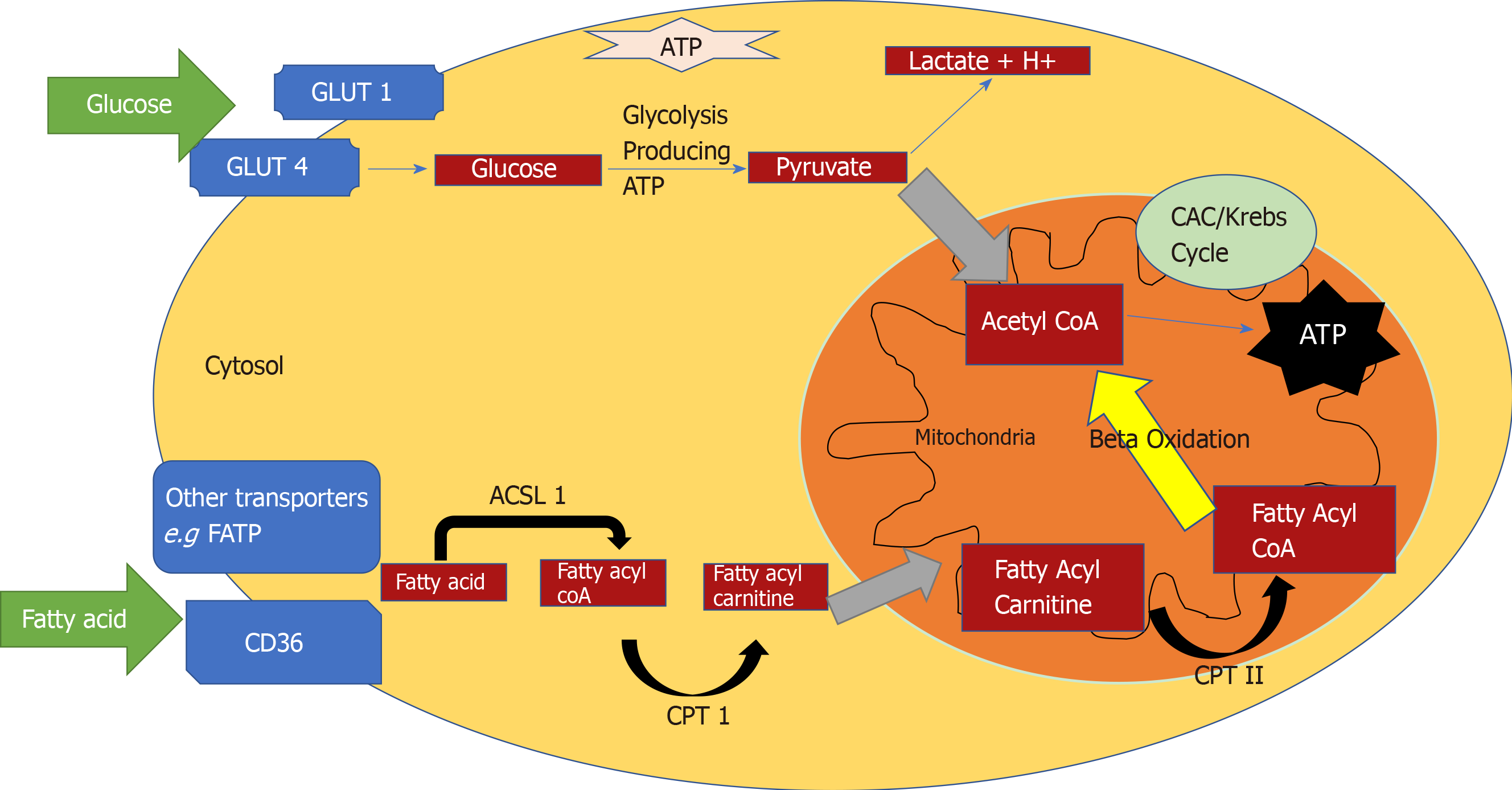
The image below shows the reactions of the citric acid cycle. label the enzymes on the diagram
Photosynthesis - Definition, Process, and Diagrams Plants capture the carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through stomata and proceed to the Calvin photosynthesis cycle. In the Calvin cycle, the ATP and NADPH formed during light reaction drive the reaction and convert 6 molecules of carbon dioxide into one sugar molecule or glucose. The chemical equation for the dark reaction can be reduced to: PDF Exam #3 Review phosphorylation (step 5) and certain intermediates of the cycle serve as precursor metabolites for anabolic pathways. *Occurs in the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells and in the mitochondrial matrix of eukaryotic cells. In this cycle the two-carbon acetyl groups are fully oxidized to CO 2. *Important points to remember about the TCA cycle: 1. Solved the image below shows the reactions of the citric ... Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Transcribed image text: The image below shows she reactions of the cltric acid cycle. Label the enzymes on the diagram dehydragars coo.
The image below shows the reactions of the citric acid cycle. label the enzymes on the diagram. Steps of cellular respiration | Biology (article) | Khan ... Citric acid cycle. The acetyl CoA made in the last step combines with a four-carbon molecule and goes through a cycle of reactions, ultimately regenerating the four-carbon starting molecule. ATP, , and are produced, and carbon dioxide is released. Oxidative phosphorylation. Cellular respiration - Wikipedia Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy from oxygen molecules or nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and then release waste products. The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions, which break large molecules into smaller ones, releasing energy because weak high-energy bonds ... Chapter 3 Extra Credit Flashcards - Quizlet Label the figure below to investigate the effects of enzymes on chemical reaction rates. ... What is the molecule that enters the citric acid cycle? Acetyl coenzyme A. The breaking of old chemical bonds and forming of new ones is called a. chemical reaction. The Glycolytic Pathway, The Gluconeogenic Pathway, The Tca ... The glycolysis, TCA cycle, fatty acid metabolism, l-threonine ... The glycolytic pathway, the gluconeogenic pathway, the TCA cycle, and ... A pathway model integrating glycolysis, TCA cycle intermediates and ... Metabolic pathways (glycolysis and TCA cycle) of differentially ...
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide - Wikipedia Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme central to metabolism.Found in all living cells, NAD is called a dinucleotide because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine nucleobase and the other nicotinamide.NAD exists in two forms: an oxidized and reduced form, abbreviated as NAD + and NADH (H for hydrogen), respectively. › resources › culture-guidesBacteriology Culture Guide - ATCC Various organic acids, such as citric, lactic, succinic, and gluconic acid, can be produced by bacterial species as a metabolic byproduct. Citric acid, for example, is a byproduct of the Citric Acid Cycle and is therefore important in metabolism. In contrast, the production of lactic acid often occurs as an end product to lactose fermentation. The Citric Acid Cycle: The Reactions of the Citric Acid ... The enzyme succinyl-CoA synthetase catalyzes the fifth reaction of the citric acid cycle. In this step a molecule of guanosine triphosphate (GTP) is synthesized. GTP is a molecule that is very similar in its structure and energetic properties to ATP and can be used in cells in much the same way. › 42749825 › Brock_Biology_of(PDF) Brock Biology of Microorganisms 13th Edition ... Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
PDF Answer: B - Forest Hills School District is reduced to NADH during both glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. B) NAD + has more chemical energy than NADH. C) NAD + is reduced by the action of hydrogenases. D) NAD + can donate electrons for use in oxidative phosphorylation. E) In the absence of NAD +, glycolysis can still function. Answer: A Topic: Concept 9.1 Skill: Knowledge ... bodycoach-online.de › chemical-reactions-pre-lab-questionsChemical reactions pre lab questions - bodycoach-online.de email protected] 1121 - Exam 2 Study Guide.docx - Study Guide for Exam 2 ... n the general importance of photosynthetic organisms to the biosphere. (read below) The three groups of photosynthetic organisms—modern land plants, eukaryotic algae, and photosynthetic bacteria—are responsible for both the oxygen in our atmosphere and the organic molecules that are the foundation of nearly every food chain. Whether or not you notice them, you could not live without them. Lab Tests InfoGlycolysis Cycle - Steps and Enzymes (with ... The third step is summed up in this equation Fructose 6-phosphate (C6H13O9P) + phosphofructokinase + ATP → ADP + Fructose 1, 6-bisphosphate (C6H14O12P2). (4, 5) #4 - Aldolase With the help of aldolase, fructose 1,6-bisphosphate is split into two sugars: dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (GAP).

33 The Image Below Shows The Reactions Of The Citric Acid Cycle. Label The Enzymes On The ...
The image below shows the reaction of the citric acid ... The image below shows the reaction of the citric acid cycle. Label the reaction types on the diagram. COO COO CH2 HO-C-COO CH2 COO acetyl-CoA CoA CH2 COO COO CH2 CH-COO NADH Formation of cOO CH-OH CH2 COO Citrate NAD Oxidation and Decarboxylation Oxidation Decarboxylation HO-C-H Coo H20 NAD+ and...
What are the sequence of events in cellular respiration ... NADH gains electrons and carbon is lost, which forms CO2. The second step is the citric acid cycle, which you can see in the image below. Simplified diagram of citric acid cycle: This complex cycle results in eight NADH, two FADH2, two ATP, and six CO2. The last main portion of cellular respiration is oxidative phosphorylation.
30 The Image Below Shows The Reactions Of The Citric Acid Cycle. Label The Enzymes On The ...
4.3 Citric Acid Cycle and Oxidative Phosphorylation ... It takes two turns of the cycle to process the equivalent of one glucose molecule. Each turn of the cycle forms three high-energy NADH molecules and one high-energy FADH 2 molecule. These high-energy carriers will connect with the last portion of aerobic respiration to produce ATP molecules. One ATP (or an equivalent) is also made in each cycle.
5.2: Electron Transport and Oxidative ... - Biology LibreTexts The role of citric acid cycle intermediates as inhibitors is thought to be due to inhibition of the reversal of the transfer process which can produce superoxide. Coenzyme Q Coenzyme Q (Figure 5.23) is a 1,4 benzoquinone whose name is often given as Coenzyme Q10, CoQ, or Q10.
0 Response to "42 the image below shows the reactions of the citric acid cycle. label the enzymes on the diagram"
Post a Comment