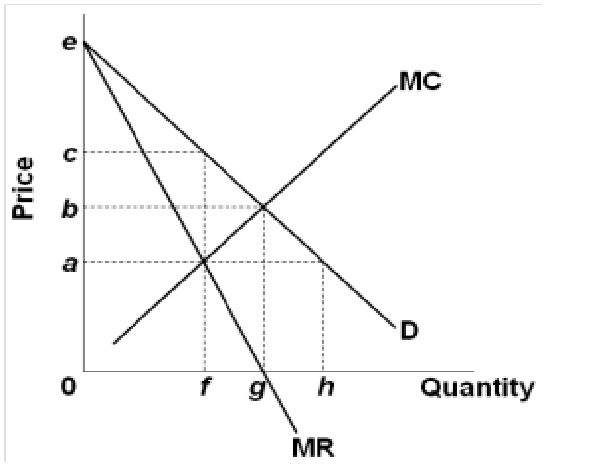
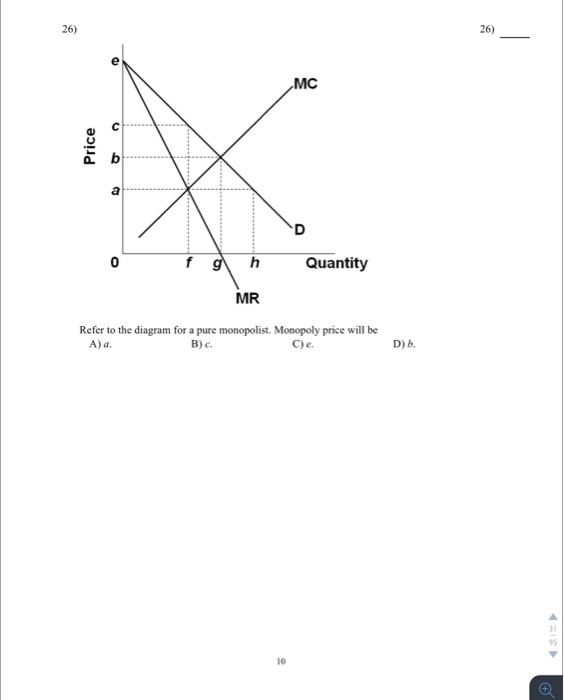
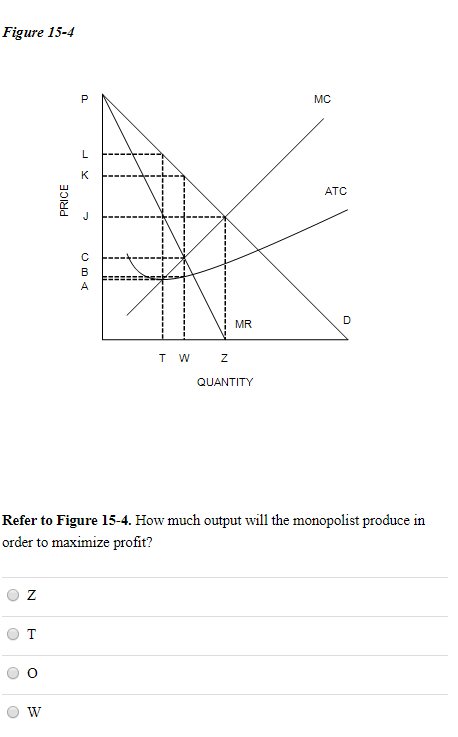
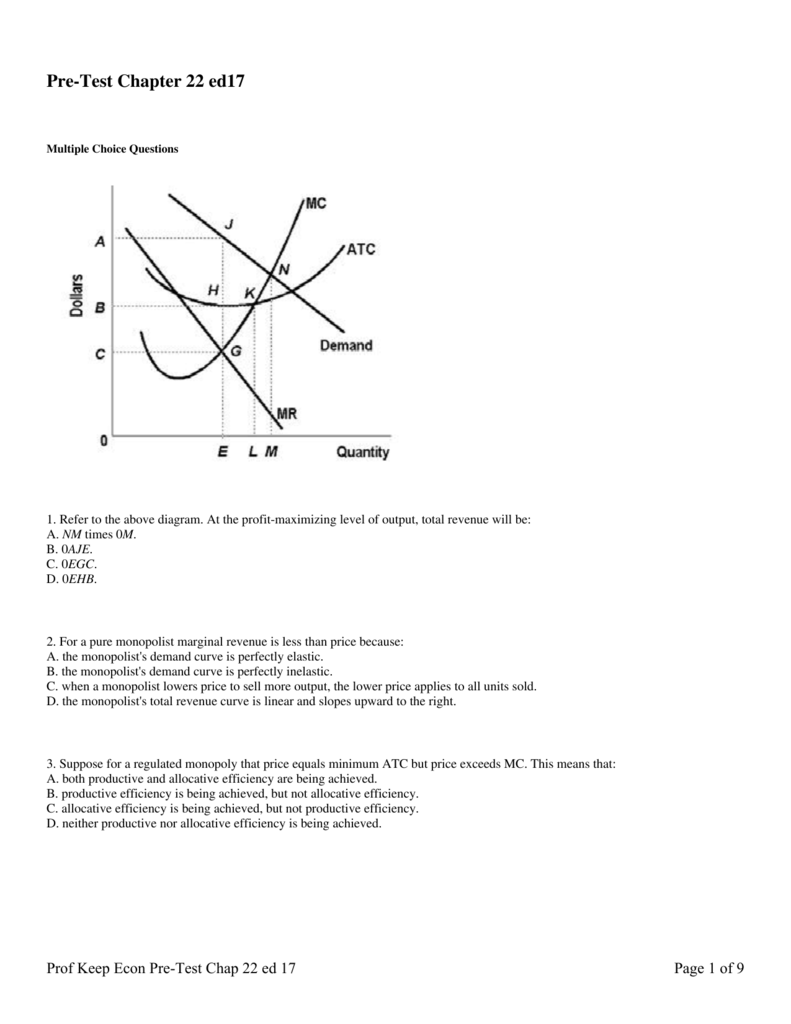
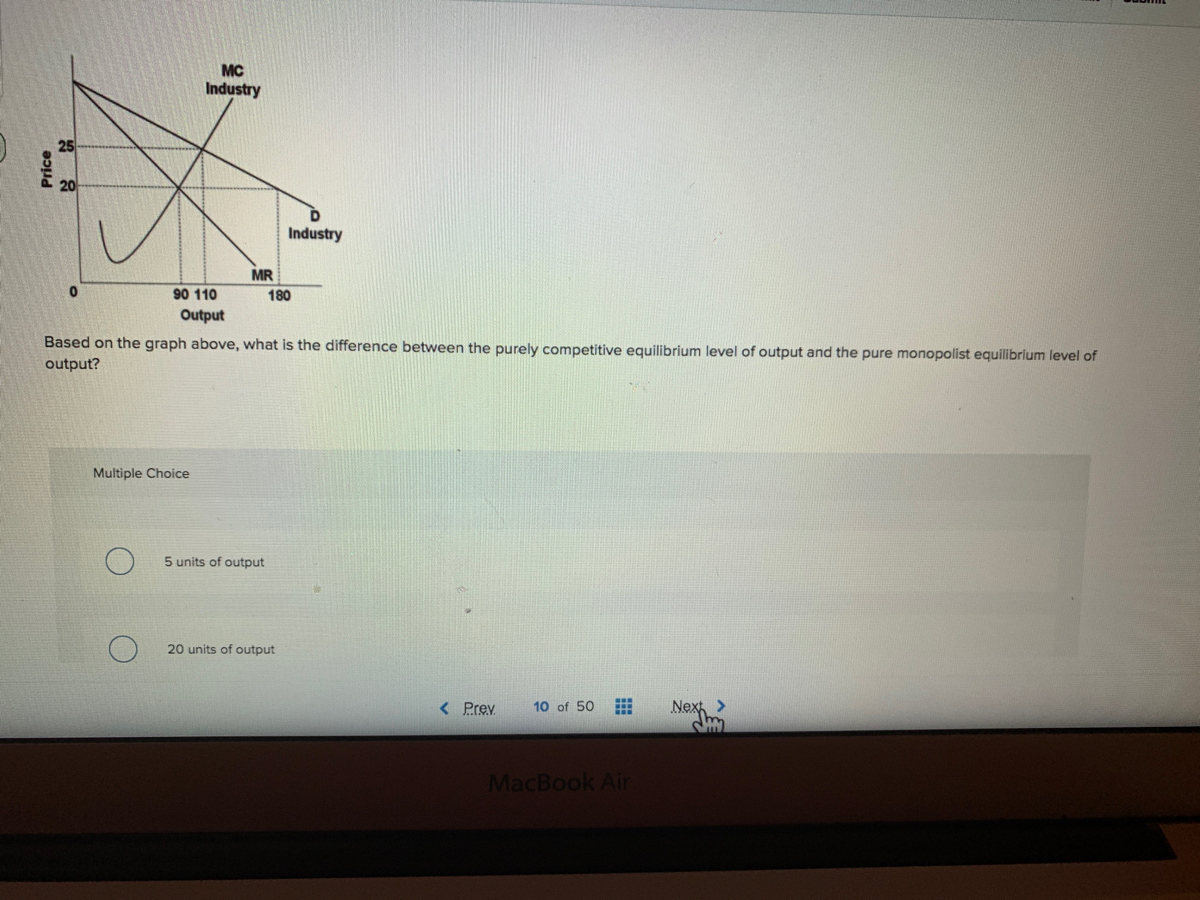
40 refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly output will be:
quizlet.com › 466513104 › econ-final-flash-cardsEcon final Flashcards | Quizlet Assume a pure monopolist is currently operating at a price-quantity combination on the inelastic segment of its demand curve. If the monopolist is seeking maximum profits, it should A) retain its current price-quantity combination. B) charge a lower price. C) increase both price and quantity sold. D) charge a higher price. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist if a - Course Hero 169. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. If a regulatory commission sets price to achieve the most efficient allocation of resources, it will have to: A. tax the monopolist P 3 P 1 per unit to prevent the monopolist from realizing an economic profit.
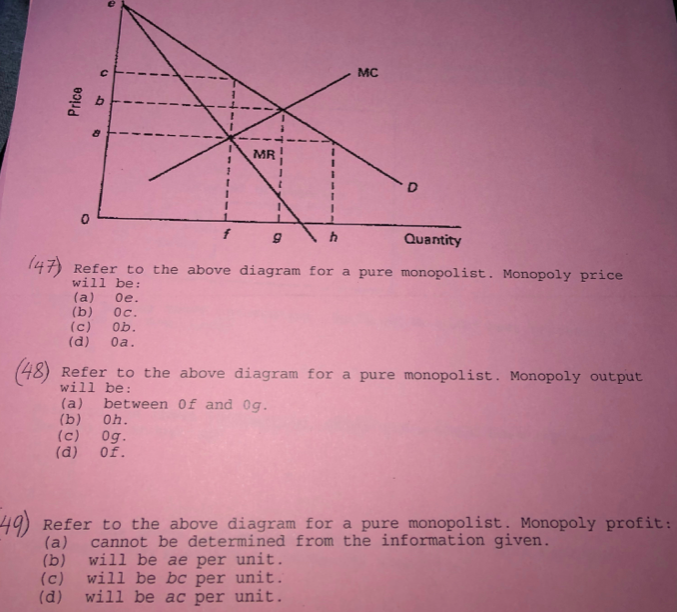
Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist Monopoly price will be ... Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly profit:A. cannot be determined from the information given. B. will beaeper unit sold. C. will bebcper unit sold. D. will beacper unit sold. 73. In the short run a pure monopolist's profit:A. will be maximized where price equals average total cost. B. may be positive, zero, or negative.
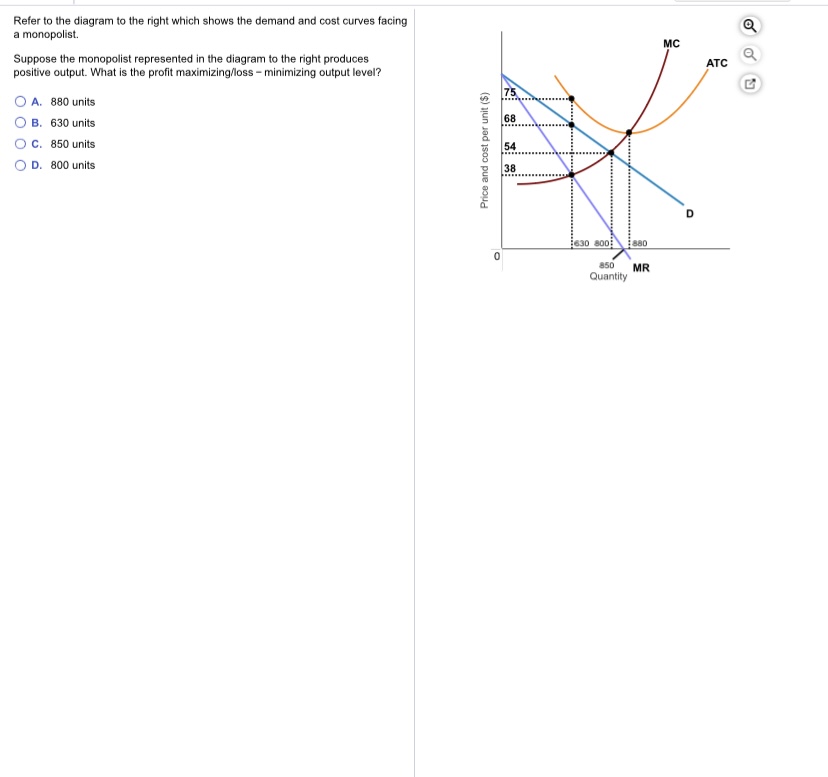
Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly output will be:
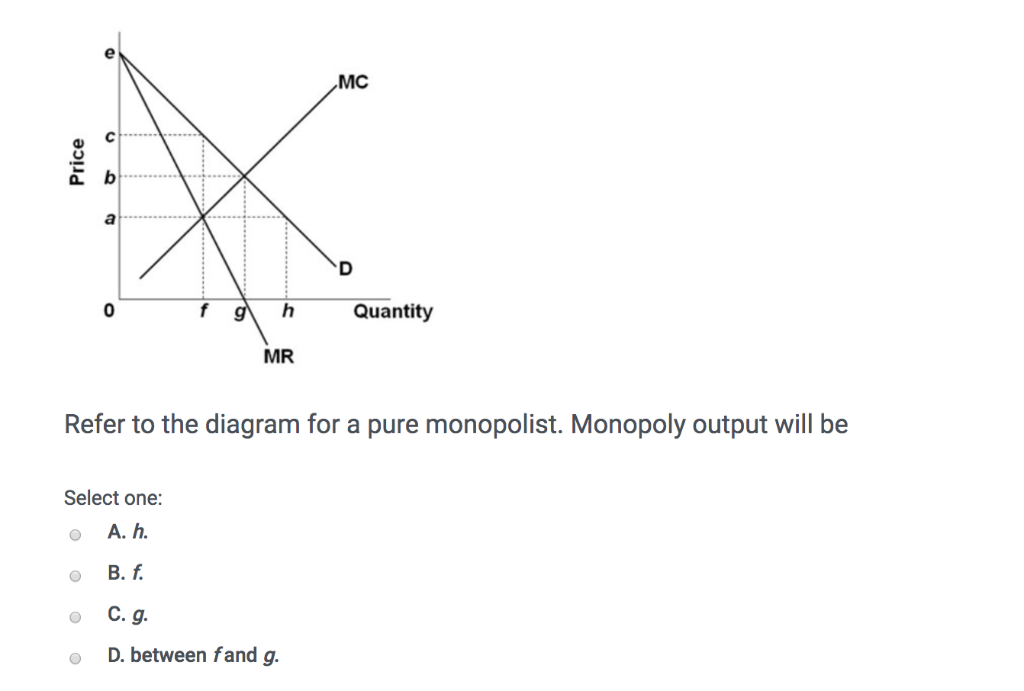
quizlet.com › 144540684 › econ-exam-2-flash-cardsecon exam #2 Flashcards | Quizlet Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like In the above diagram the range of diminishing marginal returns is:, In the above diagram, total product will be at a maximum at:, Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q total variable cost is: and more. Micro Final Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output will be A) f. C) g. B) between f and g. D) h. A A pure monopolist is generally viewed as A) both productively and allocatively inefficient. B) productively inefficient but allocatively efficient. C) both productively and allocatively efficient. Microeconomics review exam 3 Flashcards | Quizlet A) a monopolist 100% market share ensures economic profit B) the monopolist marginal revenue is less than price for any given output greater than 1 C) a monopolist firm produces a product having no close substitutes A Refer to the diagram above. The profit maximizing output: Is n 4. Refer to the above diagram.
Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly output will be:. quizlet.com › 230018662 › microecon-2-flash-cardsMicroecon 2 Flashcards | Quizlet Suppose that a pure monopolist can sell 5 units of output at $4 per unit and 6 units of output at $3.90 per unit. The monopolist will produce and sell the sixth unit if its marginal cost is: $3.40 or less Ch. 12 Pure Monopoly - Microeconomics Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. If the monopolist is unregulated, it will maximize profits by charging Pure monopolists may obtain economic profits in the long run because ... The firm described in the accompanying diagram is selling in an imperfectly competitive market Refer to the diagram. Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist suppose a - Course Hero 155. Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. If a regulatory commission sets the price to achieve the socially optimal allocation of resources, it will have to A. tax the monopolist P 3 P 1 per unit to prevent the monopolist from realizing an economic profit. B. subsidize the monopolist or the monopolist will go bankrupt in the long run. C. subsidize the monopolist P 1 P 4 per unit to ... refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly output will be ... refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. A monopoly is any business or economic entity that controls a market for its own goods and services. Think about a company that controls a market for its own products. For example, AT&T controls the AT&T store in your town and AT&T will call you and sell you its phone plans.
Use the following diagram of a pure monopolist to - Course Hero Pure monopoly is stated as a market structure where one firm is considered as a single source for a commodity, with non-availability of the close substitutes of the product. Situation of pure monopolies occurs rarely as there are limitations which prevent the competitors from entering into the market. 13. OneClass: Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output 11 Dec 2019 Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output will be: A. f B. g C. h D. between f and g Show full question Answer + 20 Watch For unlimited access to Homework Help, a Homework+ subscription is required. Sonal Bahl Lv10 17 Dec 2020 Unlock all answers Get 1 free homework help answer. Unlock Already have an account? Log in Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist if - Course Hero Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. If a regulatory commission sets the price to achieve the socially optimal allocation of resources, it will have to: A. tax the monopolistP3P1 per unit to prevent the monopolist from realizing an economic profit. quizlet.com › 290528832 › pure-monopoly-flash-cardsPure Monopoly Flashcards | Quizlet Which of the following are assumptions made in the model of pure monopoly? A. The firm is a single-price monopolist; it charges the same price for all units of output. B. No unit of government regulates the firm. C. The government regulates the firm. D. The firm is a multi-price monopolist; it charges different prices for all units of output.
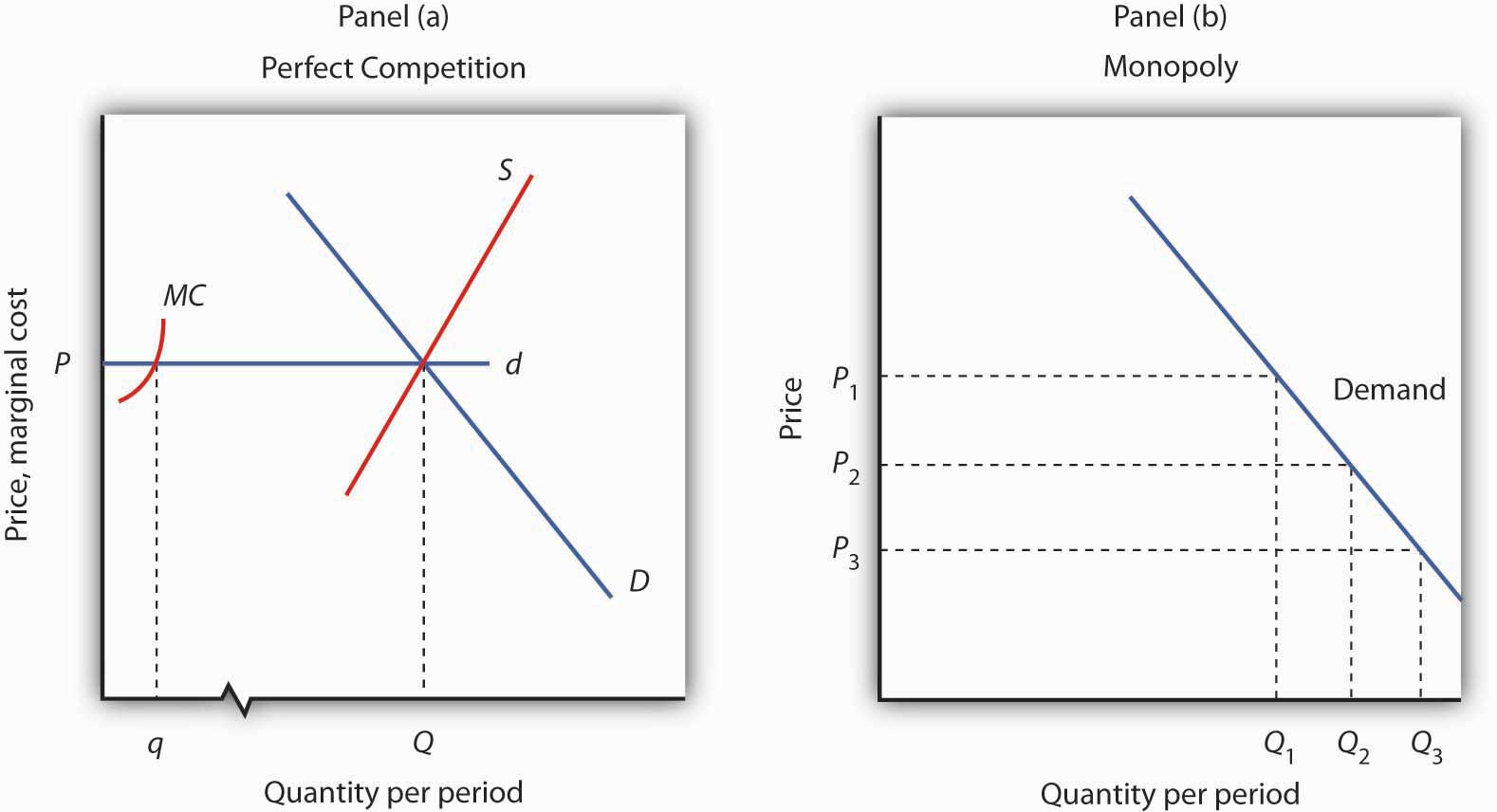
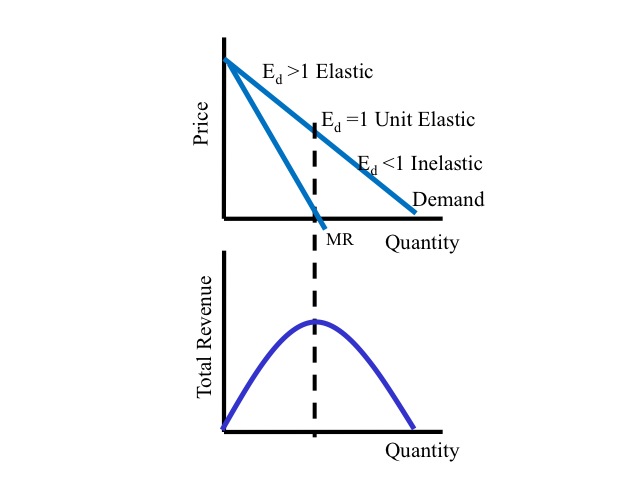
Micro Chapter 12 Monopolies Flashcards | Quizlet will be less than $35 The demand curve faced by a pure monopolist is less elastic than that faced by a single purely competitive firm A nondiscriminating profit-maximizing monopolist will never produce in the output range where demand is inelastic For a pure monopolist the relationship between total revenue and marginal revenue is such that How does a Monopolist Determine Price and Output? - Economics Discussion Under monopoly, like perfect competition, the 'golden rule of output' determination is MC - MR equality. A monopolist, in the short run, can earn pure profit or economic profit as well as normal profit. A monopolist may also incur a loss in the short run. All these possibilities have been shown in Fig. 5.2. › espp › book1. Capitalism and democracy: Affluence, inequality, and the ... monopoly A firm that is the only seller of a product without close substitutes. Also refers to a market with only one seller. See also: monopoly power, natural monopoly. He also saw that the market system had some failings, especially if sellers banded together to form monopolies, so as to avoid competing with one another. Smith specifically ... monopoly stuff Flashcards | Quizlet An unregulated pure monopolist will maximize profits by producing that output at which: A) P = MC. B) P = ATC. C) MR = MC. D) MC = AC. C Suppose that a pure monopolist can sell 5 units of output at $4 per unit and 6 units at $3.90 per unit. The monopolist will produce and sell the sixth unit if its marginal cost is: A) $4 or less. B) $3.90 or less.
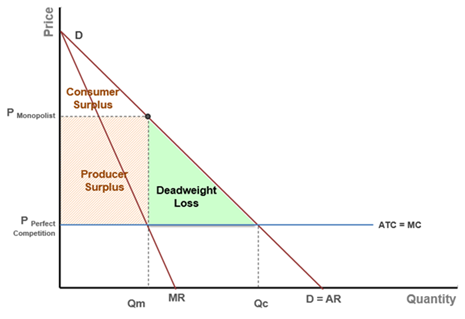
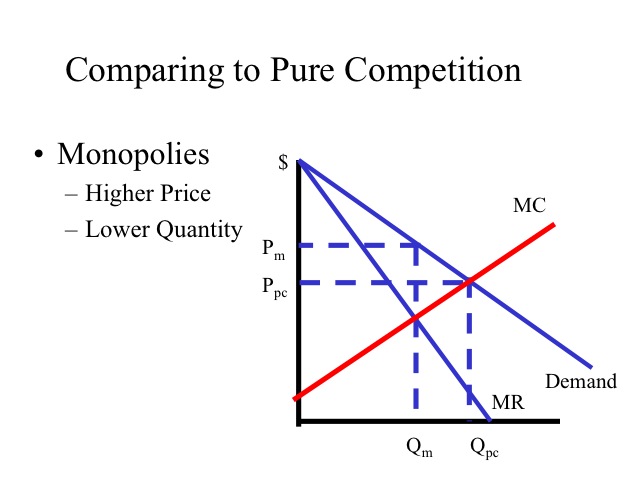
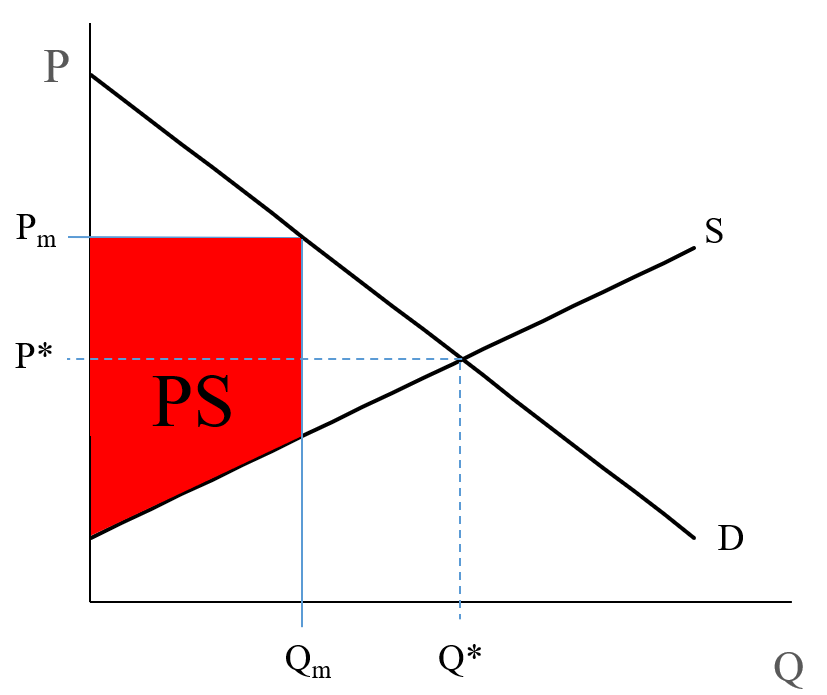
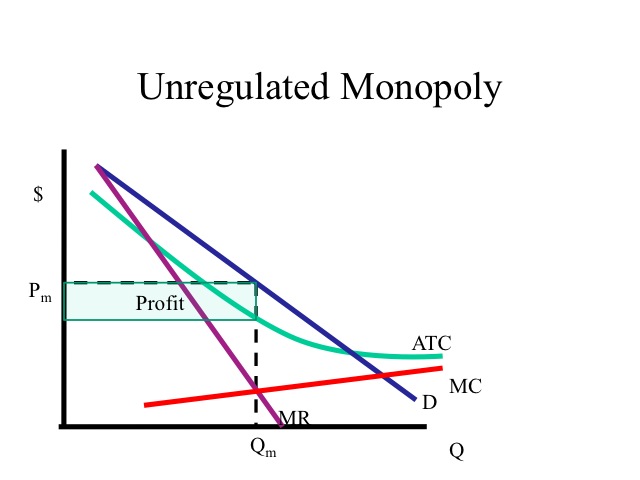
Diagram of Monopoly - Economics Help Monopoly Graph A monopolist will seek to maximise profits by setting output where MR = MC This will be at output Qm and Price Pm. Compared to a competitive market, the monopolist increases price and reduces output Red area = Supernormal Profit (AR-AC) * Q
Question 14 1 out of 1 points refer to the above - Course Hero Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly price will be: Answer s: A. e. B. c. C. b. D. a. Question 15 1 out of 1 points Which of the following is correct? Answer s: "A. Both purely competitive and monopolistic firms are ""price takers.""" "B. Both purely competitive and monopolistic firms are ""price makers.""" "C.
Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist Monopoly price will ... Monopoly output will:f . Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly profit:cannot be determined from the information given. In the short run a pure monopolist's profit:may be positive, zero, or negative. Purely competitive firms and pure monopolists are similar in that:both maximize profit where MR = MC.
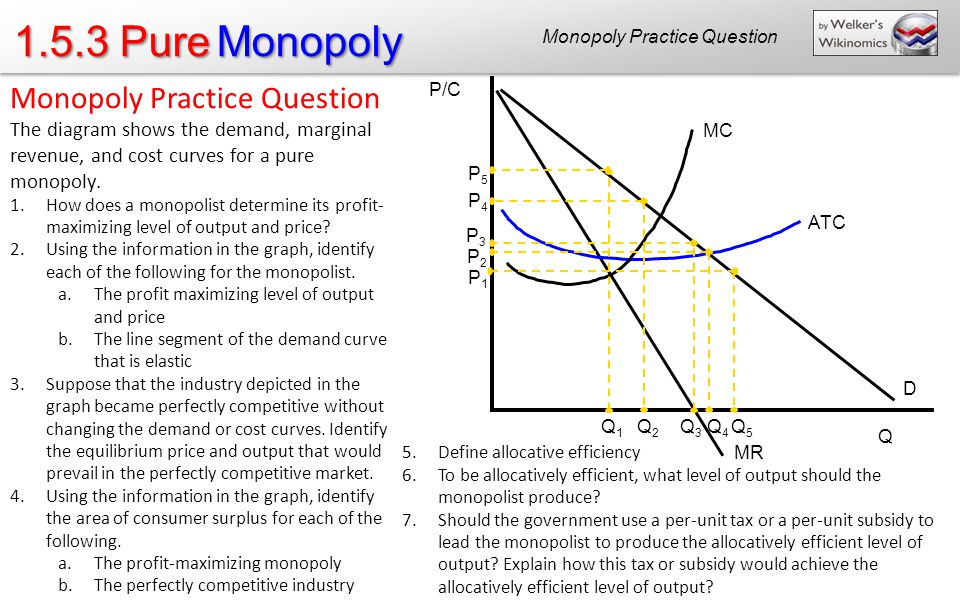
Pure Monopoly Flashcards | Quizlet Pure monopolists always earn economic profits. False Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. The profit-seeking monopolist will never produce an output larger than q2. Price discrimination is illegal in the United States under all circumstances due to antitrust regulations. False The nondiscriminating pure monopolist's demand curve
True False 192 Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist ... True False 192 Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist If the. True false 192 refer to the diagram for a. School University of Texas, Dallas; Course Title BUSINESS 1111; Uploaded By lgn130030; Pages 53 Ratings 82% (51) 42 out of 51 people found this document helpful;
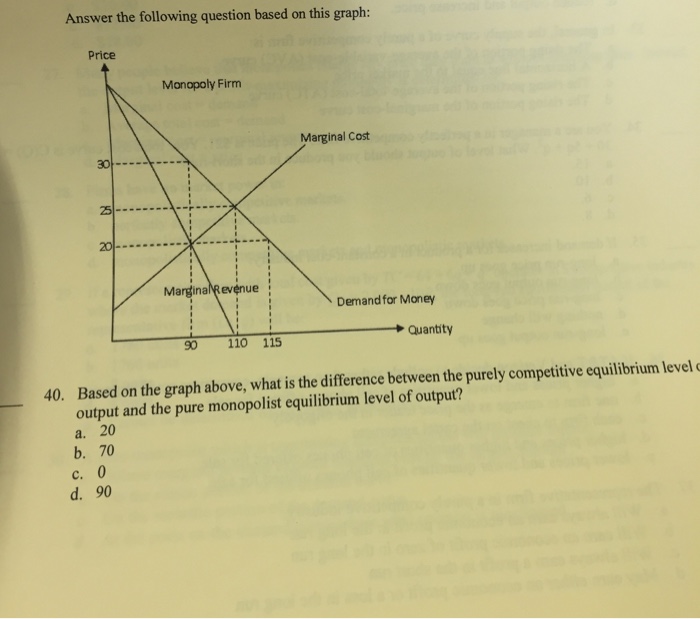
Solved > 151.Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist.:1637251 ... 151. Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. If the monopolist is unregulated, it will maximize profits by charging: A. a price above P3 and selling a quantity less than Q3. B. price P3 and producing output Q3. C. price P2 and producing output Q2. D. price P1 and producing output Q1. 152.
MICRO: CH. 13 Pure Monopoly Part II Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly price will be c. Refer to the diagrams. Diagram (A) represents equilibrium price and quantity in a purely competitive industry. Picture is diagram (B) If the industry depicted in the graph comprises only one seller, the profit-maximizing price and quantity will be P3 and Q3.
Microeconomics review exam 3 Flashcards | Quizlet A) a monopolist 100% market share ensures economic profit B) the monopolist marginal revenue is less than price for any given output greater than 1 C) a monopolist firm produces a product having no close substitutes A Refer to the diagram above. The profit maximizing output: Is n 4. Refer to the above diagram.
Micro Final Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output will be A) f. C) g. B) between f and g. D) h. A A pure monopolist is generally viewed as A) both productively and allocatively inefficient. B) productively inefficient but allocatively efficient. C) both productively and allocatively efficient.
quizlet.com › 144540684 › econ-exam-2-flash-cardsecon exam #2 Flashcards | Quizlet Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like In the above diagram the range of diminishing marginal returns is:, In the above diagram, total product will be at a maximum at:, Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q total variable cost is: and more.











.jpg)


0 Response to "40 refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly output will be:"
Post a Comment