38 atp to adp diagram
Difference Between ATP and NADPH ATP is mainly consists ADP and a phosphate group. There are three major components in an ATP molecule namely a ribose sugar, an adenine base and a triphosphate group. NADPH serves as an electron carrier in a number of reactions. It can be oxidized (NADP +) and reduced (NADPH). It also works as a coenzyme of various dehydrogenase enzymes. Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - HHMI BioInteractive When ATP binds to and activates BCR-ABL, it signals white blood cells to divide uncontrollably. Small-molecule cancer drugs such as Gleevec (imatinib) and dasatinib, which have structures similar to that of ATP, can bind to BCR-ABL in ATP's place and inhibit the kinase's activity. The 3D model can be viewed and rotated in the online 3D Viewer.
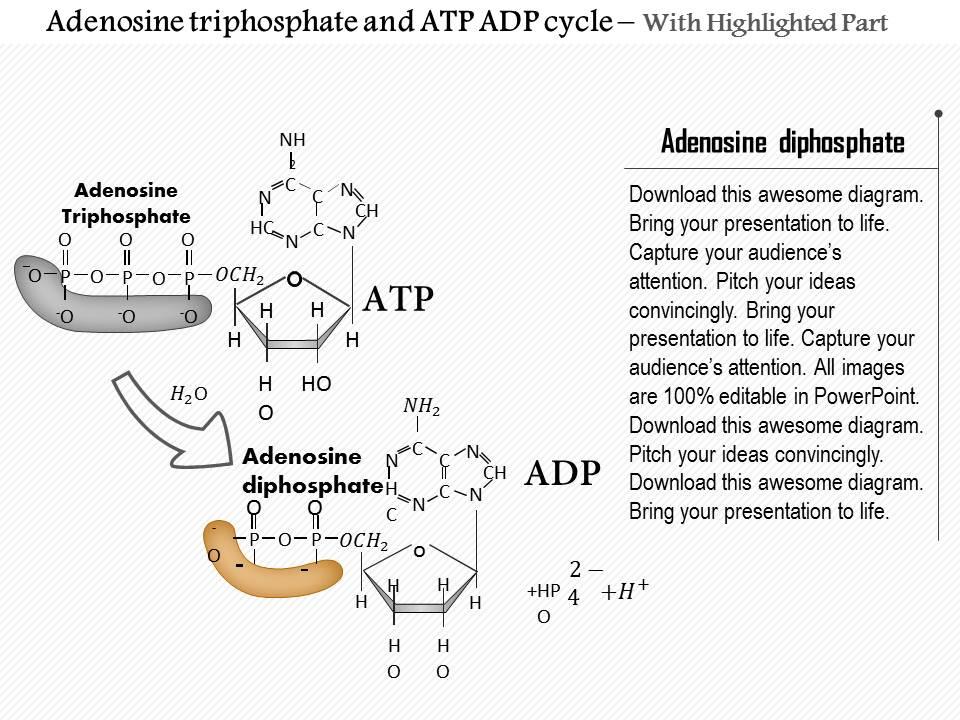
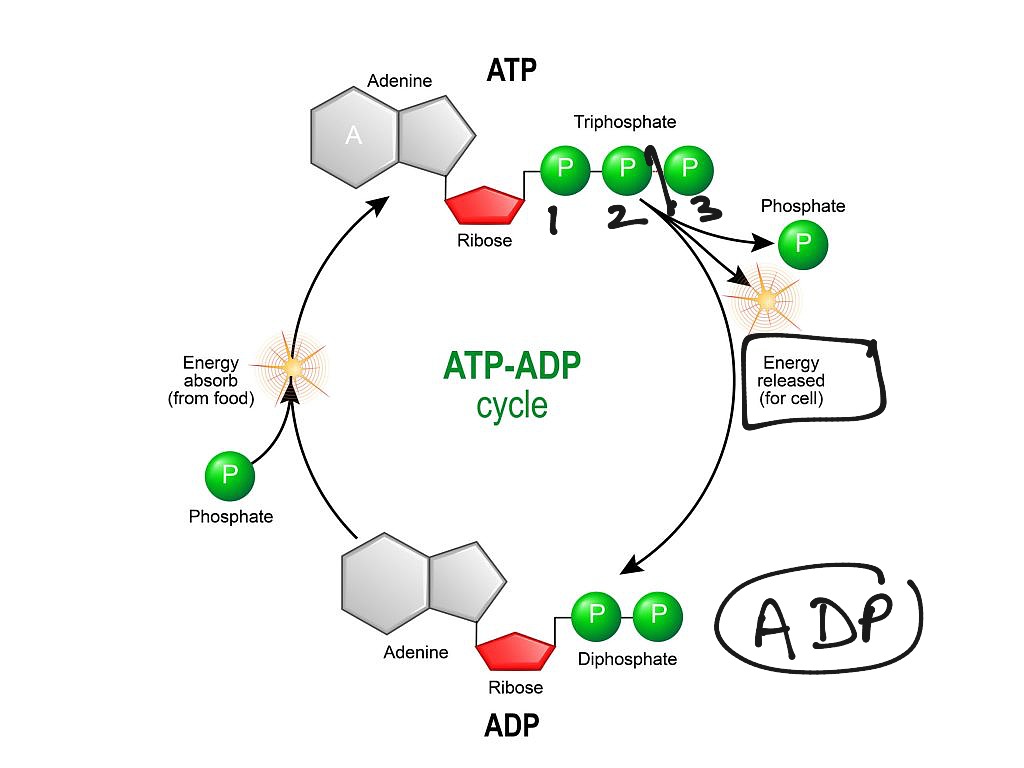
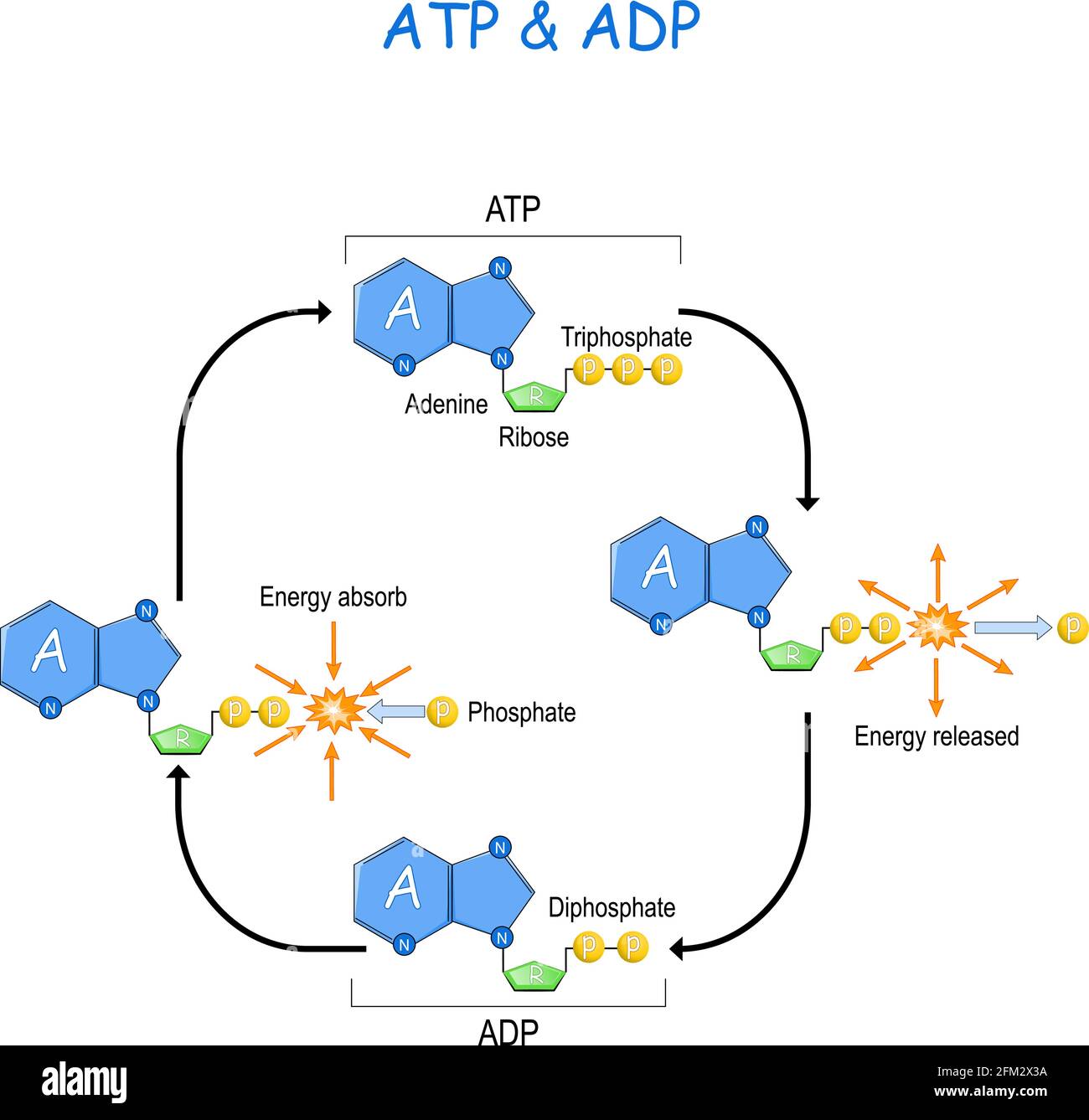
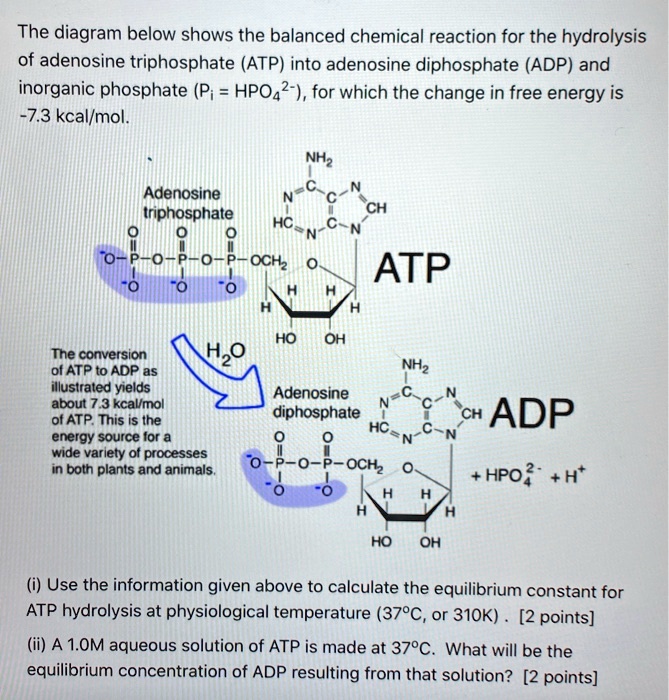
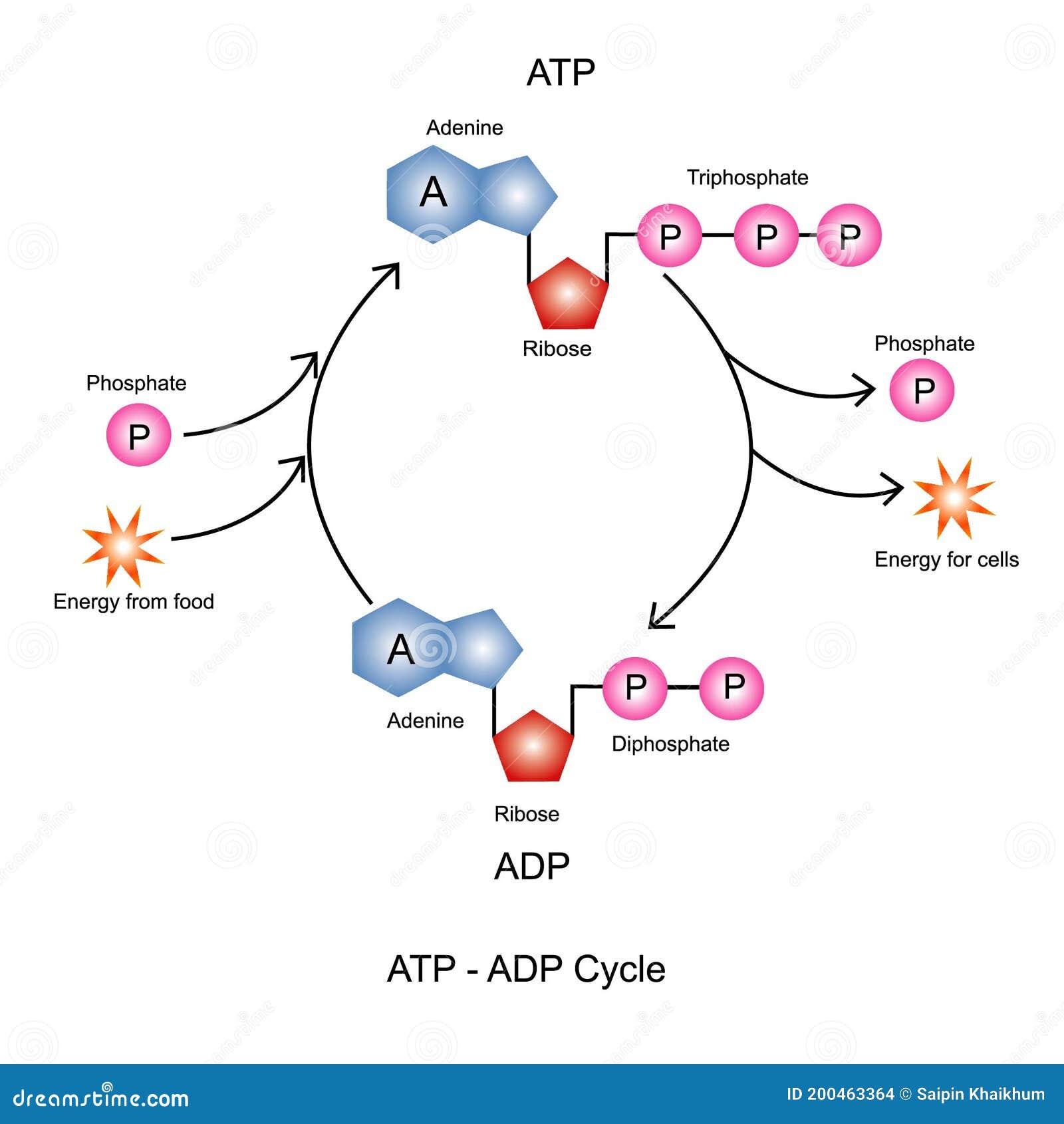
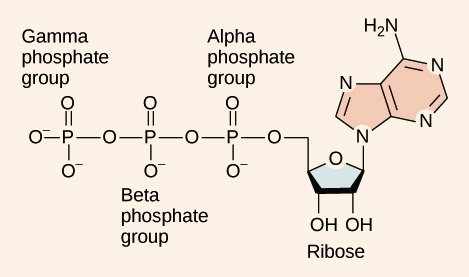
ATP and ADP Cycle diagram to label and fill the blanks.docx... It is a nucleotide consisting of a nitrogen-containing base (adenine, thymine, cytosine, or guanine), a 5-carbon sugar, and 3 phosphate groups. ATP is able to store and transport chemical energy within cells. The LAST TWO phosphate groups (PO4), are joined by HIGH-ENERGY bonds. When these bonds are broken, energy is released for cells to use

Atp to adp diagram
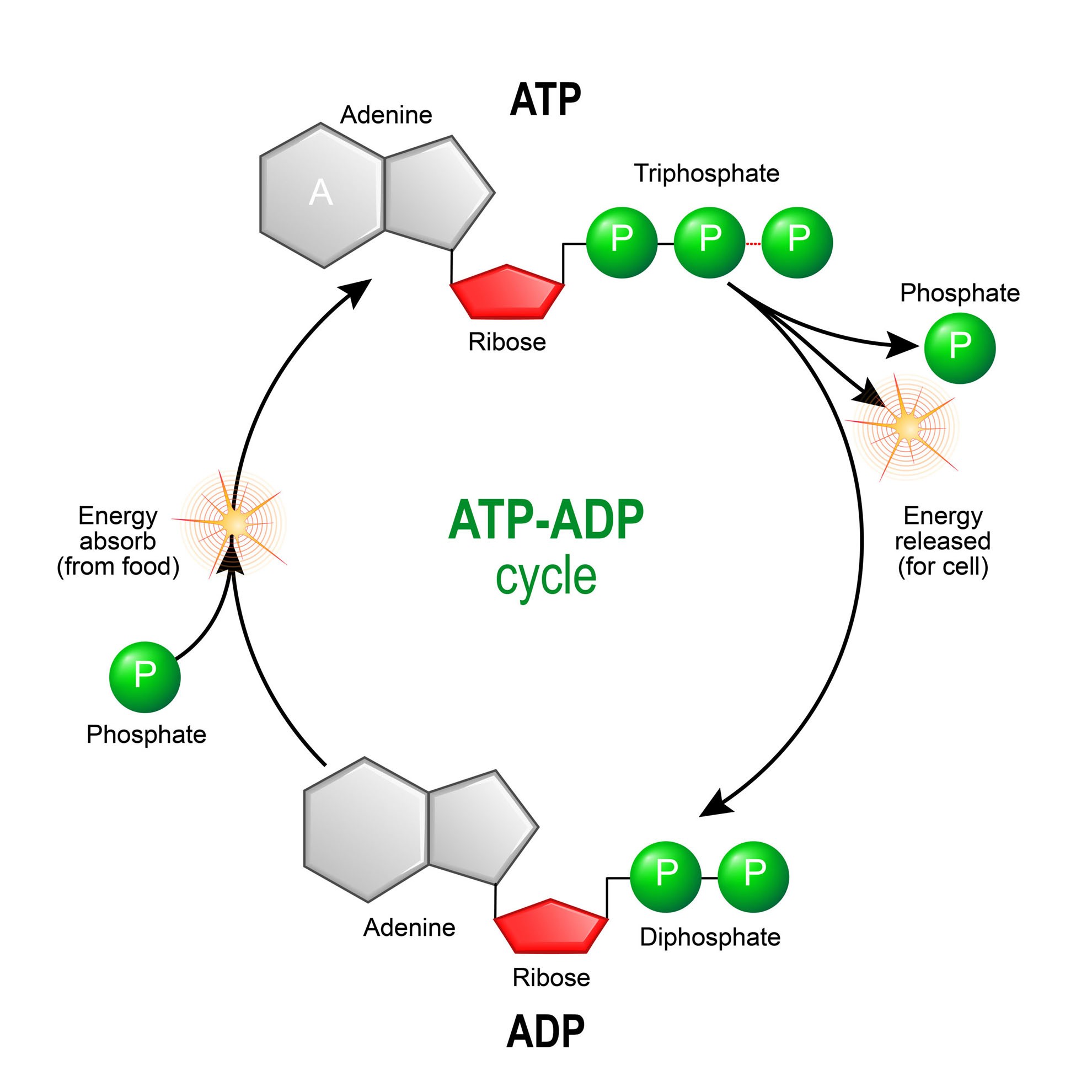
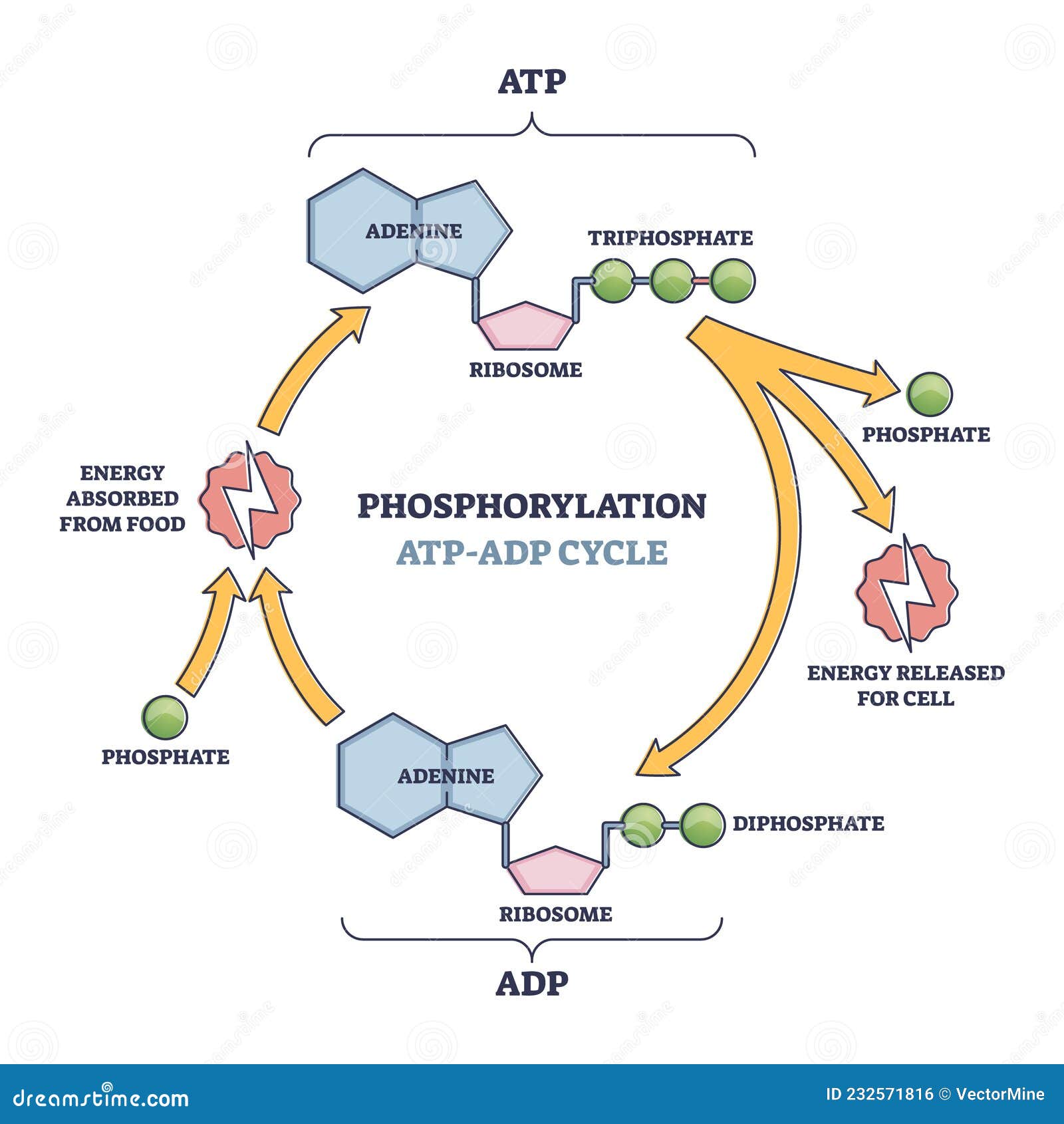
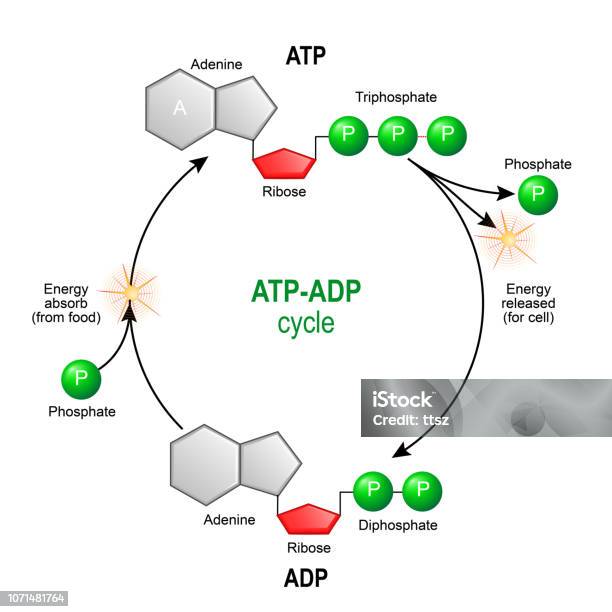
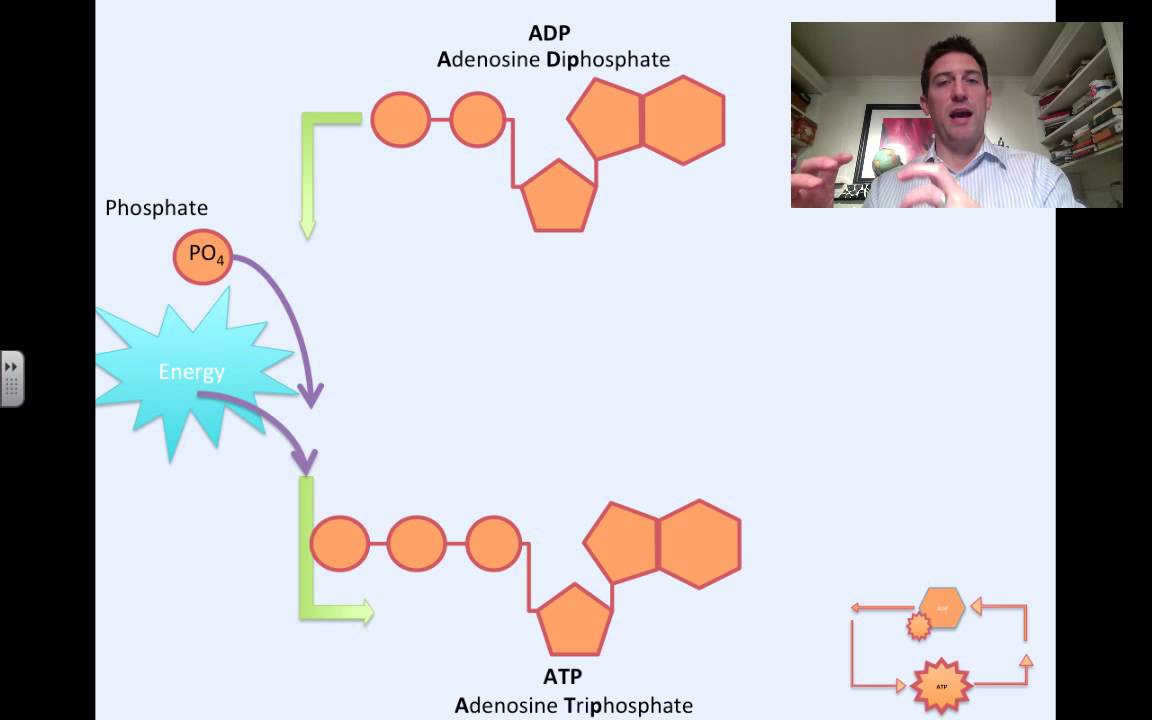
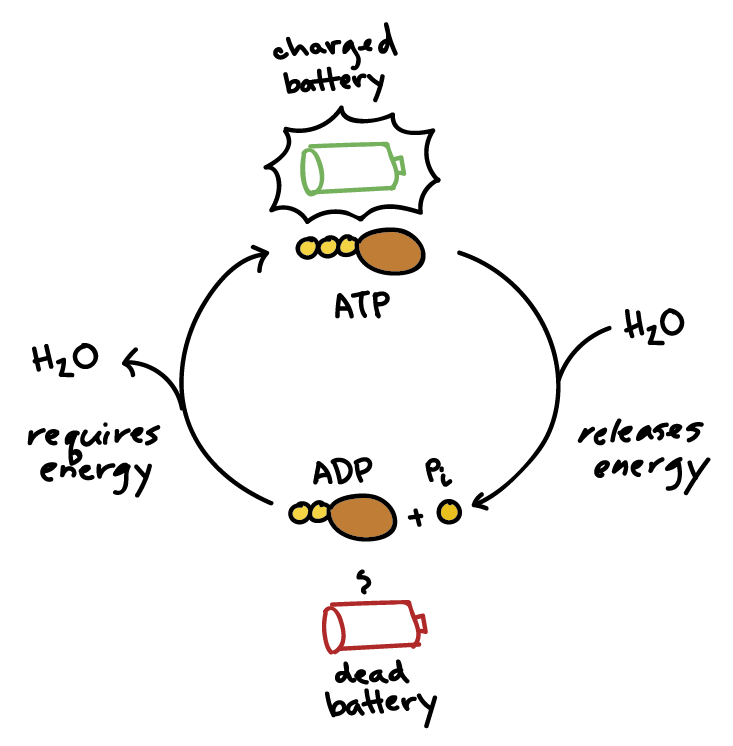
How Does ADP Become ATP? Cycle, Structure, and Function - Study.com ADP also called adenosine diphosphate, is a molecule formed in living cells. It is often converted to adenosine triphosphate (ATP), a high-energy molecule used in various biochemical reactions.... Whole blood ATP and ADP measurements on Days 1, 3, 5, and 8. ATP + ADP ... Download scientific diagram | Whole blood ATP and ADP measurements on Days 1, 3, 5, and 8. ATP + ADP concentrations are represented by solid bars with standard errors indicated. Significant ... ATP cycle and reaction coupling | Energy (article) | Khan Academy You can think of ATP and ADP as being sort of like the charged and uncharged forms of a rechargeable battery (as shown above). ATP, the charged battery, has energy that can be used to power cellular reactions. Once the energy has been used up, the uncharged battery (ADP) must be recharged before it can again be used as a power source.
Atp to adp diagram. Photosynthesis: ATP and ADP Cycle - bealsscience Below is an image of a worksheet I use in my Biology classes to help students learn the ATP Cycle to mastery. Right click the image below to download the worksheet. Fill it out as you watch the YouTube video "ATP and ADP: Chemical Energy for Cells" and explain what is happening in each step. Difference Between ATP and ADP - Biology Reader Key Differences Between ATP and ADP The molecular formula of ATP is C10H16N5O13P3. Hydrolysis causes the elimination of one hydrogen, two oxygen and one phosphate group from the ATP, and the molecular formula of ADP becomes C10H15N5O10P2. One of the common distinguishing features between ATP and ADP is the number of phosphate groups present. biologydictionary.net › atpAdenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - Definition, Structure and Function Oct 04, 2019 · Adenosine triphosphate, also known as ATP, is a molecule that carries energy within cells. It is the main energy currency of the cell, and it is an end product of the processes of photophosphorylation (adding a phosphate group to a molecule using energy from light), cellular respiration, and fermentation. All living things use ATP. › books › NBK26894National Center for Biotechnology Information National Center for Biotechnology Information
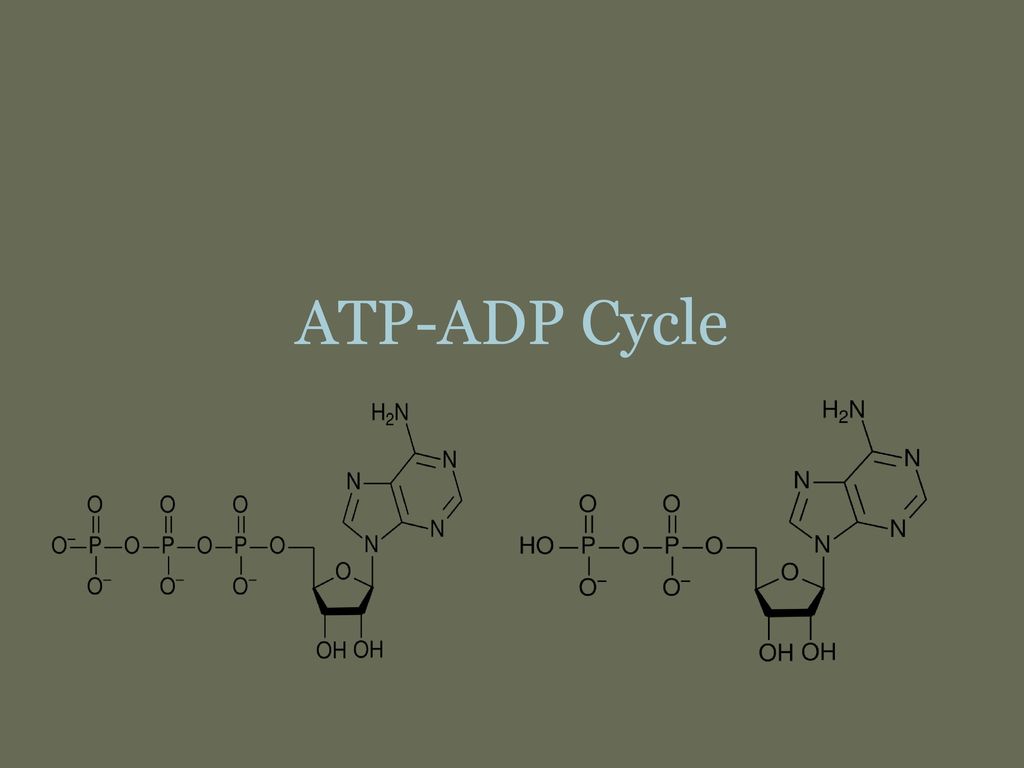
ATP/ADP - Chemistry LibreTexts Removing or adding one phosphate group interconverts ATP to ADP or ADP to AMP. Breaking one phosphoanhydride bond releases 7.3 kcal/mol of energy. (ΔG = -30.5 kJ/mol) ATP + H 2 O → ADP + P i (ΔG = -61 kJ/mol) ATP + H 2 O → AMP + 2 P i (ΔG = -61 kJ/mol) 2 ADP + H 2 O → 2 AMP + 2 P i At pH 7, ATP + 4 − H 2 O ⇌ ADP 3 − + HPO 4 2 − + H + Adenosine triphosphate - Wikipedia Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of life, ATP is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. When consumed in metabolic processes, it converts ... ATP Synthesis in Fermentation (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion ATP Synthesis in Fermentation (With Diagram) Article Shared by ADVERTISEMENTS: In fermentation, the energy conservation (ATP-synthesis) generally takes place by way of substrate-level phosphorylation and by way of decarboxylation of organic acids in certain cases. Way # 1. Substrate-level Phosphorylation and Fermentation: ATP - Energy's Ultimate Form! — PT Direct ATP is essentially the energy currency of the body. It is the breakdown of ATP that releases energy which the body's tissues such as muscle can use. An ATP molecule consists of one adenosine and three (tri) phosphate groups, as shown in the adjacent diagram. The breakdown of ATP to release the stored chemical energy within its high energy ...
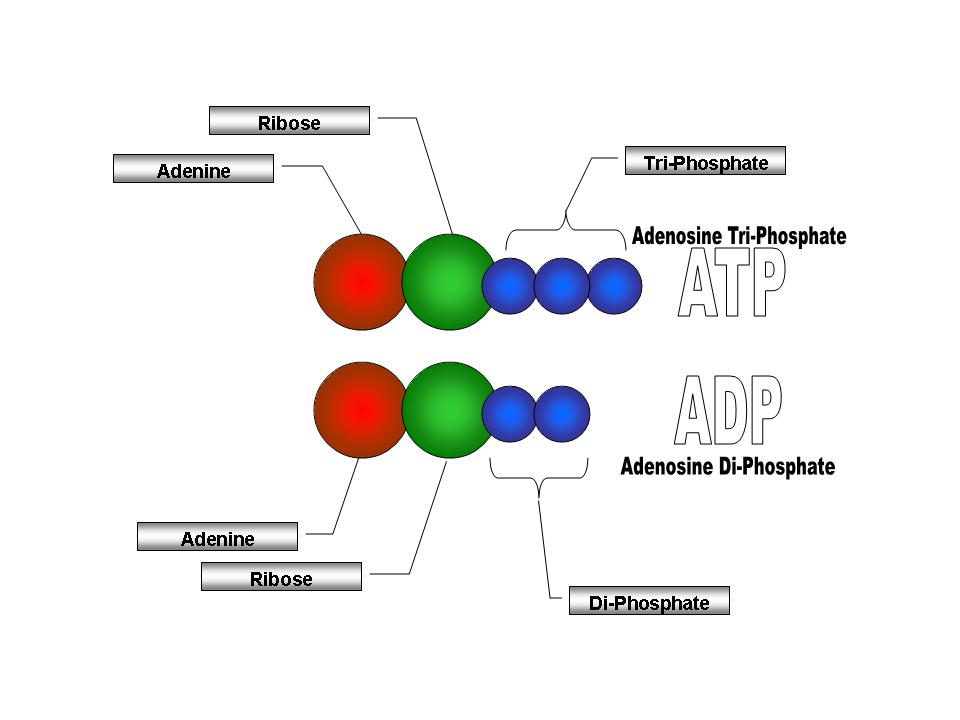
ATP | Structure, Synthesis, Hydrolysis, Functions & Summary Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a nucleotide with three phosphate groups attached. Like other nucleotides, it is made up of the following three parts; Pentose Sugar Nitrogenous base Phosphate Groups Pentose Sugar The pentose sugar in the case of ATP is ribose. It is present in the form of a five-cornered ring or pentagon called Ribofuranose. Difference Between ATP and ADP Figure 1: ATP Structure ATP molecules provide energy for all biochemical reactions in the body by ATP hydrolysis (converting into ADP). ATP hydrolysis is the reaction by which chemical energy that has been stored in the high-energy phosphoanhydride bonds in ATP is released for cellular needs. It is an exergonic reaction. ATP Cycle - YouTube This biology video tutorial discusses the ATP cycle which explains the interconversion of ATP and ADP. The conversion of ATP into ADP is an exergonic proces... Energy, Atp, And Adp | ADP RUN Explanation: ATP and ADP are macromolecules of nucleic acids as they are made up of structures similar to DNA. An ADP molecule is made up of two phosphate groups, a sugar backbone (ribose) and the nucleotide adenine.
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Calvin_cycleCalvin cycle - Wikipedia The next stage in the Calvin cycle is to regenerate RuBP. Five G3P molecules produce three RuBP molecules, using up three molecules of ATP. Since each CO 2 molecule produces two G3P molecules, three CO 2 molecules produce six G3P molecules, of which five are used to regenerate RuBP, leaving a net gain of one G3P molecule per three CO 2 molecules (as would be expected from the number of carbon ...
What is the ATP and ADP cycle? - Quora ADP ( Adenosine DiPhosphate) has the same structure as ATP, except it has two ("di") phosphate groups bound to the sugar/adenine base. AMP ( Adenosine MonoPhosphate) again has the same structure as ADP, except it has only one ("mono") phosphate group. ADP phosphorylation stores energy in high-energy phosphate bonds, and makes ATP:
How are ATP and ADP Related ? In energy and Function - Study Read Both ATP and ADP are involved in energy processes in our body. They release energy when their phosphate bond is broken. Approximately 7300 calories per mole of ATP is released from each bond and inside the body the same bond releases around 12,000 calories. When energy is needed, the ATP breaks down to ADP and releases energy.
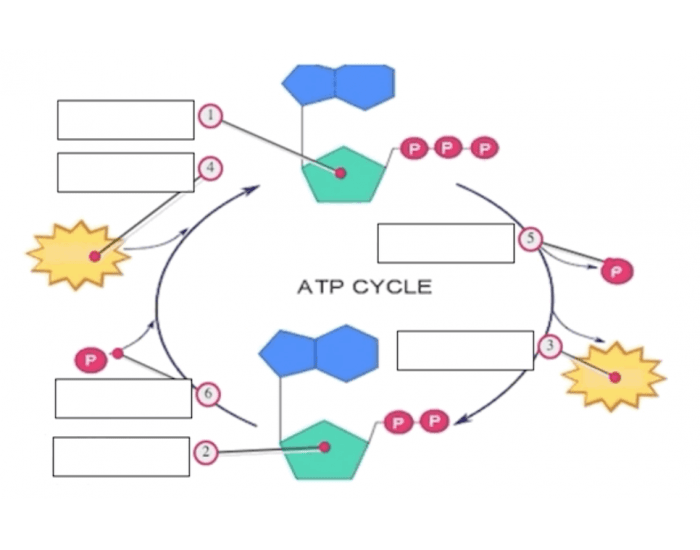
ATP to ADP Diagram | Quizlet ATP to ADP Diagram | Quizlet ATP to ADP + − Learn Test Match Created by mccauley_bayley PLUS Terms in this set (9) ATP ... ADP ... Triphosphate ... Diphosphate ... Energy Plus ... Plus Energy To Do Work ... High Energy Phosphate Bond ... Ribose ... Adenine ... A&P - Microscope + Cells 23 terms
ATP and ADP - YouTube short segment taken from "crash course biology)
ATP and ADP - Northern Arizona University When the cell has extra energy (gained from breaking down food that has been consumed or, in the case of plants, made via photosynthesis), it stores that energy by reattaching a free phosphate molecule to ADP, turning it back into ATP. The ATP molecule is just like a rechargeable battery. When it's fully charged, it's ATP.
ATP and ADP - Coggle Diagram ATP is hydrolysed into ADP, a phosphate group and energy converting between ATP and ADP ATP is unstable and not a good long term energy store Fats and carbohydrates are much better for long term energy storage Fats and carbohydrates can be broken down into the stuff needed to make ATP Phosphorylation converts ATD and a phosphate group into ATP
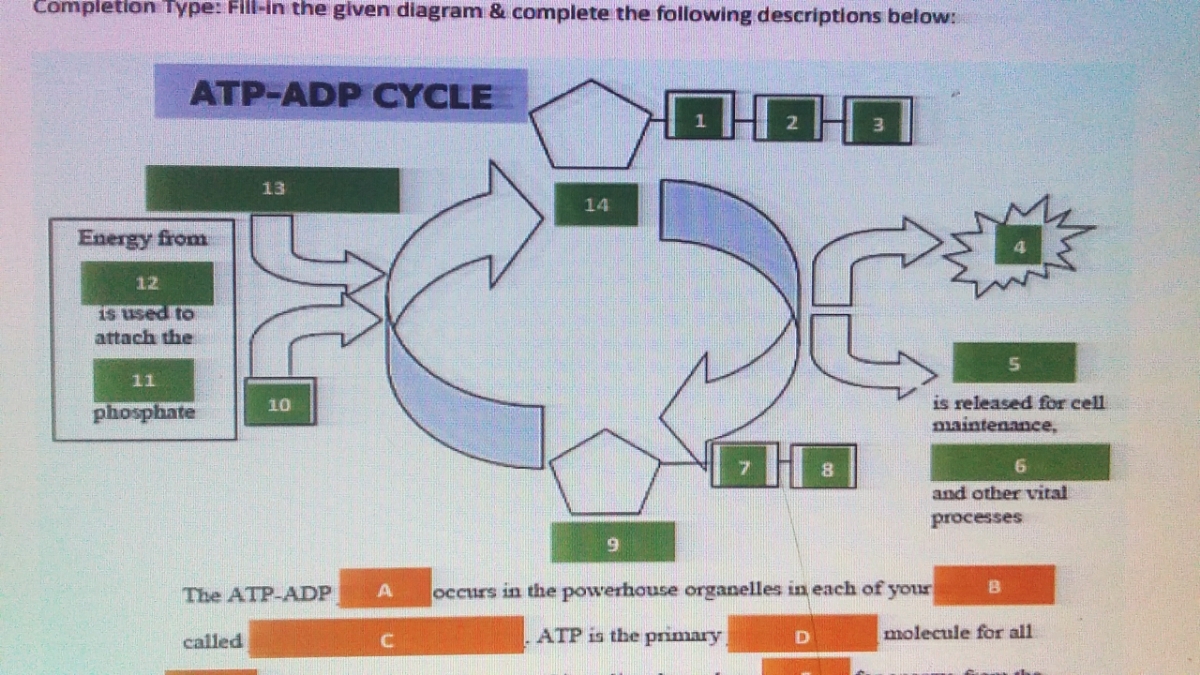
ATP / ADP Cycle Diagram | Quizlet Terms in this set (4) energy from food. carbohydrates, fats, proteins. ATP. (adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work. energy for cells. ATP. ADP. a lower-energy molecule that can be converted into ATP by the addition of a phosphate group.
ATP-ADP worksheet.docx - Name:_ Date:_ Period_ Name:_... View ATP-ADP worksheet.docx from ECO 4402 at Florida Atlantic University. Name:_ Date:_ Period_ Name:_ Date:_ Period_ Directions: Use the diagrams of the ATP-ADP cycle to answer the
ATP - powering the cell - Cellular respiration - BBC Bitesize ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is the energy-carrying molecule used in cells because it can release energy very quickly. Energy is released from ATP when the end phosphate is removed. Once ATP...
ATP and ADP: Definition, Formation, Examples I ResearchTweet ATP to ADP Energy Release. As the ATP molecule consist of 3phosphate molecule and an adenine molecule, thus when ATP is converted to ADP, a phosphate molecule is lost in this process. The reaction can be written as ATP → ADP + P i. Thus, this reaction results in energy released which is used by the cells to perform the biological process.
microbenotes.com › glycolysisGlycolysis- Definition, Equation, Enzymes, 10 Steps, Diagram Feb 05, 2022 · This step is the ATP-generating step of glycolysis. It involves the transfer of phosphate group from the 1, 3-bisphosphoglycerate to ADP by the enzyme phosphoglycerate kinase, thus producing ATP and 3-phosphoglycerate. Since two moles of 1, 3-bisphosphoglycerate are formed from one mole of glucose, two ATPs are generated in this step.
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Metabolic_pathwayMetabolic pathway - Wikipedia Catabolic pathway (catabolism) A catabolic pathway is a series of reactions that bring about a net release of energy in the form of a high energy phosphate bond formed with the energy carriers adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and guanosine diphosphate (GDP) to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and guanosine triphosphate (GTP), respectively.
› biology › sliding-filament-theorySliding Filament Theory – Definition, Diagram and Important FAQs Because it is coupled to ADP, the myosin head can create cross-bridges by binding to actin. As ADP detaches from the myosin head, the myosin heads spin toward the sarcomeres, resulting in the power stroke motion. The myosin head will remain in this position, linked to actin until another ATP molecule comes along and binds to the myosin head.
microbiologyinfo.com › glycolysis-10-stepsGlycolysis Explained in 10 Easy Steps - Microbiology Info.com Aug 10, 2022 · The phosphate group attached to the 2′ carbon of the PEP is transferred to a molecule of ADP, yielding ATP. Again, since there are two molecules of PEP, here we actually generate 2 ATP molecules. Steps 1 and 3 = – 2ATP Steps 7 and 10 = + 4 ATP Net “visible” ATP produced = 2.
ATP cycle and reaction coupling | Energy (article) | Khan Academy You can think of ATP and ADP as being sort of like the charged and uncharged forms of a rechargeable battery (as shown above). ATP, the charged battery, has energy that can be used to power cellular reactions. Once the energy has been used up, the uncharged battery (ADP) must be recharged before it can again be used as a power source.
Whole blood ATP and ADP measurements on Days 1, 3, 5, and 8. ATP + ADP ... Download scientific diagram | Whole blood ATP and ADP measurements on Days 1, 3, 5, and 8. ATP + ADP concentrations are represented by solid bars with standard errors indicated. Significant ...
How Does ADP Become ATP? Cycle, Structure, and Function - Study.com ADP also called adenosine diphosphate, is a molecule formed in living cells. It is often converted to adenosine triphosphate (ATP), a high-energy molecule used in various biochemical reactions....















![BIOCHEMISTRY MODULE] ATP-ADP Cycle in Respiration ...](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/5f02d28f35d64d2a5022eeb1/1599614605734-CO28DTSZG1P7WLPF5P6T/ATP-ADP-Cycle.png)

0 Response to "38 atp to adp diagram"
Post a Comment