41 curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's
Pure Competition A. Competition is efficient. 1. Price settles where long-run ATC is at its lowest point indicating goods are produced efficiently. 2. P = MR = MC indicating that resources are allocated efficiently as $'s spent by consumers (P) = the $'s received by producers (MR) = the $ cost of producers (MC) and economic profit is zero. B. Shortcomings 1. ECON Pure Competition 1 Short run Flashcards | Quizlet The accompanying table gives cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market. If the market price for this firm's product is $87, it will produce Multiple Choice 8 units at an economic profit of $130.72. 6 units at a loss of $90. 9 units at an economic profit of zero. 9 units at an economic profit of $281.97.
Consider the monopolistically competitive firm represented in the graph Quiz 9 Monopolistic Competition, ch.12 Microeconomics 1. Explain what kind of market is considered monopolistically competitive . 2. Give 3 examples of monopolistically comp read more. JOANNE, Given a demand curve and a cost structure for a monopolistically competitive firm , determine the profit-maximizing level of output and price and calculate profits.
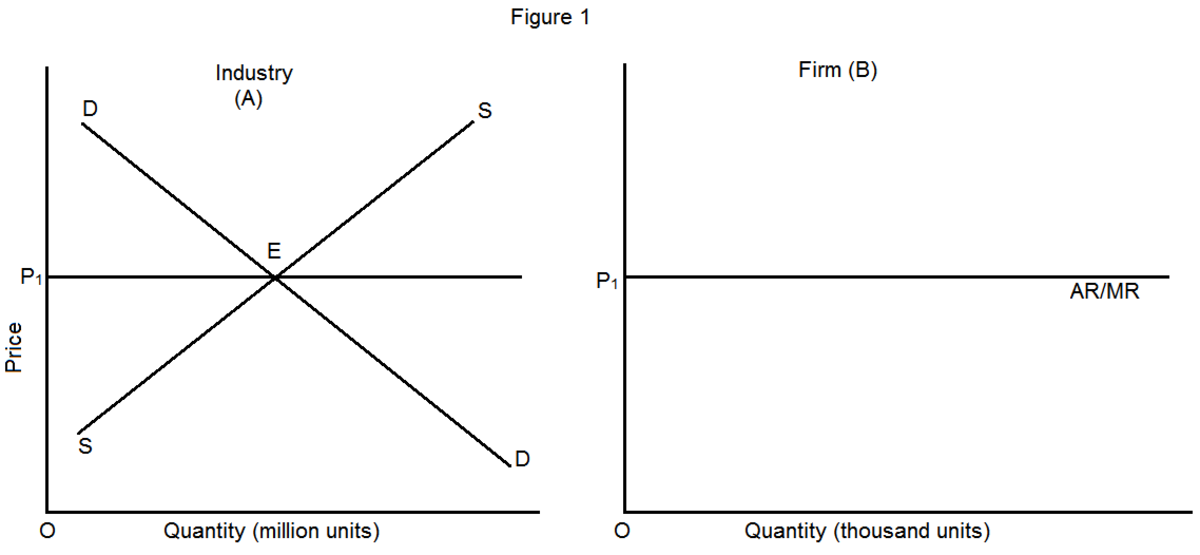
Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's
Curve 2 in the above diagram is a purely competitive - Course Hero Curve 2 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms A total cost curve B Curve 2 in the above diagram is a purely competitive School University of Sharjah Course Title ECON 302 Type Notes Uploaded By mithraism Pages 56 Ratings 95% (42) This preview shows page 13 - 16 out of 56 pages. View full document See Page 1 38. Curve 2 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms A total cost ... Curve 2 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms A total cost curve C Curve 2 in the above diagram is a purely competitive School Johnson County Community College Course Title ECON 230 Type Notes Uploaded By kaigefighter08 Pages 45 Ratings 94% (50) This preview shows page 10 - 12 out of 45 pages. View full document See Page 1 44. Exam 3 Assignments/Quizzes/In-Class (Chapters 11 - 14) Show what happens in the short run on both graphs when a new medical study shows soy beans to be an effective weight-loss supplement. On the market graph, shift a curve (or curves). On the firm's graph, use "Price 2" to draw a new price line for the firm. On both graphs, indicate the new equilibrium points with the points labeled B.
Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's. Chapter 10 Homework Flashcards | Quizlet The lowest point on a purely competitive firm's short-run supply curve corresponds to: the minimum point on its AVC curve. In the short run, a purely competitive seller will shut down if product price: ... Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's: marginal revenue curve. A purely competitive seller should produce (rather than ... (PDF) MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS Study material COMPLEMENTARY ... 2 Full PDFs related to this paper. Read Paper. Download Download PDF. Download Full PDF Package. Translate PDF ... Solved Dollar (1) 0 Quantity 5 Curve (2) in the diagram is a - Chegg Question: Dollar (1) 0 Quantity 5 Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's Multiple Choice total cost curve. total economic profit curve. marginal revenue curve. total revenue curve. This problem has been solved! You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. See Answer question 31 PPIC Statewide Survey: Californians and Their Government Oct 27, 2022 · Key findings include: Proposition 30 on reducing greenhouse gas emissions has lost ground in the past month, with support among likely voters now falling short of a majority. Democrats hold an overall edge across the state's competitive districts; the outcomes could determine which party controls the US House of Representatives. Four in ten likely voters are satisfied with how democracy is ...
Consider a monopolistically competitive market with n firms Subject: Marketing Price: 4.88 Bought 16. Share With. Consider a monopolistically competitive market with N firms . Each firm's business opportunities are described by the following equations: Demand: Q = 100/ N - P. Marginal Revenue: MR = 100/ N - 2Q. Total Cost: TC = 50 + Q2Q2. Short Run Supply Curve of a Competitive Firm and Industry (With Diagram) The supply curve shows the maximum quantities per unit of time which sellers will place in the market at various prices. At a higher price, a greater quantity will be supplied and, at a lower price, a smaller quantity will be supplied. Recall that the supply of a commodity is a derived function. It is derived from the cost function. In a monopolistically competitive market firms produce Monopolistic Competition: Characterizes an industry in which many firms offer products or services that are similar, but not perfect substitutes. Barriers to entry and exit in the industry are low. 6. The important difference between the characteristics of perfectly competitive and monopolistically competitive markets is that firms in monopolistically competitive industries: A. have a downward ... Labour economics - Wikipedia A firm's labour demand in the short run (D) and a horizontal supply curve (S) The marginal revenue product of labour can be used as the demand for labour curve for this firm in the short run. In competitive markets , a firm faces a perfectly elastic supply of labour which corresponds with the wage rate and the marginal resource cost of labour ...
Econ Unit 3 Flashcards | Quizlet In this case, the firm's fixed cost is $44,000 per day. In other words, if it shuts down, the firm would suffer losses of $44,000 per day until its fixed costs end (such as the expiration of a building lease). This firm's shutdown price—that is, the price below which it is optimal for the firm to shut down—is $10.00 per air freshener. Solved Question 14 I (3) Dollars - (2) Quantity Curve (3) in - Chegg Question: Question 14 I (3) Dollars - (2) Quantity Curve (3) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's total economic profit curve total revenue curve marginal revenue curve total cost curve This problem has been solved! See the answer Show transcribed image text Expert Answer 100% (5 ratings) Curve 3 is the total revenue curve. In a monopolistically competitive market firms produce A monopolistically competitive firm chooses the quantity to produce where marginal revenue equals marginal cost A profit-maximizing firm in a monopolistically competitive market is characterized by which of the following? price exceeds marginal cost The firm has total fixed costs of $20 and a constant marginal cost of $18 per unit. 7 Firms and markets for goods and services - CORE The firm’s unit cost of production is €60. Based on this information, which of the following are correct? At Q = 100, the firm’s profit is €20,000. The profit-maximizing output is Q = 400. The maximum profit that can be attained is €50,000. The firm will make a loss at all outputs above 800. At Q = 100, profit = (270 − 60) × 100 ...
7. The firm and its customers – The Economy - CORE If a firm’s technology exhibits economies of scale, costs per unit will fall as the firm expands its production. If a firm’s technology exhibits diseconomies of scale, doubling the inputs leads to less than doubling of the output level. With constant returns, increasing the inputs leads to the same proportional increase in output.
Exam 3 Assignments/Quizzes/In-Class (Chapters 11 - 14) Show what happens in the short run on both graphs when a new medical study shows soy beans to be an effective weight-loss supplement. On the market graph, shift a curve (or curves). On the firm's graph, use "Price 2" to draw a new price line for the firm. On both graphs, indicate the new equilibrium points with the points labeled B.
Curve 2 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms A total cost ... Curve 2 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms A total cost curve C Curve 2 in the above diagram is a purely competitive School Johnson County Community College Course Title ECON 230 Type Notes Uploaded By kaigefighter08 Pages 45 Ratings 94% (50) This preview shows page 10 - 12 out of 45 pages. View full document See Page 1 44.
Curve 2 in the above diagram is a purely competitive - Course Hero Curve 2 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms A total cost curve B Curve 2 in the above diagram is a purely competitive School University of Sharjah Course Title ECON 302 Type Notes Uploaded By mithraism Pages 56 Ratings 95% (42) This preview shows page 13 - 16 out of 56 pages. View full document See Page 1 38.
0 Response to "41 curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's"
Post a Comment