45 the diagram below shows a diploid cell with two homologous pairs of chromosomes
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › GenomeGenome - Wikipedia A typical human cell has two copies of each of 22 autosomes, one inherited from each parent, plus two sex chromosomes, making it diploid. Gametes , such as ova, sperm, spores, and pollen, are haploid, meaning they carry only one copy of each chromosome. › nature › articlesBrowse Articles | Nature Nov 21, 2022 · A theory shows that active agents can cooperate in the presence of disorder — a result that could inform the design of robots that organize on rough surfaces, or show how cells migrate en masse.
Mastering Biology CH 13 homework Flashcards | Quizlet -Homologous pairs of chromosomes line up on the metaphase plate. Both mitosis and meiosis:-Process starts with a diploid cell.-Chromosomes duplicate during interphase. The following statements discuss events associated with meiosis. Determine which statements are true and which are false. Drag "True" or "False" to the end of each statement-The second …
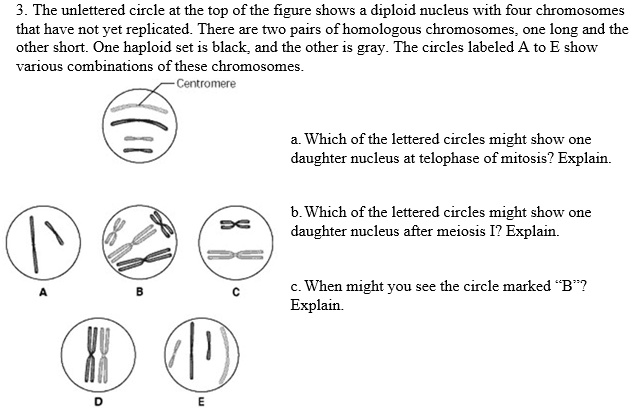
The diagram below shows a diploid cell with two homologous pairs of chromosomes
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › ChromosomeChromosome - Wikipedia The tables below give the total number of chromosomes (including sex chromosomes) in a cell nucleus. For example, most eukaryotes are diploid, like humans who have 22 different types of autosomes, each present as two homologous pairs, and two sex chromosomes. This gives 46 chromosomes in total. quizlet.com › 538109022 › mastering-biology-ch-13Mastering Biology CH 13 homework Flashcards | Quizlet -End result is two diploid cells that are genetically identical to each other and the parent cell.-A single division occurs, separating sister chromatids.-Duplicated chromosomes line up individually on the metaphase plate in a diploid cell. Meiosis:-Homologous chromosomes pair up and form chiasmata. scioly.org › wiki › indexCell Biology - Wiki - Scioly.org Oct 11, 2022 · Meiosis, divided into two stages, divides one diploid (2n) cell into 4 haploid (n) daughter cells. It occurs in cells of gonads to produce gametes (part of process of sexual reproduction). Meiosis I. Prophase I - Each chromosome pairs with its homolog. Crossover (synapsis) occurs in this phase.
The diagram below shows a diploid cell with two homologous pairs of chromosomes. Molecular Biology and Genetics – Explorations - University of … As a result, they have 23 matching pairs of chromosomes, which are known as homologous chromosomes. These homologous pairs vary in size and are generally numbered from largest (chromosome 1) to smallest (chromosome 22), as seen in Figure 3.15, with the exception of the 23rd pair, which is made up of the sex chromosomes (X and Y). Typically, the female sex is … Expert Answers to All Your Homework Questions | bartleby For each blood type in the table below, fill in the expected agglutination result from mixing the… A: To determine: To determine the agglutination result for the given each blood type Agglutination: In… Q: Instructions There are four parts to this problem. Use Excel to perform the following. a. Use the… A: using the same formula for EOQ as instructed. a. Q: You will need to extract the ... Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome | Nature 15/02/2001 · The human genome holds an extraordinary trove of information about human development, physiology, medicine and evolution. Here we report the results of an international collaboration to produce ... ch 8 mastering biology Flashcards | Quizlet Meiosis starts with a single diploid cell and produces. four haploid cells. Part B A cell preparing to undergo meiosis duplicates its chromosomes during. interphase. Part C During prophase I of meiosis, homologous chromosomes stick together in pairs. Part D The correct order of events during meiosis is. prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, telophase I, cytokinesis, meiosis II. …
quizlet.com › 536545944 › biology-chapter-14-flash-cardsBiology Chapter 14 Flashcards | Quizlet Diploid cells have two sets of chromosomes, one set inherited from each parent, that form homologous pairs. The homologs of a chromosome pair contain the same genetic loci. Therefore, each genetic locus is represented twice in a diploid cell. Variations in inherited characteristics is due to the presence of , which are alternative versions of ... en.wikipedia.org › wiki › MeiosisMeiosis - Wikipedia Meiosis I segregates homologous chromosomes, which are joined as tetrads (2n, 4c), producing two haploid cells (n chromosomes, 23 in humans) which each contain chromatid pairs (1n, 2c). Because the ploidy is reduced from diploid to haploid, meiosis I is referred to as a reductional division . Cell division: mitosis and meiosis | Biological Principles The cell cycle diagram on the left shows that a cell division cycle consists of 4 stages: ... A diploid cell starts with 2N chromosomes and 2X DNA content. After DNA replication, the cells is still genetically diploid (2N chromosome number), but has 4X DNA content because each chromosome has replicated its DNA. Each chromosome now consists of a joined pair of … Genome - Wikipedia Most eukaryotes are diploid, meaning that there are two copies of each chromosome in the nucleus but the 'genome' refers to only one copy of each chromosome. Some eukaryotes have distinctive sex chromosomes such as the X and Y chromosomes of mammals so the technical definition of the genome must include both copies of the sex chromosomes. When referring …
Chromosome - Wikipedia The tables below give the total number of chromosomes (including sex chromosomes) in a cell nucleus. For example, most eukaryotes are diploid, like humans who have 22 different types of autosomes, each present as two homologous pairs, and two sex chromosomes. This gives 46 chromosomes in total. Other organisms have more than two copies of their chromosome … Chromosome evolution and the genetic basis of agronomically 14/04/2022 · The nutrient-rich tubers of the greater yam, Dioscorea alata L., provide food and income security for millions of people around the world. Despite its global importance, however, greater yam ... Meiosis - Wikipedia Meiosis I segregates homologous chromosomes, which are joined as tetrads (2n, 4c), producing two haploid cells (n chromosomes, 23 in humans) which each contain chromatid pairs (1n, 2c). Because the ploidy is reduced from diploid to haploid, meiosis I is referred to as a reductional division . scioly.org › wiki › indexCell Biology - Wiki - Scioly.org Oct 11, 2022 · Meiosis, divided into two stages, divides one diploid (2n) cell into 4 haploid (n) daughter cells. It occurs in cells of gonads to produce gametes (part of process of sexual reproduction). Meiosis I. Prophase I - Each chromosome pairs with its homolog. Crossover (synapsis) occurs in this phase.
quizlet.com › 538109022 › mastering-biology-ch-13Mastering Biology CH 13 homework Flashcards | Quizlet -End result is two diploid cells that are genetically identical to each other and the parent cell.-A single division occurs, separating sister chromatids.-Duplicated chromosomes line up individually on the metaphase plate in a diploid cell. Meiosis:-Homologous chromosomes pair up and form chiasmata.
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › ChromosomeChromosome - Wikipedia The tables below give the total number of chromosomes (including sex chromosomes) in a cell nucleus. For example, most eukaryotes are diploid, like humans who have 22 different types of autosomes, each present as two homologous pairs, and two sex chromosomes. This gives 46 chromosomes in total.
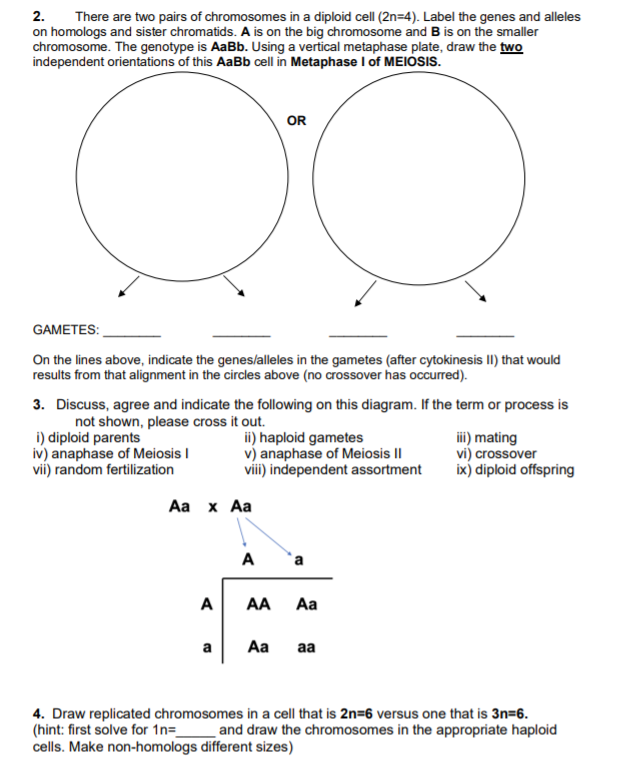

0 Response to "45 the diagram below shows a diploid cell with two homologous pairs of chromosomes"
Post a Comment