40 plant cell cytoskeleton diagram
Plant cell Structure, Definition, Diagram, Organelles Plant cytoskeleton This is a web of filaments and microtubules which play a major role in keeping the shape of the plant cell and providing the cell's support in its cytoplasm and maintaining its structural structure. The tubules and filaments extend throughout the cell and into the cell's cells cytoplasm. 10.1: Plant Cell Structure and Components - Biology LibreTexts Plant Cells. Figure 10.1. 1: A diagram of a plant cell. Plants cells differ from animal cells in that they have a cell wall (which is glued to adjacent cells by the middle lamellae), a large central vacuole, and chloroplasts. Image by LadyofHats, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons.
biologydictionary.net › animal-cellAnimal Cell - The Definitive Guide | Biology Dictionary Apr 04, 2017 · Cytoskeleton. The cytoskeleton is a network of filaments and tubules found throughout the cytoplasm of the cell. It has many functions: it gives the cell shape, provides strength, stabilizes tissues, anchors organelles within the cell, and has a role in cell signaling. It also provides mechanical support to allow cells to move and divide. There ...

Plant cell cytoskeleton diagram
Cytoskeleton - Wikipedia The cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, excluding bacteria and archaea. It extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is composed of similar proteins in the various organisms. Biology 2e, The Cell, Cell Structure, The Cytoskeleton ... As their name implies, microtubules are small hollow tubes. Polymerized dimers of α-tubulin and β-tubulin, two globular proteins, comprise the microtubule's walls ().With a diameter of about 25 nm, microtubules are cytoskeletons' widest components. They help the cell resist compression, provide a track along which vesicles move through the cell, and pull replicated chromosomes to opposite ... byjus.com › biology › diagram-of-animal-cellA Well-labelled Diagram Of Animal Cell With Explanation Also Read Different between Plant Cell and Animal Cell. Well-Labelled Diagram of Animal Cell. The Cell Organelles are membrane-bound, present within the cells. There are various organelles present within the cell and are classified into three categories based on the presence or absence of membrane. Listed below are the Cell Organelles of an ...
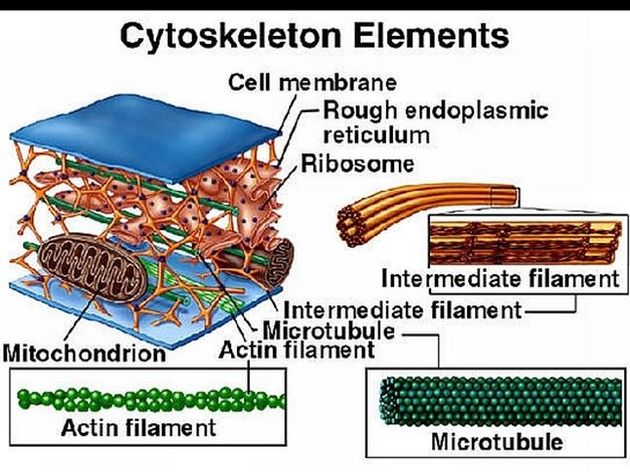
Plant cell cytoskeleton diagram. Plant Cell - Definition, Structure, Function, Diagram & Types Both plant and animal cells contain nucleus along with similar organelles. One of the distinctive aspects of a plant cell is the presence of a cell wall outside the cell membrane. Read more: Cells. Plant Cell Diagram. The plant cell is rectangular and comparatively larger than the animal cell. Cytoskeleton - Definition, Structure, Function and ... A cell's cytoskeleton ensures stability, energy, and motility. This provides a cellular scaffolding that arranges the cellular organization into. The figure represents a part of the cytoskeleton of a cell. Note the cytoskeleton is extremely extensive. Notice that the cytoskeleton seems to have many ribosomes attached to it. Cytoskeletoal Elements - Plant Cell Biology For Masters ... Protoplasmic Cytoskeleton Elements . The protoplasmic liquid without any cell organelles is known as hyaloplasm. This part of the protoplasm is known to perform various metabolic activities like glycolysis, amino acid metabolism, EMP pathway, fatty acid oxidation, charging of tRNA, protein synthesis and many others. PDF Chapter 3 The Plant Cell and the Cell Cycle the smaller organelles in the cell. 3.2 THE PLANT CELL Living cells are found throughout the plant body. They make up the internal, photosynthetic cells of the leaf that convert light energy to chemical energy. They make up the pith and cortex of the stem and the cortex of the root. They make up the bulk of fleshy fruits.
Cytoskeleton And Cell Membrane Labeled : Functions and Diagram Cytoskeleton And Cell Membrane Labeled Friday, April 9th 2021. | Diagram Cytoskeleton And Cell Membrane. The same is true of the reverse. Natural Exterior Stone Supplier UK and International Delivery Microfilaments are the thinnest of the cytoskeletal fibers and function in moving cellular components, for example, during cell division. www2.estrellamountain.edu › faculty › farabeePHOTOSYNTHESIS - Estrella Mountain Community College The carbon dioxide then enters the Calvin Cycle, with PEP returning to the mesophyll cell. The resulting sugars are now adjacent to the leaf veins and can readily be transported throughout the plant. C-4 photosynthsis involves the separation of carbon fixation and carbohydrate systhesis in space and time. Cytoskeleton In Plant Cell - Plant Ideas The plant cytoskeleton is a highly dynamic and versatile intracellular scaffold composed of microtubules and actin microfilaments and plays an important role in many aspects of plant cell growth and development, including such fundamental processes as cell division, cell expansion, and intracellular organization and. › articles › s41477/021/01021-wPlant cell polarity as the nexus of tissue mechanics and ... Dec 09, 2021 · The cell wall–PM–cytoskeleton continuum has long been hypothesized to represent the cornerstone of plant mechanical responses, although the mode of action and regulation of this continuum ...
Cell Structure: The Cytoskeleton | Saylor Academy There are three types of fibers within the cytoskeleton: microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubule s (Figure 4.22). Here, we will examine each. Figure 4.22 Microfilaments thicken the cortex around the inner edge of a cell; like rubber bands, they resist tension. Plant Cell Parts & Functions | What is a Plant Cell ... The parts of a plant cell and plant cell components, which will be discussed, are plant cell wall, plant cell membrane, smooth endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, rough endoplasmic reticulum,... Cytoskeleton - Structure and Function of Cytoskeleton Cytoskeleton Structure A cytoskeleton structure comprises the following types of fibres: Microfilaments Microtubules Intermediate Filaments Microtubules Microtubules appear like small, hollow, round tubes with a diameter of about 24 nanometers. They are made up of a protein, tubulin. Thirteen tubulins link to form a single tube. Plant Cell Diagram, Organelles, Structure & Functions ... The chloroplasts in the plant cell are organelles that contain chlorophyll and allow plant cells to do photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the process that cells use to make their own food using the...

animal cell cupcake or cake, room 233 | Classroom Inspiration, organization, creative learning ...
rsscience.com › animal-cells-vs-plant-cellsAnimal vs. Plant cells - Similarities, Differences, Chart ... Yes, both plant and animal cells have a similar cytoskeleton. Constrained by the cell wall, the plant cell’s cytoskeleton does not allow a dramatic change of the cell shape. However, the cytoskeleton network of actin filaments, microtubules, and intermediate filaments generate shape, structure, and organization to the cytoplasm of the plant ...
Cytoskeleton: Meaning and Components (With Diagram) The association of actin into cytoskeleton network has been found to be of four types: i. Association of actin molecules into actin filaments. ii. Association with non-actin proteins into microfilaments. iii. Joining of microfilaments with network. iv. Association of actin fibres with other cell components like membranes.
Cytoskeleton Diagram Labeled - Agaliprogram In cell biology the cytoskeleton is a system of fibrillar structures that pervades the cytoplasm. Animal cell diagram labeled cytoskeleton. Microtubules, microfilaments (actin filaments), and intermediate filaments. It Assists In Cell Signalling.
Cytoskeleton- Definition, Structure, Functions and Diagram Figure: Diagram of Cytoskeleton A. Microtubules The thickest are the microtubules (20 nm in diameter) which consist primarily of the tubulin protein. Each tubulin subunit is made up of one alpha and one beta-tubulin that are attached to each other, so technically tubulin is a heterodimer, not a monomer.
Cell Organelles (Plant, Animal)- Structure, Functions ... Cell Organelles Definition. The cell is the basic unit of organization or structure of living matter bound by the semipermeable membrane and is capable of self-replicating in a medium free of other living systems. Cell organelle is the cellular component that can be both membranous and non-membranous present within a cell having distinct ...
Plant Cell- Definition, Structure, Parts, Functions ... Definition of the plant cytoskeleton This is a network of microtubules and filaments that plays a primary role in maintaining the plant cell shape and giving the cell cytoplasm support and maintaining its structural organization. These filaments and tubules normally extend all over the cell, through the cell cytoplasm.
Plant Cell Diagram Cytoskeleton Simple : Functions and Diagram The cytoskeleton gives animal cells structure, strength, and the ability to change shape and move.. A plant cell diagram, like the one above, shows each part of the plant cell including the chloroplast, cell wall, plasma membrane, nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes, etc. These are large, vesicles filled with fluid, within the cytoplasm of a cell.
The Plant Cytoskeleton - Cell Plant cells display a singular architecture, necessitating a structurally and functionally unique cytoskeleton and plant specific control mechanisms. Main Text Three different types of linear proteinaceous polymers comprise the cytoskeleton in animal cells: actin filaments, microtubules, and intermediate filaments.




0 Response to "40 plant cell cytoskeleton diagram"
Post a Comment