45 pathophysiology of meningitis diagram
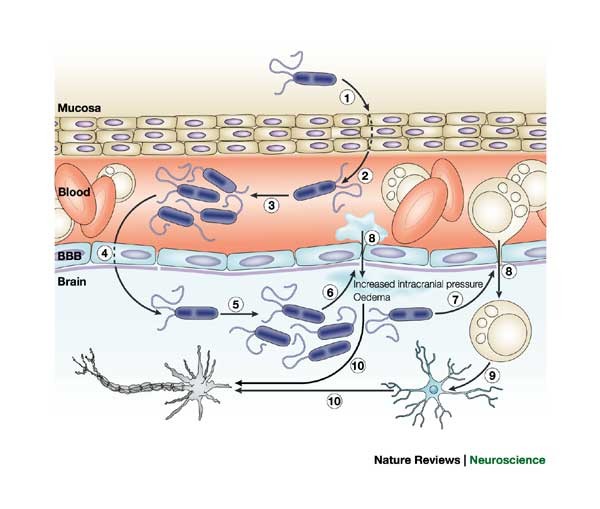
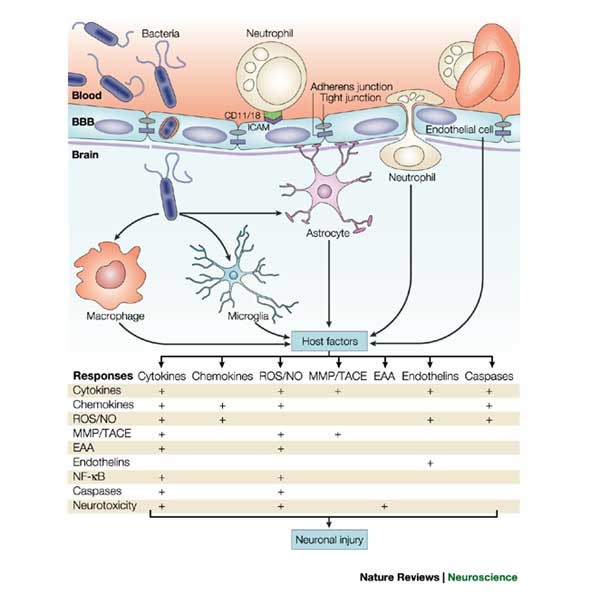
[PDF] Pathogenesis and pathophysiology of bacterial meningitis ... Pathogenesis and pathophysiology of bacterial meningitis A. Tunkel, W. Scheld Published 1 April 1993 Medicine Clinical Microbiology Reviews Bacterial meningitis remains a disease with associated unacceptable morbidity and mortality rates despite the availability of effective bactericidal antimicrobial therapy. Pathogenesis and pathophysiology of bacterial meningitis The pathogenesis and pathophysiology of bacterial meningitis involve a complex interplay between virulence factors of the pathogens and the host immune response [ 3,4 ]. Much of the damage from this infection is believed to result from cytokines released within the CSF as the host mounts an inflammatory response.
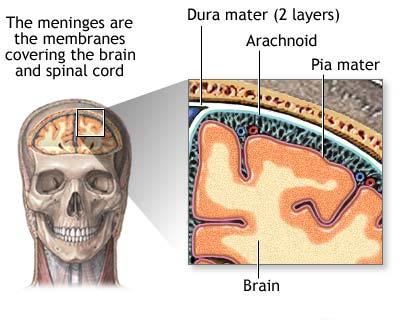
Meningitis pathophysiology - wikidoc Pathophysiology. The clinical picture of meningitis largely arises from the host response to the inciting organism in the CSF. It seems that the subcapsular components (the cell wall and lipopolysaccharide) of bacteria are more important in determining inflammation than the surface components ( pili and polysaccharide capsule).

Pathophysiology of meningitis diagram
Dementia with Lewy bodies - Wikipedia Dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) is a type of dementia characterized by changes in sleep, behavior, cognition, movement, and regulation of automatic bodily functions.Memory loss is not always an early symptom. The disease worsens over time and is usually diagnosed when cognitive impairment interferes with normal daily functioning.Together with Parkinson's disease … Meningitis: N Meningitidis Are Gram-Negative, Kidney Bean ... - Scribd Meningitis is inflammation of the thin tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord, called the meninges. There are several types of meningitis. The most common is viral meningitis, which you get when a virus enters the body through the nose or mouth and travels to the brain. Bacterial meningitis is rare, but can be deadly. Neonatal Sepsis: Background, Pathophysiology, Etiology - Medscape Jun 13, 2019 · Neonatal sepsis. Recommended regimens for intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis for prevention of early-onset group B streptococcal (GBS) disease. Diagram from Verani JR, McGee L, Schrag SJ, for the Division of Bacterial Diseases, National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Pathophysiology of meningitis diagram. Viral meningitis pathophysiology - wikidoc Viral meningitis pathophysiology differs from virus to another and depends on many factors like age, immune status and gene expression. Invasion into the meninges by a pathogen can set up a local inflammatory response. The clinical signs are due to this meningeal irritation - for example, Kernig's sign is due to pain produced by stretching of ... Pathophysiology | Meningitis - U.OSU Meningitis is a disease process where the protective layers that cover the brain and spinal cord become inflamed. Meningitis can be infectious or it can be caused by injury, cancer, and other noninfectious causes. Infectious meningitis can be caused by a bacterial, viral, or fungal infection. It can also be caused by parasites or other toxins. Central Nervous System Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Jan 06, 2022 · Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a systemic autoimmune disease characterized by multiple immunologic abnormalities and has the potential to involve the central nervous system (CNS). The prevalence of SLE seems to be growing, possibly because of earlier diagnosis and improved survival; however, the associated mortality is still high. The mortality is … Pathogenesis and pathophysiology of bacterial meningitis Most cases of bacterial meningitis begin with host acquisition of a new organism by nasopharyngeal colonization followed by systemic invasion and development of a high-grade bacteremia. Bacterial encapsulation contributes to this bacteremia by inhibiting neutrophil phagocytosis and resisting classic complement-mediated bactericidal activity.
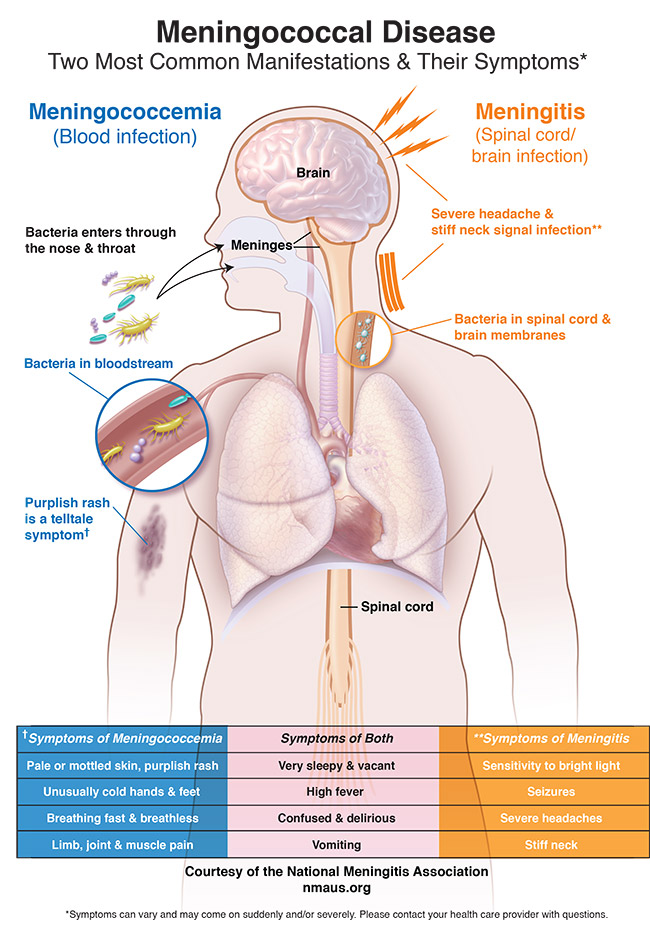
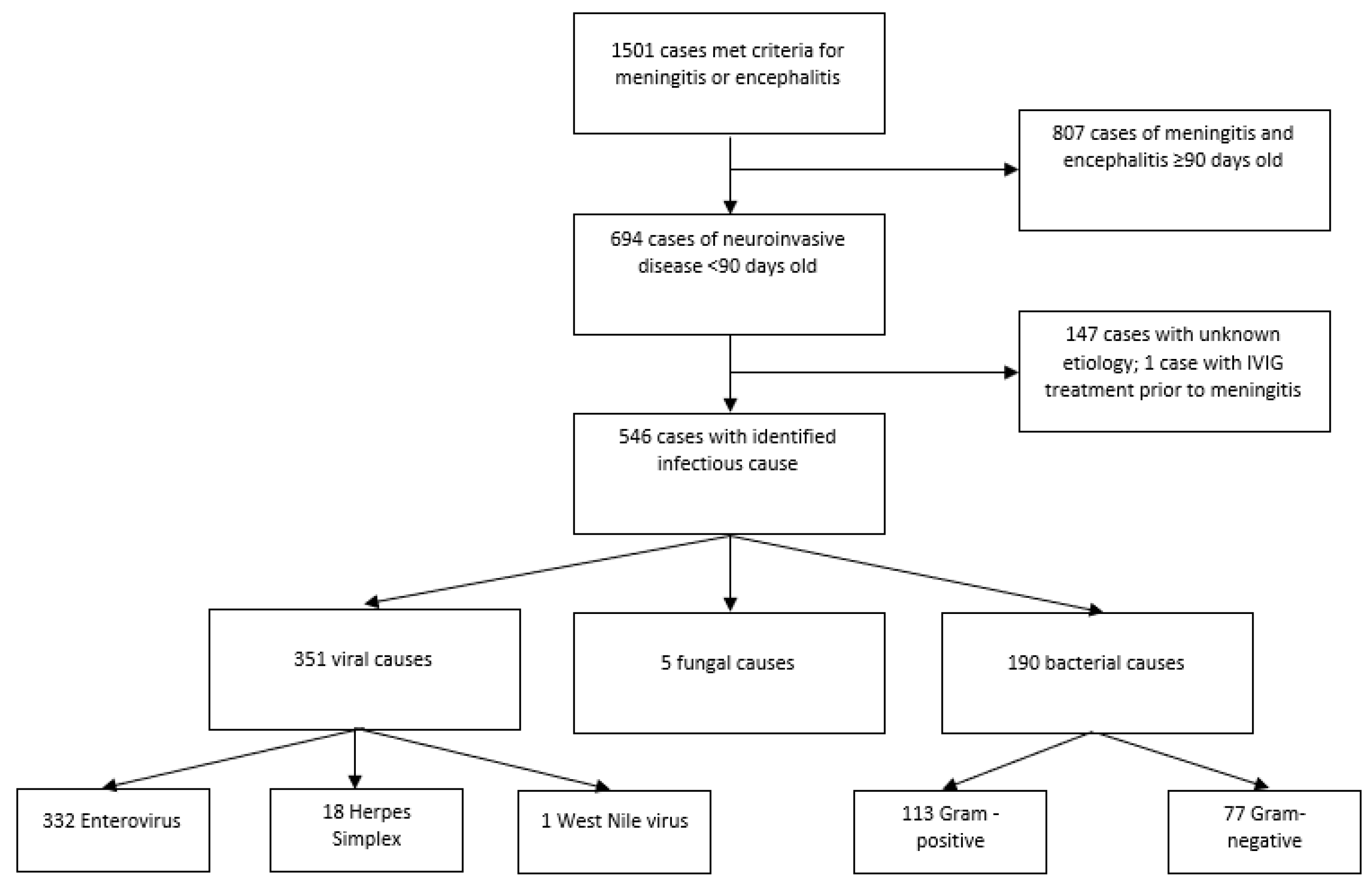
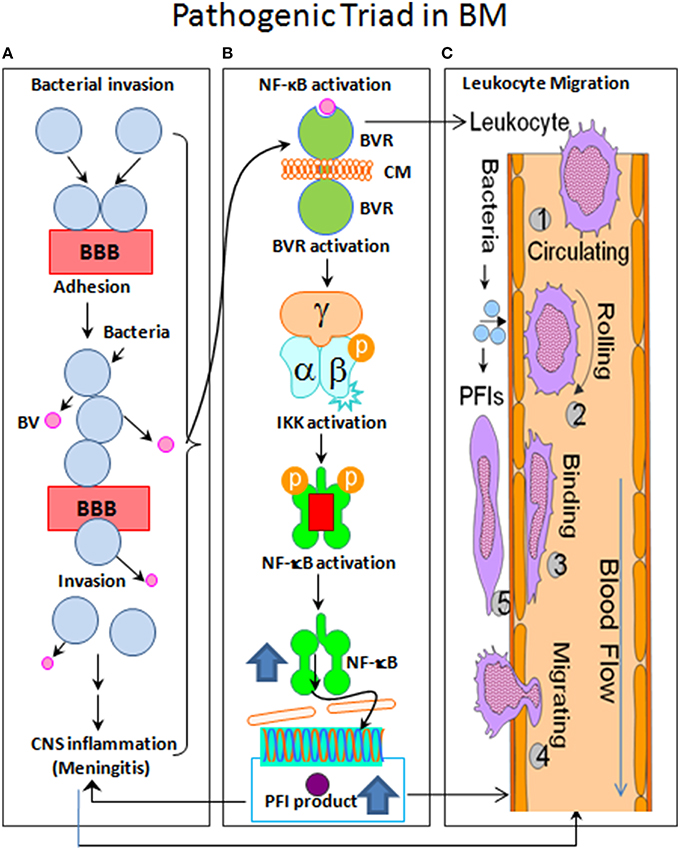
Motor neuron disease - Wikipedia Differential diagnosis can be challenging due to the number of overlapping symptoms, shared between several motor neuron diseases. Frequently, the diagnosis is based on clinical findings (i.e. LMN vs. UMN signs and symptoms, patterns of weakness), family history of MND, and a variation of tests, many of which are used to rule out disease mimics, which can manifest with … Pathophysiology of bacterial meningitis. The pathophysiology of acute ... The pathophysiology of acute meningitis involves several sequential steps. First, bacteria that colonize epithelial cells of the nasopharynx cross the mucosal barrier and enter the bloodstream,... Meningitis - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf Elevating the head of the bed to 30 degrees Inducing mild hyperventilation in the intubated patient Osmotic diuretics such as 25% mannitol or 3% saline Stroke Subdural hematoma Subarachnoid hemorrhage Metastatic brain disease Brain abscess (might coexist with meningitis) Streptococcus pneumoniae meningitis: case fatality rate, 17.9% Meningitis | Pathophysiology Clinical pathophysiology of meningitis Meningococcal meningitis generally has a better prognosis than septicaemia. Meningococci reach the brain from the bloodstream, implying that the patient's immune response has prevented bacterial proliferation in the blood and not suffered overwhelming sepsis.
Spina bifida - Wikipedia Spina bifida (Latin for 'split spine'; SB) is a birth defect in which there is incomplete closing of the spine and the membranes around the spinal cord during early development in pregnancy. There are three main types: spina bifida occulta, meningocele and myelomeningocele. Meningocele and myelomeningocele may be grouped as spina bifida cystica. The most common location is … Pathophysiology meningitis - SlideShare 5. MENINGITIS • Diagnosis: • CSF sample by lumbar puncture • Microscopic examination. 6. • Acute onset : headache, neck stiffness, photophobia, fever and vomiting • on complication or chronic : hemorrhagic skin rash, development of seizures, focal cerebral signs and cranial nerve palsies, coma and death MENINGITIS. Order Panel - collepals.com - College Pal × Are you sure? NO YES YES Meningitis | McMaster Pathophysiology Review Definition An inflammation of the meninges, especially the arachnoid mater and the pia mater, often secondary to infection. Edema and inflammatory infiltrates lead to fever, focal neurological deficits, decreased level of consciousness, and seizure. Infectious causes can be bacterial, viral, fungal, or parasitic
Pathophysiology and Treatment of Bacterial Meningitis - PMC The key to the diagnosis of bacterial meningitis is the proof of bacteria in the CSF by Gram-staining ( Figure 2) or a positive bacterial culture. Detection rates in the CSF may be as high as 90%, while about 50% positive results are observed in blood cultures.
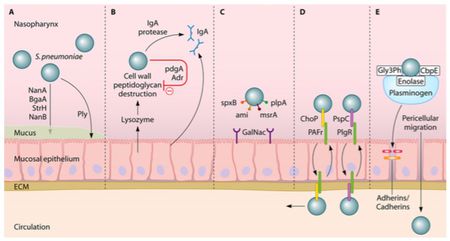
Pathophysiology - Bacterial Meningitis Many of the pathophysiologic consequences of bacterial meningitis result from virulence factor induced inflammation of the subarachnoid space. Cell Wall: The cell walls of gram positive bacteria such as S. pneumoniae trigger inflammation. More specifically, cell wall components such as teichoic acid and peptidoglycan induce severe inflammation.
Rotavirus - Wikipedia Rotavirus is a genus of double-stranded RNA viruses in the family Reoviridae.Rotaviruses are the most common cause of diarrhoeal disease among infants and young children. Nearly every child in the world is infected with a rotavirus at least once by the age of five. Immunity develops with each infection, so subsequent infections are less severe. Adults are rarely affected.
Basilar skull fracture - Wikipedia A basilar skull fracture is a break of a bone in the base of the skull. Symptoms may include bruising behind the ears, bruising around the eyes, or blood behind the ear drum. A cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak occurs in about 20% of cases and may result in fluid leaking from the nose or ear. Meningitis occurs in about 14% of cases. Other complications include injuries to the cranial …
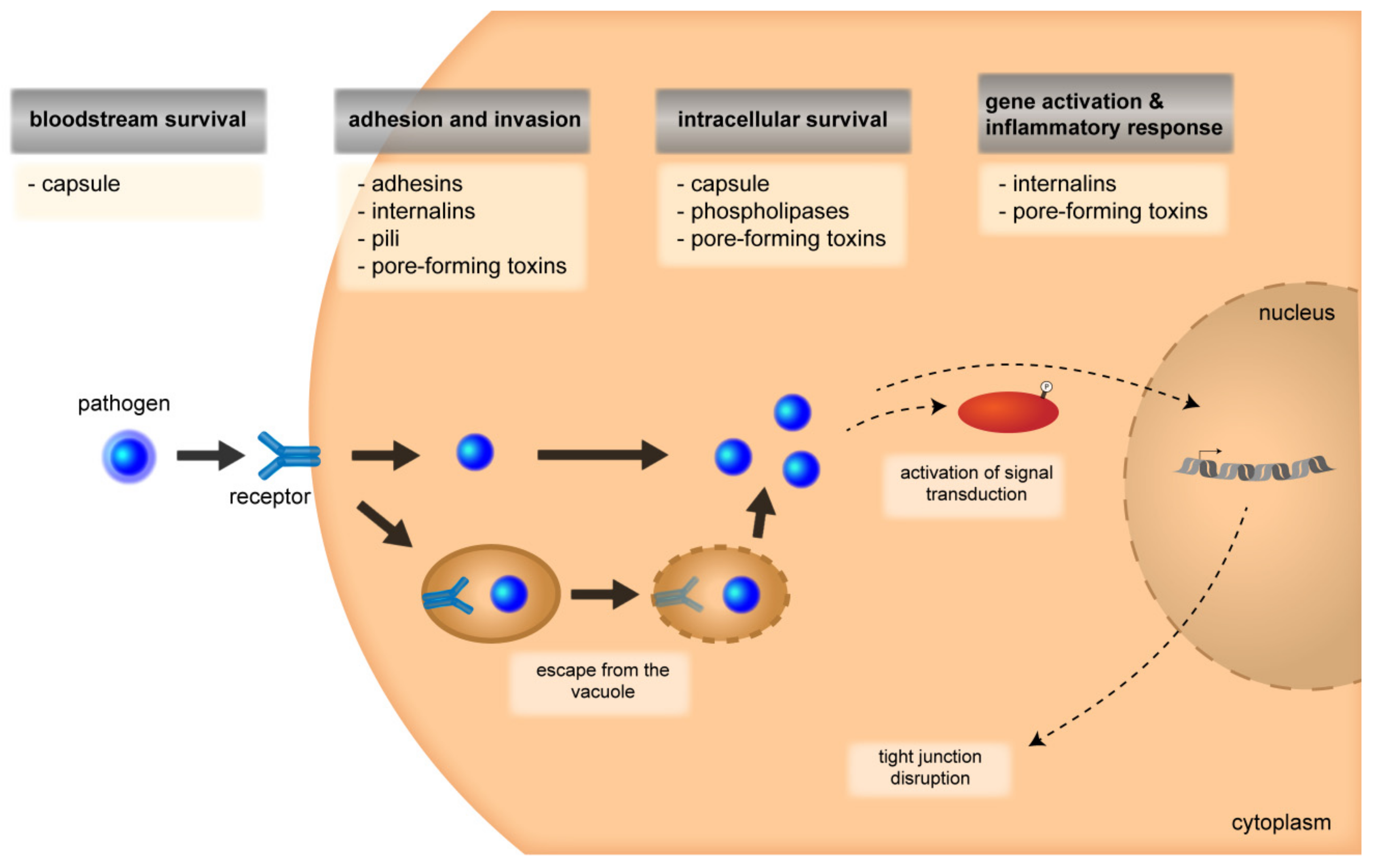
Pathogenesis and pathophysiology of meningitis - PubMed Abstract. Advances in the understanding of the pathogenesis and pathophysiology of meningitis have occurred primarily through the use of experimental animal models. These models have proven to be particularly valuable in experimental bacterial meningitis, focusing on the bacterial virulence factors responsible for the initiation of infections ...
Pathophysiology and Clinical Presentation - Correct Diagnosis PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND CLINICAL PRESENTATION - CORRECT DIAGNOSIS Viral meningitis is an inflammation and infection of the meninges of the brain and spinal cord by a virus (McCance & Huether, 2019, pp. 576-578). A variety of viruses can cause this inflammation of the meninges, and can be broken down into two categories: acute vs. chronic.
Home Page: Heart & Lung: The Journal of Cardiopulmonary and … Sep 29, 2022 · Heart & Lung: The Journal of Cardiopulmonary and Acute Care, the official publication of The American Association of Heart Failure Nurses, presents original, peer-reviewed articles on techniques, advances, investigations, and observations related to the care of patients with acute and critical illness and patients with chronic cardiac or pulmonary disorders.
Scheme depicting the pathogenesis and pathophysiology of meningitis ... Meningitis is an inflammation of the protective membranes called meninges and fluid adjacent the brain and spinal cord. The inflammatory progression expands all through subarachnoid space of the...
Vertigo - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf Mar 18, 2022 · Vertigo is a common presenting complaint in primary care offices and emergency departments. It is a symptom of vestibular dysfunction and has been described as a sensation of motion, most commonly rotational motion. It is important to differentiate vertiginous symptoms from other forms of dizziness, such as lightheadedness, which is most often associated with …
Neonatal Sepsis: Background, Pathophysiology, Etiology - Medscape Jun 13, 2019 · Neonatal sepsis. Recommended regimens for intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis for prevention of early-onset group B streptococcal (GBS) disease. Diagram from Verani JR, McGee L, Schrag SJ, for the Division of Bacterial Diseases, National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Meningitis: N Meningitidis Are Gram-Negative, Kidney Bean ... - Scribd Meningitis is inflammation of the thin tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord, called the meninges. There are several types of meningitis. The most common is viral meningitis, which you get when a virus enters the body through the nose or mouth and travels to the brain. Bacterial meningitis is rare, but can be deadly.
Dementia with Lewy bodies - Wikipedia Dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) is a type of dementia characterized by changes in sleep, behavior, cognition, movement, and regulation of automatic bodily functions.Memory loss is not always an early symptom. The disease worsens over time and is usually diagnosed when cognitive impairment interferes with normal daily functioning.Together with Parkinson's disease …



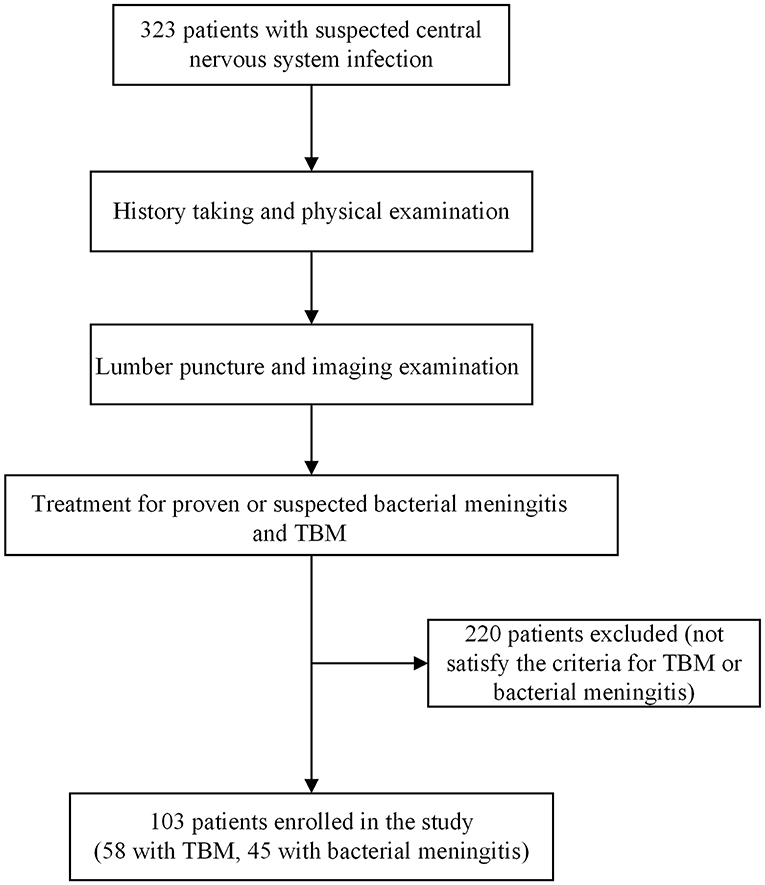




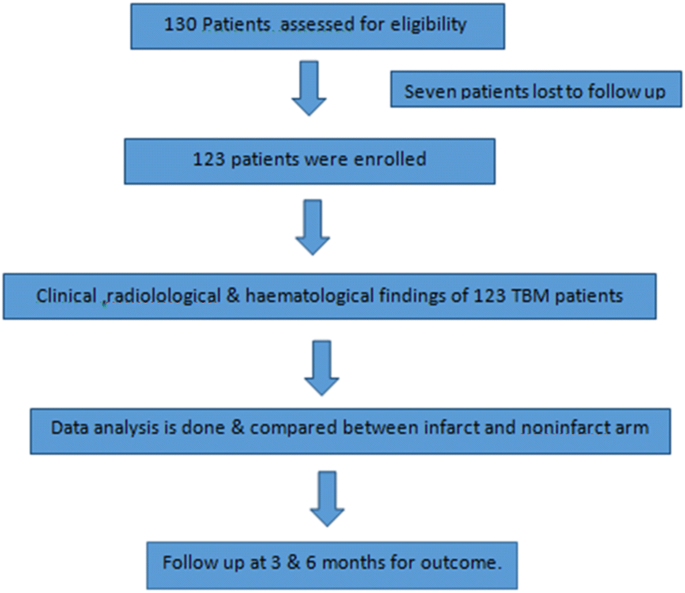
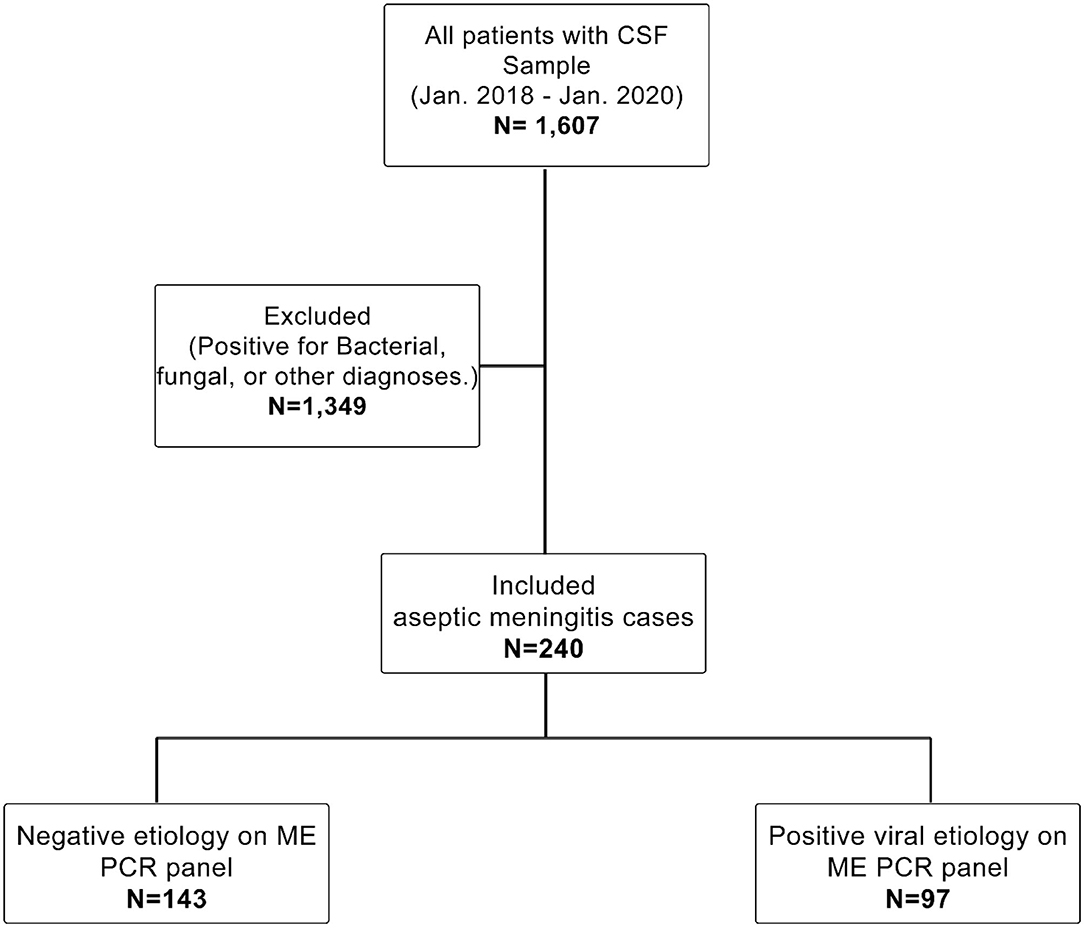






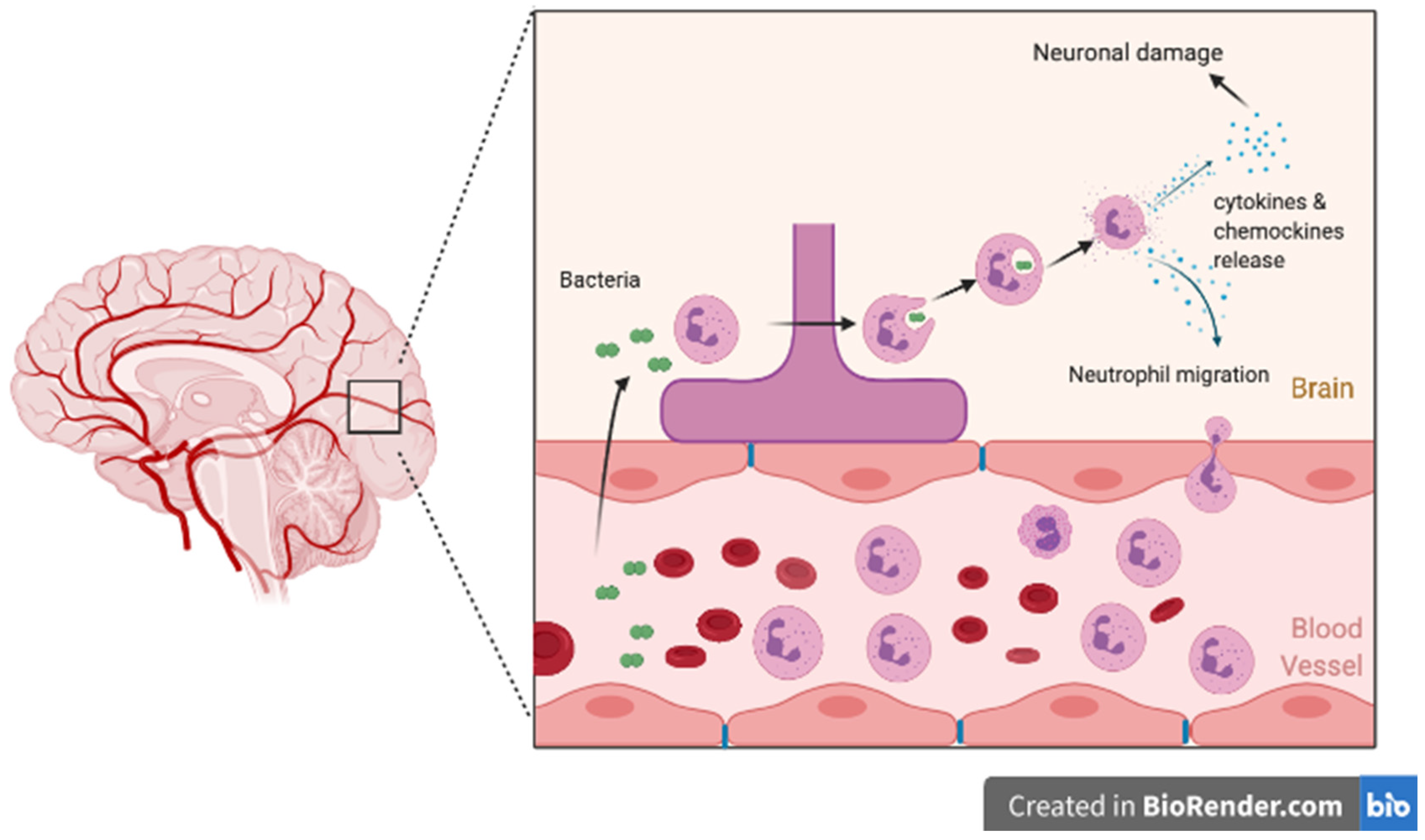














0 Response to "45 pathophysiology of meningitis diagram"
Post a Comment