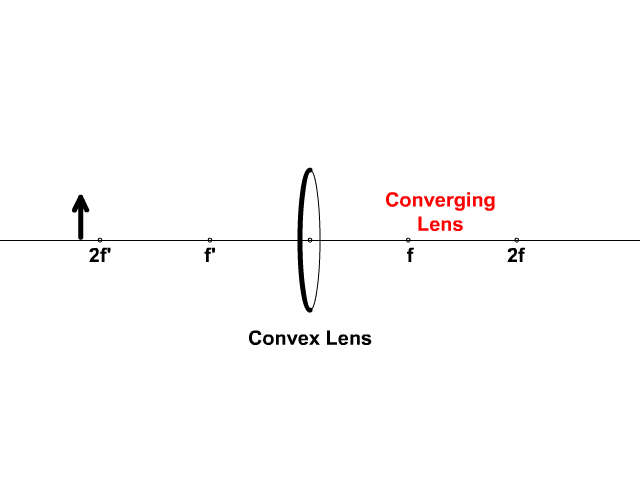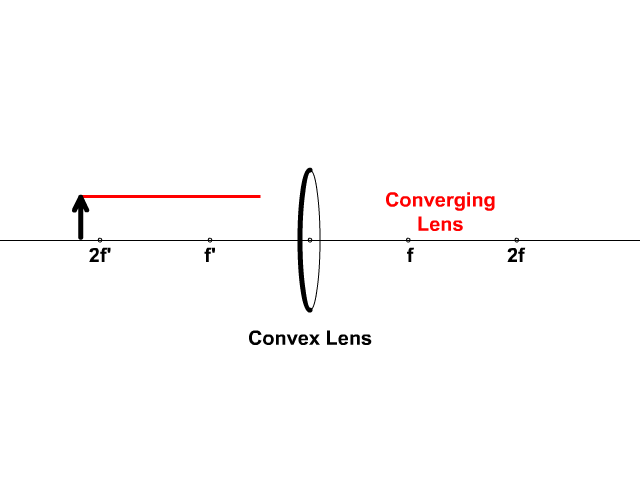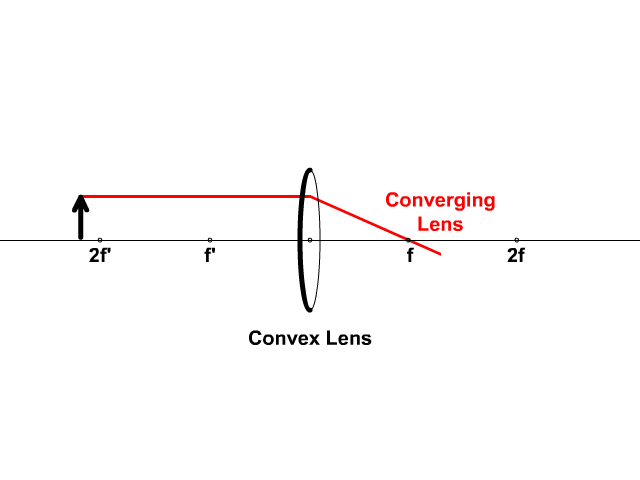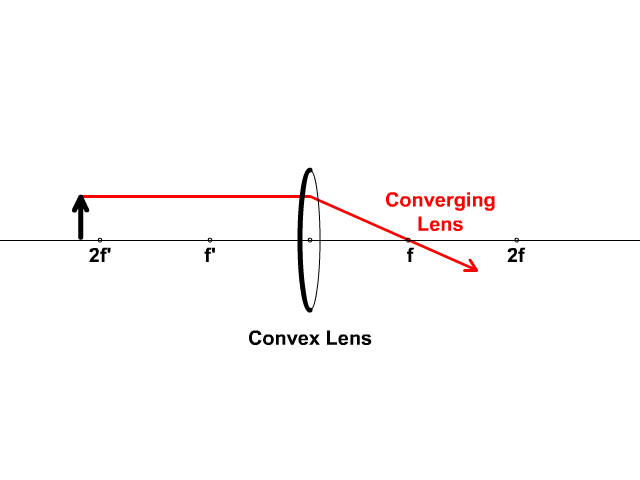
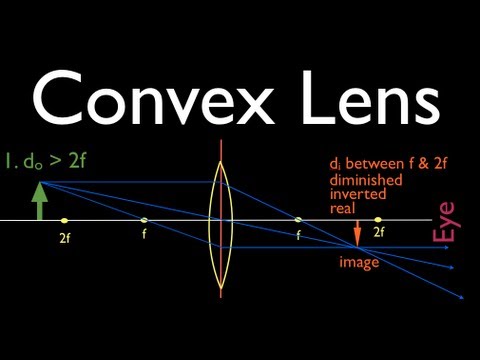
41 biconvex lens ray diagram
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Lenticular_lensLenticular lens - Wikipedia A lenticular lens is an array of lenses, designed so that when viewed from slightly different angles, different parts of the image underneath are shown. [failed verification – see discussion] The most common example is the lenses used in lenticular printing, where the technology is used to give an illusion of depth, or to make images that appear to change or move as the image is viewed from ... › natural-sciences › gr8Natural Sciences Grade 8 Ray diagrams. A ray diagram is a drawing that shows the path of light. Light rays are drawn using straight lines and arrowheads, because light travels in straight lines. The figure below shows some examples of ray diagrams. A ray diagram showing how you see another person. A ray diagram showing how you see a reflection in a mirror.
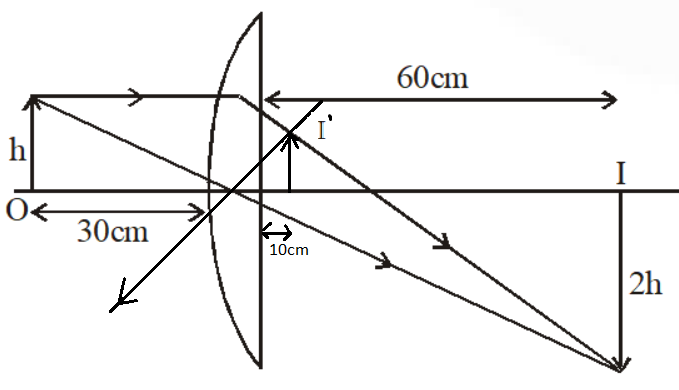
› important-questions-for-classImportant Questions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 9 Ray Optics ... Dec 06, 2019 · A convex lens of focal length 20 cm is placed coaxially with a convex mirror of radius of curvature 20 cm. The two are kept at 15 cm from each other. A point object lies 60 cm in front of the convex lens. Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image by the combination. Determine the nature and position of the image formed. Answer:
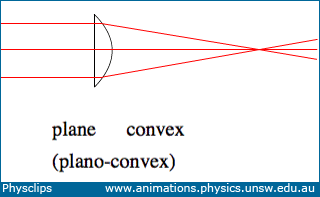
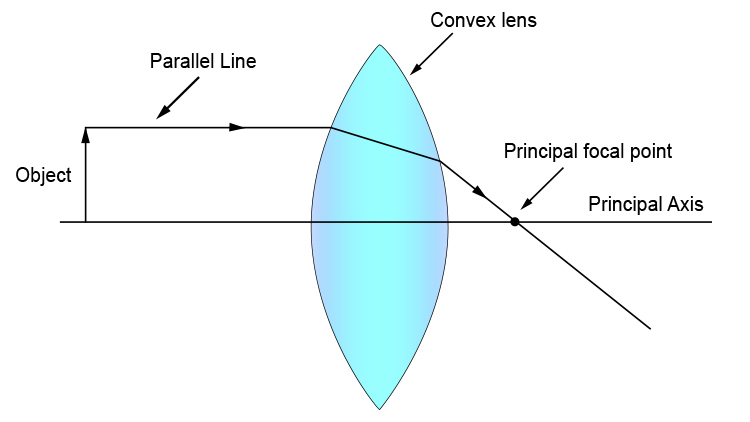
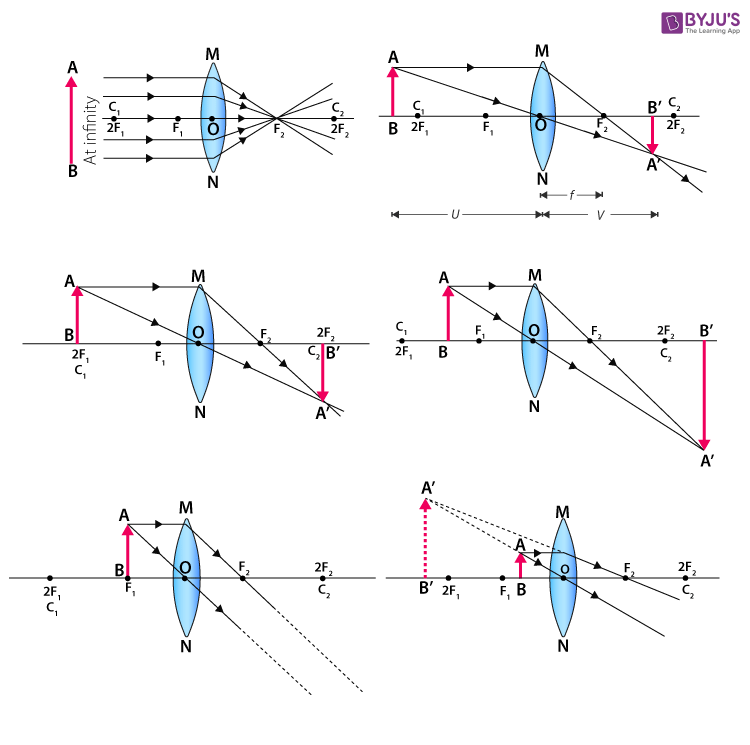
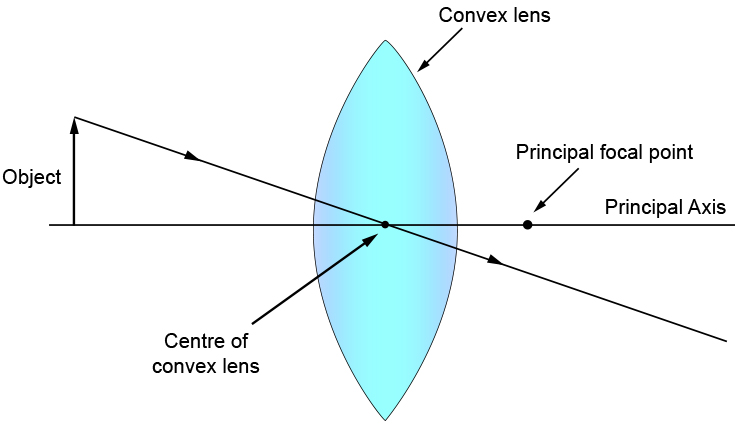
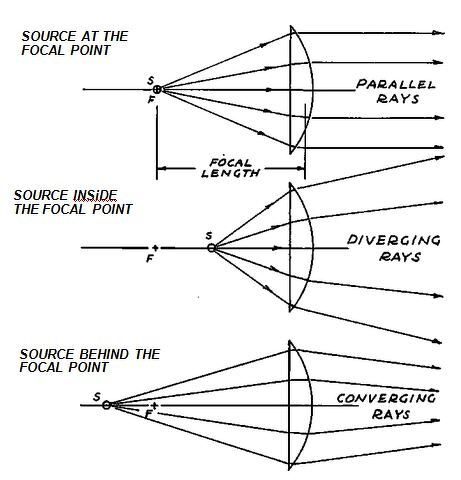
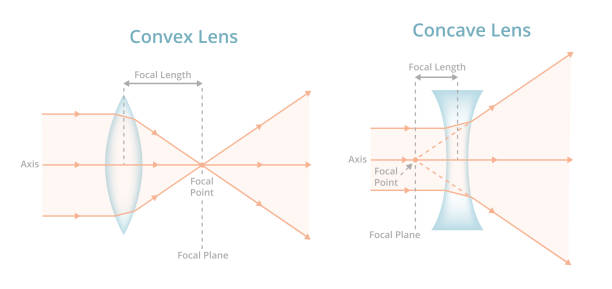
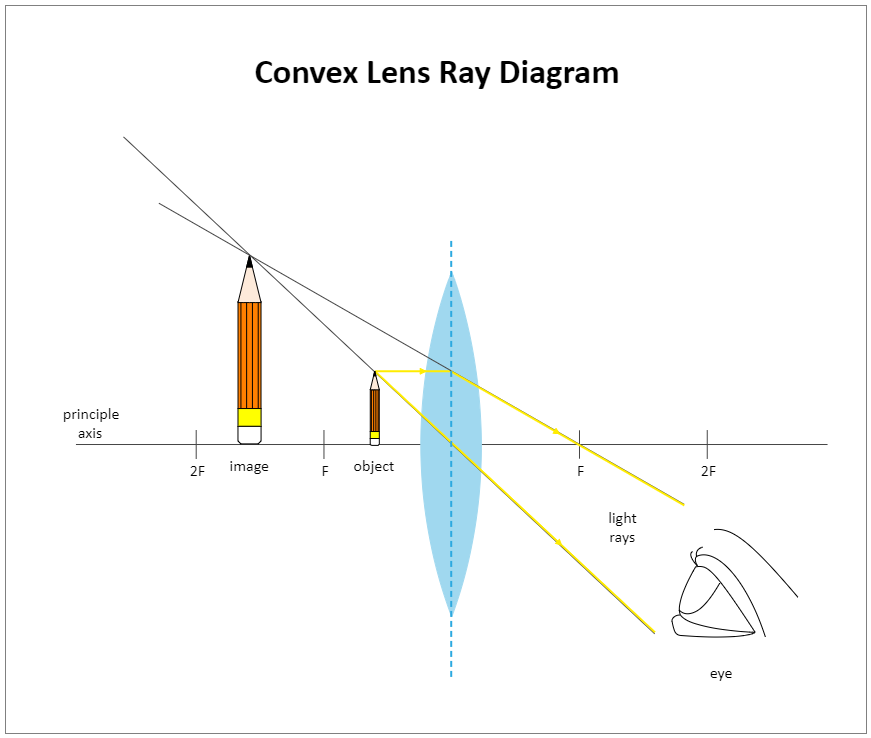
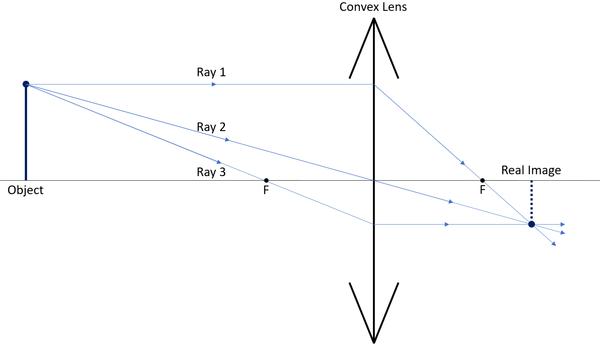
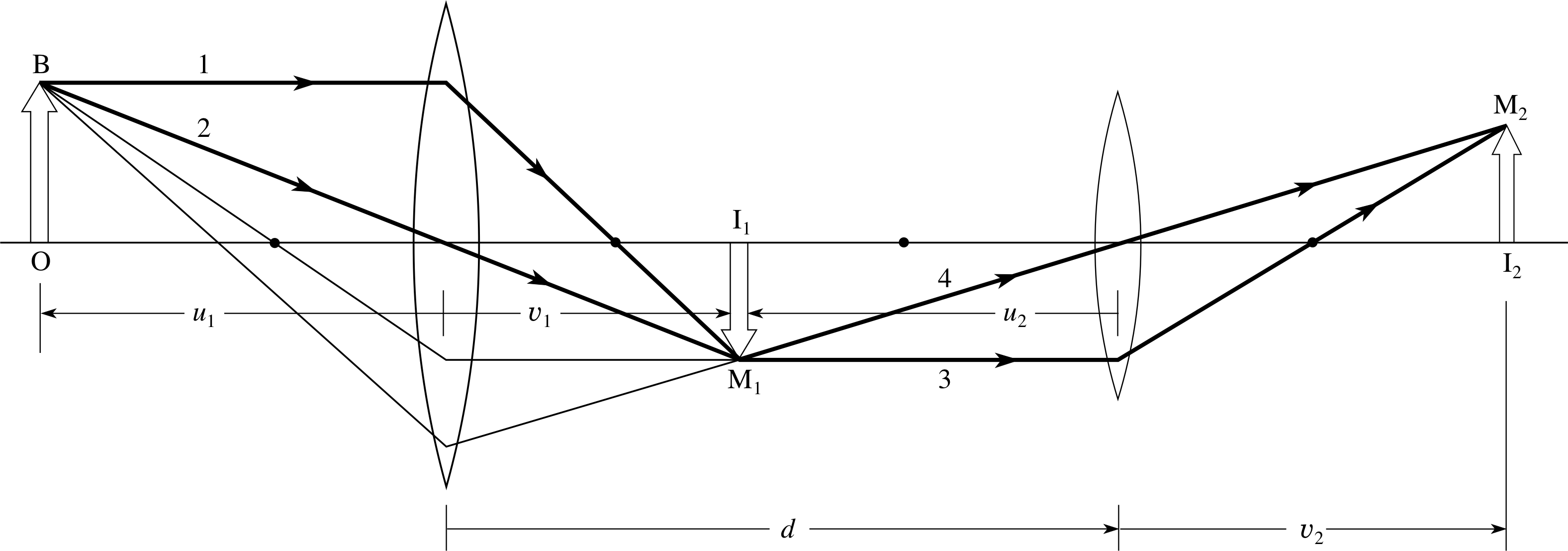
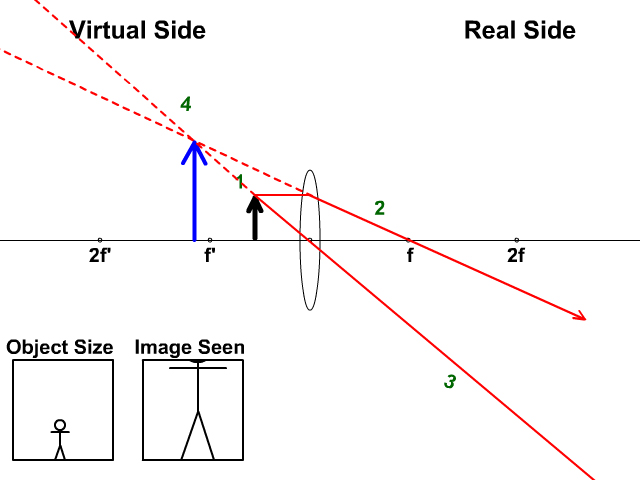
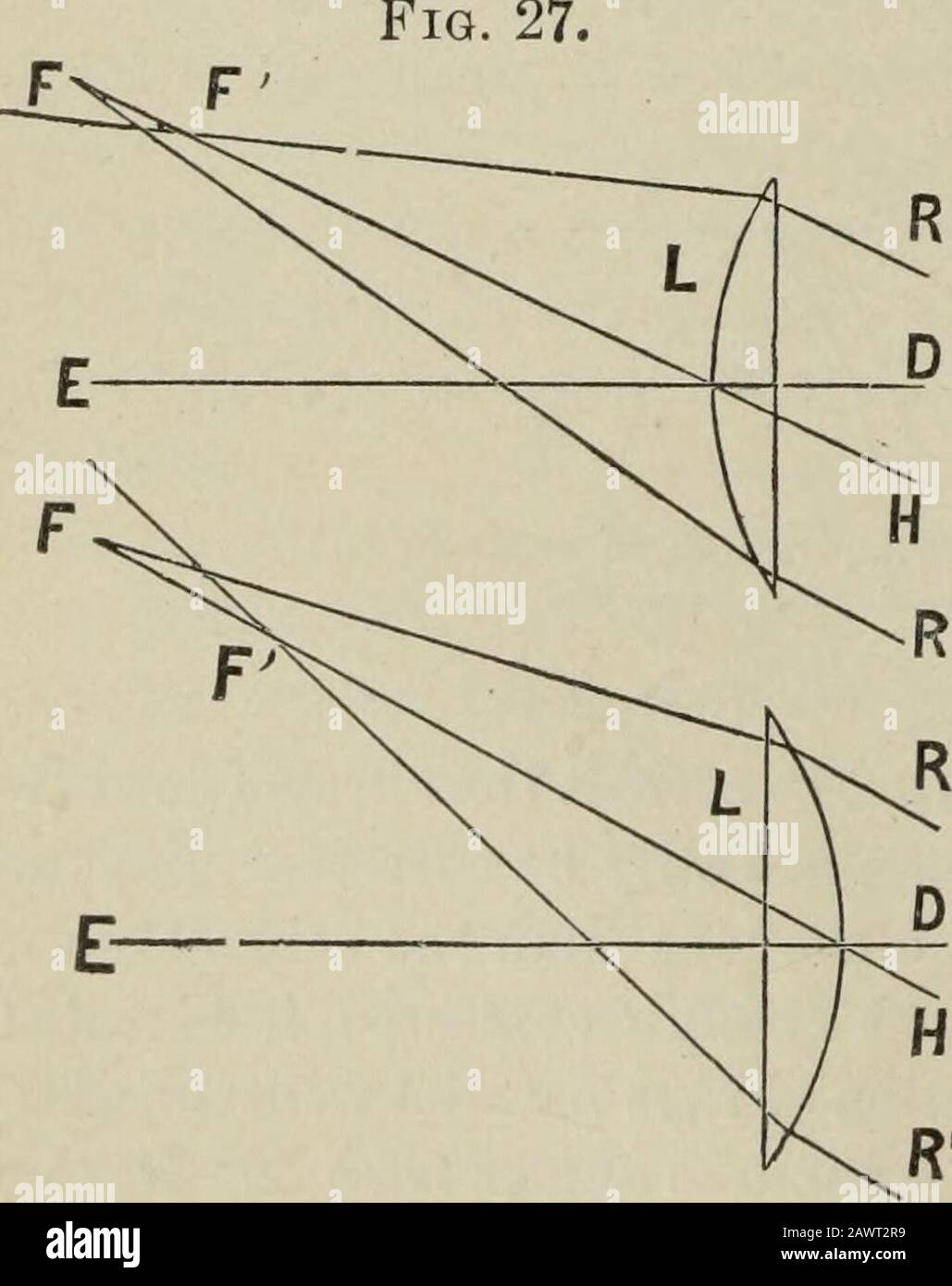
Biconvex lens ray diagram
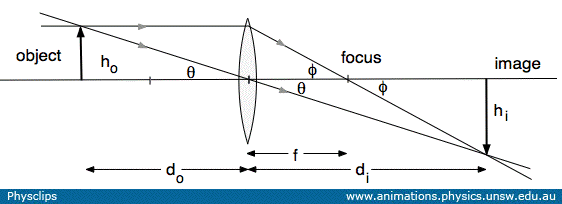
› revision-notes › cbse-class-12Wave Optics Class 12 Notes CBSE Physics Chapter 10 [PDF] 1.4. Ray of Light: The path along which light travels is known as a ray of light. If we draw an arrow normal to the wave front and which points in the direction of propagation of disturbance represents a ray of light. In a ray diagram, thick arrows represent the rays of light. › physics › simple-microscopeSimple Microscope - Definition, Types, Working Principle ... F is the focal length of the lens. An object is placed between the focal length and the centre of the curvature. A ray of light emanating from the object (source) passes through the centre of curvature of the lens (C). Another ray of light passes through the focus of the lens which lies on the other side of the lens on the principal axis. en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Augustin-Jean_FresnelAugustin-Jean Fresnel - Wikipedia Augustin-Jean Fresnel (/ ˈ f r eɪ n ɛ l,-n əl / FRAY-nel, -nəl; / ˈ f r ɛ n ɛ l,-əl / FREN-el, -əl; or / f r eɪ ˈ n ɛ l / fray-NEL; French: [oɡystɛ̃ ʒɑ̃ fʁɛnɛl]; 10 May 1788 – 14 July 1827) was a French civil engineer and physicist whose research in optics led to the almost unanimous acceptance of the wave theory of light, excluding any remnant of Newton's ...
Biconvex lens ray diagram. en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Camera_obscuraCamera obscura - Wikipedia Italian polymath Gerolamo Cardano described using a glass disc – probably a biconvex lens – in a camera obscura in his 1550 book De subtilitate, vol. I, Libri IV. He suggested to use it to view "what takes place in the street when the sun shines" and advised to use a very white sheet of paper as a projection screen so the colours wouldn't ... en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Augustin-Jean_FresnelAugustin-Jean Fresnel - Wikipedia Augustin-Jean Fresnel (/ ˈ f r eɪ n ɛ l,-n əl / FRAY-nel, -nəl; / ˈ f r ɛ n ɛ l,-əl / FREN-el, -əl; or / f r eɪ ˈ n ɛ l / fray-NEL; French: [oɡystɛ̃ ʒɑ̃ fʁɛnɛl]; 10 May 1788 – 14 July 1827) was a French civil engineer and physicist whose research in optics led to the almost unanimous acceptance of the wave theory of light, excluding any remnant of Newton's ... › physics › simple-microscopeSimple Microscope - Definition, Types, Working Principle ... F is the focal length of the lens. An object is placed between the focal length and the centre of the curvature. A ray of light emanating from the object (source) passes through the centre of curvature of the lens (C). Another ray of light passes through the focus of the lens which lies on the other side of the lens on the principal axis. › revision-notes › cbse-class-12Wave Optics Class 12 Notes CBSE Physics Chapter 10 [PDF] 1.4. Ray of Light: The path along which light travels is known as a ray of light. If we draw an arrow normal to the wave front and which points in the direction of propagation of disturbance represents a ray of light. In a ray diagram, thick arrows represent the rays of light.

















0 Response to "41 biconvex lens ray diagram"
Post a Comment