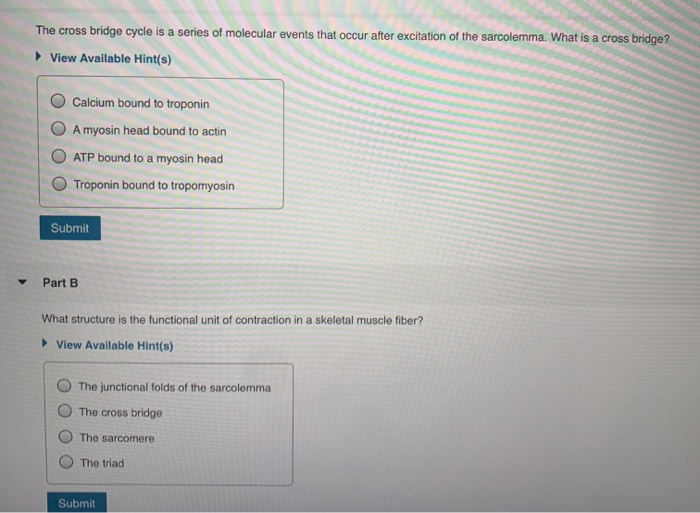
41 cross bridge cycle diagram
circuitdigest.com › electronic-circuits › singleSingle Phase Half Bridge and Full Bridge Inverter Circuit ... Jan 04, 2019 · The main difference between half bridge and full bridge inverter is the maximum value of output voltage. In half bridge inverter, peak voltage is half of the DC supply voltage. In full bridge inverter, peak voltage is same as the DC supply voltage. The circuit diagram of full bridge inverter is as shown in below figure. Myosin isoforms and the mechanochemical cross-bridge cycle ... A minimal ATPase cycle for the actin and myosin cross-bridge cycle. Filled circles represent the actin monomers in a thin filament and the blue shape represents the motor domain of myosin. M is myosin, A is actin, T is ATP, D is ADP and Pi is inorganic phosphate. AMD, for example, represents a complex between actin, myosin and ADP.
Mathematical Simulation of Muscle Cross-Bridge Cycle and ... The cross-bridge states within the cycle are divided into six attached (between myosin cross-bridges and actin filaments) states and one detached state. The population of cross-bridges in each of the states is determined by the transition rates throughout the cycle; differential equations describing the transitions are set up as a cyclic matrix.

Cross bridge cycle diagram
Cross Bridge Cycle I Binding of ATP to the myosin head ... Overview of Cross-Bridge Cycle 1. ATP binding to myosin head causes detachment of the cross-bridge from actin. 2. Myosin hydrolyzes ATP into ADP and Pi, which remain in the ATP-binding site. Myosin head is in high-energy state, 90° to thin filament. Myosin energized in resting muscle. 3. Myosin binds to actin forming a cross-bridge. 4. Cross-bridge Cycle This figure template "Cross-bridge Cycle" is assembled using dynamic BioRender assets (icons, lines, shapes and/or text) and is fully editable. You can customize your own personalized figure inside the BioRender web app using this template as a starting point. BioRender is an online tool to create beautiful, professional science figures, 50x faster than current alternatives with no drawing ... › science › cross-bridgecross bridge | biology | Britannica In muscle: Cross-bridge cycle and ATP breakdown. Smooth muscle contraction requires the release of chemical energy stored in ATP molecules. The release of this chemical energy by the myosin cross bridge and the resultant mechanical work is commonly referred to as the cross-bridge cycle, which in smooth… Read More
Cross bridge cycle diagram. Cross-bridge Cycle During Muscle Contraction | Biology | JoVE 20.8: Cross-bridge Cycle As muscle contracts, the overlap between the thin and thick filaments increases, decreasing the length of the sarcomere—the contractile unit of the muscle—using energy in the form of ATP. At the molecular level, this is a cyclic, multistep process that involves binding and hydrolysis of ATP, and movement of actin by myosin. when does cross bridge cycling end - Lisbdnet.com A single cross-bridge cycle consists of four basic stages. First, myosin binds actin, forming the high-energy/attached state. The power stroke occurs when myosin changes its shape, pulling the thin filaments towards the middle of the sarcomere - that's what causes sarcomere shortening in muscular contraction.Aug 24, 2021 A cross-bridge model that is able to explain mechanical ... The responses of muscle to steady and stepwise shortening are simulated with a model in which actin-myosin cross-bridges cycle through two pathways distinct for the attachment-detachment kinetics and for the proportion of energy converted into work. Cross Bridge Cycle Quiz - PurposeGames.com Cross Bridge Cycle. ... Label the diagram of a long bone 12p Image Quiz. Label Skin Layers and Hair 4p Image Quiz. GRAM+ Vs. GRAM- 13p Multiple-Choice. Match the Eukaryotic Cell Organelles 14p Multiple-Choice. Microbe Quiz 16p Multiple-Choice. Membranes 8p Multiple-Choice. Playlists by same creator.
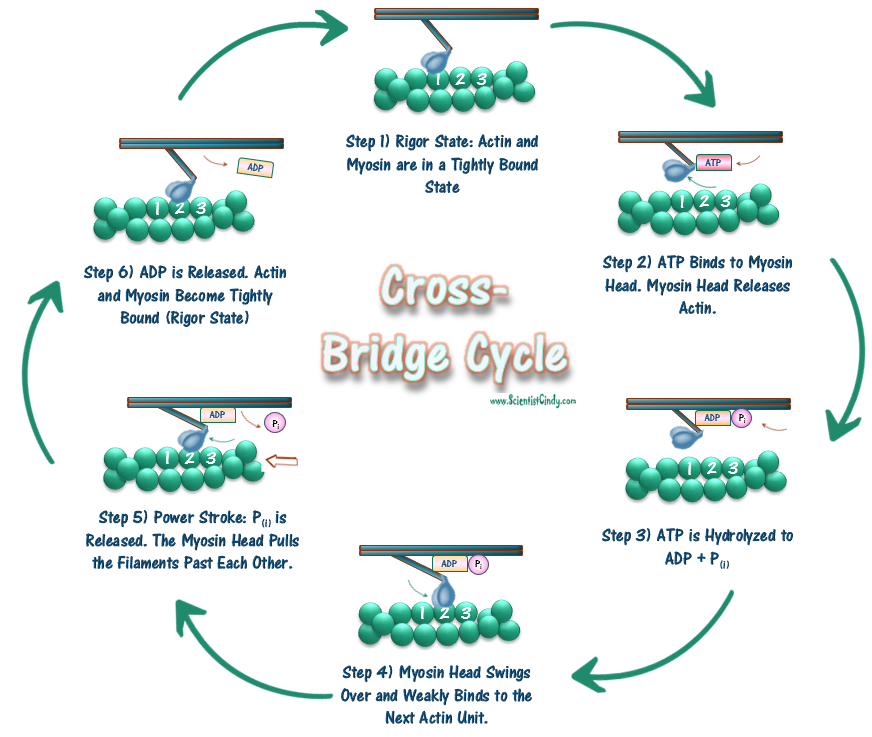
Steps of the Crossbridge Cycle Flashcards CardsReturn to Set Details. Term. Step 1: Binding of myosin to actin. [image] Definition. ADP and Pi are bound to ATPase site of myosin head. Creates high affinity for actin and the myosin head binds to thin filament. Term. Step 2: Power Stroke. Focus Figure 9.3: Cross Bridge Cycle Diagram | Quizlet Location of higher Ca2+ concentration for cross bridge formation Actin-Binding Sites Exposed Actin Status to begin CBF ADP and Pi Molecule(s) bound to the myosin head at the start of the cross bridge cycle Energized/Cocked Myosin head Energy state of myosin for beginning cross bridge formation ADP and Pi Molecules released just before power stroke Learn About Cross Bridge Cycle Activity | Chegg.com The cross-bridge cycle refers to the cascade of repeated events where thin filaments slide over the thick filaments during muscle contraction with the help of myosin heads pulling the actin at the binding sites followed by detaching itself and then attaching to more binding sites and then keep detaching and binding to another site. Sliding Filament Theory of Muscle ... - Online Biology Notes After sliding the cross bridge detached and the actin and myosin filament come back to original position. The active cross bridge form and reform for 50-100 time within a second using ATP in rapid fashion. Therefore, muscle fiber consists of numerous mitochondria. In muscle contraction, sarcomere can contracts by 30-60% of its length
actin myosin cross bridge cycle mnemonic? : Mcat Not really a mnemonic but I think of it like a golf swing in my head. Also I haven't seen this diagram before but I typically think of the cross bridge cycle beginning with the power stroke, so: Taking the club back to gain energy (ATP) Right as you make contact with the ball, energy is released (ATP hydrolysis now forms ADP + Pi) The ball gets ... Schematic diagram of the cross-bridge cycle. a ATP binds ... schematic diagram of the cross-bridge cycle. a atp binds to the atp-binding domain on the myosin head. b atp is hydrolyzed to adp and a phosphate allowing the myosin head to move towards the actin... Cross Bridge Cycle Diagram - Quizlet Start studying Cross Bridge Cycle. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. PPT PowerPoint Presentation Diagram the chemical and mechanical steps in the cross-bridge cycle and explain the effect on the muscle fiber length. Describe the end of contraction mechanisms. Muscle excitation and energy sources. Three roles of ATP in muscle function. Three sources of ATP for muscle function.
quizlet.com › 265729985 › mastering-ap-chapter-9Mastering A&P Chapter 9 - Muscle and Muscle Tissue Diagram ... 1. Location of higher concentration of Ca2+ needed for cross bridge formation and cycling: cytoplasm 2. Actin status to begin cross bridge formation: actin-binding sites exposed 3. Molecule(s) bound to the myosin head at the start of the cross bridge cycle: ADP and Pi 4.
study.com › academy › lessonMuscular Contraction: Cross-Bridge Formation - Video & Lesson ... Aug 24, 2021 · The cross-bridge will continue to cycle and cause contraction as long as the muscle is stimulated. Lesson Summary In summary, cross-bridge cycling between actin and myosin is responsible for ...

ATP driven actomyosin cross-bridge cycle. The black circles represent... | Download Scientific ...
circuitdigest.com › electronic-circuits › full-waveFull Wave Rectifier Circuit Diagram (Center Tapped & Bridge ... Aug 10, 2017 · Center tapped full-wave rectifier; Bridge rectifier (Using four diodes) If two branches of a circuit is connected by a third branch to form a loop, then the network is called a bridge circuit.Out of these two the preferable type is Bridge rectifier circuit using four diodes because the two diode type requires a center tapped transformer and not reliable when compared to bridge type.
Cross Bridges - Human Physiology - 78 ... - 78 Steps Health Figure 12.12 The cross-bridge cycle that causes sliding of the filaments and muscle contraction. Hydrolysis of ATP is required for activation of the cross bridge, and the binding of a new ATP is required for the cross bridge to release from the actin at the end of a cycle. obvious that the contraction cycles must be repeated many times.
Muscle Contraction - Cross Bridge Cycle, Animation ... (USMLE topics) Molecular basis of the sliding filament theory (skeletal muscle contraction) - the cross bridge cycle. This video is available for instant dow...
The cross-bridge cycle and skeletal muscle fatigue ... This kinetic scheme has proven useful in assessing the cellular mechanisms of muscle fatigue for those factors acting at the cross bridge ( 21, 23 ). Fig. 1. Actomyosin ATPase cycle. A: minimal description of the myosin (M) and actomyosin (A·M) ATPase as defined in solution.
A Cross-Bridge Cycle with Two Tension-Generating Steps ... The model of the cross-bridge cycle with a single tensing step is based on the Lymn-Taylor kinetic scheme for actomyosin ATPase . Although our modeling does not consider the structure or nucleotide composition of the intermediates of the cycle, the detached states can be pictured as being in the M.ATP state with an open conformation ( 38 ) or ...

The myosin cross-bridge cycle including the mechanism of action of... | Download Scientific Diagram
Learn About Cross Bridge Cycle Diagram | Chegg.com Four Stages of Cross-Bridge Cycle Step 1: The Design of Cross-Bridges- When excitation-contraction coupling causes the sites of myosin binding on actin to be released, the cycle begins. Myosin heads, forming cross bridges, connect to these sites. Myosin begins in its high-energy state, in which ADP and inorganic phosphate occupy the ATP.
› articles › s41467/022/28948-8Deciphering the mechanism of the Ni-photocatalyzed C‒O cross ... Mar 14, 2022 · d A simplified excited-state diagram ... to the steric hindrance of the ethylene bridge that blocks the ... probe the key steps of the C–O cross-coupling catalytic cycle involving ...
Excitation contraction coupling with cross-bridge cycle ... View in full-text Context 2 ... contraction is explained by the sliding filament theory, [6] which states that the cytoskeletal structures of muscles rearrange and form cross-bridges in the...
What is cross bridge cycling and why is it important in ... The cross bridge cycle can be broken down as follows: Hydrolysis of ATP to ADP and Pi, with products still covalently bonded to myosin, cause it to enter an energised state. Cross bridge binds to actin. It undergoes a conformational change. ADP and Pi are released. You then get a power stroke (ie cross bridge moves, pulling actin along which ...
Image of a bridge using cross-laminated timber (CLT) floor slabs. | Download Scientific Diagram
Elementary steps of the cross-bridge cycle in bovine ... The role of regulatory proteins in the elementary steps of the cross-bridge cycle in bovine myocardium was investigated. The thin filament was selectively removed by gelsolin and the actin filament was reconstituted without tropomyosin or troponin.
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Carnot_heat_engineCarnot heat engine - Wikipedia A Carnot heat engine is a heat engine that operates on the Carnot cycle.The basic model for this engine was developed by Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot in 1824. The Carnot engine model was graphically expanded by Benoît Paul Émile Clapeyron in 1834 and mathematically explored by Rudolf Clausius in 1857, work that led to the fundamental thermodynamic concept of entropy.
10.3 Muscle Fiber Excitation, Contraction, and Relaxation ... Diagram the process of cross-bridge cycling The Neuromuscular Junction The process of muscle contraction begins at the site where a motor neuron's terminal meets the muscle fiber—called the neuromuscular junction (NMJ). Every skeletal muscle fiber in every skeletal muscle is innervated by a motor neuron at a NMJ.
Chapter I.II: Muscle contraction - The ... - The Biomechanist The mechanics of muscle contraction The cross-bridge cycle - the "mechanical" muscle contraction - begins with the rearrangement of troponin C by the calcium, so that the binding sites on the actin are released. The myosin head can now bind onto the free binding sites of the actin. The myosin heavy chains are loaded with ADP and a phosphate.
› science › cross-bridgecross bridge | biology | Britannica In muscle: Cross-bridge cycle and ATP breakdown. Smooth muscle contraction requires the release of chemical energy stored in ATP molecules. The release of this chemical energy by the myosin cross bridge and the resultant mechanical work is commonly referred to as the cross-bridge cycle, which in smooth… Read More
Cross-bridge Cycle This figure template "Cross-bridge Cycle" is assembled using dynamic BioRender assets (icons, lines, shapes and/or text) and is fully editable. You can customize your own personalized figure inside the BioRender web app using this template as a starting point. BioRender is an online tool to create beautiful, professional science figures, 50x faster than current alternatives with no drawing ...






0 Response to "41 cross bridge cycle diagram"
Post a Comment